
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 253-263.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00019
Min Chen1( ), Baosheng Li1,2(
), Baosheng Li1,2( ), Fengnian Wang3, Dongfeng Niu4, Xiaohao Wen1, Peixian Shu2, Yuejun Si5, Qinjiang Yang6, Chen Wang7
), Fengnian Wang3, Dongfeng Niu4, Xiaohao Wen1, Peixian Shu2, Yuejun Si5, Qinjiang Yang6, Chen Wang7
Received:2021-11-17
Revised:2022-02-18
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-08-29
Contact:
Baosheng Li
CLC Number:
Min Chen, Baosheng Li, Fengnian Wang, Dongfeng Niu, Xiaohao Wen, Peixian Shu, Yuejun Si, Qinjiang Yang, Chen Wang. High-resolution monsoonal environment change in MIS3 based on trace elements in the Tumen Section on the southweest edge of Tegger Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 253-263.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00019
| 层序 | 深度/m | 实验室编号 | δ13C/‰ | 14C年代/a | 测年材料 | 日历年代/a(±2σ误差) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64Al | 12.64 | Beta-365692 | -20.40 | 19 050±80 | 有机质 | 22 490±310 |
| 66S | 13.46 | Beta-365693 | -21.00 | 23 750±100 | 有机质 | 27 820±200 |
| 68Ld | 13.74 | Beta-365694 | -20.10 | 25 550±130 | 有机质 | 29 740±440 |
| 84Ls | 16.07 | Beta-365695 | -21.00 | 19 430±80 | 有机质 | 23 370±290 |
Table 1 AMS 14C dating results in some layers of the TMS3
| 层序 | 深度/m | 实验室编号 | δ13C/‰ | 14C年代/a | 测年材料 | 日历年代/a(±2σ误差) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64Al | 12.64 | Beta-365692 | -20.40 | 19 050±80 | 有机质 | 22 490±310 |
| 66S | 13.46 | Beta-365693 | -21.00 | 23 750±100 | 有机质 | 27 820±200 |
| 68Ld | 13.74 | Beta-365694 | -20.10 | 25 550±130 | 有机质 | 29 740±440 |
| 84Ls | 16.07 | Beta-365695 | -21.00 | 19 430±80 | 有机质 | 23 370±290 |
采样层号 (实验室编号) | 深度 /m | U/10-6 | Th/10-6 | K/% | 等效剂量 E.D/Gy | 年剂量 /mGy | 含水量 /% | 年龄 /a | 实验 方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68Ld(TGD813) | 13.74 | 2.07±0.10 | 9.97±0.20 | 1.97±0.016 | 102.00±9.90 | 3.47±0.10 | 5 | 29 400±2 900 | TL |
| 69D(TGD821) | 13.96 | 2.12±0.11 | 14.72±0.30 | 1.90±0.015 | 118.00±11.21 | 3.81±0.11 | 5 | 31 000±2 900 | TL |
| 70L(TGD814) | 14.09 | 1.61±0.08 | 14.73±0.30 | 1.88±0.015 | 147.90±11.00 | 4.58±0.14 | 8 | 32 100±3 000 | TL |
| 76L(TGD796) | 14.80 | 1.12±0.06 | 16.12±0.32 | 2.34±0.019 | 159.60±12.00 | 4.19±0.13 | 10 | 38 100±3 800 | TL |
| 82LD(14G-453) | 15.70 | 2.18±0.09 | 8.98±0.26 | 1.70±0.06 | 154.21±1.04 | 3.37±0.13 | 5 | 45 700±1 900 | OSL |
| 95D(14G-454) | 17.51 | 1.92±0.08 | 7.69±0.23 | 1.76±0.06 | 197.16±3.11 | 3.20±0.13 | 5 | 61 500±2 600 | OSL |
Table 2 TL and OSL dating results and parameters in some horizons of the TMS3
采样层号 (实验室编号) | 深度 /m | U/10-6 | Th/10-6 | K/% | 等效剂量 E.D/Gy | 年剂量 /mGy | 含水量 /% | 年龄 /a | 实验 方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68Ld(TGD813) | 13.74 | 2.07±0.10 | 9.97±0.20 | 1.97±0.016 | 102.00±9.90 | 3.47±0.10 | 5 | 29 400±2 900 | TL |
| 69D(TGD821) | 13.96 | 2.12±0.11 | 14.72±0.30 | 1.90±0.015 | 118.00±11.21 | 3.81±0.11 | 5 | 31 000±2 900 | TL |
| 70L(TGD814) | 14.09 | 1.61±0.08 | 14.73±0.30 | 1.88±0.015 | 147.90±11.00 | 4.58±0.14 | 8 | 32 100±3 000 | TL |
| 76L(TGD796) | 14.80 | 1.12±0.06 | 16.12±0.32 | 2.34±0.019 | 159.60±12.00 | 4.19±0.13 | 10 | 38 100±3 800 | TL |
| 82LD(14G-453) | 15.70 | 2.18±0.09 | 8.98±0.26 | 1.70±0.06 | 154.21±1.04 | 3.37±0.13 | 5 | 45 700±1 900 | OSL |
| 95D(14G-454) | 17.51 | 1.92±0.08 | 7.69±0.23 | 1.76±0.06 | 197.16±3.11 | 3.20±0.13 | 5 | 61 500±2 600 | OSL |
| 元素/比值 | 沉积相 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS 3层段 | 沙丘砂 | 黄土状亚砂土 | 砂黄土 | 古土壤 | 湖相 | 水成黄土 | ||
| Mn | 范围 | 301—702 | 301—471 | 470—584 | 502—565 | 503—569 | 524—702 | 522—676 |
| 平均值 | 502 | 377 | 522 | 536 | 528 | 608 | 561 | |
| P | 范围 | 250—561 | 250—435 | 451—546 | 485—542 | 487—554 | 501—561 | 492—541 |
| 平均值 | 406 | 311 | 493 | 515 | 516 | 538 | 525 | |
| Sr | 范围 | 130—268 | 130—217 | 194—232 | 204—255 | 188—247 | 202—268 | 198—233 |
| 平均值 | 199 | 174 | 206 | 222 | 210 | 229 | 210 | |
| Rb | 范围 | 79—116 | 79—89 | 82—91 | 84—95 | 84—93 | 87—114 | 88—116 |
| 平均值 | 88 | 82 | 88 | 89 | 87 | 97 | 94 | |
| V | 范围 | 39—94 | 39—68 | 60—77 | 58—77 | 54—73 | 57—94 | 56—80 |
| 平均值 | 66 | 52 | 65 | 68 | 62 | 73 | 71 | |
| Cr | 范围 | 36—86 | 36—59 | 61—77 | 63—78 | 69—77 | 62—86 | 64—82 |
| 平均值 | 64 | 47 | 68 | 68 | 72 | 72 | 73 | |
| Zn | 范围 | 31—98 | 31—45 | 48—68 | 51—60 | 47—66 | 54—98 | 51—77 |
| 平均值 | 61 | 36 | 57 | 55 | 53 | 66 | 57 | |
| Ni | 范围 | 16—47 | 16—27 | 27—32 | 26—34 | 27—34 | 28—47 | 29—40 |
| 平均值 | 31 | 22 | 29 | 31 | 30 | 35 | 32 | |
| Cu | 范围 | 10—32 | 10—20 | 17—21 | 17—20 | 17—21 | 18—32 | 16—31 |
| 平均值 | 21 | 13 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 23 | 20 | |
| Nb | 范围 | 7—13 | 7—11 | 10—13 | 9.5—12 | 11—12 | 11—13 | 11—13 |
| 平均值 | 10 | 8.8 | 11 | 11 | 11.3 | 12 | 12 | |
| Rb/Sr | 范围 | 0.35—0.61 | 0.39—0.61 | 0.37—0.46 | 0.35—0.44 | 0.38—0.45 | 0.40—0.47 | 0.41—0.51 |
| 平均值 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.45 | |
Table 3 The distribution of trace elements (mg·kg-1 ) and Rb/Sr in different sedimentary facies of the TMS3
| 元素/比值 | 沉积相 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMS 3层段 | 沙丘砂 | 黄土状亚砂土 | 砂黄土 | 古土壤 | 湖相 | 水成黄土 | ||
| Mn | 范围 | 301—702 | 301—471 | 470—584 | 502—565 | 503—569 | 524—702 | 522—676 |
| 平均值 | 502 | 377 | 522 | 536 | 528 | 608 | 561 | |
| P | 范围 | 250—561 | 250—435 | 451—546 | 485—542 | 487—554 | 501—561 | 492—541 |
| 平均值 | 406 | 311 | 493 | 515 | 516 | 538 | 525 | |
| Sr | 范围 | 130—268 | 130—217 | 194—232 | 204—255 | 188—247 | 202—268 | 198—233 |
| 平均值 | 199 | 174 | 206 | 222 | 210 | 229 | 210 | |
| Rb | 范围 | 79—116 | 79—89 | 82—91 | 84—95 | 84—93 | 87—114 | 88—116 |
| 平均值 | 88 | 82 | 88 | 89 | 87 | 97 | 94 | |
| V | 范围 | 39—94 | 39—68 | 60—77 | 58—77 | 54—73 | 57—94 | 56—80 |
| 平均值 | 66 | 52 | 65 | 68 | 62 | 73 | 71 | |
| Cr | 范围 | 36—86 | 36—59 | 61—77 | 63—78 | 69—77 | 62—86 | 64—82 |
| 平均值 | 64 | 47 | 68 | 68 | 72 | 72 | 73 | |
| Zn | 范围 | 31—98 | 31—45 | 48—68 | 51—60 | 47—66 | 54—98 | 51—77 |
| 平均值 | 61 | 36 | 57 | 55 | 53 | 66 | 57 | |
| Ni | 范围 | 16—47 | 16—27 | 27—32 | 26—34 | 27—34 | 28—47 | 29—40 |
| 平均值 | 31 | 22 | 29 | 31 | 30 | 35 | 32 | |
| Cu | 范围 | 10—32 | 10—20 | 17—21 | 17—20 | 17—21 | 18—32 | 16—31 |
| 平均值 | 21 | 13 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 23 | 20 | |
| Nb | 范围 | 7—13 | 7—11 | 10—13 | 9.5—12 | 11—12 | 11—13 | 11—13 |
| 平均值 | 10 | 8.8 | 11 | 11 | 11.3 | 12 | 12 | |
| Rb/Sr | 范围 | 0.35—0.61 | 0.39—0.61 | 0.37—0.46 | 0.35—0.44 | 0.38—0.45 | 0.40—0.47 | 0.41—0.51 |
| 平均值 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.45 | |
| Mn | P | Sr | Rb | V | Zn | Cr | Ni | Cu | Nb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.92 | |||||||||
| Sr | 0.84 | 0.77 | ||||||||
| Rb | 0.88 | 0.66 | 0.76 | |||||||
| V | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.84 | ||||||
| Zn | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.86 | |||||
| Cr | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.86 | ||||
| Ni | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.87 | |||
| Cu | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.94 | 0.80 | 0.89 | ||
| Nb | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | |
| Rb/Sr | -0.49 | -0.57 | -0.81 | -0.25 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.49 | -0.45 | -0.38 | -0.45 |
Table 4 Correlation between Rb/Sr and trace elements in the TMS3
| Mn | P | Sr | Rb | V | Zn | Cr | Ni | Cu | Nb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 0.92 | |||||||||
| Sr | 0.84 | 0.77 | ||||||||
| Rb | 0.88 | 0.66 | 0.76 | |||||||
| V | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.84 | ||||||
| Zn | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.86 | |||||
| Cr | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.86 | ||||
| Ni | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.87 | |||
| Cu | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.94 | 0.80 | 0.89 | ||
| Nb | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.82 | |
| Rb/Sr | -0.49 | -0.57 | -0.81 | -0.25 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.49 | -0.45 | -0.38 | -0.45 |
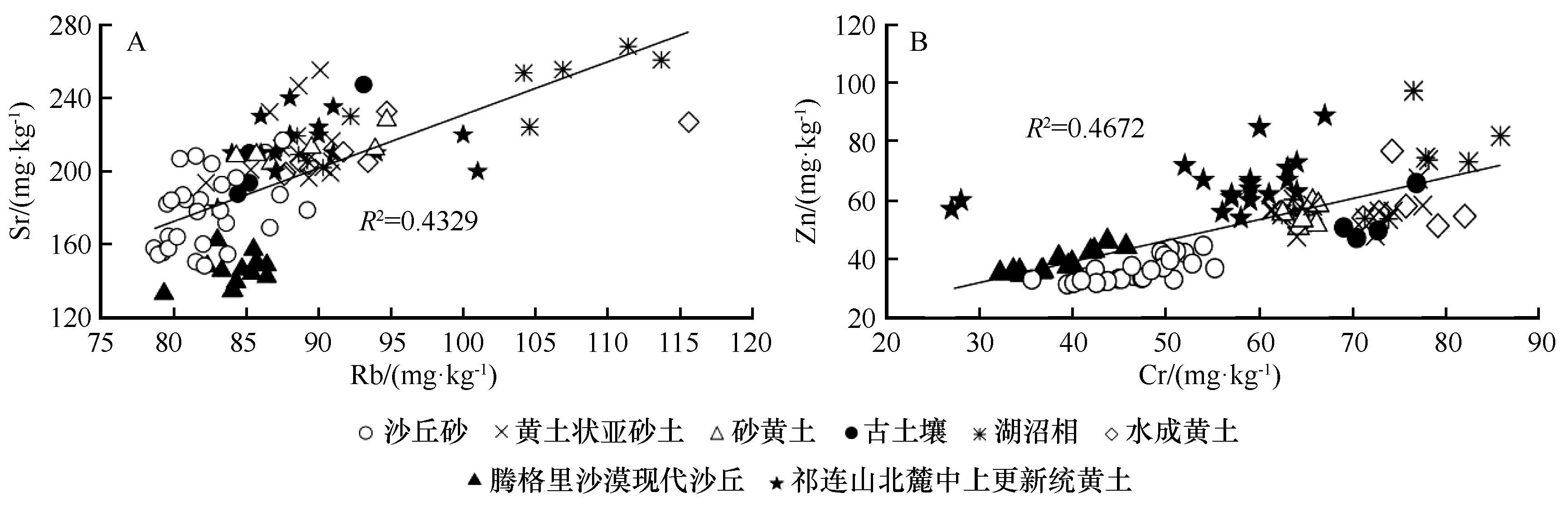
Fig.4 The scatter plot of Rb-Sr and Cr-Zn in the sedimentary facies of the TMS3, modern dune sands in the Tengger Desert and Middle-Upper-Pleistocene loess in the northern foot of the Qilian Mountains
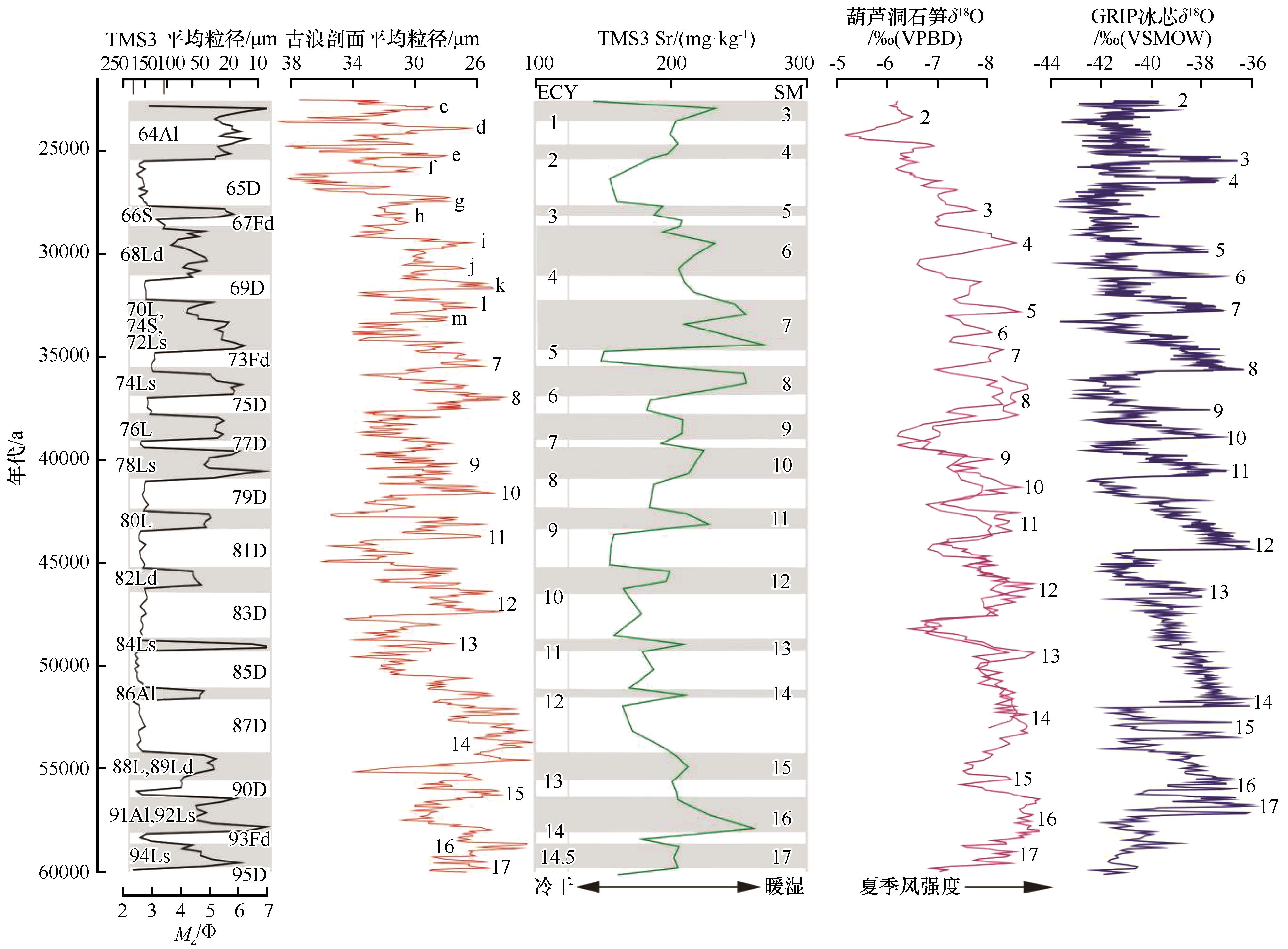
Fig.7 Comparison between element/monsoon cycles and summer monsoon events indicated by Sr in the TMS3 and interstadials in GRIP ice core [25], δ18O curve of stalagmites in Huludong Cave[5] and loess revealed by the grain size in Gulang in the MIS3[7]
| 1 | Bond G, Roecker W, Johnsen S,et al.Correlations between climate records from North Atlantic sediments and Greenland ice[J].Nature,1993,365(6442):143-147. |
| 2 | Heinrich H.Origin and consequences of cyclic ice rafting in the northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past 130,000 years[J].Quaternary Research,1988,29(2):142-152. |
| 3 | Stephen C P, An Z S.Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China durng the last glaciation[J].Nature,1995,375(25):305-308. |
| 4 | 丁仲礼,任剑璋,刘东生,等.晚更新世季风-沙漠系统千年尺度的不规则变化及其机制问题[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学),1996,26(5):385-391. |
| 5 | Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L,et al.A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave,China[J].Science,2001,2940(555):2345-2348. |
| 6 | Cai Y J, Fung L Y, Edwards R L,et al.Variability of stalagmite-inferred Indian monsoon precipitation over the past 252,000 y[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2015,112(10):2954-2959. |
| 7 | Sun Y B, Clemens S C, Morrill C,et al.Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon[J].Nature Geoscience,2012,5(1):46-49. |
| 8 | 叶玮,董光荣,袁玉江,等.新疆伊犁地区末次冰期气候的不稳定性[J].科学通报,2000(6):641-646. |
| 9 | 吴利杰,施雅风,郭娇,等.金丁剖面MIS3阶段黄土地层记录的温湿气候特征初步研究[J].地球与环境,2015,43(4):4425-4431. |
| 10 | 刘明光.中国自然地理图集[M].北京:中国地图出版社,1997:111. |
| 11 | 古浪县地方志编辑委员会.古浪县志[M].兰州:甘肃文化出版社,2000:45-142. |
| 12 | 杨庆江,温小浩,李保生,等.腾格里沙漠南缘土门剖面末次间冰阶层段的粒度特征及其反映的气候-沉积环境[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(4):666-677. |
| 13 | Stuiver M, Reimer P J, Bard E,et al.INTCAL98 Radiocarbon age calibration 24 000~0 cal a BP[J].Radiocarbon,1998,40:1041-1083. |
| 14 | Reimer P J, Baillie M G L, Bard E,et al.IntCal04 Terrest rial radiocarbon age calib ration,0~26 cal kyr BP[J].Radiocarbon,2004,46(3):1029-1058. |
| 15 | Aitken M J.An Introduction to Optical Dating[M].New York,USA:Oxford Science Publication,1998. |
| 16 | Konert M, Vandenberghe J E F.Comparison of laser grain size analysis with pipette and sieve analysis:a solution for the underestimation of the clay fraction[J].Sedimentology,1997,44(3):523-535. |
| 17 | 刘东生,周问辅,邵正华.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社,1985. |
| 18 | Krumbein W C, Pettijohn F J.Manual of Sedimentary Petrography[M].New York,USA:Appleton-Century,1938. |
| 19 | Folk R L, Ward W C.Brazos Reviver bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1957,27:3-26. |
| 20 | Kim M C, Gibbard P L.Regional chronostratigraphical correlation table for the last 270,000 years Europe north of the Mediterranean[J].Quaternary International,2012,279:93. |
| 21 | 张虎才,李吉均,马玉贞,等.腾格里沙漠南缘武威黄土沉积元素地球化学特征[J].沉积学报,1997(4):154-160. |
| 22 | Brass G W.The effect of weathering on the distribution of strontium isotopes in weathering profiles[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1975,39:1647-1653. |
| 23 | Chen J, An Z S, Head J.Variation of Rb/Sr ratios in the loess-paleosol sequences of central China during the last 130,000 years and their implications for monsoon paleoclimatology[J].Quaternary Research,1999,51:215-219. |
| 24 | 金章东,王苏民,沈吉,等.内陆湖泊流域的化学风化及气候变化:以内蒙古岱海为例[J].地质评论,2001,47(1):42-46. |
| 25 | Rasmussen S O, Andersen K K, Svensson A M,et al.A new Greenland ice core chronology for the last glacial termination[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2006,111(D6):1984-2012. |
| 26 | Ellen C C, Russell N D, John C H,et al.Synchronous timing of abrupt climate changes during the last glacial period[J].Science,2020,369:963-969. |
| [1] | Jianhua He, Wenhua Qin, Jiabing Guo, Peiyuan Chen, Jinzhu Ma. The characteristics of groundwater trace elements and its controlling factors in Dunhuang Oasis [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 109-119. |
| [2] | Wenfan Wang, Rentao Liu, Zhixia Guo, Yonghong Feng, Jiayu Jiang. Physical and chemical properties and fractal dimension distribution of soil under shrubs in the southern area of Tengger Dseart [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 209-218. |
| [3] | Haotian Yang, Xinrong Li, Peijie Yan, Yunfei Li, Quanlin Ma. Soil types and spatial distribution in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 154-162. |
| [4] | Bingyao Wang, Xingchen Liu, Lichao Liu. Characteristics of precipitation in the surrounding area of Tengger Desert in 1957-2017 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 163-170. |
| [5] | Yingwu Chen, Qingxiao Chen, Haotian Yang. Diversity and fauna of terrestrial wild vertebrate in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 171-182. |
| [6] | Changzhen Yan, Sen Li, Junfeng Lu, Lichao Liu. Lake number and area in the Tengger Desert during 1975-2015 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 183-189. |
| [7] | Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Dekui Zhang, Linyuan Wei. Mechanism and dynamics for succession of artificial Hedysarum scoparium sand-binding forests at the southern edge of Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 206-215. |
| [8] | Yingwu Chen, Qingxiao Chen, Haotian Yang. Diversity and fauna of terrestrial wild vertebrates in the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 216-222. |
| [9] | Delu Li, Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Xinrong Li, Hongbo Yuan, Linyuan Wei, Haotian Yang, Zhong Zhang. Vegetation characteristics of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| [10] | Wang Yansong, Liu Yubing, Wang Zengru, Zhao Lina, Qi Jinghua, Zhang Wenli. Iron metabolism microbial composition and functional genes response to succession of biological soil crust [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 193-200. |
| [11] | Yang Lizhen, Feng Li, Yang Guisen, Huang Lei. Water absorption potential and influencing factors of leaf in Caragana korshinskii, Artemisia ordosica, Hedysarum scoparium in a revegetated area of the Tengger Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 214-221. |
| [12] | Ma Xiaojun, Li Yunfei. Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities during Revegetation Process in the Southeastern Fringe of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 159-166. |
| [13] | Li Yunfei, Xie Ting, Shi Wanli, Li Xiaojun. Response of Topsoil Organic Carbon Mineralization to Litter Addition in the Revegetation Area in the Southeastern Fringe of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 200-209. |
| [14] | Cao Zhihong, An Chengbang, Gao Xinjuan. Drought and flood disasters on the edge of Tengger Desert during 1426-1949 AD [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 171-178. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhengcai, Dong Zhibao, Guan Mengluan. The Reversing Dune Geomorphology Development Process in the Southeast Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(4): 709-715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech