
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 29-39.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00050
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhulei Dong1( ), Xuegong Jiang2(
), Xuegong Jiang2( ), Nana Yi3, Zhili Xu3, Yuehe Hang2, Shuiyan Yu3
), Nana Yi3, Zhili Xu3, Yuehe Hang2, Shuiyan Yu3
Received:2023-02-02
Revised:2023-04-19
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-11-30
Contact:
Xuegong Jiang
CLC Number:
Zhulei Dong, Xuegong Jiang, Nana Yi, Zhili Xu, Yuehe Hang, Shuiyan Yu. Numerical simulation of the influence of wind speed and vegetation on dust weather in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 29-39.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00050
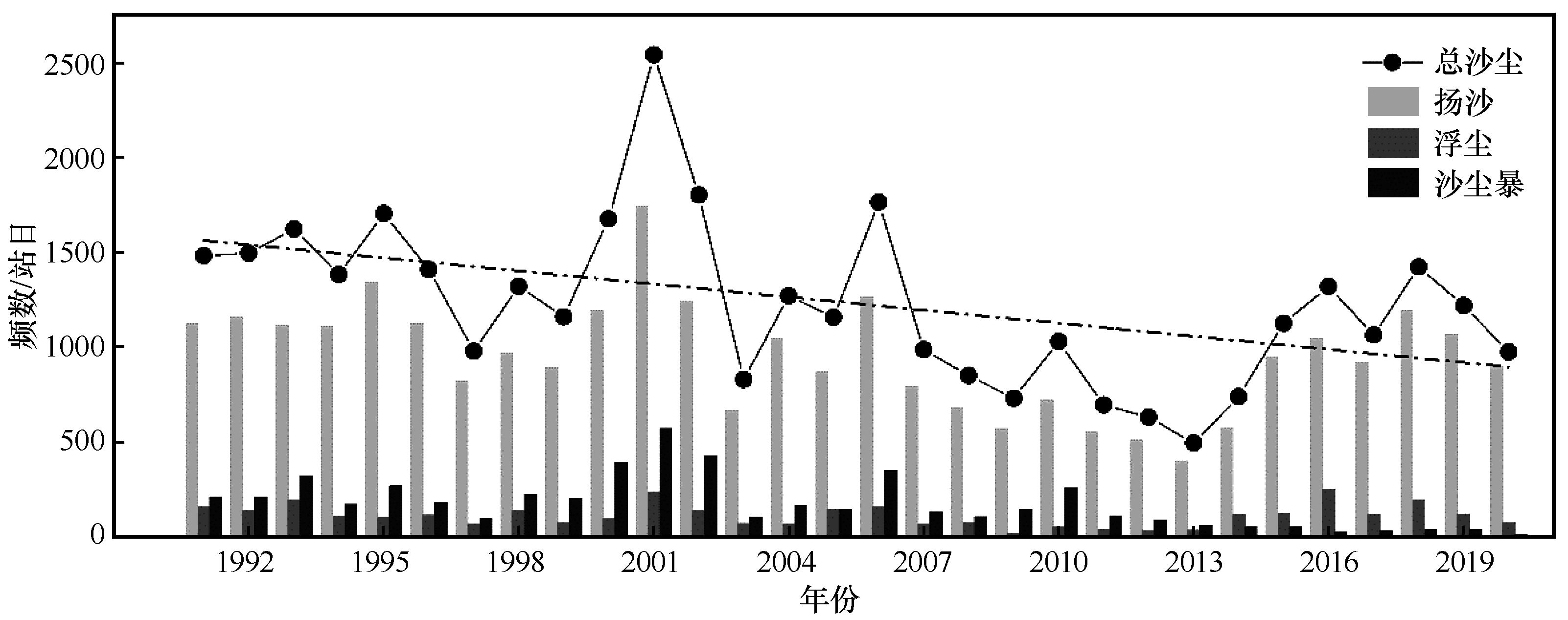
Fig.3 The time changes of frequency of sand lifting, dust floating, sandstorms and total dust weather in Inner Mongolia from 1991 to 2020, and the dotted line represents the trend of total dust weather frequency
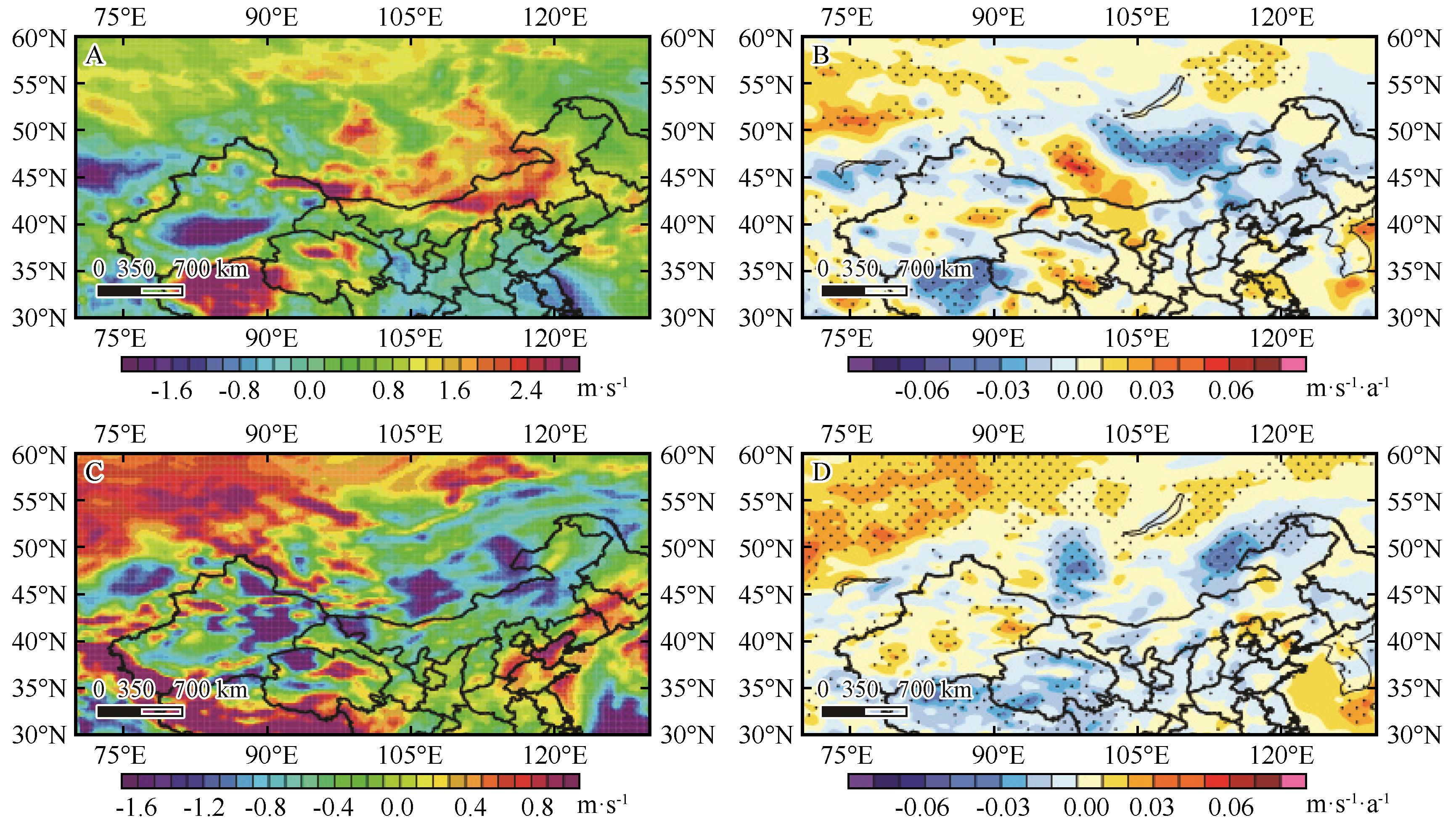
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of zonal (A) and meridional (C) average wind speed at 10 m height and zonal (B) and meridional (D) climatic variability in spring in Inner Mongolia and surrounding areas from 1991 to 2020. The dotted area passed the 90% reliability test
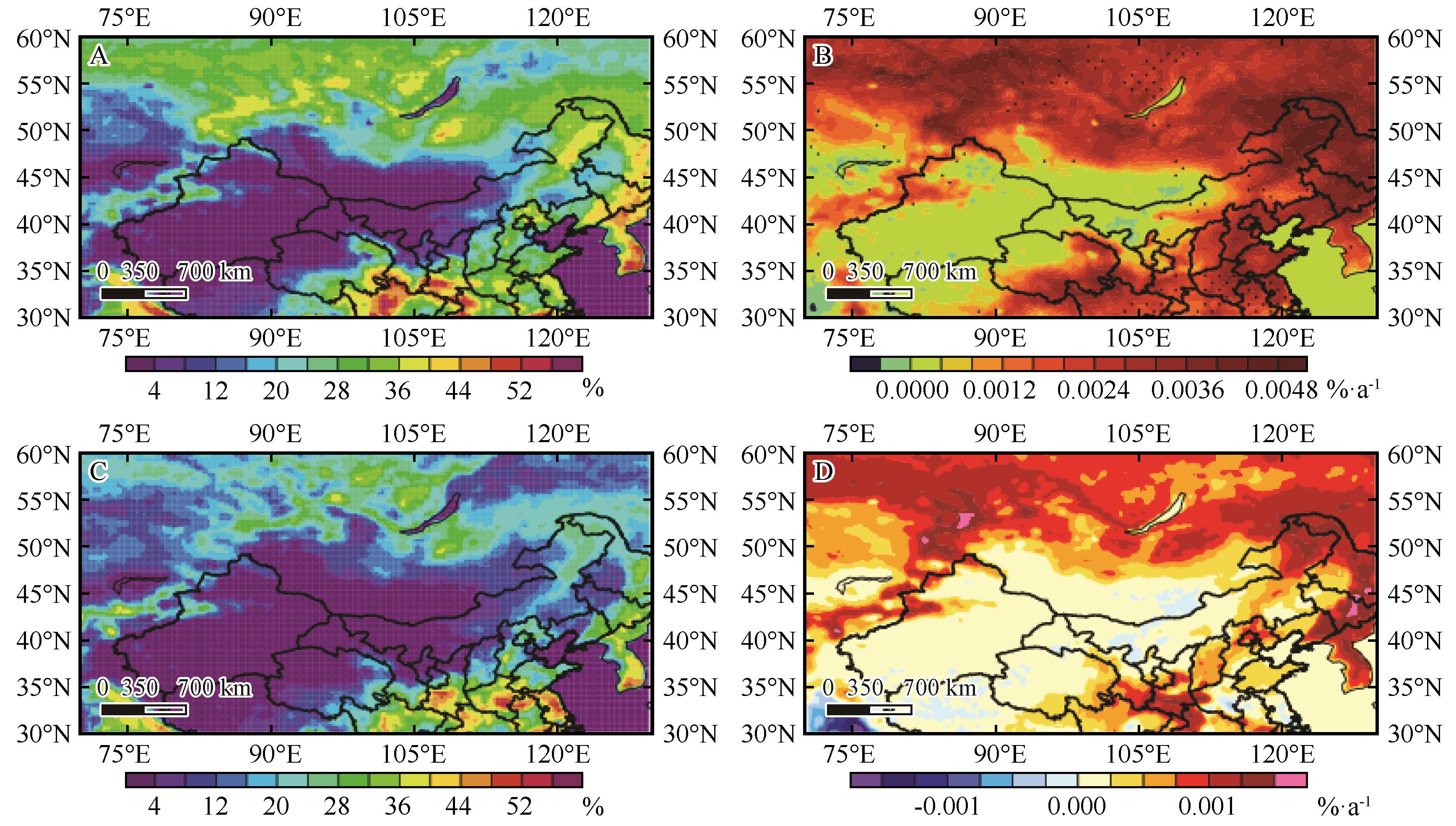
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of average vegetation coverage (unit: %) in year (A) and spring (C) and climatic variability (unit: %·a-1) in year (B) and spring (D) in Inner Mongolia and surrounding areas from 1991 to 2020. The dotted area passed the 90% reliability test
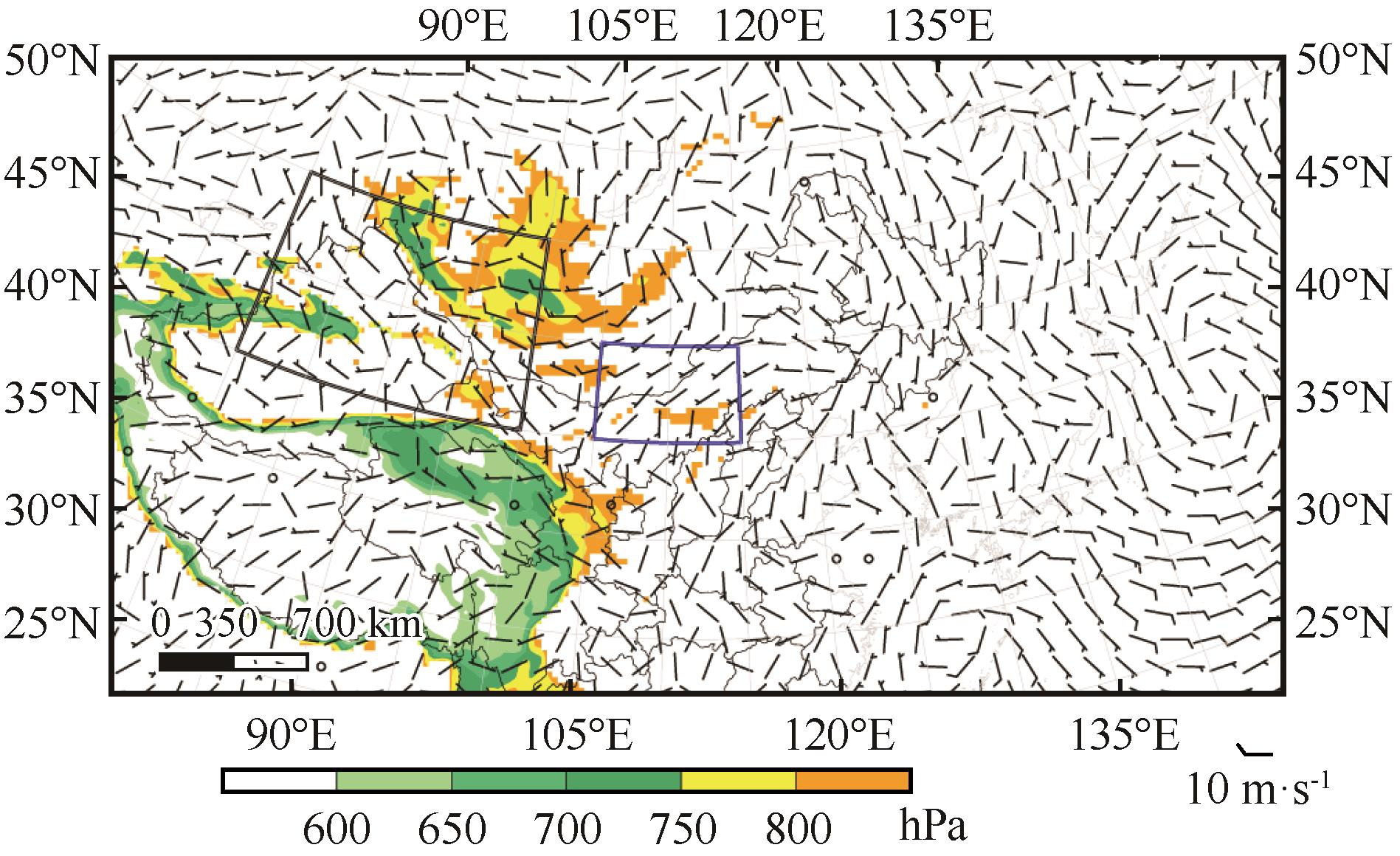
Fig.6 The sea level pressure field (unit: hPa) and wind field (unit: m·s-1) at the initial moment of the model. The black rectangular box area represents the windy area which was modified in sensitivity experiments, and the blue recta-ngular box area represents the vegetation cover was modified by the simulation experiment
| 植被覆盖率敏感性 试验分组 | 植被覆盖率 变化方案 | 风速敏感性 试验分组 | 风速变化 方案 |
|---|---|---|---|
| casev1 | +5% | casew1 | -20% |
| casev2 | +10% | casew2 | -30% |
| casev3 | +15% | casew3 | -40% |
| casev4 | +20% | casew4 | -50% |
Table 1 Subgroup of sensitivity experiments
| 植被覆盖率敏感性 试验分组 | 植被覆盖率 变化方案 | 风速敏感性 试验分组 | 风速变化 方案 |
|---|---|---|---|
| casev1 | +5% | casew1 | -20% |
| casev2 | +10% | casew2 | -30% |
| casev3 | +15% | casew3 | -40% |
| casev4 | +20% | casew4 | -50% |
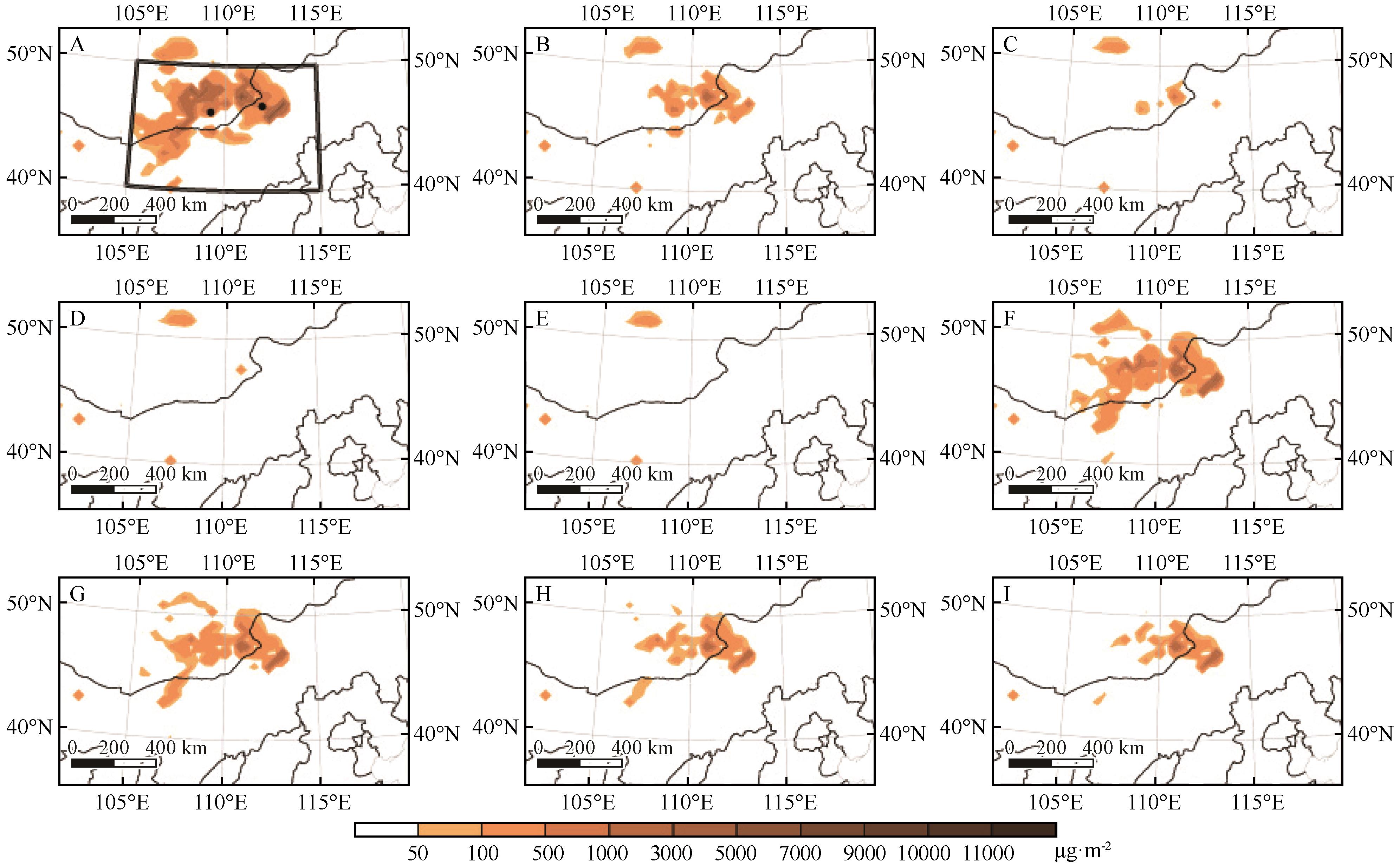
Fig.7 The spatial distribution of actual sand emission (A) and sand emission (unit: μg·m-2) simulated by casev1 (B), casev2 (C), casev3 (D), casev4 (E), casew1 (F), casew2 (G), casew3 (H), casew4 (I) at 04:00 on May 15, 2019. The black rectangular box area is sand source, and the black dots indicate the southern site of Mongolia (43.12°N,109.21°E) and Erenhot (43.39°N,112.00°E)
| 分组 | 蒙古国南部 | 二连浩特(第一次) | 二连浩特(第二次) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总起沙量/(μg·m-2) | 削减率% | 总起沙量/(μg·m-2) | 削减率/% | 总起沙量/(μg·m-2) | 削减率/% | |||
| 实际 | 6 673.8 | — | 11 145.0 | — | 722.3 | — | ||
| casev1 | 2 362.8 | 64.6 | 2 634.8 | 76.4 | 63.4 | 91.2 | ||
| casev2 | 365.5 | 94.5 | 444.0 | 96.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| casev3 | 13.9 | 99.8 | 38.6 | 99.7 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| casev4 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| casew1 | 2 918.7 | 56.3 | 4 419.1 | 60.3 | 417.9 | 42.1 | ||
| casew2 | 2 013.6 | 69.8 | 2 938.5 | 73.6 | 270.8 | 62.5 | ||
| casew3 | 1 199.2 | 82.0 | 1 869.8 | 83.2 | 199.1 | 72.4 | ||
| casew4 | 884.5 | 86.7 | 1 502.7 | 86.5 | 170.5 | 76.4 | ||
Table 2 Total sand emission and the reduction of total sand emission by vegetation and wind in southern Mongolia and Erenhot in different sensitivity experiments
| 分组 | 蒙古国南部 | 二连浩特(第一次) | 二连浩特(第二次) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总起沙量/(μg·m-2) | 削减率% | 总起沙量/(μg·m-2) | 削减率/% | 总起沙量/(μg·m-2) | 削减率/% | |||
| 实际 | 6 673.8 | — | 11 145.0 | — | 722.3 | — | ||
| casev1 | 2 362.8 | 64.6 | 2 634.8 | 76.4 | 63.4 | 91.2 | ||
| casev2 | 365.5 | 94.5 | 444.0 | 96.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| casev3 | 13.9 | 99.8 | 38.6 | 99.7 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| casev4 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 100 | 0.0 | 100.0 | ||
| casew1 | 2 918.7 | 56.3 | 4 419.1 | 60.3 | 417.9 | 42.1 | ||
| casew2 | 2 013.6 | 69.8 | 2 938.5 | 73.6 | 270.8 | 62.5 | ||
| casew3 | 1 199.2 | 82.0 | 1 869.8 | 83.2 | 199.1 | 72.4 | ||
| casew4 | 884.5 | 86.7 | 1 502.7 | 86.5 | 170.5 | 76.4 | ||
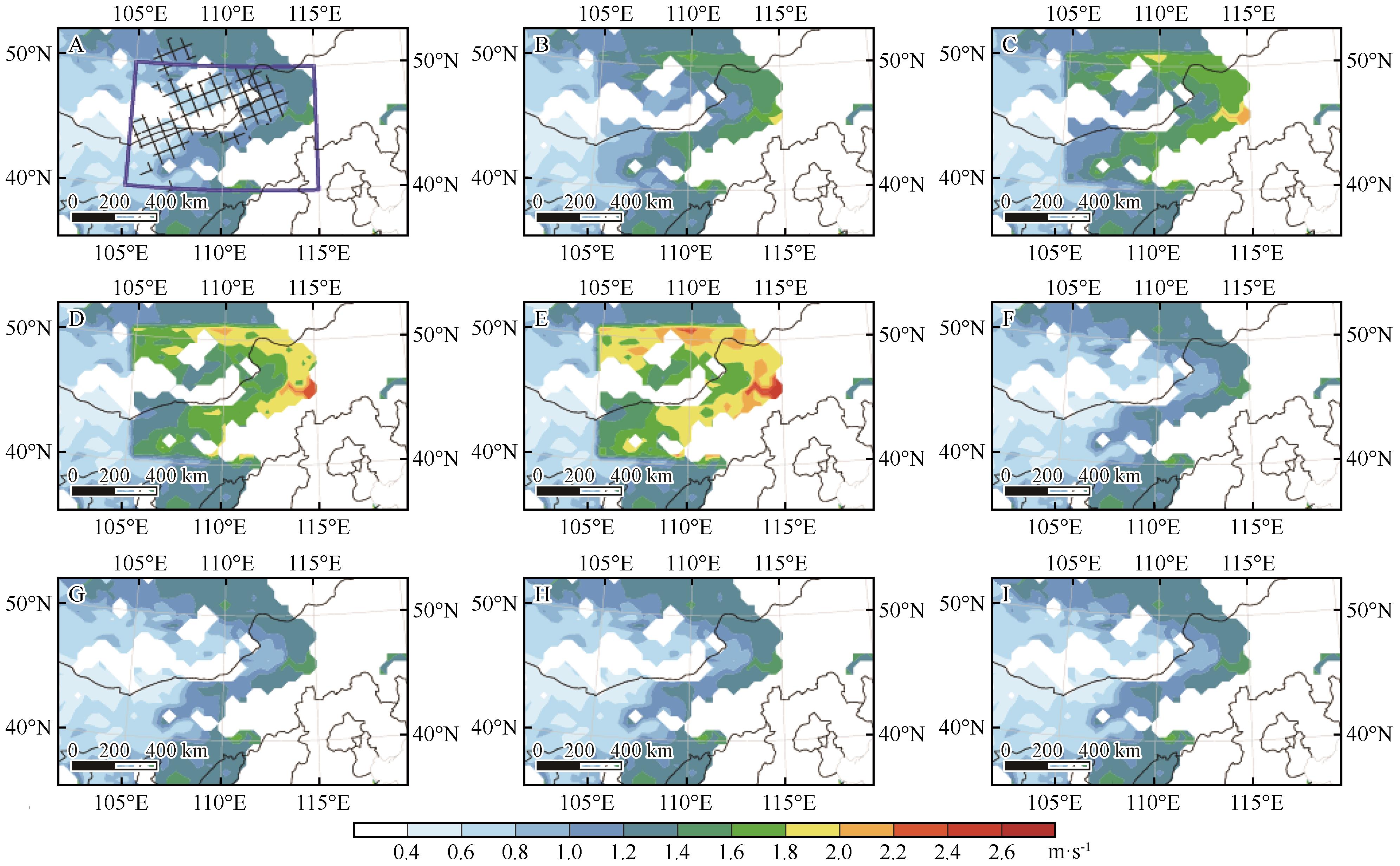
Fig.9 The spatial distribution of actual critical friction velocity (A) and critical friction velocity simulated by casev1 (B), casev2 (C), casev3 (D), casev4 (E), casew1 (F), casew2 (G), casew3 (H), casew4 (I) at 04:00 on May 15. The black grid area indicates sand emission flux is 50-3 000 μg·m-2. The blue box area indicates the sand source of the process
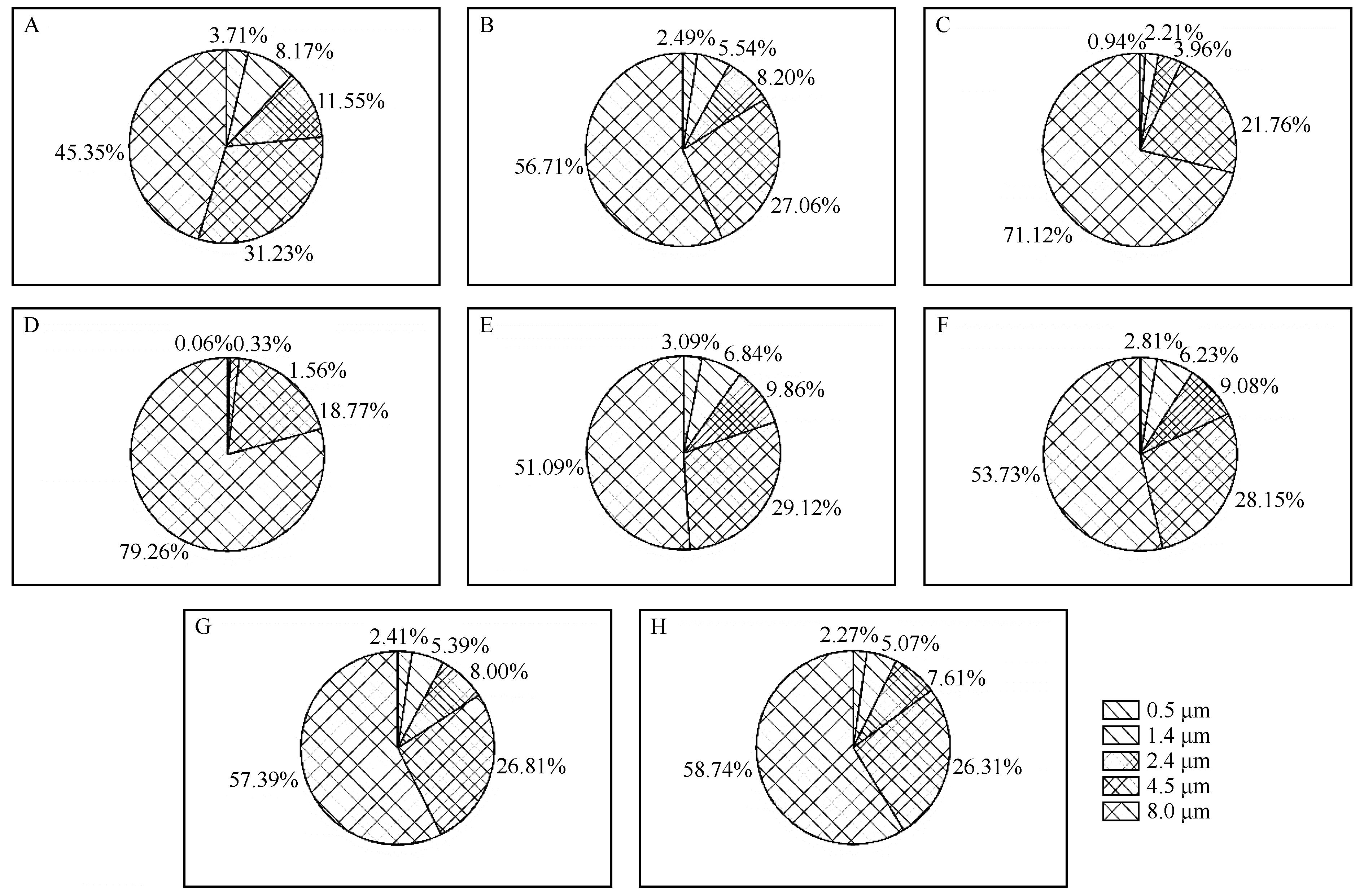
Fig.10 The actual contribution rate (A) of different particle sizes to the sand emission in Erenhot and contribution rates simulated by casev1 (B), casev2 (C), casev3 (D), casew1 (E), casew2 (F), casew3 (G), casew4 (H)
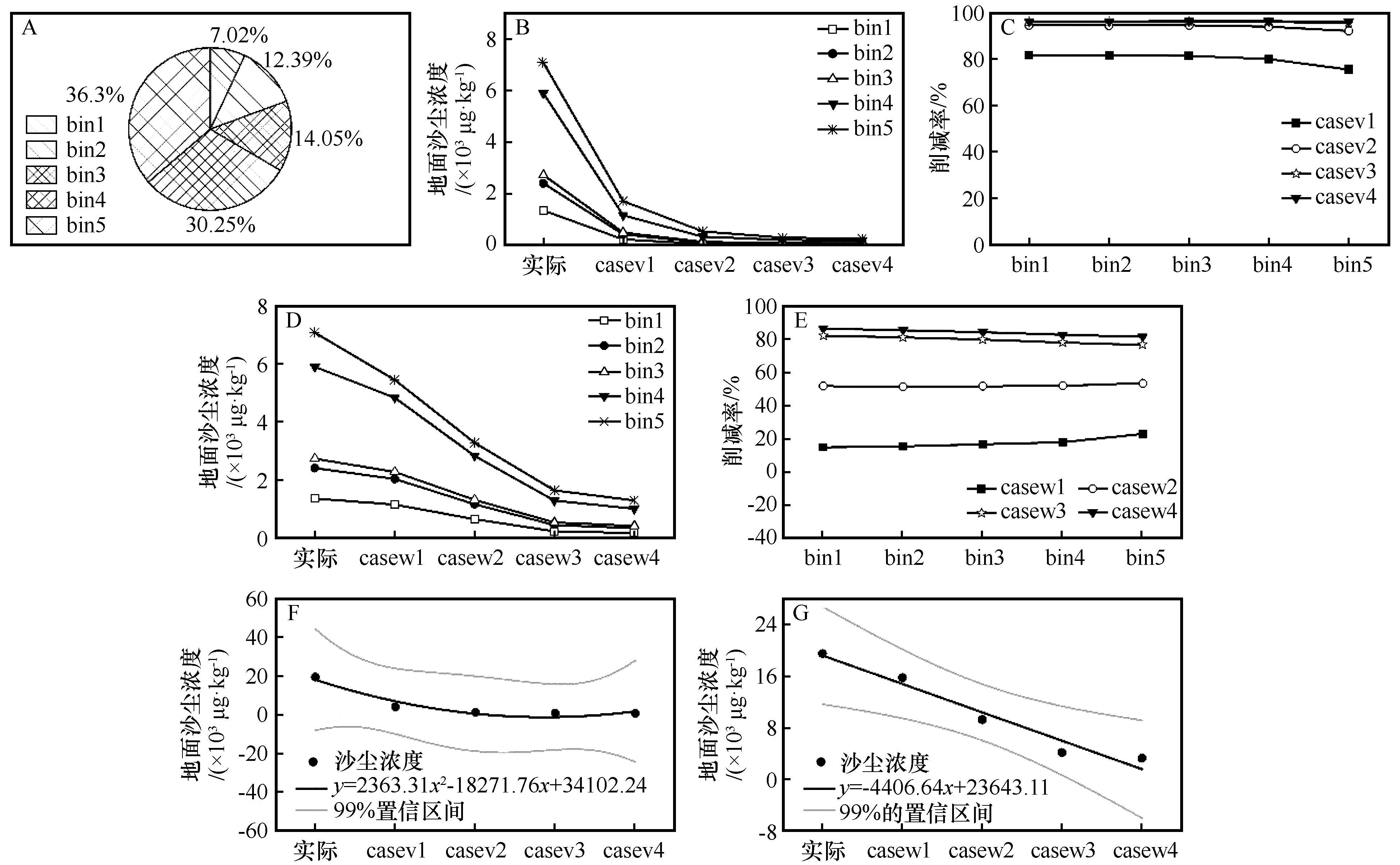
Fig.11 The actual contribution rate of different sizes particle to the surface sand concentration (A) in Baicheng Station in downstream of the sand source, the concentration of different sizes particle in different vegetation coverage (B) and wind speed (D) sensitivity tests, the concentrations reduction rate of vegetation coverage (C) and wind speed (E) to different sizes particle, and fitting of surface sand concentrations in different vegetation coverage (F) and wind speed (G) sensitivity experiments
| 1 | 陈亿,尚可政,王式功,等.21世纪初中国北方沙尘天气特征及其与地面风速和植被的关系研究[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(6):1702-1709. |
| 2 | 钱正安,蔡英,刘景涛,等.中蒙地区沙尘暴研究的若干进展[J].地球物理学报,2006,49(1):83-92. |
| 3 | 李宽,熊鑫,王海兵,等.内蒙古西部高频沙尘活动空间分布及其成因[J].干旱区研究,2019,36(3):657-663. |
| 4 | 魏巍,张稳定,陈焕盛,等.库布齐沙漠治理对京津冀地区空气质量影响:2017年 5月3-6日沙尘天气模拟[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):77-87. |
| 5 | 王春学,秦宁生.中国北方春季沙尘暴周期变化特征及其对最大风速的响应[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(3):133-141. |
| 6 | 张莉,任国玉.中国北方沙尘暴频数演化及其气候成因分析[J].气象学报,2003,61(6):744-750. |
| 7 | 曹晓云,肖建设,乔斌,等.1961-2019 年柴达木盆地沙尘强度时空变化特征[J].干旱气象,2021,39(1):46-53. |
| 8 | 赵剑琦.中国北方沙尘过程及未来气候变化情景下起沙通量的数值模拟研究[D].南京:南京信息工程大学,2021. |
| 9 | 段海霞,赵建华,李耀辉.2011年春季中国北方沙尘天气过程及其成因[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(1):179-186. |
| 10 | 王学强,迎春,玉刚,等.气象因子与锡林郭勒盟地区沙尘天气的关系[J].农业灾害研究,2015,5(12):24-26. |
| 11 | Xu C, Guan Q, Lin J,et al.Spatiotemporal variations and driving factors of dust storm events in northern China based on high-temporal-resolution analysis of meteorological data (1960-2007)[J].Environmental Pollution,2020,260:114084. |
| 12 | 吴占华,任国玉,徐卫丽,等.我国北方沙尘天气的气候成因分析[J].干旱区地理,2011,34(3):429-435. |
| 13 | 吴成来.近20年沙尘暴为什么减弱了[J].科学大观园,2023,4:50-53. |
| 14 | Xu X K, Chen H.Influence of vegetations and snow cover on sand-dust events in the west of China[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2006,51:331-340. |
| 15 | Mao R, Ho C H, Feng S,et al.The influence of vegetation variation on Northeast Asian dust activity[J].Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences,2013,49:87-94. |
| 16 | 崔晓,赵媛媛,丁国栋,等.京津风沙源治理工程区植被对沙尘天气的时空影响[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(12):171-179. |
| 17 | 覃云斌,信忠保,易扬,等.京津风沙源治理工程区沙尘暴时空变化及其与植被恢复关系[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(24):196-204. |
| 18 | Wang H Q, Richdson M I.The origin,evolution,and trajectory of large dust storms on Mars during Mars years 24-30 (1999-2011)[J].Icarus,2015,251:112-127. |
| 19 | 陈楠,陈豫英,范小明,等.西北地区东部沙尘暴转型的环流演变及差异特征分析[J].干旱区地理,2010,33(5):676-683. |
| 20 | Gong S L, Zhang X Y, Zhao T L,et al.A simulated climatology of Asian dust aerosol and its trans-Pacific transport.Part II:interannual variability and climate connections[J].Journal of Climate,2016,19(1):104-122. |
| 21 | Huang J, Minnis P, Chen B,et al.Long-range transport and vertical structure of Asian dust from CALIPSO and surface measurements during PACDEX[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2008,113(D23):1-13. |
| 22 | 王彩霞,黄安宁,郑鹏,等.中国第一代全球陆面再分析(CRA40/Land)气温和降水产品在中国大陆的适用性评估[J].高原气象,2022,41(5):1325-1334. |
| 23 | 宋海清,朱仲元,李云鹏.陆面同化及再分析降水资料在内蒙古地区的适用性[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(6):1624-1636. |
| 24 | 衣娜娜,姜学恭,董祝雷,等.植被覆盖率对内蒙古沙尘天气影响的模拟研究[J].大气科学.doi:10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2204.22017 . |
| 25 | 袁国波.21世纪以来内蒙古沙尘暴特征及成因[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(6):1204-1209. |
| 26 | 李延香,周自江,高拴柱.2001年沙尘暴天气气候特征和成因分析及预警服务[C]//中国气象学会.中国科协2002年减轻自然灾害研讨会论文汇编之一.北京:中国气象学会,2002:15-25. |
| 27 | 张晔.中国北方沙区冬春季沙尘空间分布及尘源路径研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2020. |
| 28 | 特日格乐.蒙古国沙尘暴对内蒙古沙尘暴的影响研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学,2016. |
| 29 | 李彰俊,陈光明,刘景涛,等.内蒙古自治区天气预报手册[M].北京:气象出版社,2012. |
| 30 | Shao Y.Simplification of a dust emission scheme and comparison with data[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2004,109(D10202):1-6 |
| 31 | 赵建华,张强,袁铁,等.沙粒启动机制的理论分析[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(6):61-70. |
| 32 | 李晓岚,张宏升.科尔沁沙地起沙过程沙尘气溶胶粒径分布特征[C]//中国颗粒学会气溶胶专业委员会.第十二届全国气溶胶会议暨第十三届海峡两岸气溶胶技术研讨会论文集.重庆:中国颗粒学会气溶胶专业委员会,2015. |
| 33 | Zhang Q, Xu C Y, Yang T.Variability of water resource in the Yellow River basin of past 50 years,China[J].Water Resources Management,2009,23(6):1157-1170. |
| 34 | Yuan Z, Yan D H, Xu J J,et al.Effects of the precipitiation pattern and vegetation coverage variation on the surface runoff characteristics in the eastern Taihang Mountain[J].Applied Ecology and Environmental Research,2019,17(3):5753-5764. |
| 35 | Jia X, Shao M A, Zhang C,et al.Regional temporal persistence of dried soil layer along south-north transect of the Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2015,528:152-160. |
| 36 | Liu B, Shao M A.Estimation of soil water storage using temporal stability in four land uses over 10 years on the Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2014,517:974-984. |
| 37 | Sun W Y, Song X Y, Mu X M,et al.Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2015,209:87-99. |
| [1] | Ting Liu, Xiaopeng Jia, Dingmei Chen, Lamu Yixi, Yan Zhang, Kaijia Pan, Zhengcai Zhang. Surface aerodynamic characteristics of flat quicksand in the middle reaches of Yarlung Tsangpo River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 194-203. |
| [2] | Qingshuang Meng, Hejun Zuo, Min Yan, Haibing Wang, Cheng Xi. Relationship between constant elements and granularity of the surface sediment in the Kubuqi Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 107-117. |
| [3] | Xueyang Guo, Linhai Yang, Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu. Physical and chemical characteristics of aeolian sands in Jiudong Sandy Land of Hexi Corridor and its environmental significance [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 17-30. |
| [4] | Yawei Fan, Heqiang Du, Shanlong Lu, Zhiwen Han, Xiufan Liu, Xinlei Liu. Surface particle size composition and aeolian-sand flow structure of Zuo Lake Basin in the source of Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 47-56. |
| [5] | Xiaohong Ma, Fei Lin, Liming Yuan, Junjie Niu. Vegetation coverage change and its response to ecological protection project in Fenhe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 86-95. |
| [6] | Fanrui Bu, Ying Liu, Xueyong Zou. Response of vegetation coverage to precipitation change in the typical sandy lands of eastern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 9-20. |
| [7] | Jingping Chen, Ziying Yu, Fan Yang, Mi Wang, Han Hu, Guanzhong Ni, Xin Gao, Xin Wang. Particle size characteristics of sandstorm and surface sand at Tazhong area of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [8] | Jiaqi Zhao, Chunlai Zhang, Guoru Wei. Probability distribution of wind speed at different time scales in Alxa Right Banner, Inner Mongolia,China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 37-42. |
| [9] | Xuying Bai, Yujie Wang, Yunqi Wang, Wenbin Yang, Tao Wang, Yiben Cheng. Changes and driving factors of water body area in Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 65-73. |
| [10] | Jiawang Yin, Ala Musa, Yuhang Su. Effects of dune vegetation on water dynamics in interdune lowland in the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 194-203. |
| [11] | Wen Zhang, Dingding Du, Zhiwen Li, Wangyang Wu, Xiangjie Li, Yonghui Bai. Grain size characteristics of sediments in sandy land around the Poyang Lake and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 122-132. |
| [12] | Zhenliang Yin, Qi Feng, Lingge Wang, Zexia Chen, Yabin Chang, Rui Zhu. Vegetation coverage change and its influencing factors across the northwest region of China during 2000-2019 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 11-21. |
| [13] | Jingjing Hu, Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong. Particle size characteristics of aeolian desertified land in Madoi Basin of the source region of Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 242-252. |
| [14] | Shufeng Qu, Guoming Zhang, Lianyou Liu, Li Li, Yuting Xiao, Mingzhu Xiang, Xuran Sun, Xujiao Han. The surface abrasion and dust emission of mud desert in dry rump lake basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 81-88. |
| [15] | Siyu Chen, Yawen Guan, Dan Zhao, Gaotong Lou, Yu Chen. Influence of dust aerosol on land surface diurnal temperature range over East Asia Simulated with the WRF-Chem model [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 127-138. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech