
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 1-9.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00158
Yayun Li1,2( ), Wei Cheng1, Ning Wang1, Xin Li3, Rui Gao1
), Wei Cheng1, Ning Wang1, Xin Li3, Rui Gao1
Received:2022-08-08
Revised:2022-11-22
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
CLC Number:
Yayun Li, Wei Cheng, Ning Wang, Xin Li, Rui Gao. Comparative study on the characteristic of spring sandstorms and the related meteorological factors of the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 1-9.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00158
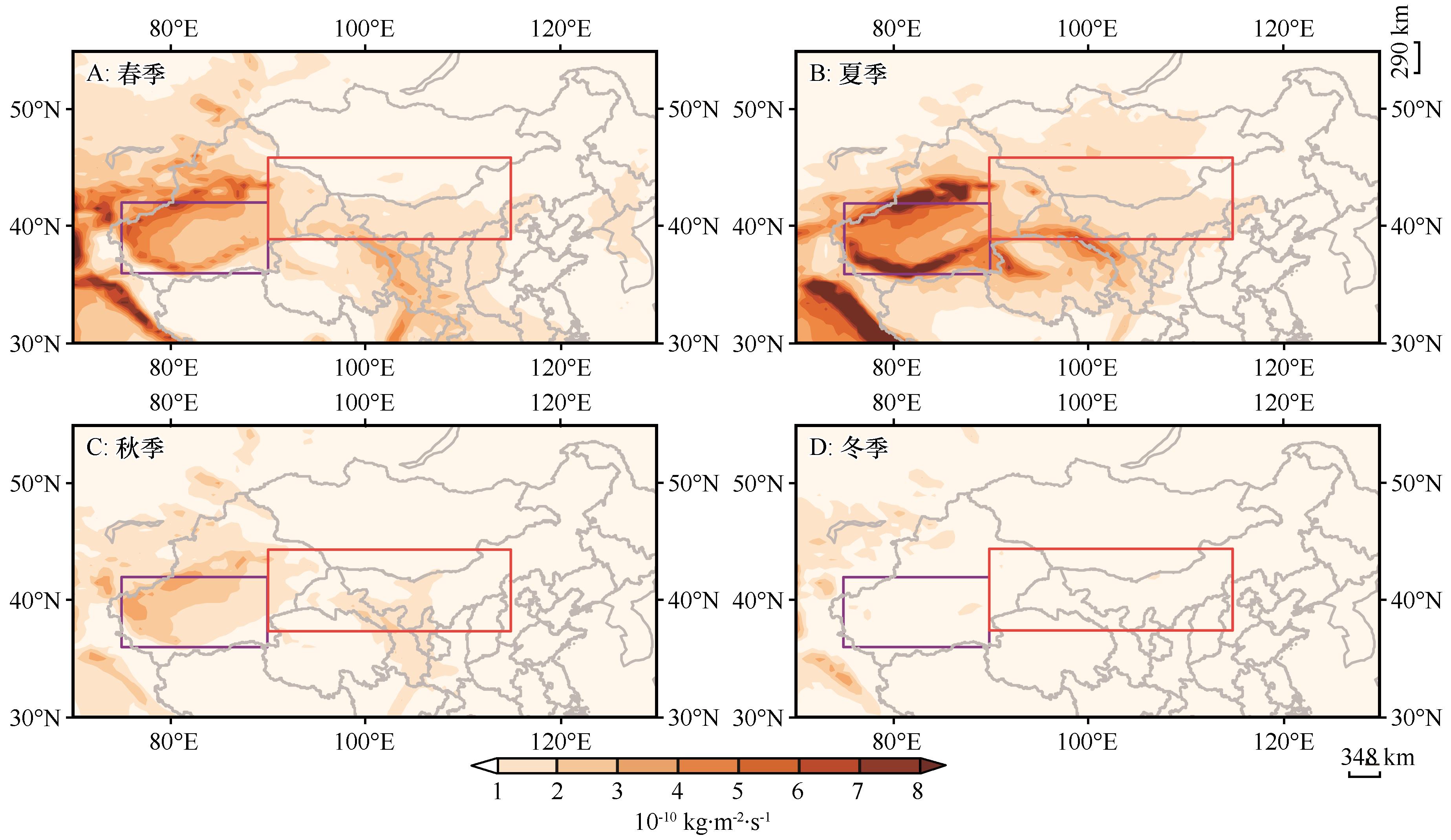
Fig.5 Distribution of annual dry and wet deposition in spring (A), summer (B), autumn (C), winter (D) in Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert from 2007 to 2021
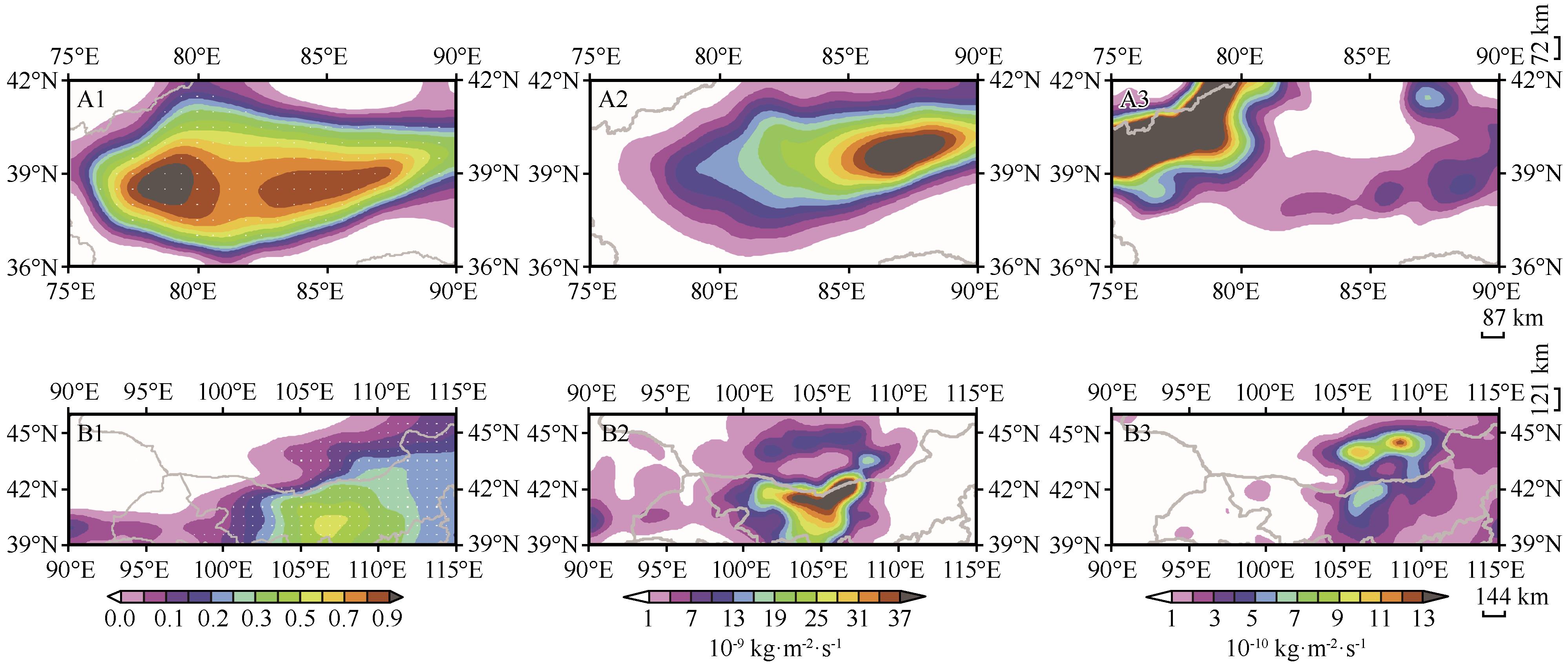
Fig.7 Anomaly distribution of dust AOD (A1\B1), emission (A2\B2), dry and wet deposition (A3\B3) of spring sandstorms in Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert from 2007 to 2021
| 1 | Jia R, Liu Y Z, Chen B,et al.Source and transportation of summer dust over the Tibetan Plateau[J].Atmospheric Environment,2015,123:210-219. |
| 2 | Chen S Y, Huang J P, Kang L T,et al.Emission,transport,and radiative effects of mineral dust from the Taklimakan and Gobi deserts comparison of measurements and model results[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2017,17(3):2401-2421. |
| 3 | Huang J P, Minnis P, Chen B,et al.Long-range transport and vertical structure of Asian dust from CALIPSO and surface measurements during PACDEX[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2008,113:D23212. |
| 4 | Kang L T, Huang J P, Chen S Y,et al.Long-term trends of dust events over Tibetan Plateau during 1961-2010[J].Atmospheric Environment,2016,125:188-198. |
| 5 | Kim J.Transport routes and source regions of Asian dust observed in Korea during the past 40 years (1965-2004)[J].Atmospheric Environment,2008,42:4778-4789. |
| 6 | Xiao F, Zhou C.Dust storms evolution in Taklimakan Desert and its correlation with climatic parameters[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2008,18(4):415-424. |
| 7 | 熊洁,赵天良,韩永翔,等.1995-2004年东亚沙尘气溶胶的模拟源汇分布及垂直结构[J].中国环境科学,2013,33(6):961-968. |
| 8 | 茹建波,王天河,李积明,等.东亚沙尘源区晴空和云上沙尘气溶胶特征[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(2):372-383. |
| 9 | 包春玲,咏梅,金额尔德木吐,等.东亚沙尘区域时空变化特征分析[J].地理研究,2021,40(11):3002-3015. |
| 10 | 杨婕,赵天良,程叙耕,等.2000-2019年中国北方地区沙尘暴时空变化及其相关影响因素[J].环境科学学报,2021,41(8):2966-2975. |
| 11 | 延昊,王长耀,牛铮,等.东亚沙尘源地、沙尘输送路径的遥感研究[J].地理科学进展,2002,21(1):90-94. |
| 12 | 高会旺,祁建华,石金辉,等.亚洲沙尘的远距离输送及对海洋生态系统的影响[J].地球科学进展,2009,24(1):1-10. |
| 13 | 钱胜利,李成才,张庆红.东亚高空大气气溶胶的分布及沙尘输送特征研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2010,46(4):547-554. |
| 14 | 于兴娜,张慧娟,登增然登,等.沙尘源区与下游地区沙尘期间气溶胶光学特性分析[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(6):1710-1715. |
| 15 | 刘建慧,赵天良,刘煜,等.沙尘气溶胶的跨亚欧大陆传输对东亚地区大气环境的影响[J].环境科学学报,2014,34(12):3102-3111. |
| 16 | 郭俊,银燕,王咏薇,等.东亚沙尘分布、源汇及输送特征的模拟研究[J].中国环境科学,2017,37(3):801-812. |
| 17 | 陈思宇,黄建平,李景鑫,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠和戈壁沙尘起沙、传输和沉降的对比研究[J].中国科学:地球科学,2017,47(8):939-957. |
| 18 | 贾瑞,刘玉芝,吴楚樵,等.2007-2017年中国沙尘气溶胶的三维分布特征及输送过程[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):108-117. |
| 19 | 宿兴涛,王汉杰,宋帅,等.近10年东亚沙尘气溶胶辐射强迫与温度响应[J].高原气象,2011,30(5):1300-1307. |
| 20 | 宿兴涛,王汉杰.近10年东亚沙尘气溶胶时空分布与起尘通量的数值研究[J].高原气象,2012,31(3):676-687. |
| 21 | 徐成鹏,葛觐铭,黄建平,等.基于CALIPSO星载激光雷达的中国沙尘气溶胶观测[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(5):1353-1362. |
| 22 | 钱正安,蔡英,刘景涛,等.中蒙地区沙尘暴研究的若干进展[J].地球物理学报,2006,49(1):83-92. |
| 23 | 贺沅平,张云伟,顾兆林.特强沙尘暴灾害性天气的研究及展望[J].中国环境科学,2021,41(8):3511-3522. |
| 24 | 庞舒婷,林莹晶,汤晨光,等.基于MERRA2再分析资料的全球AOD和沙尘AOD空间分布及趋势[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(1):54-62. |
| 25 | Christian A,Gueymard, Yang D Z.Worldwide validation of CAMS and MERRA-2 reanalysis aerosol optical depth products using 15 years of AERONET observations[J].Atmospheric Environment,2020,225:117216. |
| 26 | Wang A, Xie X, Liu X,et al.Direct radiative effect(DRE) of dust aerosols on West African and East Asian monsoon:the role of ocean-atmosphere interactions[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2022,127:e2021JD035917. |
| 27 | 贾瑞,李君,祝清哲,等.中国西北地区气溶胶的三维分布特征及其成因[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(3):34-43. |
| 28 | 沙尘天气等级: [S].2017. |
| 29 | 徐祥德,王继康,张碧辉,等.大气环境气象公报(2020年)[R].北京:中国气象局,2021. |
| 30 | 刘冲,赵天良,熊洁,等.1991-2010年全球沙尘气溶胶排放量气候特征及其大气环流影响因子[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(4):959-970. |
| [1] | Jingping Chen, Ziying Yu, Fan Yang, Mi Wang, Han Hu, Guanzhong Ni, Xin Gao, Xin Wang. Particle size characteristics of sandstorm and surface sand at Tazhong area of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [2] | Dagang Wang, Yang Yu, Lingxiao Sun, Jing He, Malik Ireneusz, Wistuba Malgorzata, Fengqing Jiang, Ruide Yu. Adaptability evaluation and modification of ET0 models in a typical oases on southern margin of the Taklimakan Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 41-53. |
| [3] | Kailu Liu, Xinping Wu, Yongqiang Liu, Mamtimin Ali, Fan Yang, Qing He. Estimation of hourly surface net radiation in Taklimakan Desert based on multi-source remote sensing data and reanalysis data [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 51-61. |
| [4] | Jiliang Liu, Wenzhi Zhao, Fengrui Li, Yibin Ba. Community dynamics of ground arachnid arthropods in a gravel gobi desert of the middle of the Hexi Corridor, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 155-164. |
| [5] | Jiantao Zhang, Minzhong Wang, Qing He, Honglin Pan, Lu Meng, Yanhui Wang. Variation characteristics of nocturnal low-level jet in summer over the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 89-100. |
| [6] | Pan Kaijia, Zhang Zhengcai, Liang Aimin, Dong Zhibao, Li Xingcai. Nebkhas geomorphology in the gobi desert using the unmanned aerial vehicle and tilt camera [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 24-32. |
| [7] | Zhao Jiawei, He Qing, Jin Lili, Li Zhenjie, Ali Mamtimin, Zhang Jiantao, Aikedai Shalamu. The surface layer micrometeorological characteristics of fluctuated surface in the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 144-155. |
| [8] | Li Aimin, Han Zhiwen. Relationship between moving speed and morphological parameters of barchan dunes [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 29-40. |
| [9] | Jin Lili, Li Zhenjie, He Qing, Ali Mamtimin, Huo Wen, Zhang Jiantao. Characteristic of Surface-Layer Turbulence Spectra on Typical Sunny Days over the Northern Marginal Zone of the Taklimakan Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 1-12. |
| [10] | Zhao Jiawei, He Qing, Jin Lili, Li Zhenjie, Ali Mamtimin, Zhang Jiantao. Characteristics of Land Surface Processes in the Hinterland of Taklimakan Desert in Autumn [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 159-167. |
| [11] | Zhou Xueying, Jia Jian, Liu Guoqiang, Wang Fang, Qiu Huimin, Sun Huaiqin. Characteristics of Precipitation at Hinterland of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 187-194. |
| [12] | Wang Minzhong, Xu Hongxiong, Wang Yinjun, Ali Mamtimin, Zhang Jiantao. Large-Eddy Simulation of Summer Clear Sky Convective Boundary Layer in the Taklimakan Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(6): 1275-1286. |
| [13] | Jin Lili, Li Zhenjie, He Qing, Liu Yongqiang, Ali Mamtimin, Xin Yu. Evaluation on Modeling of Land-Atmosphere Interaction in the Northern Marginal Zone of Taklimakan Desert with CoLM and Correction [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(6): 1287-1302. |
| [14] | Li Aimin, Han Zhiwen, Zhong Shuai, Guo Caiyun. Attributive Parameter Extraction of the Barchan Dune Based on CASS and ArcGIS [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(3): 484-491. |
| [15] | Peng Yanmei, Wang Shu, Xiao Gaoxiang, Gao Lei, He Qing, Liu Xinchun. Impact Factors of Atmospheric Aerosol Scattering Coefficient in the Tazhong Area of the Taklimakan Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2018, 38(2): 384-392. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech