
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 68-77.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaogan Zhou1( ), Yongzhong Luo1(
), Yongzhong Luo1( ), Quanlin Ma1,2, Jiliang Liu3, Jialong Ren4, Ziting Wang1,2, Qihan Yan4, Chang Qin4, Jiaqi Zhai1
), Quanlin Ma1,2, Jiliang Liu3, Jialong Ren4, Ziting Wang1,2, Qihan Yan4, Chang Qin4, Jiaqi Zhai1
Received:2024-10-17
Revised:2024-12-28
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-27
Contact:
Yongzhong Luo
CLC Number:
Xiaogan Zhou, Yongzhong Luo, Quanlin Ma, Jiliang Liu, Jialong Ren, Ziting Wang, Qihan Yan, Chang Qin, Jiaqi Zhai. Long-term effects of the introduction of Haloxylon ammodendron on desert soil characteristics[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 68-77.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00009
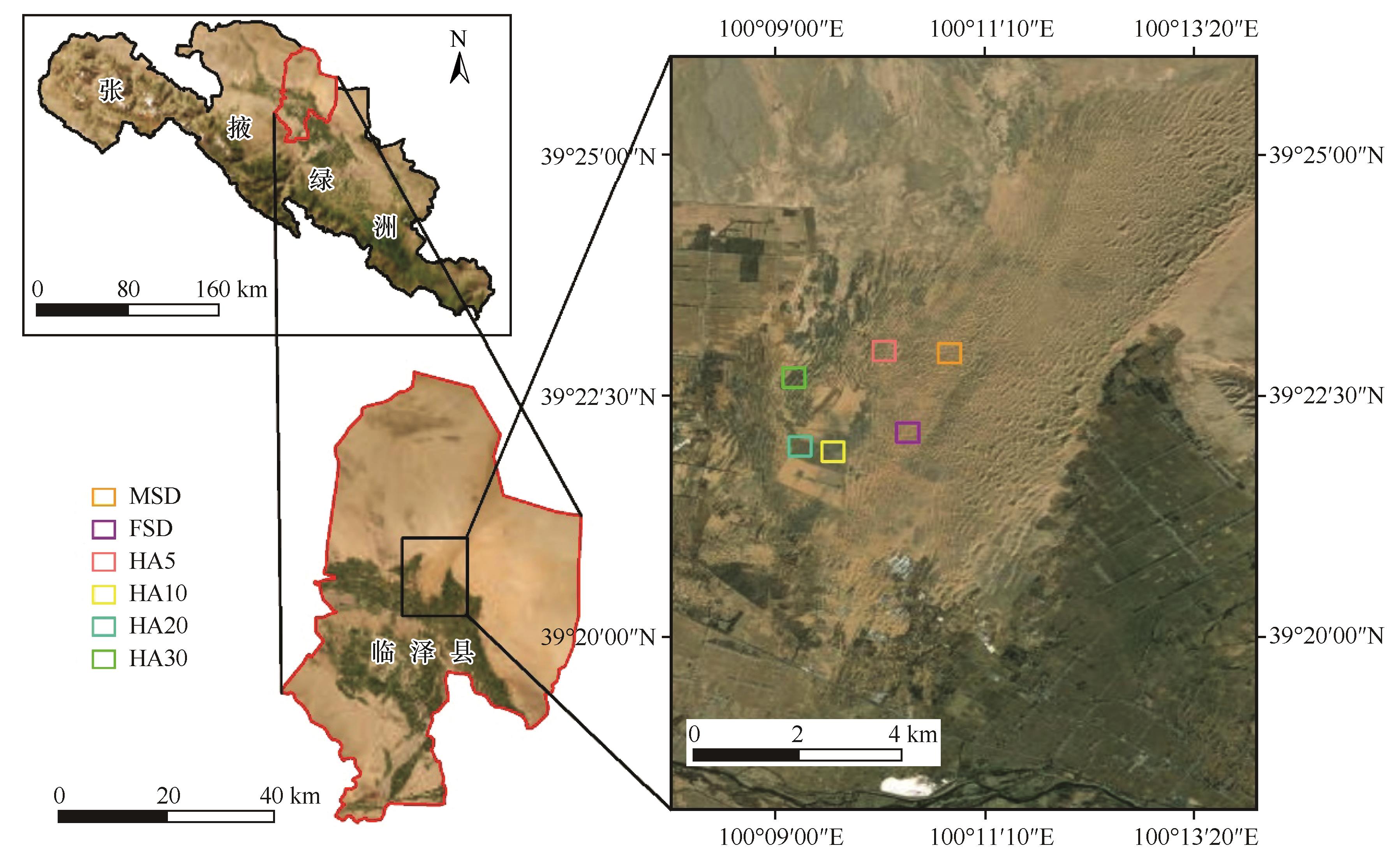
Fig.1 Distribution of sampling sites for mobile and fixed sandy dunes and Haloxylon ammodendron plantations of different ages in the middle reaches of the Heihe River
| 指标 | FSD | MSD | HA5 | HA10 | HA20 | HA30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 梭梭幼苗密度/(株/100 m2) | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 0.83±0.72b | 3.08±3.94a |
| 灌木密度/(株/100 m2) | 0.00±0.00f | 4.67±1.44e | 32.92±1.88a | 21.58±1.00b | 10.92±1.83c | 6.50±2.97d |
| 灌木物种丰富度 | 0.00±0.00d | 1.92±0.51ab | 1.75±0.75b | 2.33±0.65a | 1.83±0.72b | 1.00±0.00c |
| 灌木盖度/% | 0.00±0.00f | 18.42±7.76e | 50.00±5.22c | 56.25±7.42b | 65.00±9.53a | 38.33±7.18d |
| 草本盖度/% | 2.00±0.00bc | 4.33±1.30a | 2.67±1.07b | 1.42±0.51c | 2.50±1.07bc | 4.25±2.80a |
| 草本物种丰富度 | 1.00±0.00d | 1.67±0.65b | 1.25±0.45cd | 1.00±0.00d | 1.50±0.67bc | 2.42±0.51a |
Table 1 Vegetation community characteristics of mobile sandy dunes, fixed sandy dunes, and Haloxylon ammodendron plantations of different ages
| 指标 | FSD | MSD | HA5 | HA10 | HA20 | HA30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 梭梭幼苗密度/(株/100 m2) | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 0.00±0.00b | 0.83±0.72b | 3.08±3.94a |
| 灌木密度/(株/100 m2) | 0.00±0.00f | 4.67±1.44e | 32.92±1.88a | 21.58±1.00b | 10.92±1.83c | 6.50±2.97d |
| 灌木物种丰富度 | 0.00±0.00d | 1.92±0.51ab | 1.75±0.75b | 2.33±0.65a | 1.83±0.72b | 1.00±0.00c |
| 灌木盖度/% | 0.00±0.00f | 18.42±7.76e | 50.00±5.22c | 56.25±7.42b | 65.00±9.53a | 38.33±7.18d |
| 草本盖度/% | 2.00±0.00bc | 4.33±1.30a | 2.67±1.07b | 1.42±0.51c | 2.50±1.07bc | 4.25±2.80a |
| 草本物种丰富度 | 1.00±0.00d | 1.67±0.65b | 1.25±0.45cd | 1.00±0.00d | 1.50±0.67bc | 2.42±0.51a |
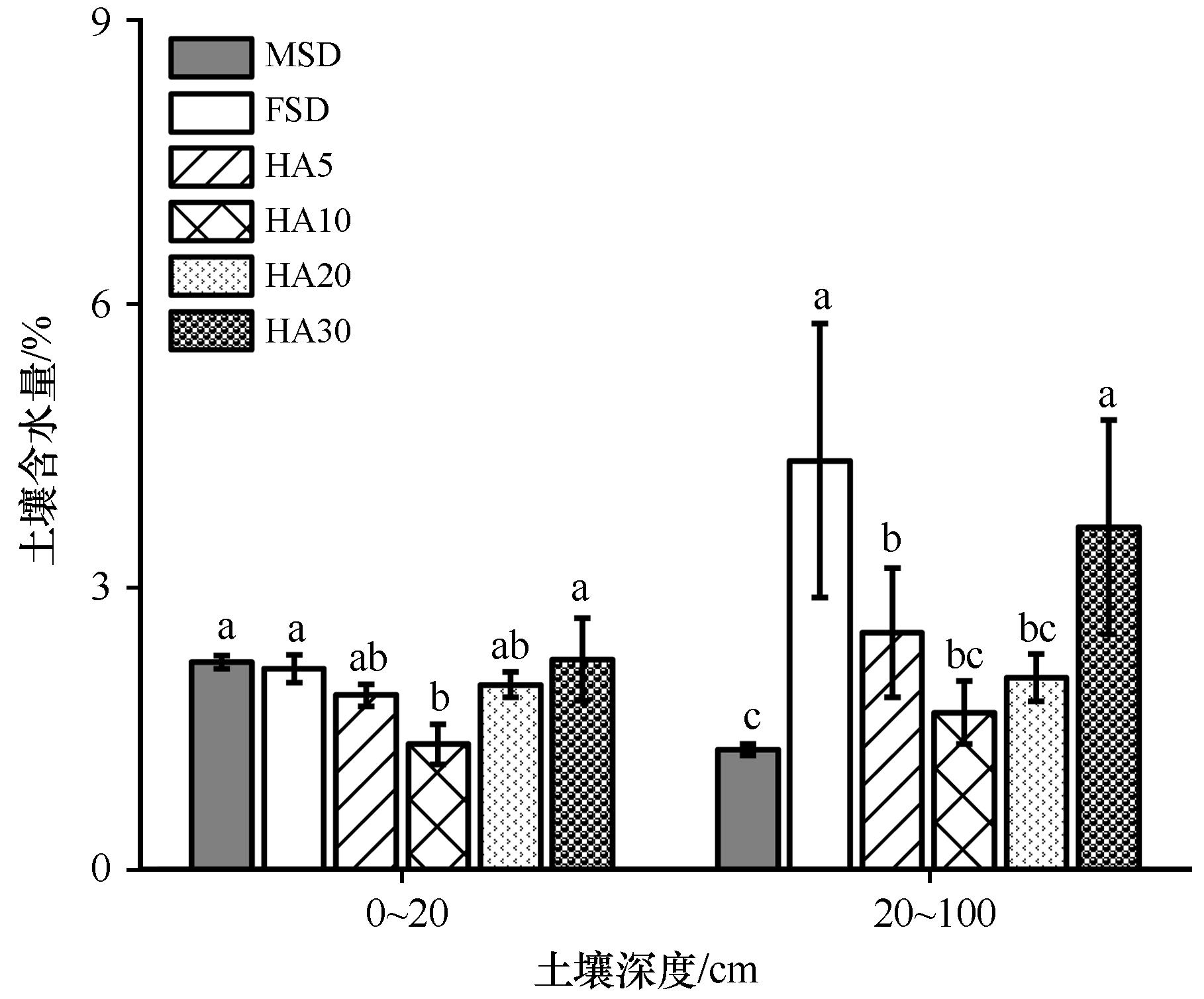
Fig.2 Changes in soil water content at depth of 0-100 cm in mobile sandy dunes, fixed sandy dunes, and Haloxylonammodendron plantations of different ages
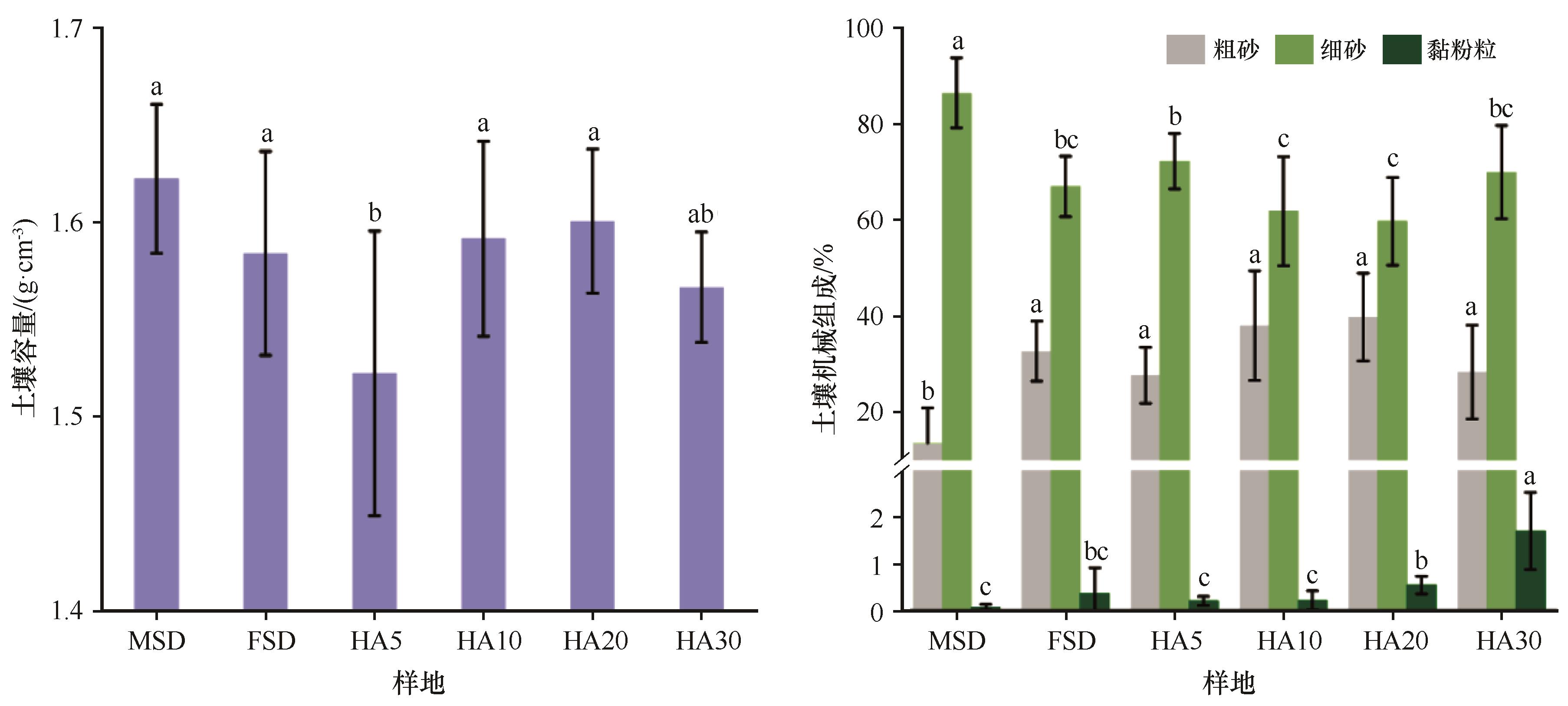
Fig. 3 Comparison of soil bulk density and soil texture in mobile sandy dunes, fixed sandy dunes, and Haloxylon ammodendron plantations of different ages
| 指标 | MSD | FSD | HA5 | HA10 | HA20 | HA30 | F5,72 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.78±0.03c | 9.19±0.14ab | 9.34±0.12a | 9.08±0.12b | 9.09±0.09b | 8.82±0.11c | 34.59*** |
| EC | 0.049±0.005c | 0.109±0.019c | 0.101±0.02c | 0.101±0.015c | 0.267±0.045b | 0.392±0.233a | 30.16*** |
| SOC | 0.13±0.02cd | 0.15±0.02b | 0.13±0.01bc | 0.11±0.01d | 0.15±0.01b | 0.22±0.03a | 49.44*** |
| TN | 0.006±0.001c | 0.009±0.001c | 0.013±0.001a | 0.012±0.001b | 0.022±0.001a | 0.018±0.002a | 48.96*** |
| TP | 0.022±0.001d | 0.024±0.001c | 0.025±0.001c | 0.025±0.001c | 0.027±0.001b | 0.030±0.002a | 70.08*** |
Table 2 Comparison of soil pH,electrical conductivity, organic carbon, total nitrogen and total phosphorus contents in mobile sand dunes, fixed sand dunes, and Haloxylon ammodendron plantations of different ages
| 指标 | MSD | FSD | HA5 | HA10 | HA20 | HA30 | F5,72 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.78±0.03c | 9.19±0.14ab | 9.34±0.12a | 9.08±0.12b | 9.09±0.09b | 8.82±0.11c | 34.59*** |
| EC | 0.049±0.005c | 0.109±0.019c | 0.101±0.02c | 0.101±0.015c | 0.267±0.045b | 0.392±0.233a | 30.16*** |
| SOC | 0.13±0.02cd | 0.15±0.02b | 0.13±0.01bc | 0.11±0.01d | 0.15±0.01b | 0.22±0.03a | 49.44*** |
| TN | 0.006±0.001c | 0.009±0.001c | 0.013±0.001a | 0.012±0.001b | 0.022±0.001a | 0.018±0.002a | 48.96*** |
| TP | 0.022±0.001d | 0.024±0.001c | 0.025±0.001c | 0.025±0.001c | 0.027±0.001b | 0.030±0.002a | 70.08*** |
| 指标 | 流动和固定沙丘 | 人工梭梭林 | 流动和固定沙丘与人工梭梭林 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | 20~100 cm | 0~20 cm | 20~100 cm | 0~20 cm | 20~100 cm | ||||||||||||
| r | P | r | P | r | P | r | P | r | P | r | P | ||||||
| 灌木密度/(株/100 m2) | -0.47 | 0.237 | 0.65 | 0.080 | -0.35 | 0.189 | -0.38 | 0.150 | -0.62 | <0.002 | 0.02 | 0.924 | |||||
| 灌木盖度/% | -0.05 | 0.905 | 0.79 | 0.021 | -0.16 | 0.566 | -0.3 | 0.257 | -0.49 | 0.014 | 0.09 | 0.688 | |||||
| 灌木物种丰富度 | -0.27 | 0.521 | 0.42 | 0.298 | -0.42 | 0.102 | -0.38 | 0.146 | -0.46 | 0.024 | 0.09 | 0.689 | |||||
| 草本盖度/% | -0.25 | 0.544 | 0.74 | 0.038 | 0.31 | 0.246 | 0.53 | 0.035 | 0.22 | 0.294 | 0.58 | 0.003 | |||||
| 草本物种丰富度 | -0.57 | 0.138 | 0.46 | 0.247 | 0.37 | 0.157 | 0.39 | 0.141 | 0.07 | 0.734 | 0.48 | 0.017 | |||||
Table 3 Spearman correlation coefficients between 0-20 cm and 20-100 cm soil water content and shrub density, cover, species richness, herbaceous cover, and herbaceous species richness
| 指标 | 流动和固定沙丘 | 人工梭梭林 | 流动和固定沙丘与人工梭梭林 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | 20~100 cm | 0~20 cm | 20~100 cm | 0~20 cm | 20~100 cm | ||||||||||||
| r | P | r | P | r | P | r | P | r | P | r | P | ||||||
| 灌木密度/(株/100 m2) | -0.47 | 0.237 | 0.65 | 0.080 | -0.35 | 0.189 | -0.38 | 0.150 | -0.62 | <0.002 | 0.02 | 0.924 | |||||
| 灌木盖度/% | -0.05 | 0.905 | 0.79 | 0.021 | -0.16 | 0.566 | -0.3 | 0.257 | -0.49 | 0.014 | 0.09 | 0.688 | |||||
| 灌木物种丰富度 | -0.27 | 0.521 | 0.42 | 0.298 | -0.42 | 0.102 | -0.38 | 0.146 | -0.46 | 0.024 | 0.09 | 0.689 | |||||
| 草本盖度/% | -0.25 | 0.544 | 0.74 | 0.038 | 0.31 | 0.246 | 0.53 | 0.035 | 0.22 | 0.294 | 0.58 | 0.003 | |||||
| 草本物种丰富度 | -0.57 | 0.138 | 0.46 | 0.247 | 0.37 | 0.157 | 0.39 | 0.141 | 0.07 | 0.734 | 0.48 | 0.017 | |||||
| 变量 | 惯量 | 解释率/% | 贡献率/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 0.225 | 22.5 | 53.8 | 23 | <0.001 |
| SD | 0.035 | 3.5 | 8.3 | 4.6 | <0.012 |
| SSR | 0.016 | 1.6 | 3.8 | 2.1 | <0.112 |
| HC | 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | <0.894 |
| HSR | 0.141 | 14.1 | 33.9 | 18 | <0.001 |
| 总计 | 0.418 | 41.8 | 100 | ||
| 残差 | 0.582 |
Table 4 The relative contributions of explanatory variables to the variation in the soil environment
| 变量 | 惯量 | 解释率/% | 贡献率/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 0.225 | 22.5 | 53.8 | 23 | <0.001 |
| SD | 0.035 | 3.5 | 8.3 | 4.6 | <0.012 |
| SSR | 0.016 | 1.6 | 3.8 | 2.1 | <0.112 |
| HC | 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | <0.894 |
| HSR | 0.141 | 14.1 | 33.9 | 18 | <0.001 |
| 总计 | 0.418 | 41.8 | 100 | ||
| 残差 | 0.582 |
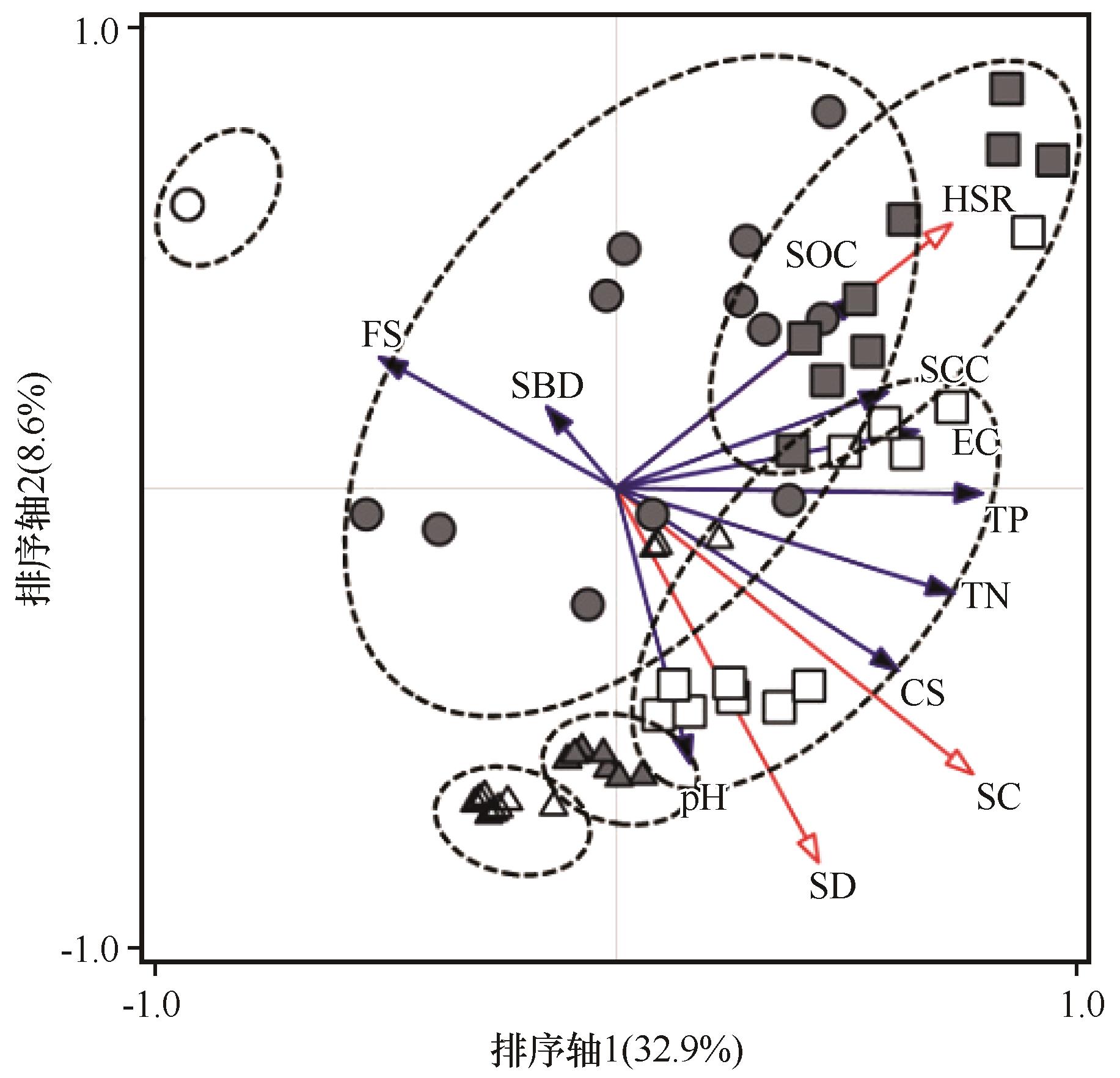
Fig.4 The RDA two-dimensional ordination diagram of soil environment with explanatory variables among mobile sandy dune (MSD), fixed sandy dune (FSD) and Haloxylonammodendron plantations (HAs) of different ages
| 指标 | 灌木盖度/% | 灌木密度/(株/100m2) | 草本物种丰富度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | r | P | |
| 土壤容重/(g·cm-3) | -0.07 | 0.538 | -0.27 | 0.020 | -0.18 | 0.142 |
| 粗砂/% | 0.51 | <0.001 | 0.32 | 0.006 | 0.14 | 0.247 |
| 细砂/% | -0.50 | <0.001 | -0.31 | 0.008 | -0.18 | 0.132 |
| 黏粉粒/% | 0.29 | 0.015 | 0.09 | 0.458 | 0.51 | <0.001 |
| 土壤pH | 0.40 | <0.001 | 0.61 | <0.001 | -0.12 | 0.308 |
| 土壤电导率/(μS·cm-1) | 0.49 | <0.001 | 0.18 | 0.131 | 0.57 | <0.001 |
| 土壤有机碳/% | -0.06 | 0.623 | -0.20 | 0.089 | 0.65 | <0.001 |
| 土壤全氮/% | 0.65 | <0.001 | 0.04 | 0.766 | 0.25 | 0.033 |
| 土壤全磷/% | 0.53 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 0.027 | 0.52 | <0.001 |
Table 5 The correlation of shrub cover and herbaceous species richness with soil physical chemical factors
| 指标 | 灌木盖度/% | 灌木密度/(株/100m2) | 草本物种丰富度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | P | r | P | r | P | |
| 土壤容重/(g·cm-3) | -0.07 | 0.538 | -0.27 | 0.020 | -0.18 | 0.142 |
| 粗砂/% | 0.51 | <0.001 | 0.32 | 0.006 | 0.14 | 0.247 |
| 细砂/% | -0.50 | <0.001 | -0.31 | 0.008 | -0.18 | 0.132 |
| 黏粉粒/% | 0.29 | 0.015 | 0.09 | 0.458 | 0.51 | <0.001 |
| 土壤pH | 0.40 | <0.001 | 0.61 | <0.001 | -0.12 | 0.308 |
| 土壤电导率/(μS·cm-1) | 0.49 | <0.001 | 0.18 | 0.131 | 0.57 | <0.001 |
| 土壤有机碳/% | -0.06 | 0.623 | -0.20 | 0.089 | 0.65 | <0.001 |
| 土壤全氮/% | 0.65 | <0.001 | 0.04 | 0.766 | 0.25 | 0.033 |
| 土壤全磷/% | 0.53 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 0.027 | 0.52 | <0.001 |
| [1] | Li X R, Xiao H L, Zhang J G,et al.Long-term ecosystem effects of sand-binding vegetation in the Tengger Desert,northern China[J].Restoration Ecology,2004,12(3):376-390. |
| [2] | Su Y Z, Zhao W Z, Su P X,et al.Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis-desert ecotone in an arid region: a case study in Hexi Corridor,Northwest China[J].Ecological Engineering,2007,29(2):117-124. |
| [3] | Zhao W Z, Hu G L, Zhang Z H,et al.Shielding effect of oasis-protection systems composed of various forms of wind break on sand fixation in an arid region:a case study in the Hexi Corridor,Northwest China[J].Ecological Engineering,2008,33(2):119-125. |
| [4] | Orlovsky N, Birnbaum E.The role of Haloxylon species for combating desertification in Central Asia[J].Plant Biosystems-An International Journal Dealing with All Aspects of Plant Biology,2002,136(2):233-240. |
| [5] | 郭泉水,王春玲,郭志华,等.我国现存梭梭荒漠植被地理分布及其斑块特征[J].林业科学,2005,41(5):2-7. |
| [6] | 张丹,马松梅,魏博,等.中国梭梭属植物历史分布格局及其驱动机制[J].生物多样性,2022,30(1): 38-47. |
| [7] | Zheng Y, Zhao W Z, Zhang G F.Spatial analysis of a Haloxylon ammodendron plantation in an oasis-desert ecotone in the Hexi Corridor,northwestern China[J].Forests,2017,8(6):200. |
| [8] | An F J, Niu Z R, Liu T N,et al.Succession of soil bacterial community along a 46-year Choron sequence artificial revegetation in an arid oasis-desert ecotone[J].Science of the Total Environment,2022,814:152496. |
| [9] | 安芳娇,苏永中,牛子儒,等.干旱区荒漠绿洲过渡带建植梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)林后土壤线虫群落演变[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(2):133-142. |
| [10] | 刘继亮,冯怡琳,王永珍,等.黑河中游人工固沙植被恢复对爬行类和兽类动物多样性的影响[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(6):167-177. |
| [11] | 赵文智,郑颖,张格非.绿洲边缘人工固沙植被自组织过程[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(1):1-7. |
| [12] | Zhang G F, Zhao L W, Yang Q Y,et al.Effect of desert shrubs on fine-scale spatial patterns of understory vegetation in a dry-land[J].Plant Ecology,2016,217:1141-1155. |
| [13] | Zhang K, Su Y Z, Wang T,et al.Soil properties and herbaceous characteristics in an age sequence of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations in an oasis-desert ecotone of northwestern China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2016,8:960-972. |
| [14] | Yu K L, Wang G H.Long-term impacts of shrub plantations in a desert-oasis ecotone: accumulation of soil nutrients,salinity,and development of herbaceour layer[J].Land Degradation & Development,2018,29(8):2681-2693. |
| [15] | Fan B L, Zhang A P, Yang Y,et al.Long-term effects of xerophytic shrub Haloxylon ammodendron plantations on soil properties and vegetation dynamics in Northwest China[J].PLoS One,2016,11(12):e0168000. |
| [16] | Su Y Z, Liu T N, Kong J Q.The establishment and development of Haloxylon ammodendron promotes salt accumulation in surface soil of arid sandy land[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2019,11(2):116-125. |
| [17] | 王继和,张锦春,袁宏波,等.库姆塔格沙漠梭梭群落特征研究[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(5):809-813. |
| [18] | 司朗明,刘彤,信誉.古尔班通古特沙漠土壤因素对退化梭梭更新局限的影响[J].生态学杂志,2010,29(10):1925-1930. |
| [19] | 冯怡琳,王永珍,林永一,等.河西走廊中部荒漠收获蚁(Messor desertus)蚁穴对秋季地表节肢动物群落结构的影响[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(6):121-130. |
| [20] | 李禄军,蒋志荣,车克钧,等.绿洲-荒漠交错带不同沙丘土壤水分时空动态变化规律[J].水土保持学报,2007,21(1):123-127. |
| [21] | Li F R, Zhang H, Zhang T H,et al.Variations of sand transportation rates in sandy grasslands along a desertification gradient in northern China[J].Catena,2003,53(3):255-272. |
| [22] | 中国科学院南京土壤研究所.土壤理化分析[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,1978. |
| [23] | Ter Braak C J F, Šmilauer P.Canoco Reference Manual and User's Guide: Software for Ordination[M].Ithaca,USA: Microcomputer Power,2012. |
| [24] | Aguiar M R, Sala O E.Patch structure,dynamics and implications for the functioning of arid ecosystems[J].Trends in Ecology & Evolution,1999,14(7):273-277. |
| [25] | 侯东杰,李楠,曲孝云,等.青藏高原北部干旱区梭梭群落空间分布特征及其驱动因子[J].生态学报,2024,44(24):11307-11316. |
| [26] | 高利颖,王海兵,廖承贤,等.阿拉善戈壁区人工梭梭林保存率及生长状况研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2024,38(6):159-165. |
| [27] | 朱美菲,韩政伟,雷春英,等.准噶尔盆地荒漠绿洲过渡带地下水埋深对人工梭梭林年龄结构及动态特征的影响[J].生态学报,2024,44(19):8688-8698. |
| [28] | Wang Z T, Liu J L, Luo Y Z,et al.Changes in tenebrionid beetle and ant assembly influenced by different‐aged Haloxylon ammodendron plantations in northwest China[J].Land Degradation & Development,2025,36(9):2940-2954. |
| [29] | Alper J.Ecosystem “engineers” shape habitats for other species[J].Science,1998,280(5367): 1195-1196. |
| [30] | Hastings A, Byers J E, Crooks J A,et al.Ecosystem engineering in space and time[J].Ecology Letters,2007,10(2):153-164. |
| [31] | Romero G Q, Gonçalves‐Souza T, Vieira C,et al.Ecosystem engineering effects on species diversity across ecosystems: a meta-analysis[J].Biological Reviews,2015,90(3):877-890. |
| [32] | 苏永中,刘婷娜.流动沙地建植人工固沙梭梭林的土壤演变过程[J].土壤学报,2020,57(1):84-91. |
| [33] | Song J, Wan S Q, Zhang K S,et al.Ecological restoration enhances dryland carbon stock by reducing surface soil carbon loss due to wind erosion[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2024,121(46):e2416281121. |
| [34] | Su Y Z.The establishment and development of Haloxylon ammodendron promotes salt accumulation in surface soil of arid sandy land[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2019,11(2):116-125. |
| [35] | 安芳娇,苏永中,牛子儒,等.干旱区流动沙地建植梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)林后细粒物质输入对土壤碳氮积累的影响[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(5):147-156. |
| [36] | 李从娟,雷加强,徐新文,等.树干径流对梭梭“肥岛”和“盐岛”效应的作用机制[J].生态学报,2012,32(15):4819-4826. |
| [37] | 黄振英,张新时, Gutterman Y,等.光照、温度和盐分对梭梭种子萌发的影响[J].植物生理学报,2001,27(3):275-280. |
| [38] | 刘继亮,李锋瑞.干旱区绿洲扩张方式对土壤生物优势类群及功能的影响[J].生物多样性,2018,26(10):1116-1126. |
| [39] | 肖洪浪,李新荣,段争虎,等.流沙固定过程中土壤-植被系统演变[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(6):605-611. |
| [40] | 安富博,纪永福,赵艳丽,等.民勤绿洲地下水对人工梭梭林生长的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(9):183-188. |
| [41] | 胡广录,赵文智,王岗.干旱荒漠区斑块状植被空间格局及其防沙效应研究进展[J].生态学报,2011,31(24):7609-7616. |
| [42] | 赵文智,白雪莲,刘婵.巴丹吉林沙漠南缘的植物固沙问题[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):5-11. |
| [43] | 刘丹一,冯伟,王涛,等.低覆盖治沙理论下人工与自然耦合的植被修复机理综述[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(1):170-177. |
| [44] | 邹慧,杨文斌,朱斌,等.低覆盖度治沙理论及其实践[J].生态学报,2024,44(3):1-7. |
| [45] | 罗青红,宁虎森,陈启民.人工梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)林固沙过程中植被与土壤耦合关系[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(4):780-790. |
| [1] | Ziting Wang, Jiliang Liu, Yongzhong Luo, Quanlin Ma, Xiaogan Zhou, Xin Luo, Wenzhen Zong. Long-term effects of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations on topsoil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus stoichiometry and stocks in the desert-oasis ecotone [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 241-252. |
| [2] | Miaomiao Shi, Jianqiang Huo, Gaoling Han, Yicong Nan, Xiaojuan Zhu, Rui Hu, Xue Su. Characteristics of herbaceous community in revegetation Caraganakorshinskii shrublands in Yanchi, Ningxia, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(3): 337-345. |
| [3] | Ren Mu, Jun Qiao, Guangfu Xu, Jingfu Han, Xiao Yu, Chuijiu Kong, Xinle Li. The effect of graphene addition on the growth of different types of grass and soil nutrients in arid areas [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(2): 155-165. |
| [4] | Jun Lei, Xinping Cheng, Chun Xue, Hongmei Liu, Yuhong Zhao, Mingmin Xiao. The characteristics and stability of plant communities in the northern desert area of the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 187-194. |
| [5] | Jiliang Liu, Yilin Feng, Yongzhen Wang, Chengchen Pan, Tianling Bao, Jialong Ren, Wenzhi Zhao. Effects of restoration of artificial sand-fixing vegetation on the diversity of reptiles and mammals in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 167-177. |
| [6] | Li Cheng, Zhiying Ning, Hongling Yang, Yulin Li. Effects of different sand-fixation measures on vegetation and soil characteristics of high and flat mobile dunes [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 273-282. |
| [7] | Rende Wang, Hongjun Jiang, Qing Li, Gang Fu, Yuqiang Li, Yixiao Yuan, Chunping Chang, Zhongling Guo. Preliminary research on the relationship between soil dust emission ability and soil properties [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 43-49. |
| [8] | Jiapeng Pan, Kecun Zhang, Zhishan An, Hongxue Zhang, Chengjie Xue. Analysis of comprehensive benefits of wind-blown sand control projects: a case study of Heishanzui, Dunhuang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 233-242. |
| [9] | Hairong Liang, Tao Wang, Yu Yang, Wei Feng, Honglin Lian, Xuefeng Liu, Jiatao Li, Jia Liu. Comparison of deep soil recharge characteristics between Mu Us Sandy Land and Hunshandake Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 69-76. |
| [10] | Yao Jiaozhuan, Liu Tingxi, Tong Xin, Wang Tianshuai, Wang Haiyan. Soil Particle Fractal Dimension in the Dune-meadow Ecotone of the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(2): 433-440. |
| [11] | WANG Jin;ZHOU Rui-lian;ZHAO Ha-lin;ZHAO Xue-yong. Comparison of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in the Desertification Process of Hulunbeier Sandy Land and Songnen Sandy Land [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(2): 309-314. |
| [12] | DU Jian-hui;YAN Ping;DING Lian-gang;E You-hao;ZHU Meng-jun. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties of Nitraria tangutorun Nebkhas Surface at Different Development Stages in Minqin Oasis [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2009, 29(2): 248-253. |
| [13] | MA Yao-ming, MA Wei-qiang, LI Mao-shan, SUN Fang-lin, WAN Jie-min. Remote Sensing Parameterization of Land Surface Heat Fluxes over the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2004, 24(4): 392-399. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech