
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 17-30.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00156
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xueyang Guo( ), Linhai Yang(
), Linhai Yang( ), Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu
), Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu
Received:2022-10-25
Revised:2022-11-24
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Linhai Yang
CLC Number:
Xueyang Guo, Linhai Yang, Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu. Physical and chemical characteristics of aeolian sands in Jiudong Sandy Land of Hexi Corridor and its environmental significance[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 17-30.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00156
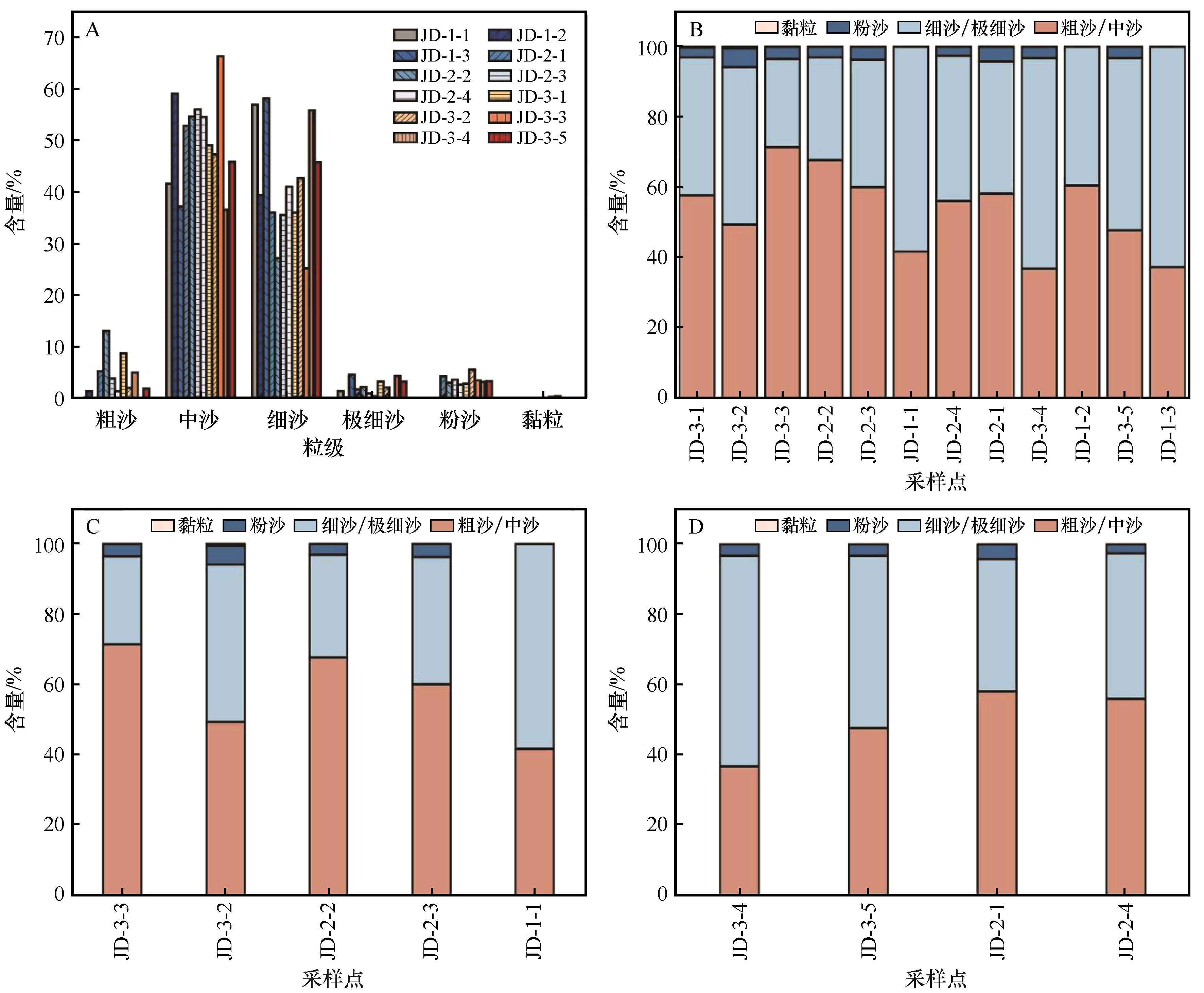
Fig.2 Gradation of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land (A), grain size variation characteristics from north to south (B) and from west to east (C: hinterland of the sandy land, D: south edge of the sandy land)
| 采样点 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 68.92 | 6.9 | 2.22 | 1.36 | 2.80 | 1.86 | 1.53 |
| JD-1-2 | 66.95 | 7.28 | 2.61 | 1.59 | 3.65 | 1.95 | 1.57 |
| JD-1-3 | 68.52 | 7.06 | 2.36 | 1.51 | 3.30 | 1.86 | 1.59 |
| JD-2-1 | 60.21 | 7.91 | 4.09 | 2.59 | 6.58 | 2.06 | 1.45 |
| JD-2-2 | 71.83 | 7.26 | 2.06 | 1.48 | 3.21 | 2.07 | 1.64 |
| JD-2-3 | 64.30 | 7.15 | 2.62 | 1.96 | 4.61 | 2.06 | 1.47 |
| JD-2-4 | 60.69 | 7.52 | 3.13 | 2.43 | 6.06 | 2.02 | 1.41 |
| JD-3-1 | 69.23 | 7.4 | 2.41 | 1.53 | 3.56 | 2.09 | 1.63 |
| JD-3-2 | 63.09 | 7.53 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 5.93 | 1.99 | 1.47 |
| JD-3-3 | 62.12 | 7.59 | 2.85 | 1.92 | 4.95 | 2.18 | 1.54 |
| JD-3-4 | 61.65 | 7.95 | 3.16 | 2.22 | 5.64 | 2.05 | 1.64 |
| JD-3-5 | 66.96 | 7.87 | 2.80 | 1.71 | 3.87 | 2.02 | 1.77 |
| 变化范围 | 60.21~71.83 | 6.9~7.95 | 2.06~4.09 | 1.36~2.59 | 2.8~6.58 | 1.86~2.18 | 1.41~1.77 |
| 平均值 | 65.37 | 7.45 | 2.80 | 1.89 | 4.51 | 2.02 | 1.56 |
| 标准差 | 3.85 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 1.29 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 变异系数 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| 上部陆壳 | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 2.20 | 4.20 | 3.90 | 3.40 |
| 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 80.27 | 7.78 | 1.93 | 1.19 | 2.06 | 1.90 | 2.00 |
| 腾格里沙漠 | 80.94 | 8.26 | 1.96 | 1.12 | 1.30 | 1.88 | 2.25 |
| 塔克拉玛干沙漠 | 62.05 | 10.18 | 2.36 | 1.58 | 7.30 | 2.33 | 2.40 |
Table 1 Major element contents of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land and other deserts in China (%)
| 采样点 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 68.92 | 6.9 | 2.22 | 1.36 | 2.80 | 1.86 | 1.53 |
| JD-1-2 | 66.95 | 7.28 | 2.61 | 1.59 | 3.65 | 1.95 | 1.57 |
| JD-1-3 | 68.52 | 7.06 | 2.36 | 1.51 | 3.30 | 1.86 | 1.59 |
| JD-2-1 | 60.21 | 7.91 | 4.09 | 2.59 | 6.58 | 2.06 | 1.45 |
| JD-2-2 | 71.83 | 7.26 | 2.06 | 1.48 | 3.21 | 2.07 | 1.64 |
| JD-2-3 | 64.30 | 7.15 | 2.62 | 1.96 | 4.61 | 2.06 | 1.47 |
| JD-2-4 | 60.69 | 7.52 | 3.13 | 2.43 | 6.06 | 2.02 | 1.41 |
| JD-3-1 | 69.23 | 7.4 | 2.41 | 1.53 | 3.56 | 2.09 | 1.63 |
| JD-3-2 | 63.09 | 7.53 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 5.93 | 1.99 | 1.47 |
| JD-3-3 | 62.12 | 7.59 | 2.85 | 1.92 | 4.95 | 2.18 | 1.54 |
| JD-3-4 | 61.65 | 7.95 | 3.16 | 2.22 | 5.64 | 2.05 | 1.64 |
| JD-3-5 | 66.96 | 7.87 | 2.80 | 1.71 | 3.87 | 2.02 | 1.77 |
| 变化范围 | 60.21~71.83 | 6.9~7.95 | 2.06~4.09 | 1.36~2.59 | 2.8~6.58 | 1.86~2.18 | 1.41~1.77 |
| 平均值 | 65.37 | 7.45 | 2.80 | 1.89 | 4.51 | 2.02 | 1.56 |
| 标准差 | 3.85 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 1.29 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 变异系数 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| 上部陆壳 | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 2.20 | 4.20 | 3.90 | 3.40 |
| 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 80.27 | 7.78 | 1.93 | 1.19 | 2.06 | 1.90 | 2.00 |
| 腾格里沙漠 | 80.94 | 8.26 | 1.96 | 1.12 | 1.30 | 1.88 | 2.25 |
| 塔克拉玛干沙漠 | 62.05 | 10.18 | 2.36 | 1.58 | 7.30 | 2.33 | 2.40 |
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值 | 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 腾格里沙漠 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 458.2~507.4 | 474.3 | 13.8 | 0.03 | 550.0 | 544.5 | 619.61 |
| Sr | 136.1~196.0 | 165.3 | 20.0 | 0.12 | 350.0 | 168.1 | 171.77 |
| Cr | 40.2~356.8 | 175.8 | 91.9 | 0.52 | 35.0 | 105.1 | 95.53 |
| Zr | 72.9~147.9 | 93.6 | 22.2 | 0.24 | 190.0 | 89.5 | 105.13 |
| Rb | 51.4~66.1 | 57.7 | 4.4 | 0.08 | 112.0 | 62.8 | 70.69 |
| V | 38.9~76.2 | 52.0 | 10.5 | 0.20 | 60.0 | — | — |
| Co | 4.1~107.3 | 29.8 | 37.5 | 1.26 | 10.0 | 124.1 | 121.23 |
| Zn | 21.6~39.0 | 29.4 | 5.1 | 0.17 | 71.0 | — | — |
| La | 11.0~26.0 | 16.5 | 4.3 | 0.26 | 30.0 | — | — |
| Pb | 11.6~13.7 | 12.8 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 15.0 | — | — |
| Cu | 11.6~16.4 | 13.6 | 1.5 | 0.11 | 25.0 | 13.8 | 12.67 |
| Y | 12.1~18.7 | 14.4 | 2.1 | 0.15 | 22.0 | — | — |
| Ga | 8.9~10.7 | 9.7 | 0.7 | 0.07 | 17.0 | 10.7 | 11.13 |
| Ni | 18.9~37.4 | 26.6 | 5.0 | 0.19 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 16.65 |
| Nb | 6.3~11.1 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 0.19 | 25.0 | — | — |
| Bi | 5.8~5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 | — | — |
Table 2 Trace element contents of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land and adjacent deserts in China (μg·g-1 )
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值 | 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 腾格里沙漠 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 458.2~507.4 | 474.3 | 13.8 | 0.03 | 550.0 | 544.5 | 619.61 |
| Sr | 136.1~196.0 | 165.3 | 20.0 | 0.12 | 350.0 | 168.1 | 171.77 |
| Cr | 40.2~356.8 | 175.8 | 91.9 | 0.52 | 35.0 | 105.1 | 95.53 |
| Zr | 72.9~147.9 | 93.6 | 22.2 | 0.24 | 190.0 | 89.5 | 105.13 |
| Rb | 51.4~66.1 | 57.7 | 4.4 | 0.08 | 112.0 | 62.8 | 70.69 |
| V | 38.9~76.2 | 52.0 | 10.5 | 0.20 | 60.0 | — | — |
| Co | 4.1~107.3 | 29.8 | 37.5 | 1.26 | 10.0 | 124.1 | 121.23 |
| Zn | 21.6~39.0 | 29.4 | 5.1 | 0.17 | 71.0 | — | — |
| La | 11.0~26.0 | 16.5 | 4.3 | 0.26 | 30.0 | — | — |
| Pb | 11.6~13.7 | 12.8 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 15.0 | — | — |
| Cu | 11.6~16.4 | 13.6 | 1.5 | 0.11 | 25.0 | 13.8 | 12.67 |
| Y | 12.1~18.7 | 14.4 | 2.1 | 0.15 | 22.0 | — | — |
| Ga | 8.9~10.7 | 9.7 | 0.7 | 0.07 | 17.0 | 10.7 | 11.13 |
| Ni | 18.9~37.4 | 26.6 | 5.0 | 0.19 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 16.65 |
| Nb | 6.3~11.1 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 0.19 | 25.0 | — | — |
| Bi | 5.8~5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 | — | — |
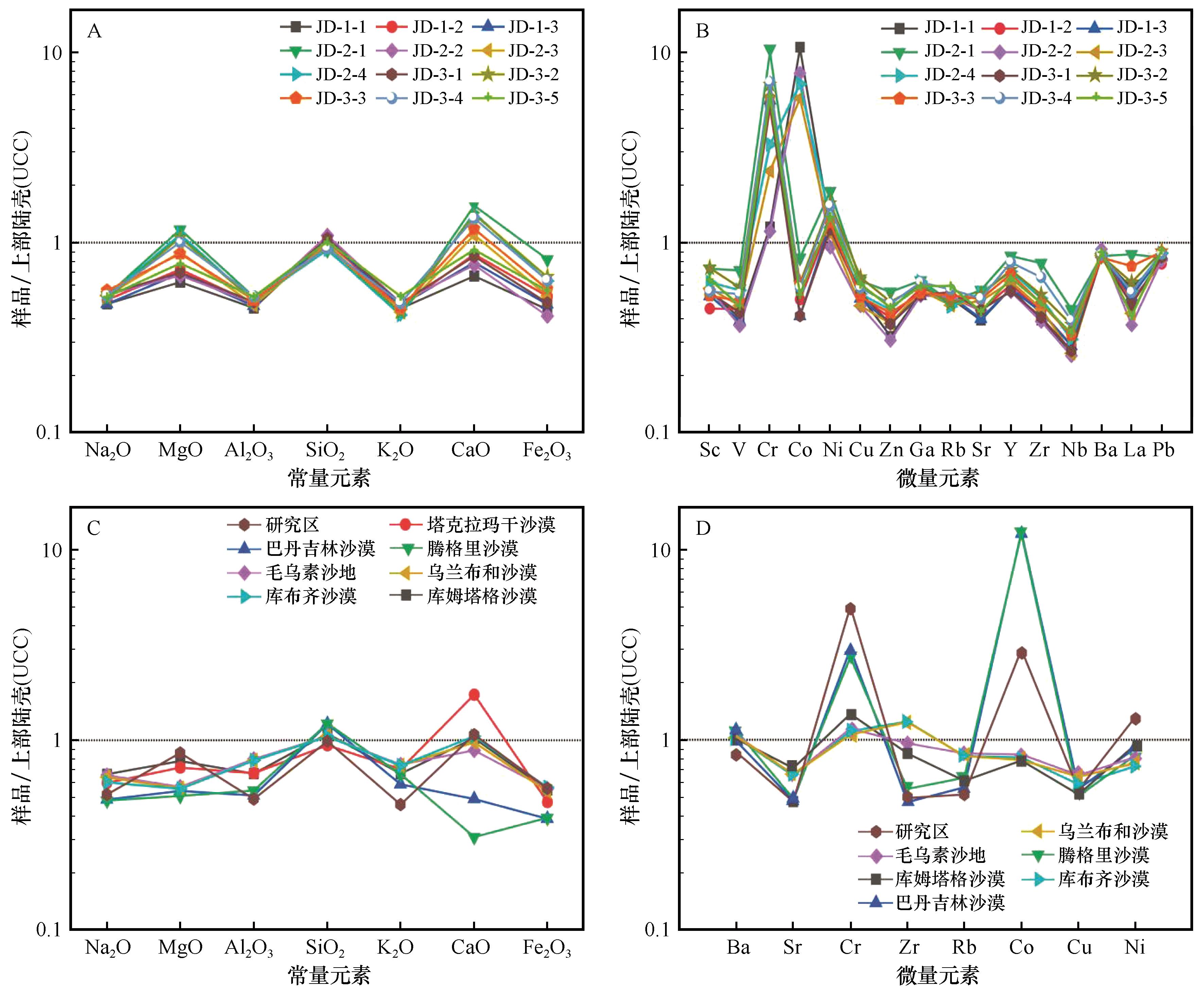
Fig.6 Distribution of UCC standardized values of geochemical elements in aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land (the values of other deserts are shown for comparison)
| 指数 | JD-1-1 | JD-1-2 | JD-1-3 | JD-2-1 | JD-2-2 | JD-2-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rb/Sr | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.30 |
| 淋溶系数 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 0.95 | 1.14 |
| CIA | 45.98 | 46.24 | 46.35 | 47.58 | 44.77 | 45.00 |
| 指数 | JD-2-4 | JD-3-1 | JD-3-2 | JD-3-3 | JD-3-4 | JD-3-5 |
| Rb/Sr | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.44 |
| 淋溶系数 | 1.26 | 0.98 | 1.25 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 0.97 |
| CIA | 46.85 | 45.08 | 46.99 | 45.13 | 47.22 | 46.86 |
Table 3 Chemical weathering degree of the aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land
| 指数 | JD-1-1 | JD-1-2 | JD-1-3 | JD-2-1 | JD-2-2 | JD-2-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rb/Sr | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.30 |
| 淋溶系数 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 0.95 | 1.14 |
| CIA | 45.98 | 46.24 | 46.35 | 47.58 | 44.77 | 45.00 |
| 指数 | JD-2-4 | JD-3-1 | JD-3-2 | JD-3-3 | JD-3-4 | JD-3-5 |
| Rb/Sr | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.44 |
| 淋溶系数 | 1.26 | 0.98 | 1.25 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 0.97 |
| CIA | 46.85 | 45.08 | 46.99 | 45.13 | 47.22 | 46.86 |
| 采样点 | 石英 | 长石 | 白云石 | 磷酸钠 铍石 | 铁锂 云母 | Q/TF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 75 | 25 | 3.00 | |||
| JD-1-2 | 69 | 31 | 2.23 | |||
| JD-1-3 | 68 | 30 | 2 | 2.27 | ||
| JD-2-1 | 63 | 33 | 4 | 1.91 | ||
| JD-2-2 | 69 | 28 | 2 | 2.46 | ||
| JD-2-3 | 65 | 32 | 3 | 2.03 | ||
| JD-2-4 | 63 | 32 | 5 | 1.97 | ||
| JD-3-1 | 66 | 32 | 2 | 2.06 | ||
| JD-3-2 | 65 | 29 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2.24 |
| JD-3-3 | 60 | 36 | 4 | 1 | 1.67 | |
| JD-3-4 | 61 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 2.03 | |
| JD-3-5 | 65 | 34 | 1 | 1.91 |
Table 4 Average mineral content and maturity index of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land
| 采样点 | 石英 | 长石 | 白云石 | 磷酸钠 铍石 | 铁锂 云母 | Q/TF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 75 | 25 | 3.00 | |||
| JD-1-2 | 69 | 31 | 2.23 | |||
| JD-1-3 | 68 | 30 | 2 | 2.27 | ||
| JD-2-1 | 63 | 33 | 4 | 1.91 | ||
| JD-2-2 | 69 | 28 | 2 | 2.46 | ||
| JD-2-3 | 65 | 32 | 3 | 2.03 | ||
| JD-2-4 | 63 | 32 | 5 | 1.97 | ||
| JD-3-1 | 66 | 32 | 2 | 2.06 | ||
| JD-3-2 | 65 | 29 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2.24 |
| JD-3-3 | 60 | 36 | 4 | 1 | 1.67 | |
| JD-3-4 | 61 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 2.03 | |
| JD-3-5 | 65 | 34 | 1 | 1.91 |
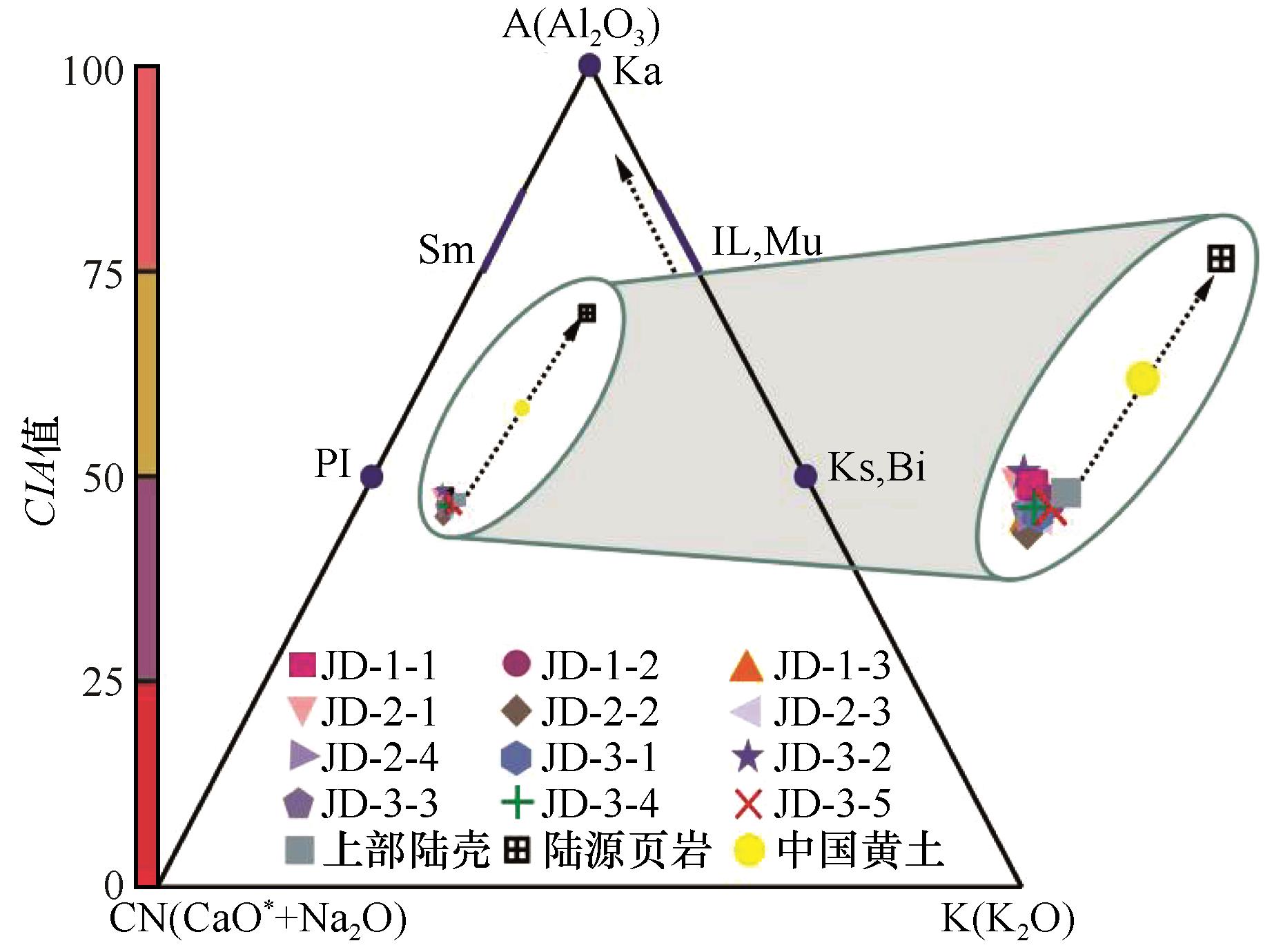
Fig.7 A-CN-K triangle diagram of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land (Long dashed arrows indicate early continental weathering trends; Short dashed arrows indicate the mediμm-term continental weathering trends; Ka= kaolinite,Sm=montmorillonite,PI=plagioclase,IL=Illite,Mu=muscovite,Bi=black mica,Ks=potassiμm feldspar)
| 1 | 董治宝,吕萍.70年来中国风沙地貌学的发展[J].地理学报,2020,75(3):509-528. |
| 2 | 吴正.风沙地貌学[M].北京:科学出版社,1987:1-18. |
| 3 | 朱秉启.中纬度荒漠区河西走廊沙丘地貌的演化特征及其环境指示[J].地理学报,2021,76(11):2710-2729. |
| 4 | 马建军.1988-2017年西藏定结地区风沙地貌格局变化及其对气候的响应[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2019. |
| 5 | Thomas D S G, Wiggs G F S.Aeolian system responses to global change:challenges of scale,process and temporal integration[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2008,33(9):1396-1418. |
| 6 | 陈国祥.毛乌素沙地风成沉积物沉积学特征[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2019. |
| 7 | 钱亦兵,吴兆宁,石井武政,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠沙物质成分特征及其来源[J].中国沙漠,1993,13(4):32-38. |
| 8 | 徐志伟,鹿化煜,赵存法,等.库姆塔格沙漠地表物质组成、来源和风化过程[J].地理学报,2010,65(1):53-64. |
| 9 | Liu B, Qu J, Ning D,et al.Grain-size study of aeolian sediments found east of Kumtagh Desert[J].Aeolian Research,2014,13:1-6. |
| 10 | 崔徐甲,孙虎,董治宝,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山沉积物地球化学元素组成及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(1):17-25. |
| 11 | Ren X Z.Major and trace elemental geochemistry of dune surface sands in the southeastern margin of the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Quaternary International,2012,279/280:399-399. |
| 12 | Wen Y L, Wu Y Q, Tan L H,et al.End-member modeling of the grain size record of loess in the Mu Us Desert and implications for dust sources[J].Quaternary International,2019,532:87-97. |
| 13 | Yang L H, Wang T, Long H,et al.Late Holocene dune mobilization in the Horqin dunefield of northern China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,138:136-147. |
| 14 | 程弘毅.河西地区历史时期沙漠化研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2007. |
| 15 | Chen D B, Pan B T, Hu X F,et al.Formation age of Jiudong Sandy Land,in the western Hexi Corridor,NW China[J].Quaternary International,2019,513:47-55. |
| 16 | 张正偲,董治宝.黑河流域中游沙漠风能环境与风沙地貌[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(2):332-341. |
| 17 | Zhang Z C, Dong Z B.Grain size characteristics in the Hexi Corridor Desert[J].Aeolian research,2015,18:55-67. |
| 18 | Zhang Z C, Pan K J, Zhang C X,et al.Geochemical characteristics and the provenance of aeolian material in the Hexi Corridor Desert,China[J].Catena,2020,190:1-10. |
| 19 | Xu Z W, Zhao C F, Wang X Y,et al.Composition,origin and weathering process of surface sediment in Kumtagh Desert,Northwest China[J].Geograpjical Sciences,2011,21(6):1062-1076. |
| 20 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K,et al.Grain-size distribution function of polygonal sediments in hydraulic and environments,and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J].Sedimentary Geology,2002,152:263-277. |
| 21 | Yang X P, Zhang F, Fu X D,et al.Oxygen isotopic compositions of quartz in the sand seas and sandy lands of northern China and their implications for understanding the provenances of aeolian sands[J].Geomorphology,2008,102:278-285. |
| 22 | 马金凤.河西走廊酒东盆地 1.7Ma以来的沉积物粘土矿物特征及其古环境意义[D].兰州:兰州大学,2018. |
| 23 | 常兆丰,张剑挥,王强强,等.新月形沙丘及新月形沙丘链存在的环境条件:以甘肃河西沙区为例[J].干旱区资源与环境,2016,30(11):167-173. |
| 24 | 潘凯佳,张正偲,董治宝,等.河西走廊新月形沙丘表层沉积物的理化性质[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(1):44-51. |
| 25 | Zhang C X, Wang X M, Dong Z B,et al.Aeolian process of the dried-up riverbeds of the Hexi Corridor,China:a wind tunnel experiment[J].Environmental Monitoring & Assessment,2017,189(8):419. |
| 26 | Li X D, Liu T, Zhao C L,et al.Land use drives the spatial variability of soil phosphorus in the Hexi Corridor,China[J].Biogeochemistry,2021,155:59-75. |
| 27 | Lancaster N.The Namib Sand Sea:Dunes Forms,Processes and Sediments[M].Rotterdam,Nertherlands:Balkema,1989. |
| 28 | Zhao H, Li G, Sheng Y,et al.Early-middle Holocene lake-desert evolution in northern Ulan Buh desert,China[J].Palaeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2012,331:31-38. |
| 29 | 董治宝,胡光印,颜长珍,等.江河源区沙漠化[M].北京:科学出版社,2013. |
| 30 | Dasch E J.Strontium isotopes in weathering profiles,deep-sea sediments,and sedimentary rocks[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1969,33(12):1521-1552. |
| 31 | 陈秋洁.巴丹吉林沙漠地表风成沉积物的元素组成特征与环境指示意义[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| 32 | Lancaster N.Aeolian processes[M]//Elias S A.Reference Module in Earth Systems and Enviromental Sciences.New York,USA:Elsevier,2014:1-17. |
| 33 | 王晓枝,董治宝,南维鸽,等.拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘沉积物特征[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):22-31. |
| 34 | Visher G.Grain size distributions and depositional processes[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1969,39(3):1074-1106. |
| 35 | 冯铄,刘志飞, Sompongchaiyakul P,等.泰国湾表层沉积物陆源碎屑的粒度特征及其展现的沉积动力环境[J].地学前缘,2022,29(4):211-220. |
| 36 | 徐树建,倪志超,丁新潮.山东平阴黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2016,35(2):353-359. |
| 37 | Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continenal Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M].Boston,USA:Blackwell Scientific,1985. |
| 38 | 李恩菊.巴丹吉林沙漠与腾格里沙漠沉积物特征的对比研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2011. |
| 39 | 赵万苍,刘连文,陈骏,等.中国沙漠元素地球化学区域特征及其对黄土物源的指示意义[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(9):1425-1438. |
| 40 | 李继彦,周玲,刘益,等.晋西北地区表层土壤粒度与地球化学元素组成[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):155-162. |
| 41 | 柳本立,屈建军,杨根生,等.库姆塔格沙漠东部复杂地貌地表沉积物化学元素组成初步研究[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(5):1194-1199. |
| 42 | 赵杰.古尔班通古特沙漠风成沉积物特征研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2020. |
| 43 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoric climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,229:715-717. |
| 44 | Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J].Geology,1995,23(10):921-924. |
| 45 | Pettijohn F J, Paul E P, Raymond S.Sand and Sandstone[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer Verlag,1973. |
| 46 | 宁凯,李卓仑,王乃昂,等.巴丹吉林沙漠地表风积砂粒度空间分布及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(3):642-648. |
| 47 | 宋洁,春喜,白雪梅,等.中国沙漠粒度分析研究综述[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(3):597-603. |
| 48 | 张余,张克存,安志山,等.敦煌沙漠绿洲过渡带地表沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境[J].水土保持通报,2017,37(4):69-73. |
| 49 | 何清,杨兴华,霍文,等.库姆塔格沙漠粒度分布特征及环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(1):18-22. |
| 50 | 吉启慧.粒度分析在塔克拉玛干沙漠研究中的应用[J].中国沙漠,1996,16(2):173-179. |
| 51 | 李超,董治宝,崔徐甲.腾格里沙漠东南缘不同发育阶段横向沙丘粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(1):129-135. |
| 52 | 舒培仙,牛东风,李保生,等.毛乌素沙地现代沙丘沙的粒度特征及其意义[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(1):158-166. |
| 53 | Lancaster D.Grain size characteristics of linear dunes in the southwestern Kalahari[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1986,56(3):395-400. |
| 54 | Mischke S.New evidence for origin of Badain Jaran Desert of lnner Mongolia from granulometry and thermoluminescence dating[J].Journal of Palaeogeography,2005,7(1):79-97. |
| 55 | 李玲萍,李岩瑛,李晓京,等.河西走廊不同强度冷锋型沙尘暴环流和动力特征[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(5):219-228. |
| 56 | Pye K.Aeolian Dust and Dust Deposits[M].London,UK:Academic Press,1987:1-256. |
| 57 | Sun D H, Su R X, Bloemendal J,et al.Grain-size and accumulation rate records from Late Cenozoic aeolian sequences in Northern China:implication for variations in the East Asian winter monsoon and westerly atmospheric circulation [J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2008,264(1/2):39-53. |
| 58 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K,et al.Bimodal grain-size distribution of Chinese loess,and its palaeoclimatic implications[J].Catena,2004,55(3):325-340. |
| 59 | Vandenberghe J.Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:a powerful proxy for process identification[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2013,121:18-30. |
| 60 | 孔凡彪,陈海涛,徐树建,等.山东章丘黄土粒度指示的粉尘堆积过程及古气候意义[J].地理学报,2021,76(5):1163-1176. |
| 61 | Nottebaum V, Stauch G, Hartmann K,et al.Unmixed loess grain size populations along the northern Qilian Shan (China):relationships between geomorphologic,sedimentologic and climatic controls[J].Quaternary International,2015,372:151-166. |
| 62 | 梁爱民,屈建军,董治宝,等.库姆塔格沙漠沉积物粒度端元特征及其物源启示[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(2):33-42. |
| 63 | Wang X M, Dong Z B, Zhang J W,et al.Grain size characteristics of dune sand in the central Taklimakan Sand Sea[J].Sedimentary Geology,2003,16:1-4. |
| 64 | 唐进年.库姆塔格沙漠沉积物特征与沉积环境研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2018. |
| 65 | 王立强.河西走廊及其毗邻地区地表沉积与亚洲粉尘源区示踪[D].兰州:兰州大学,2011. |
| 66 | 罗万银,董治宝,钱广强,等.戈壁表层沉积物地球化学元素组成及其沉积意义[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1441-1453. |
| 67 | 胡观冠,李保生,温小浩,等.毛乌素沙地现代流动沙丘沙的矿物成分[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1454-1460. |
| 68 | 王祎.青藏高原东北缘尖扎盆地沉积物矿物特征及其古环境意义[D].西安:长安大学,2019. |
| [1] | Qingshuang Meng, Hejun Zuo, Min Yan, Haibing Wang, Cheng Xi. Relationship between constant elements and granularity of the surface sediment in the Kubuqi Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 107-117. |
| [2] | Yawei Fan, Heqiang Du, Shanlong Lu, Zhiwen Han, Xiufan Liu, Xinlei Liu. Surface particle size composition and aeolian-sand flow structure of Zuo Lake Basin in the source of Yangtze River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 47-56. |
| [3] | Mengjun Hu, Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Aokang Xu. Geochemical characteristics of major elements and environmental evolution in the Holocene in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 11-20. |
| [4] | Jingping Chen, Ziying Yu, Fan Yang, Mi Wang, Han Hu, Guanzhong Ni, Xin Gao, Xin Wang. Particle size characteristics of sandstorm and surface sand at Tazhong area of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [5] | Wen Zhang, Dingding Du, Zhiwen Li, Wangyang Wu, Xiangjie Li, Yonghui Bai. Grain size characteristics of sediments in sandy land around the Poyang Lake and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 122-132. |
| [6] | Jinqiu Wang, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Yunping Chi, Lei Sun, Peng Wu, Zhenyu Wei. Changing provenance of Harbin loess since the Middle Pleistocene: evidence from TIMA automated quantification of minerals [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 25-35. |
| [7] | Hongli Pang, Hongshan Gao, Fuqiang Li, Lianke Zhang. Geochemical element composition and spatial distribution characteristics of sediments in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia section of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 44-53. |
| [8] | Xiaozhi Wang, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang. Sediment characteristics of climbing dunes in Lhasa River Valley, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 22-31. |
| [9] | Jingjing Hu, Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong. Particle size characteristics of aeolian desertified land in Madoi Basin of the source region of Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 242-252. |
| [10] | Min Chen, Baosheng Li, Fengnian Wang, Dongfeng Niu, Xiaohao Wen, Peixian Shu, Yuejun Si, Qinjiang Yang, Chen Wang. High-resolution monsoonal environment change in MIS3 based on trace elements in the Tumen Section on the southweest edge of Tegger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 253-263. |
| [11] | Shufeng Qu, Guoming Zhang, Lianyou Liu, Li Li, Yuting Xiao, Mingzhu Xiang, Xuran Sun, Xujiao Han. The surface abrasion and dust emission of mud desert in dry rump lake basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 81-88. |
| [12] | Chong Gao, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan, Zhengyao Liu, Chunming Zhu, Xiaozhi Wang, Nan Xiao, Xin Zhang. Physicochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of honeycomb dunes in Gurbantunggut Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 14-24. |
| [13] | Miao Dong, Ping Yan, Xiaoxu Wang, Guoming Zhang, Xiaonan Meng, Xinran Ji, Yong Wang. Characteristics of surface sediments on the climbing dunes in Shannan wide valley section of Yarlung Tsangpo River, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 153-163. |
| [14] | Weixin Zhou, Xiaohao Wen, Baosheng Li, Chen Wang, Mengyuan Tian, Mingqun Qiu. Geochemical characteristics of holocene lacustrine sediments in Gangouzi section and its sedimentary sources in the Salawusu River Valley [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 114-122. |
| [15] | Mengjun Hu, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun. Geochemical characteristics of major element oxides and environmental evolution inferred from lacustrine sediments in Gonghe Basin, China during the early Late Pleistocene [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 147-157. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech