
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 194-206.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00103
Jin Zhan1,2( ), Dan Han1,2, Hongling Yang1,2, Yulin Li1(
), Dan Han1,2, Hongling Yang1,2, Yulin Li1( )
)
Received:2021-05-25
Revised:2021-08-18
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-03-30
Contact:
Yulin Li
CLC Number:
Jin Zhan, Dan Han, Hongling Yang, Yulin Li. Evolution characteristics of vegetation community composition and diversity during the restoration of Horqin Sandy Land in 2005-2019[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 194-206.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00103
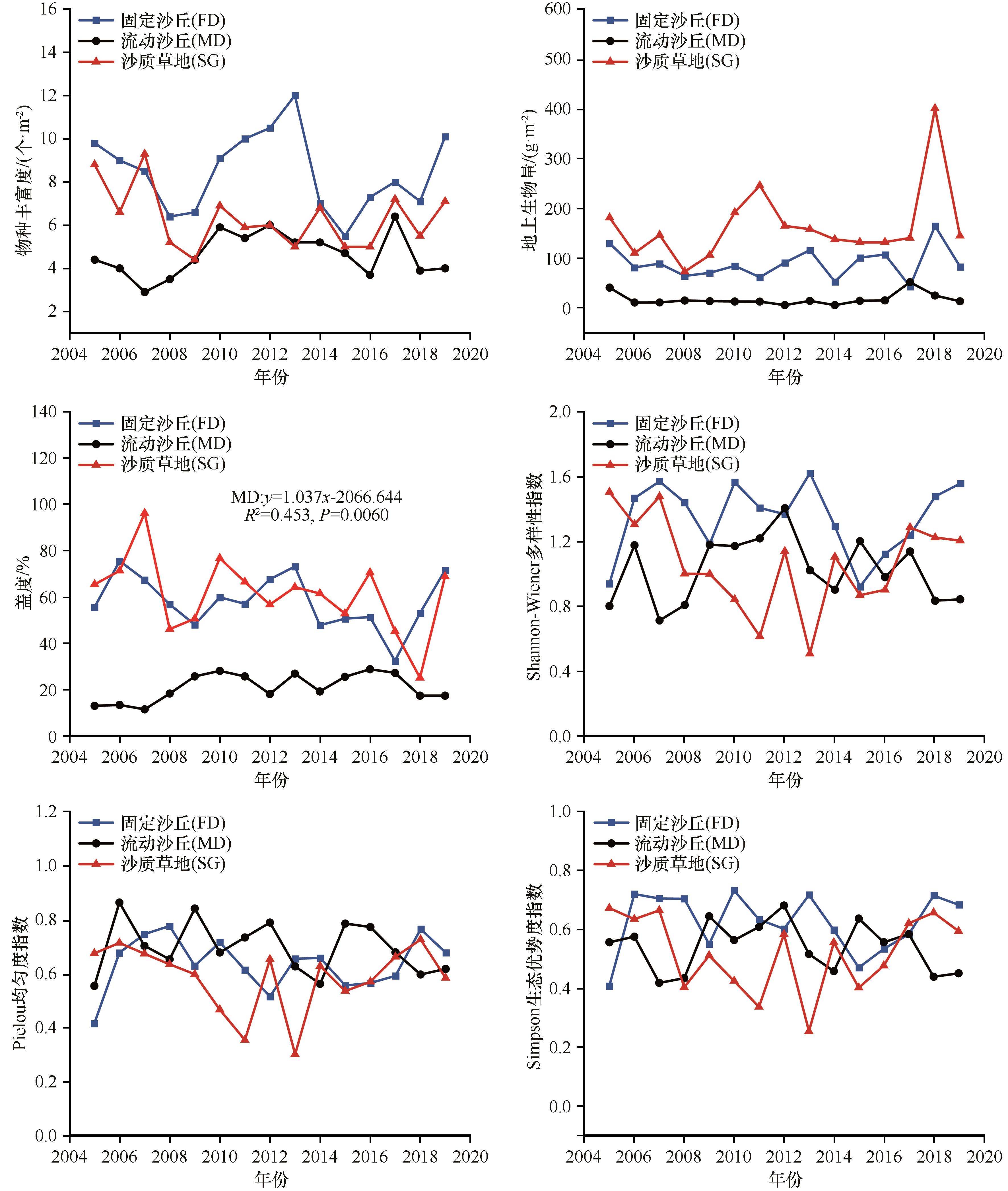
Fig.2 Characteristics of interannual variation of community in the process of vegetation restoration in Horqin Sandy Land (mean±SD). MD, mobile dune; FD, fixed dune; SG, sandy grassland. R2,Correlation coefficient; P, statistical significance (P<0.05 indicates the change trend is significant). Only the regression equation, R2, and P values with significantly higher changes are listed in the figure
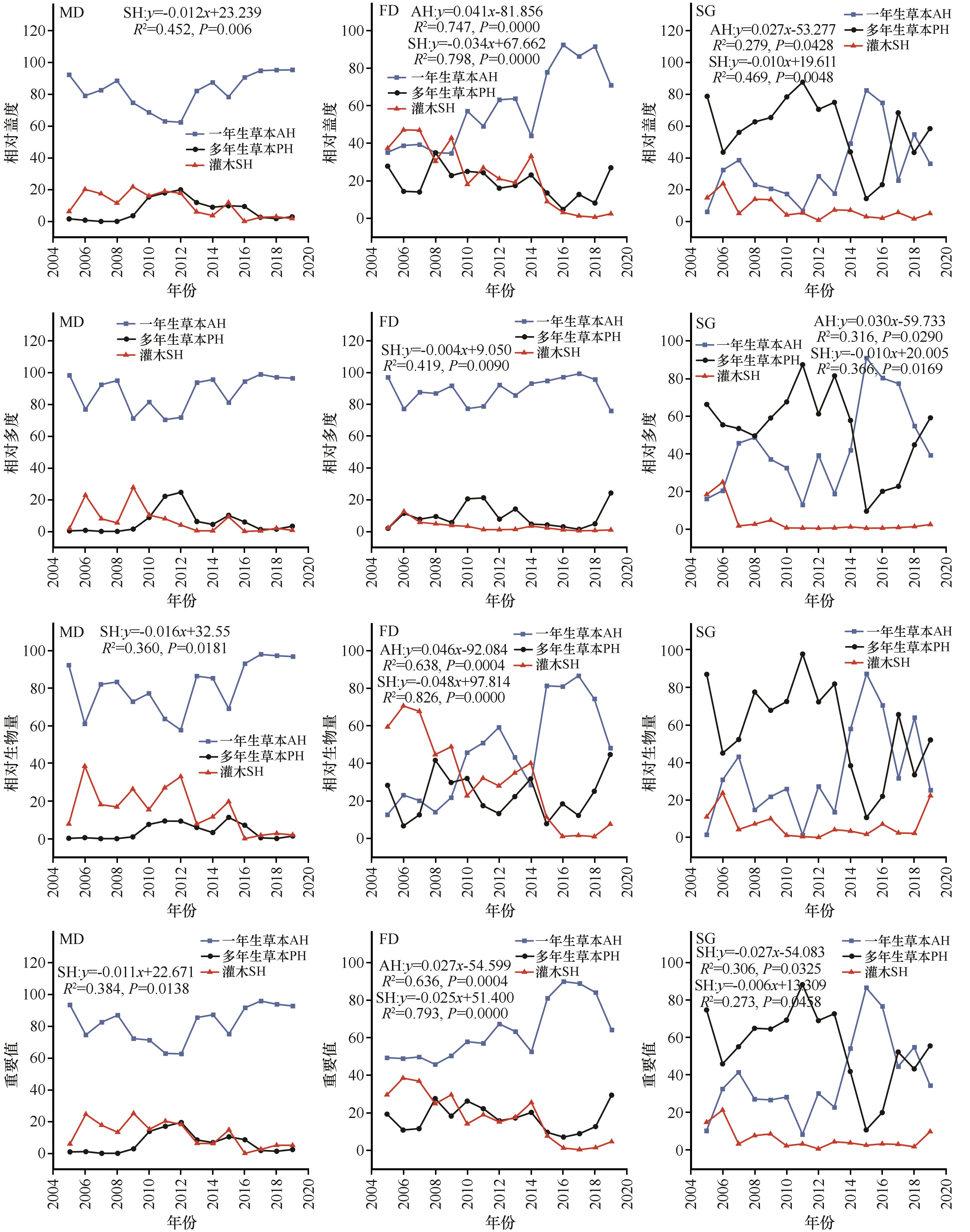
Fig.3 Interannual variation of plant species composition of different life forms in the process of restoration in Horqin Sandy Land (mean). AH, annual herbs; PH, perennial herbs; SH, shrubs. R2, Correlation coefficient; P, statistical "significance (P<0.05 indicates the change trend is significant). Only the regression equation, R2, and P values with significantly higher changes are listed in the figure
| 物种 | 生活型 | 重要值/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2019年 | ||
| 沙米(Agriophyllum squarrosum) | AH | 5.86 | 15.14 | 14.68 | 0.65 |
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | AH | 6.69 | 6.44 | 3.37 | 4.92 |
| 光梗蒺藜草(Cenchrus calyculatus) | AH | 0.92 | 0.33 | 3.10 | 2.41 |
| 欧亚旋覆花(Inula britanica) | AH | 20.18 | 13.11 | 24.70 | 21.54 |
| 虫实(Corispermum hyssopifolium) | AH | 10.04 | 3.38 | 27.94 | 20.67 |
| 差巴嘎蒿(Artemisia halodendron) | SH | 2.75 | 11.06 | — | — |
| 苦苣菜(Sonchus oleraceus) | AH | 1.66 | 0.38 | — | — |
| 马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis) | AH | 7.46 | — | — | — |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum thesioides) | PH | 43.67 | 3.20 | — | 7.74 |
| 五星蒿(Bassia dasyphylla) | AH | 0.78 | — | — | — |
| 杠柳(Periploca sepium) | SH | — | — | — | 4.39 |
| 苦苣菜(Sonchus oleraceus) | AH | — | — | 2.90 | 2.76 |
| 蓼子朴(Inula salsoloides) | AH | — | 45.30 | 16.05 | 34.93 |
| 薄翅猪毛菜(Salsola pellucida) | AH | — | 1.29 | — | — |
| 丝叶小苦荬(Ixeridium graminifolium) | PH | — | 0.36 | — | — |
| 白山蓟(Olgaea leucophylla) | PH | — | — | 4.90 | — |
| 狭叶苦卖菜(Ixeridium graminifolium) | PH | — | — | 2.36 | — |
| 物种数 | — | 10 | 11 | 9 | 9 |
Table 1 Changes of important values of species during vegetation restoration of mobile dunes in Horqin Sandy Land
| 物种 | 生活型 | 重要值/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2019年 | ||
| 沙米(Agriophyllum squarrosum) | AH | 5.86 | 15.14 | 14.68 | 0.65 |
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | AH | 6.69 | 6.44 | 3.37 | 4.92 |
| 光梗蒺藜草(Cenchrus calyculatus) | AH | 0.92 | 0.33 | 3.10 | 2.41 |
| 欧亚旋覆花(Inula britanica) | AH | 20.18 | 13.11 | 24.70 | 21.54 |
| 虫实(Corispermum hyssopifolium) | AH | 10.04 | 3.38 | 27.94 | 20.67 |
| 差巴嘎蒿(Artemisia halodendron) | SH | 2.75 | 11.06 | — | — |
| 苦苣菜(Sonchus oleraceus) | AH | 1.66 | 0.38 | — | — |
| 马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis) | AH | 7.46 | — | — | — |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum thesioides) | PH | 43.67 | 3.20 | — | 7.74 |
| 五星蒿(Bassia dasyphylla) | AH | 0.78 | — | — | — |
| 杠柳(Periploca sepium) | SH | — | — | — | 4.39 |
| 苦苣菜(Sonchus oleraceus) | AH | — | — | 2.90 | 2.76 |
| 蓼子朴(Inula salsoloides) | AH | — | 45.30 | 16.05 | 34.93 |
| 薄翅猪毛菜(Salsola pellucida) | AH | — | 1.29 | — | — |
| 丝叶小苦荬(Ixeridium graminifolium) | PH | — | 0.36 | — | — |
| 白山蓟(Olgaea leucophylla) | PH | — | — | 4.90 | — |
| 狭叶苦卖菜(Ixeridium graminifolium) | PH | — | — | 2.36 | — |
| 物种数 | — | 10 | 11 | 9 | 9 |
| 物种 | 生活型 | 重要值/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2019年 | ||
| 差巴嘎蒿(Artemisia halodendron) | SH | 29.25 | 9.52 | 5.11 | — |
| 地锦(Euphorbia humifusa) | AH | 22.86 | 8.40 | — | 0.73 |
| 扁蓄豆(Melissitus ruthenicus) | PH | 16.24 | 3.07 | 6.53 | 0.35 |
| 马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis) | AH | 7.24 | 8.86 | — | — |
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | AH | 6.76 | 19.40 | 1.54 | 8.60 |
| 五星蒿(Bassia dasyphylla) | AH | 2.87 | 16.07 | 30.95 | 3.71 |
| 绿藜(Kochia scoparia) | AH | 2.84 | — | — | — |
| 虫实(Corispermum hyssopifolium) | AH | 2.68 | 6.87 | 10.81 | 4.16 |
| 苦荬菜(Sonchus oleraceus) | PH | 1.87 | 0.24 | — | — |
| 画眉草(Eragrostis pilosa) | AH | 1.63 | 5.35 | — | 0.69 |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum theisiodes) | PH | 1.41 | 2.00 | 3.79 | 5.79 |
| 三芒草(Aristida adscensionis) | AH | 1.05 | 1.15 | — | 14.78 |
| 光梗蒺藜草(Cenchrus incertus) | AH | 0.66 | — | — | — |
| 猪毛菜(Salsola collina) | AH | 0.64 | 2.40 | 26.45 | 7.96 |
| 胡枝子(Lespedeza bicolor) | SH | 0.47 | — | 0.87 | — |
| 小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla) | SH | 0.47 | — | — | — |
| 白草(Pennisetum centrasiaticum) | PH | 0.44 | 2.02 | — | 6.52 |
| 灰绿藜(Chenopodium glaucum) | AH | 0.32 | — | — | — |
| 砂蓝刺头(Echinops gmelini) | AH | 0.29 | 4.01 | 3.53 | 10.36 |
| 达乌里胡枝子(Lespedeza davurica) | SH | — | 5.27 | — | 2.60 |
| 冠芒草(Enneapogon brachystachyus) | AH | — | 0.60 | — | 0.22 |
| 尖头叶藜(Chenopodium acuminatum) | AH | — | 4.78 | 7.45 | 11.38 |
| 杠柳(Periploca sepium) | SH | — | — | 2.45 | 2.82 |
| 黄蒿(Artemisia scoparia) | AH | — | — | 0.52 | 16.79 |
| 糙隐子草(Cleistogenes squarrosa) | PH | — | — | — | 0.58 |
| 蒺藜(Tribulus terrester) | AH | — | — | — | 0.57 |
| 止血马唐(Digitaria ischaemum) | AH | — | — | — | 1.39 |
| 物种数 | — | 19 | 17 | 12 | 19 |
Table 2 Changes of important values of species during restoration of fixed dunes in Horqin Sandy Land
| 物种 | 生活型 | 重要值/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2019年 | ||
| 差巴嘎蒿(Artemisia halodendron) | SH | 29.25 | 9.52 | 5.11 | — |
| 地锦(Euphorbia humifusa) | AH | 22.86 | 8.40 | — | 0.73 |
| 扁蓄豆(Melissitus ruthenicus) | PH | 16.24 | 3.07 | 6.53 | 0.35 |
| 马唐(Digitaria sanguinalis) | AH | 7.24 | 8.86 | — | — |
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | AH | 6.76 | 19.40 | 1.54 | 8.60 |
| 五星蒿(Bassia dasyphylla) | AH | 2.87 | 16.07 | 30.95 | 3.71 |
| 绿藜(Kochia scoparia) | AH | 2.84 | — | — | — |
| 虫实(Corispermum hyssopifolium) | AH | 2.68 | 6.87 | 10.81 | 4.16 |
| 苦荬菜(Sonchus oleraceus) | PH | 1.87 | 0.24 | — | — |
| 画眉草(Eragrostis pilosa) | AH | 1.63 | 5.35 | — | 0.69 |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum theisiodes) | PH | 1.41 | 2.00 | 3.79 | 5.79 |
| 三芒草(Aristida adscensionis) | AH | 1.05 | 1.15 | — | 14.78 |
| 光梗蒺藜草(Cenchrus incertus) | AH | 0.66 | — | — | — |
| 猪毛菜(Salsola collina) | AH | 0.64 | 2.40 | 26.45 | 7.96 |
| 胡枝子(Lespedeza bicolor) | SH | 0.47 | — | 0.87 | — |
| 小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla) | SH | 0.47 | — | — | — |
| 白草(Pennisetum centrasiaticum) | PH | 0.44 | 2.02 | — | 6.52 |
| 灰绿藜(Chenopodium glaucum) | AH | 0.32 | — | — | — |
| 砂蓝刺头(Echinops gmelini) | AH | 0.29 | 4.01 | 3.53 | 10.36 |
| 达乌里胡枝子(Lespedeza davurica) | SH | — | 5.27 | — | 2.60 |
| 冠芒草(Enneapogon brachystachyus) | AH | — | 0.60 | — | 0.22 |
| 尖头叶藜(Chenopodium acuminatum) | AH | — | 4.78 | 7.45 | 11.38 |
| 杠柳(Periploca sepium) | SH | — | — | 2.45 | 2.82 |
| 黄蒿(Artemisia scoparia) | AH | — | — | 0.52 | 16.79 |
| 糙隐子草(Cleistogenes squarrosa) | PH | — | — | — | 0.58 |
| 蒺藜(Tribulus terrester) | AH | — | — | — | 0.57 |
| 止血马唐(Digitaria ischaemum) | AH | — | — | — | 1.39 |
| 物种数 | — | 19 | 17 | 12 | 19 |
| 物种 | 生活型 | 重要值/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2019年 | ||
| 黄蒿(Artemisia scoparia) | PH | 46.47 | 8.55 | 10.93 | 6.42 |
| 芦草(Agropyron mongolicum) | PH | 15.23 | — | — | — |
| 糙隐子草(Cleistogenes squarrosa) | PH | 8.73 | 2.35 | 5.14 | 2.92 |
| 白草(Pennisetum centrasiaticum) | PH | 8.29 | 17.72 | — | 25.18 |
| 胡枝子(Lespedeza bicolor) | SH | 6.18 | 2.40 | 2.70 | 9.95 |
| 三芒草(Aristida adscensionis) | AH | 4.64 | 0.33 | — | — |
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | AH | 3.20 | 29.44 | 6.39 | 18.91 |
| 猪毛菜(Salsola collina) | AH | 1.44 | 0.93 | 25.17 | 2.34 |
| 太阳花(Erodium stephanianum) | PH | 1.19 | — | — | — |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum theisiodes) | PH | 1.17 | 0.40 | 0.89 | 0.28 |
| 扁蓄豆(Melissitus ruthenicus) | PH | 1.15 | — | — | — |
| 大仔蒿(Artemisia sieversiana) | PH | 0.70 | — | — | — |
| 鸡眼草(Kummerowia striata) | AH | 0.47 | — | — | — |
| 虎尾草(Chloris virgata) | AH | 0.39 | 0.63 | — | — |
| 米口袋(Gueldenstaedtia verna) | PH | 0.25 | 0.10 | — | 0.30 |
| 马唐Digitaria sanguinalis) | AH | 0.21 | — | — | — |
| 二裂萎陵菜(Potentilla bifurca) | PH | 0.16 | 1.99 | 4.84 | 3.19 |
| 绿藜(Kochia scoparia) | AH | 0.12 | — | — | — |
| 地锦(Euphorbia humifusa) | AH | — | 0.80 | — | 0.89 |
| 冠芒草(Enneapogon brachystachyus) | AH | — | 5.56 | — | 0.60 |
| 蒺藜(Tribulus terrester) | AH | — | 3.08 | — | 0.15 |
| 尖头叶藜(Chenopodium acuminatum) | AH | — | 14.55 | 31.75 | 7.53 |
| 芦苇(Phragmites australis) | PH | — | 8.29 | 12.19 | 9.38 |
| 牻牛儿苗(Erodium stephanianum) | PH | — | 0.27 | — | 7.62 |
| 乳浆大戟(Euphorbia esula) | PH | — | — | — | 0.26 |
| 田旋花(Convolvulus arvensis) | PH | — | 0.14 | — | 0.18 |
| 野糜子(Panicum ruderale) | AH | — | — | — | 3.89 |
| 地肤(Kochia scoparia) | AH | — | 0.11 | — | — |
| 画眉草(Eragrostis pilosa) | AH | — | 1.67 | — | — |
| 稷(Panicum miliaceum) | AH | — | 0.68 | — | — |
| 物种数 | — | 18 | 21 | 9 | 18 |
Table 3 Changes of important values of species during restoration of sandy grassland in Horqin Sandy Land
| 物种 | 生活型 | 重要值/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 2010年 | 2015年 | 2019年 | ||
| 黄蒿(Artemisia scoparia) | PH | 46.47 | 8.55 | 10.93 | 6.42 |
| 芦草(Agropyron mongolicum) | PH | 15.23 | — | — | — |
| 糙隐子草(Cleistogenes squarrosa) | PH | 8.73 | 2.35 | 5.14 | 2.92 |
| 白草(Pennisetum centrasiaticum) | PH | 8.29 | 17.72 | — | 25.18 |
| 胡枝子(Lespedeza bicolor) | SH | 6.18 | 2.40 | 2.70 | 9.95 |
| 三芒草(Aristida adscensionis) | AH | 4.64 | 0.33 | — | — |
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | AH | 3.20 | 29.44 | 6.39 | 18.91 |
| 猪毛菜(Salsola collina) | AH | 1.44 | 0.93 | 25.17 | 2.34 |
| 太阳花(Erodium stephanianum) | PH | 1.19 | — | — | — |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum theisiodes) | PH | 1.17 | 0.40 | 0.89 | 0.28 |
| 扁蓄豆(Melissitus ruthenicus) | PH | 1.15 | — | — | — |
| 大仔蒿(Artemisia sieversiana) | PH | 0.70 | — | — | — |
| 鸡眼草(Kummerowia striata) | AH | 0.47 | — | — | — |
| 虎尾草(Chloris virgata) | AH | 0.39 | 0.63 | — | — |
| 米口袋(Gueldenstaedtia verna) | PH | 0.25 | 0.10 | — | 0.30 |
| 马唐Digitaria sanguinalis) | AH | 0.21 | — | — | — |
| 二裂萎陵菜(Potentilla bifurca) | PH | 0.16 | 1.99 | 4.84 | 3.19 |
| 绿藜(Kochia scoparia) | AH | 0.12 | — | — | — |
| 地锦(Euphorbia humifusa) | AH | — | 0.80 | — | 0.89 |
| 冠芒草(Enneapogon brachystachyus) | AH | — | 5.56 | — | 0.60 |
| 蒺藜(Tribulus terrester) | AH | — | 3.08 | — | 0.15 |
| 尖头叶藜(Chenopodium acuminatum) | AH | — | 14.55 | 31.75 | 7.53 |
| 芦苇(Phragmites australis) | PH | — | 8.29 | 12.19 | 9.38 |
| 牻牛儿苗(Erodium stephanianum) | PH | — | 0.27 | — | 7.62 |
| 乳浆大戟(Euphorbia esula) | PH | — | — | — | 0.26 |
| 田旋花(Convolvulus arvensis) | PH | — | 0.14 | — | 0.18 |
| 野糜子(Panicum ruderale) | AH | — | — | — | 3.89 |
| 地肤(Kochia scoparia) | AH | — | 0.11 | — | — |
| 画眉草(Eragrostis pilosa) | AH | — | 1.67 | — | — |
| 稷(Panicum miliaceum) | AH | — | 0.68 | — | — |
| 物种数 | — | 18 | 21 | 9 | 18 |
| 沙地类型 | 生活型 | 一年生草本 | 多年生草本 | 灌木 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流动沙丘 | AH | 1 | ||
| PH | -0.711** | 1 | ||
| SH | -0.830** | 0.197 | 1 | |
| 固定沙丘 | AH | 1 | ||
| PH | -0.569* | 1 | ||
| SH | -0.892** | 0.135 | 1 | |
| 沙质草地 | AH | 1 | ||
| PH | -0.967** | 1 | ||
| SH | -0.351 | 0.099 | 1 |
Table 4 Correlation analysis of important values of different life form species in different types of restoration sands in Horqin Sandy Land
| 沙地类型 | 生活型 | 一年生草本 | 多年生草本 | 灌木 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流动沙丘 | AH | 1 | ||
| PH | -0.711** | 1 | ||
| SH | -0.830** | 0.197 | 1 | |
| 固定沙丘 | AH | 1 | ||
| PH | -0.569* | 1 | ||
| SH | -0.892** | 0.135 | 1 | |
| 沙质草地 | AH | 1 | ||
| PH | -0.967** | 1 | ||
| SH | -0.351 | 0.099 | 1 |
| 年份 | 植物群落稳定性 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 固定沙丘 | 流动沙丘 | 沙质草地 | |
| 2005 | 3.32 | 1.11 | 10.38 |
| 2006 | 3.19 | 1.36 | 5.46 |
| 2007 | 2.96 | 1.75 | 5.65 |
| 2008 | 2.43 | 1.75 | 2.62 |
| 2009 | 2.90 | 1.36 | 2.16 |
| 2010 | 3.17 | 2.50 | 1.47 |
| 2011 | 4.51 | 1.37 | 3.91 |
| 2012 | 2.52 | 1.26 | 9.07 |
| 2013 | 1.94 | 2.63 | 2.28 |
| 2014 | 1.72 | 1.35 | 5.85 |
| 2015 | 2.19 | 2.26 | 2.81 |
| 2016 | 1.30 | 1.30 | 2.49 |
| 2017 | 2.31 | 6.16 | 1.59 |
| 2018 | 1.63 | 1.18 | 2.30 |
| 2019 | 2.35 | 2.68 | 5.05 |
Table 5 Stability of plant communities in different sandy land types during the restoration process of Horqin Sandy Land
| 年份 | 植物群落稳定性 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 固定沙丘 | 流动沙丘 | 沙质草地 | |
| 2005 | 3.32 | 1.11 | 10.38 |
| 2006 | 3.19 | 1.36 | 5.46 |
| 2007 | 2.96 | 1.75 | 5.65 |
| 2008 | 2.43 | 1.75 | 2.62 |
| 2009 | 2.90 | 1.36 | 2.16 |
| 2010 | 3.17 | 2.50 | 1.47 |
| 2011 | 4.51 | 1.37 | 3.91 |
| 2012 | 2.52 | 1.26 | 9.07 |
| 2013 | 1.94 | 2.63 | 2.28 |
| 2014 | 1.72 | 1.35 | 5.85 |
| 2015 | 2.19 | 2.26 | 2.81 |
| 2016 | 1.30 | 1.30 | 2.49 |
| 2017 | 2.31 | 6.16 | 1.59 |
| 2018 | 1.63 | 1.18 | 2.30 |
| 2019 | 2.35 | 2.68 | 5.05 |
| 1 | 李玉霖,赵学勇,刘新平,等.沙漠化土地及其治理研究推动北方农牧交错区生态恢复和农牧业可持续发展[J].中国科学院院刊,2019,34(7):832-840. |
| 2 | 姜海光.浅谈内蒙古沙漠沙地治理现状、问题与建议[C]//中国治沙暨沙业学会.中国治沙暨沙业学会2018年学术年会论文集.2018:7. |
| 3 | D'Odorico P, Bhattachan A, Davis K F,et al.Global desertification: drivers and feedbacks[J].Advances in Water Resources,2013,51:326-344. |
| 4 | Li X, Yang D, Zheng C,et al.Ecohydrology[M].Singapore:Springer,2017. |
| 5 | Deng J F, Li J H, Deng G,et al.Fractal scaling of particle-size distribution and associations with soil properties of Mongolian pine plantations in the Mu Us Desert,China.[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):6742. |
| 6 | 宋永昌.植被生态学[M].上海:华东师范大学出版社,2001. |
| 7 | 吕朋,左小安,岳喜元,等.科尔沁沙地封育过程中植被特征的动态变化[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(10):2880-2888. |
| 8 | 赵哈林,苏永中,周瑞莲.我国北方沙区退化植被的恢复机理[J].中国沙漠,2006, 26 (3):323-328. |
| 9 | 王蕾,张宏,哈斯,等.基于冠幅直径和植株高度的灌木地上生物量估测方法研究[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2004,40(5):700-704. |
| 10 | Wairore J N, Mureithi S M, Wasonga O V,et al.Benefits derived from rehabilitating a degraded semi-arid rangeland in private enclosures in West Pokot County, Kenya[J].Land Degradation & Development,2016,27:532-541. |
| 11 | 王明明,刘新平,何玉惠,等.科尔沁沙地封育恢复过程中植物群落特征变化及影响因素[J].植物生态学报,2019,43(8):672-684. |
| 12 | 李玉霖,孟庆涛,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地流动沙丘植被恢复过程中群落组成及植物多样性演变特征[J].草业学报,2007,16(6):54-61. |
| 13 | 陈银萍,李晓辉,罗永清,等.科尔沁不同沙地类型植被动态特征及其与凋落物的关系研究[J].草地学报,2021,29(1):114-120. |
| 14 | 赵丽娅,高丹丹,熊炳桥,等.科尔沁沙地恢复演替进程中群落物种多样性与地上生物量的关系[J].生态学报,2017,37(12):4108-4117. |
| 15 | 赵珍珍.基于多源数据的科尔沁沙地生态环境变化研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2017. |
| 16 | 李玉霖,崔建垣,苏永中.不同沙丘生境主要植物比叶面积和叶干物质含量的比较[J].生态学报,2005,25(2):304-311. |
| 17 | 左小安,赵哈林,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地不同尺度上沙丘景观格局动态变化分析[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(5):785-795. |
| 18 | 王少昆,赵学勇,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地几种灌木对根际微生物的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,2012,26(5):140-144. |
| 19 | Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, Zhao H L,et al.Scale dependent effects of environmental factors on vegetation pattern and composition in Horqin Sandy Land,Northern China[J].Geoderma,2012,173-174:1-9. |
| 20 | 王洪义,常继方,王正文.退化草地恢复过程中群落物种多样性及生产力对氮磷养分的响应[J].中国农业科学,2020,53(13):2604-2613. |
| 21 | 常继方.氮磷添加对呼伦贝尔草地植物群落物种多样性与稳定性的影响[D].黑龙江大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学,2020. |
| 22 | 张继义,赵哈林,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地植物群落恢复演替系列种群生态位动态特征[J].生态学报,2003,23(12):2741-2746. |
| 23 | 曹成有,蒋德明,朱丽辉,等.科尔沁沙地草甸草场退化的原因与植物多样性变化[J].草业学报,2006,15(3):18-26. |
| 24 | Bakker J P, Grootjans A P, Hermy M,et al.How to define targets for ecological restoration?Introduction[J].Applied Vegetation Sciences,2000(3):3-6. |
| 25 | 刘志民,蒋德明,阎巧玲,等.科尔沁草原主要草地植物传播生物学简析[J].草业学报,2005,14(6):23-33. |
| 26 | 张继义,赵哈林,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地植被恢复系列上群落演替与物种多样性的恢复动态[J].植物生态学报,2004,28(1):86-92. |
| 27 | 张继义,赵哈林,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地植物群落恢复演替系列种群生态位动态特征[J].生态学报,2003,23(12):2741-2746. |
| 28 | 张继义,赵哈林.科尔沁沙地草地植被恢复演替进程中群落优势种群空间分布格局研究[J].生态学杂志,2004,23(2):1-6. |
| 29 | 王敏,苏永中,杨荣,等.黑河中游荒漠草地地上和地下生物量的分配格局[J].植物生态学报,2013,37(3): 209-219. |
| 30 | 高凯,朱铁霞,韩国栋.围封年限对内蒙古羊草-针茅典型草原植物功能群及其多样性的影响[J].草业学报,2013,22(6):39-45. |
| 31 | 方楷,宋乃平,魏乐,等.不同放牧制度对荒漠草原地上生物量及种间关系的影响[J].草业学报,2012,21(5):12-22. |
| 32 | 程积民,邹厚远.黄土高原草地合理利用与草地植被演替过程的试验研究[J].草业学报,1995,4(4):17-22. |
| [1] | Xiaolong Zhao, Yuhong Xie, Xujun Ma, Shaokun Wang. Vegetation structure and its relationship with soil physicochemical properties in restoring sandy grassland in Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [2] | Danhui Qi, Hongxiao Yang, Qi Lu, Jianmin Chu, Qi Yuan, Honghao Gan, Shuai Zhao, Jiawei Chen, Xiaoqing Xu. Biodiversity of plant communities and its environmental interpretation in the Otindag Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 65-77. |
| [3] | Danhui Qi, Hongxiao Yang, Qi Lu, Honghao Gan, Jianmin Chu. Types and characteristics of plant communities in the Otingdag Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 23-33. |
| [4] | Dan Han, Yulin Li, Jin Zhan, Hongling Yang. Emergy-based comparison on sustainable development of villages with different farming and pastoral ratios in Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 235-244. |
| [5] | Yinping Chen, Wenjie Cao, Peidong Yu, Huan Yang, Xuyang Wang, Yuqiang Li. The effects of soil water content on sand flow structure and wind erosion amount with wind tunnel experiment in semi-arid area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 173-180. |
| [6] | Xiaobing Zhou, Bingchang Zhang, Yuanming Zhang. The theory and practices of biological soil crust rehabilitation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 164-173. |
| [7] | Yuanzheng He, Wenda Huang, Xin Zhao, Peng Lv, Huaihai Wang. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [8] | Yimei Sun, Qing Tian, Aixia Guo, Xiaoan Zuo, Peng Lv, Senxi Zhang. Effects of water and nitrogen changes on vegetation characteristics and leaf traits in Horqin Sandy land, Northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 223-232. |
| [9] | Jin Zhan, Yulin Li, Dan Han, Hongling Yang. Biomass allocation and its ecological significance of three dominant sand-fixing shrubs in the semi-arid desert area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 149-157. |
| [10] | Delu Li, Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Xinrong Li, Hongbo Yuan, Linyuan Wei, Haotian Yang, Zhong Zhang. Vegetation characteristics of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| [11] | Huang Tianyu, Liu Tingxi, Duan Limin, Li Dongfang, Wang Guanli, Chen Xiaoping. Characteristics of Water and Heat Fluxes and Its Footprint Climatology in Horqin Cascade Ecological Zone [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 30-39. |
| [12] | Yang Hongling, Li Yulin, Ning Zhiying, Zhang Ziqian. Home-field Effects of Leaf Litter Decomposition of Dominate Sand-fixing Shrubs in the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 62-70. |
| [13] | Chelmeg, Liu Xinping, He Yuhui, Wang Mingming, Wei Shuilian, Li Yulin, Sun Shanshan. Characteristics on Direct Foliar Rainwater Absorption of Several Common Plants in Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(5): 1017-1023. |
| [14] | Cao Rui, Liu Guohou, Lan Qing, Liu Guanzhi, Mu Zongjie, Gui Rong, Liu Lihong, Wang Jian. Change of Plant Community in Air-Seeding Area of the Hunshandake Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(3): 535-544. |
| [15] | Luo Weicheng, Zhao Wenzhi, Sun Chengpeng, Yan Jialiang. Changes in Species Composition, Diversity and Soil Water Content of Pinus sylvestris Artificial Sand-fixation Forest along An Afforestation Successional Gradient in Horqin [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2018, 38(1): 126-132. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech