中国沙漠 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 65-77.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00080
齐丹卉1,4( ), 杨洪晓5, 卢琦1,2, 褚建民3(
), 杨洪晓5, 卢琦1,2, 褚建民3( ), 袁祺3, 甘红豪3, 赵帅3, 陈加伟3, 徐晓庆3
), 袁祺3, 甘红豪3, 赵帅3, 陈加伟3, 徐晓庆3
收稿日期:2021-05-24
修回日期:2021-07-14
出版日期:2021-11-20
发布日期:2021-12-17
通讯作者:
褚建民
作者简介:褚建民,E-mail: cjmcaf@163.com基金资助:
Danhui Qi1,4( ), Hongxiao Yang5, Qi Lu1,2, Jianmin Chu3(
), Hongxiao Yang5, Qi Lu1,2, Jianmin Chu3( ), Qi Yuan3, Honghao Gan3, Shuai Zhao3, Jiawei Chen3, Xiaoqing Xu3
), Qi Yuan3, Honghao Gan3, Shuai Zhao3, Jiawei Chen3, Xiaoqing Xu3
Received:2021-05-24
Revised:2021-07-14
Online:2021-11-20
Published:2021-12-17
Contact:
Jianmin Chu
摘要:
认识沙地植物群落物种多样性及其与环境的关系,对维护沙地生态系统的结构与功能具有重要意义。本研究基于浑善达克沙地83个样地的群落数据及环境数据,通过数量生态学方法对群落物种多样性及其影响因子进行分析,探讨浑善达克沙地物种多样性特征及其环境解释。结果表明:(1)主要群落有榆树(Ulmus pumila)群落、小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)群落、黄柳(Salixgordejevii)群落及长梗扁桃(Prunus pedunculata)群落等,其中榆树群落分布在降水和土壤养分都比较高的区域,小叶锦鸡儿群落适生生境为降水较少且土壤贫瘠的区域;影响该区群落分布的主要环境因子依次为生长季降水量、生长季温度、土壤全氮和全钾含量,降水量的差异显著影响群落分布格局。(2)浑善达克沙地植物多样性的分布呈现出一定的规律性变化。物种多样性指数均随经度和海拔的增加而增加;Patrick指数与Shannon-wiener指数随纬度的增加呈现减少的趋势;Simpson指数与Pielou指数随纬度增加而增加;Patrick指数、Simpson指数和Shannon-wiener指数与生长季降水量、土壤有机碳和有效氮含量呈显著正相关,与生长季均温、≥0 ℃积温、生长季风速呈显著负相关,所有环境变量与Pielou指数均无显著相关性。研究结果阐明了浑善达克沙地物种多样性及植物群落分布的规律以及与关键环境因子之间的关系,有利于提高沙地植物多样性和稳定性,增强沙地植被的生态功能。
中图分类号:
齐丹卉, 杨洪晓, 卢琦, 褚建民, 袁祺, 甘红豪, 赵帅, 陈加伟, 徐晓庆. 浑善达克沙地植物群落物种多样性及环境解释[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 65-77.
Danhui Qi, Hongxiao Yang, Qi Lu, Jianmin Chu, Qi Yuan, Honghao Gan, Shuai Zhao, Jiawei Chen, Xiaoqing Xu. Biodiversity of plant communities and its environmental interpretation in the Otindag Sandy Land, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 65-77.
| 环境因子 | 简称 | 单位 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 气候因子 | 生长季降水量 | PGS | mm |
| 生长季均温 | TGS | ℃ | |
| ≥0 ℃积温 | AT0 | ℃ | |
| 生长季平均风速 | WGS | m·s-1 | |
| 土壤因子 | 有机碳 | SOC | g·kg-1 |
| 全氮 | TN | g·kg-1 | |
| 全磷 | TP | g·kg-1 | |
| 全钾 | TK | g·kg-1 | |
| 有效氮 | AN | mg·kg-1 | |
| 有效磷 | AP | mg·kg-1 | |
| 有效钾 | AK | mg·kg-1 | |
表1 环境因子对照表
Table 1 Environmental factors in the study area
| 环境因子 | 简称 | 单位 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 气候因子 | 生长季降水量 | PGS | mm |
| 生长季均温 | TGS | ℃ | |
| ≥0 ℃积温 | AT0 | ℃ | |
| 生长季平均风速 | WGS | m·s-1 | |
| 土壤因子 | 有机碳 | SOC | g·kg-1 |
| 全氮 | TN | g·kg-1 | |
| 全磷 | TP | g·kg-1 | |
| 全钾 | TK | g·kg-1 | |
| 有效氮 | AN | mg·kg-1 | |
| 有效磷 | AP | mg·kg-1 | |
| 有效钾 | AK | mg·kg-1 | |
| 群落名称 | 样方数 | 优势种 |
|---|---|---|
| 榆树群落 | 23 | 榆树(Ulmuspumila)、盐蒿(Artemisiahalodendron)、冰草(Agropyroncristatum)、蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum)、冷蒿(Artemisiafrigida)、黄柳(Salixgordejevii) |
| 小叶锦鸡儿群落 | 18 | 小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla)、沙鞭(Psammochloavillosa)、蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum)、猪毛菜(Salsolacollina)、狗尾草(Setariaviridis)、雾冰藜(Bassiadasyphylla) |
| 黄柳群落 | 7 | 黄柳(Salixgordejevii)、蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum)、小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla)、沙鞭(Psammochloavillosa)、盐蒿(Artemisiahalodendron)、乌柳(Salixcheilophila) |
| 长梗扁桃群落 | 8 | 长梗扁桃(Prunuspedunculata)、糙隐子草(Cleistogenessquarrosa)、大针茅(Stipagrandis)、小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla)、画眉草(Eragrostispilosa)、狭叶锦鸡儿(Caraganastenophylla) |
表2 浑善达克沙地主要植物群落类型
Table 2 Mean community types of the Otindag Sandy Land
| 群落名称 | 样方数 | 优势种 |
|---|---|---|
| 榆树群落 | 23 | 榆树(Ulmuspumila)、盐蒿(Artemisiahalodendron)、冰草(Agropyroncristatum)、蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum)、冷蒿(Artemisiafrigida)、黄柳(Salixgordejevii) |
| 小叶锦鸡儿群落 | 18 | 小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla)、沙鞭(Psammochloavillosa)、蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum)、猪毛菜(Salsolacollina)、狗尾草(Setariaviridis)、雾冰藜(Bassiadasyphylla) |
| 黄柳群落 | 7 | 黄柳(Salixgordejevii)、蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum)、小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla)、沙鞭(Psammochloavillosa)、盐蒿(Artemisiahalodendron)、乌柳(Salixcheilophila) |
| 长梗扁桃群落 | 8 | 长梗扁桃(Prunuspedunculata)、糙隐子草(Cleistogenessquarrosa)、大针茅(Stipagrandis)、小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla)、画眉草(Eragrostispilosa)、狭叶锦鸡儿(Caraganastenophylla) |
| 物种 | 科 | 生活型 | 生态类型 | 存在度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙隐子草(Cleistogenessquarrosa) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 81.93 |
| 蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 旱生 | 80.72 |
| 猪毛菜(Salsolacollina) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 旱中生 | 77.11 |
| 雾冰藜(Bassiadasyphylla) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 旱生 | 66.27 |
| 狗尾草(Setariaviridis) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 一年生草本 | 中生 | 62.65 |
| 冷蒿(Artemisiafrigida) | 菊科(Asteraceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 61.45 |
| 盐蒿(Artemisiahalodendron) | 菊科(Asteraceae) | 半灌木 | 中旱生 | 60.24 |
| 小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla) | 豆科(Fabaceae) | 灌木 | 旱生 | 57.83 |
| 冰草(Agropyroncristatum) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 45.78 |
| 蒙古韭(Alliummongolicum) | 石蒜科(Amaryllidaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 43.37 |
| 细叶韭(Alliumtenuissimum) | 石蒜科(Amaryllidaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 43.37 |
| 花苜蓿(Medicagoruthenica) | 豆科(Fabaceae) | 多年生草本 | 中旱生 | 42.17 |
| 寸草(Carexduriuscula) | 莎草科(Cyperaceae) | 多年生草本 | 中旱生 | 42.17 |
| 藜(Chenopodiumalbum) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 中生 | 39.76 |
| 羊草(Leymuschinensis) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生-中旱生 | 39.76 |
| 沙鞭(Psammochloavillosa) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 38.55 |
| 榆树(Ulmuspumila) | 榆科(Ulmaceae) | 乔木 | 旱中生 | 33.73 |
| 画眉草(Eragrostispilosa) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 一年生草本 | 中生 | 33.73 |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchumthesioides) | 夹竹桃科(Apocynaceae) | 多年生草本 | 中旱生 | 30.12 |
表3 浑善达克沙地常见植物(存在度>30%)
Table 3 Common plant species in the Otindag Sandy Land (Presence>30%)
| 物种 | 科 | 生活型 | 生态类型 | 存在度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 糙隐子草(Cleistogenessquarrosa) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 81.93 |
| 蒙古虫实(Corispermummongolicum) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 旱生 | 80.72 |
| 猪毛菜(Salsolacollina) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 旱中生 | 77.11 |
| 雾冰藜(Bassiadasyphylla) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 旱生 | 66.27 |
| 狗尾草(Setariaviridis) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 一年生草本 | 中生 | 62.65 |
| 冷蒿(Artemisiafrigida) | 菊科(Asteraceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 61.45 |
| 盐蒿(Artemisiahalodendron) | 菊科(Asteraceae) | 半灌木 | 中旱生 | 60.24 |
| 小叶锦鸡儿(Caraganamicrophylla) | 豆科(Fabaceae) | 灌木 | 旱生 | 57.83 |
| 冰草(Agropyroncristatum) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 45.78 |
| 蒙古韭(Alliummongolicum) | 石蒜科(Amaryllidaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 43.37 |
| 细叶韭(Alliumtenuissimum) | 石蒜科(Amaryllidaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 43.37 |
| 花苜蓿(Medicagoruthenica) | 豆科(Fabaceae) | 多年生草本 | 中旱生 | 42.17 |
| 寸草(Carexduriuscula) | 莎草科(Cyperaceae) | 多年生草本 | 中旱生 | 42.17 |
| 藜(Chenopodiumalbum) | 苋科(Amaranthaceae) | 一年生草本 | 中生 | 39.76 |
| 羊草(Leymuschinensis) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生-中旱生 | 39.76 |
| 沙鞭(Psammochloavillosa) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 多年生草本 | 旱生 | 38.55 |
| 榆树(Ulmuspumila) | 榆科(Ulmaceae) | 乔木 | 旱中生 | 33.73 |
| 画眉草(Eragrostispilosa) | 禾本科(Poaceae) | 一年生草本 | 中生 | 33.73 |
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchumthesioides) | 夹竹桃科(Apocynaceae) | 多年生草本 | 中旱生 | 30.12 |
| 环境因子 | 多样性指数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patrick指数 | Simpson指数 | Shannon-Wiener指数 | Pielou指数 | ||
| 气候因子 | 生长季降水量 | 0.426** | 0.289** | 0.394** | 0.114 |
| 生长季均温 | -0.458** | -0.321** | -0.445** | -0.173 | |
| ≥0 ℃积温 | -0.426** | -0.332** | -0.418** | -0.163 | |
| 生长季风速 | -0.356** | -0.329** | -0.318** | -0.097 | |
| 土壤因子 | 有机碳 | 0.275* | 0.439** | 0.244* | 0.128 |
| 有效氮 | 0.382** | 0.465** | 0.332** | 0.131 | |
| 全磷 | -0.215 | -0.185 | -0.263* | -0.153 | |
表4 浑善达克沙地植物群落物种多样性与环境因子的相关性(n=83)
Table 4 Pearson correlation analysis between species diversity indices and environmental factors of plant communities in the Otindag Sandy Land
| 环境因子 | 多样性指数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patrick指数 | Simpson指数 | Shannon-Wiener指数 | Pielou指数 | ||
| 气候因子 | 生长季降水量 | 0.426** | 0.289** | 0.394** | 0.114 |
| 生长季均温 | -0.458** | -0.321** | -0.445** | -0.173 | |
| ≥0 ℃积温 | -0.426** | -0.332** | -0.418** | -0.163 | |
| 生长季风速 | -0.356** | -0.329** | -0.318** | -0.097 | |
| 土壤因子 | 有机碳 | 0.275* | 0.439** | 0.244* | 0.128 |
| 有效氮 | 0.382** | 0.465** | 0.332** | 0.131 | |
| 全磷 | -0.215 | -0.185 | -0.263* | -0.153 | |
| 统计轴 | 特征值 | 物种-环境 相关性 | 累计变异率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数据 方差 | 物种-环境 关系 | |||
| 第1轴 | 0.398 | 0.941 | 7.19 | 26.87 |
| 第2轴 | 0.312 | 0.938 | 12.81 | 47.87 |
| 第3轴 | 0.204 | 0.928 | 16.49 | 61.65 |
| 第4轴 | 0.151 | 0.897 | 19.23 | 71.87 |
表5 浑善达克沙地植物群落与环境因子的CCA对应分析结果
Table 5 Results for the first four axes of the CCA of communities and environmental factors in the Otindag Sandy Land
| 统计轴 | 特征值 | 物种-环境 相关性 | 累计变异率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种数据 方差 | 物种-环境 关系 | |||
| 第1轴 | 0.398 | 0.941 | 7.19 | 26.87 |
| 第2轴 | 0.312 | 0.938 | 12.81 | 47.87 |
| 第3轴 | 0.204 | 0.928 | 16.49 | 61.65 |
| 第4轴 | 0.151 | 0.897 | 19.23 | 71.87 |
| 环境因子 | 解释率/% | 贡献率/% | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生长季降水量 | 6.7 | 25.1 | 0.002 |
| 生长季温度 | 4.8 | 18.1 | 0.002 |
| 全氮 | 4.1 | 15.2 | 0.004 |
| 全钾 | 2.8 | 10.3 | 0.054 |
| 生长季风速 | 2.4 | 8.9 | 0.248 |
| 土壤有机碳 | 2.3 | 8.6 | 0.172 |
| ≥0 ℃积温 | 1.8 | 6.6 | 0.782 |
| 全磷 | 2 | 7.4 | 0.572 |
表6 浑善达克沙地环境因子对群落的解释与贡献率
Table 6 Explains and Contribution rate of community with environmental factors in the Otindag Sandy Land
| 环境因子 | 解释率/% | 贡献率/% | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生长季降水量 | 6.7 | 25.1 | 0.002 |
| 生长季温度 | 4.8 | 18.1 | 0.002 |
| 全氮 | 4.1 | 15.2 | 0.004 |
| 全钾 | 2.8 | 10.3 | 0.054 |
| 生长季风速 | 2.4 | 8.9 | 0.248 |
| 土壤有机碳 | 2.3 | 8.6 | 0.172 |
| ≥0 ℃积温 | 1.8 | 6.6 | 0.782 |
| 全磷 | 2 | 7.4 | 0.572 |
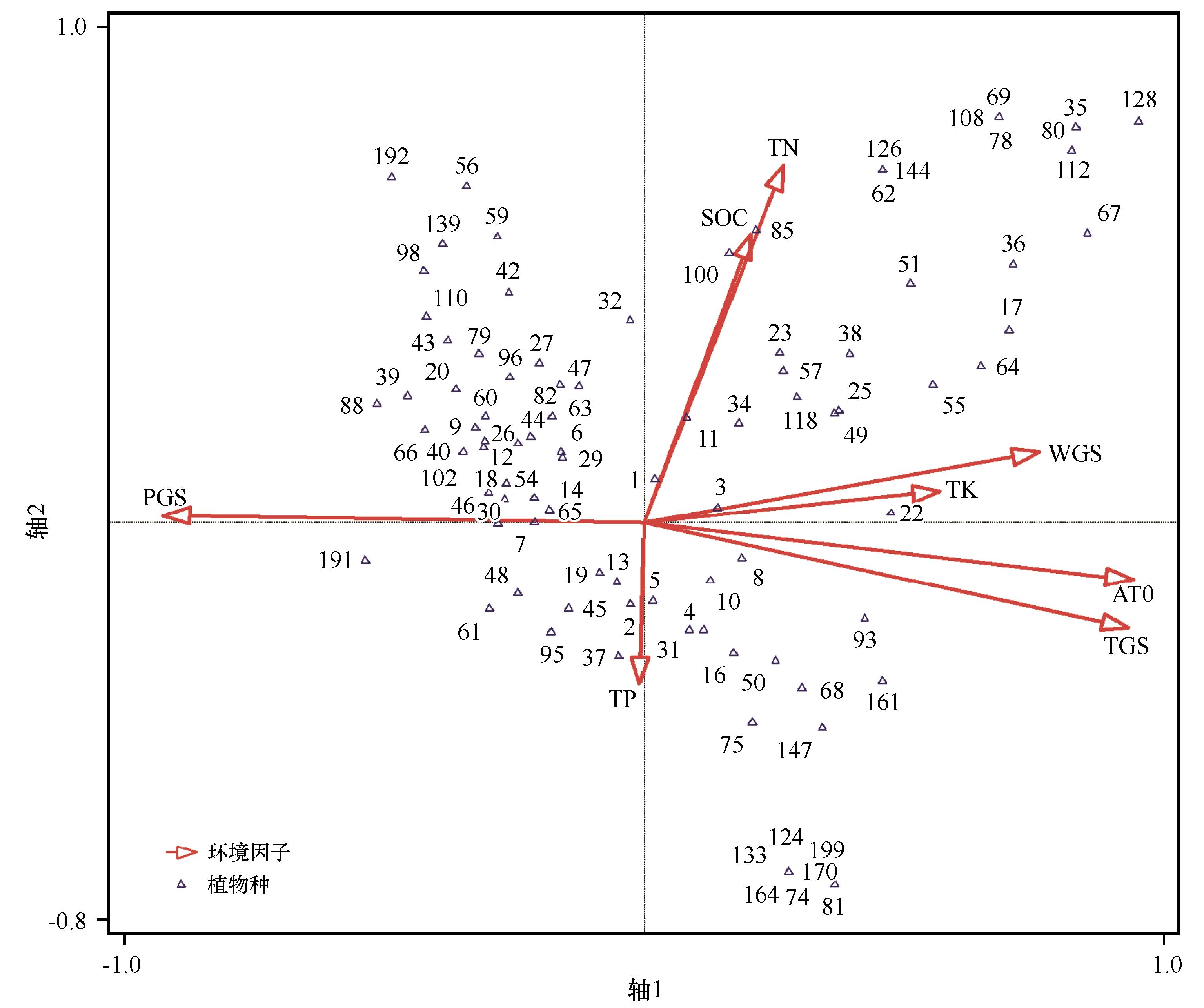
图5 浑善达克沙地群落的物种分布与气候和土壤因子的 CCA 排序图PGS:生长季降水量; TGS:生长季均温; AT0:≥0 ℃积温; WGS:生长季风速; SOC:有机碳; AN:有效氮,TP:全磷
Fig.5 CCA ordination of species distribution and climatic and edaphic factors in the Otindag Sandy Land
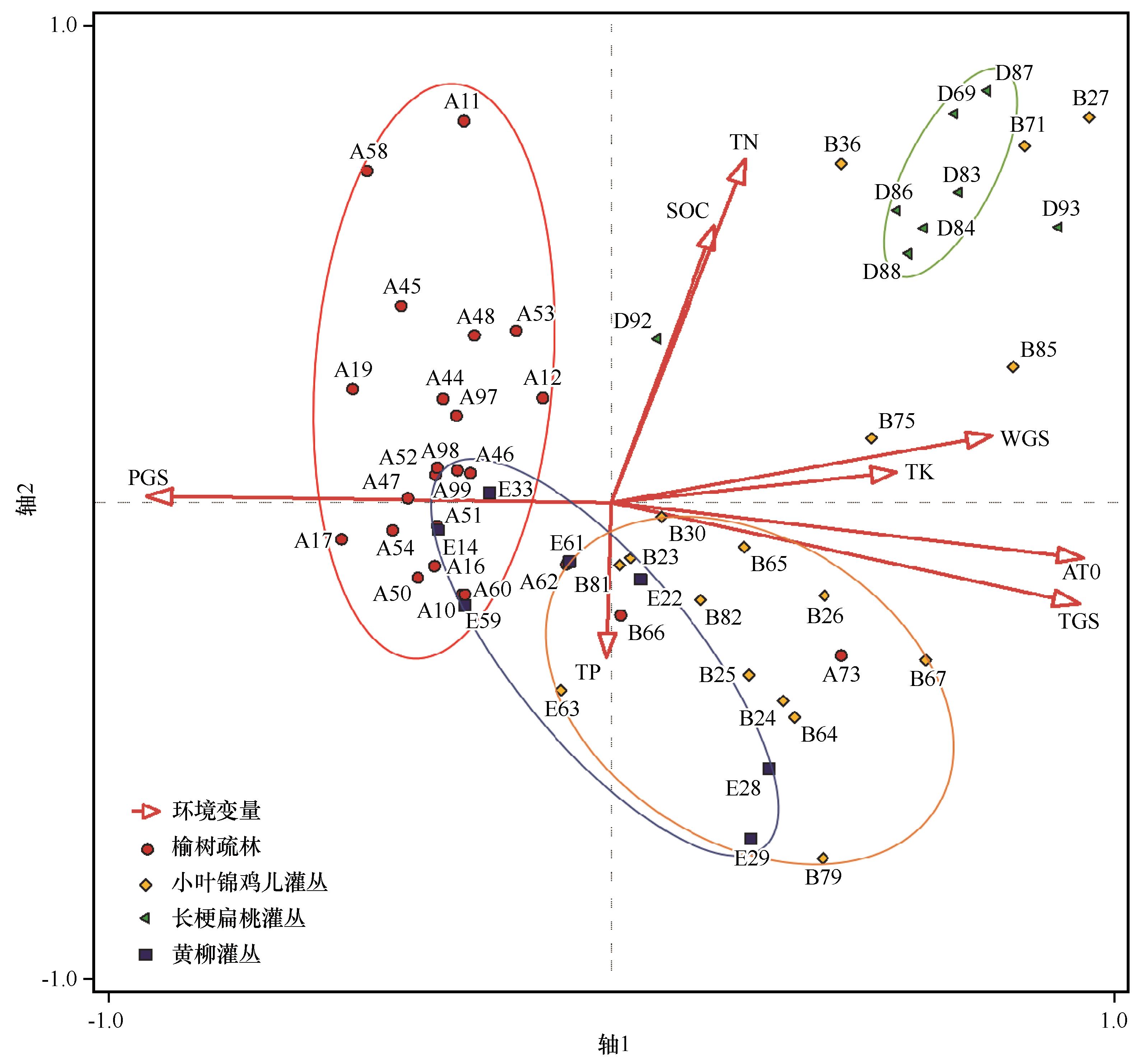
图6 浑善达克沙地不同群落类型与气候和土壤因子的 CCA 排序图PGS:生长季降水量; TGS:生长季均温; AT0:≥0 ℃积温; WGS:生长季风速; SOC:有机碳; AN:有效氮,TP:全磷
Fig.6 CCA ordination of different community types and climatic and edaphic factors in the Otindag Sandy Land
| 1 | Kratochwil A,Okologie F.Biodiversity in Ecosystems:Some Principles[M].Netherlands:Springer,1999. |
| 2 | 马克平.生物多样性科学的热点问题[J].生物多样性,2016,24(1):1-2. |
| 3 | 高贤明,马克平,黄建辉,等.北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅺ.山地草甸β多样性[J].生态学报,1998,18(1):24-24. |
| 4 | Huang E,Chen Y,Fang M,et al.Environmental drivers of plant distributions at global and regional scales[J].Global Ecology and Biogeography,2021,30(3):697-709. |
| 5 | Whittaker R J,Field W R.Scale and species richness:towards a general,hierarchical theory of species diversity[J].Journal of Biogeography,2001,28(4):453-470. |
| 6 | Harrison S,Cornell H.Toward a better understanding of the regional causes of local community richness[J].Ecology Letters,2008,11(9):969-979. |
| 7 | 杨崇曜,李恩贵,陈慧颖,等.内蒙古西部自然植被的物种多样性及其影响因素[J].生物多样性,2017,25(12):1303-1312. |
| 8 | 汪殿蓓,暨淑仪,陈飞鹏.植物群落物种多样性研究综述[J].生态学杂志,2001,20(4):55-60. |
| 9 | Tilman D,Wedin D,Knops J.Productivity and sustainability influenced by biodiversity in grassland ecosystems[J].Nature,1996,379(6567):718-720. |
| 10 | Phillips O L,Vargas P N,Monteagudo A L,et al.Habitat association among Amazonian tree species:a landscape-scale approach[J].Journal of Ecology,2003,91(5):757-775. |
| 11 | Hansen J,Ruedy R,Sato M,et al.Global surface temperature change[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2010,48(4):1-29. |
| 12 | Isaac M H.Climate science:the cause of the pause[J].Nature,2013,501(7467):318-319. |
| 13 | Poulter B,Pederson N,Liu H Y,et al.Recent trends in inner Asian forest dynamics to temperature and precipitation indicate high sensitivity to climate change[J].Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,2013,178:31-45. |
| 14 | 方精云.群落生态学迎来新的辉煌时代[J].生物多样性,2009,17(6):531-532. |
| 15 | Hawkins B A.Ecology's oldest pattern?[J].Trends in Ecology and Evolution,2001,16:470. |
| 16 | Hawkins B A,Porter E E,Diniz-Filho J A F.Productivity and history as predictors of the latitudinal diversity gradient of terrestrial birds[J].Ecology,2003,84:1608-1623. |
| 17 | Allen A P,Brown J H,Gillooly J F.Global biodiversity,biochemical kinetics,and the energetic-equivalence rule[J].Science,2002,297:1545-1548. |
| 18 | Stegen J C,Enquist B J,Ferriere R.Advancing the metabolic theory of biodiversity[J].Ecology Letters,2009,12:1001-1015. |
| 19 | O’Brien E M.Water-energy dynamics,climate,and prediction of woody plant species richness:an interim general model[J].Journal of Biogeography,1998,25:379-398. |
| 20 | Hawkins B A,Field R,Cornell H V,et al.Energy,water,and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness[J].Ecology,2003,84:3105-3117. |
| 21 | Xu H,Ca O M,Wu Y,et al.Disentangling the determinants of species richness of vascular plants and mammals from national to regional scales[J].Scientific Reports,2016,6:21988. |
| 22 | Wang Z H,Fang J Y,Tang Z Y,et al.Relative role of contemporary environment versus history in shaping diversity patterns of China's woody plants[J].Ecography,2013,35(12):1124-1133. |
| 23 | 王志恒,唐志尧,方精云.物种多样性地理格局的能量假说[J].生物多样性,2009,17(6):613-624. |
| 24 | Wang J,Long T,Zhong Y,et al.Disentangling the influence of climate,soil and belowground microbes on local species richness in a dryland ecosystem of Northwest China[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):18029. |
| 25 | Zellweger F,Braunisch V,Morsdorf F,et al.Disentangling the effects of climate,topography,soil and vegetation on stand-scale species richness in temperate forests[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2015,349:36-44. |
| 26 | Tuomisto H,Zuquim G,Glenda C.Species richness and diversity along edaphic and climatic gradients in Amazonia[J].Ecography,2014,37(11):1034-1046. |
| 27 | 吕丽莎,蔡宏宇,杨永,等.中国裸子植物的物种多样性格局及其影响因子[J].生物多样性,2018,26(11):1133-1146. |
| 28 | 齐丹卉,杨洪晓,卢琦,等.浑善达克沙地植物群落主要类型与特征[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):24-34. |
| 29 | 宋创业,郭柯,刘高焕.浑善达克沙地植物群落物种多样性与土壤因子的关系[J].生态学杂志,2008,27(1):10-15. |
| 30 | 张志永,时忠杰,张晓,等.浑善达克沙地不同微地形的土壤物理性质和草本群落分布及其相关性分析[J].植物资源与环境学报,2017(1):69-76. |
| 31 | 詹瑾,李玉霖,韩丹,等.放牧对浑善达克沙地丘间低地植被群落及土壤的影响[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):187-194. |
| 32 | 李红丽.浑善达克沙地沙漠化过程及其植被恢复的基础研究:以正蓝旗为例[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2003. |
| 33 | 张志永,时忠杰,杨晓晖,等.浑善达克沙地榆树疏林中木本植物空间格局及种内和种间关系分析[J].植物资源与环境学报,2019,28(3):33-43. |
| 34 | 李钢铁,姚云峰,左合君.浑善达克沙地桑根达来地区榆树疏林的分布与立地因子的关系的研究[J].世界林业研究,2008,21:82-86. |
| 35 | 丁国栋,蔡京艳,王贤,等.浑善达克沙地沙漠化成因、过程及其防治对策研究:以内蒙古正蓝旗为例[J].北京林业大学学报,2004,26(4):15-19. |
| 36 | 王璇,陈国科,郭柯,等.1∶100万中国植被图森林和灌丛群系类型的补充资料[J].生物多样性,2019,27(10):1138-1142. |
| 37 | 方精云,朱江玲,郭兆迪,等.植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J].生物多样性,2009,17(6):533-548. |
| 38 | 阳坤,何杰.中国区域地面气象要素驱动数据集(1979-2018)[DS].时空三极环境大数据平台,2019.DOI:10.11888/ AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file.CSTR:18406.11.AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file. |
| 39 | 徐新良,张亚庆.中国气象背景数据集[DS].中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心数据注册与出版系统,2017.DOI:10. 12078/2017121301. |
| 40 | 张金屯.数量生态学 [M].北京:科学出版社,2011. |
| 41 | 马克平,黄建辉,于顺利,等.北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅱ丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数[J].生态学报,1995,15(3):268-277. |
| 42 | 赵娜.浑善达克沙地榆分布与地面因素关系的研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2009. |
| 43 | 段义忠,李娟,杜忠毓,等.毛乌素沙地天然植物多样性组成及区系特征分析[J].西北植物学报,2018,38(4):188-197. |
| 44 | 王寅.科尔沁沙地植物物种丰富度格局及其影响因素[D].北京:北京林业大学,2019. |
| 45 | 彭羽,蒋高明,李永庚,等.浑善达克沙地榆树疏林自然保护区核心区设计的初步研究[J].植物生态学报,2005,29(5):775-780. |
| 46 | Hillebrand H,Bennett D M,Cadotte M W.Consequences of dominance:a review of evenness effects on local and regional ecosystem processes[J].Ecology,2008,89(6):1510-1520. |
| 47 | Gaston K J.Global patterns in biodiversity[J].Nature,2000,405(6783):220-227. |
| 48 | 朱媛君,张璞进,邢娜,等.毛乌素沙地丘间低地植物群落分类与排序[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(6):1580-1589. |
| 49 | 马龙,王静茹,刘廷玺,等.2000-2012年科尔沁沙地植被与气候因子间的响应关系[J].农业机械学报,2016,47(4):162-172. |
| 50 | 张腊梅,刘新平,赵学勇,等.科尔沁固定沙地植被特征对降雨变化的响应[J].生态学报,2014,34(10):2737-2745. |
| 51 | 常学礼,赵爱芬,李胜功.科尔沁沙地固定沙丘植被物种多样性对降水变化的响应[J].植物生态学报,2000,24(2):147-151. |
| 52 | 元志辉,包刚,银山,等.2000-2014年浑善达克沙地植被覆盖变化研究[J].草业学报,2016,25(1):33-46. |
| 53 | 姚雪玲,李龙,王锋,等.放牧方式对浑善达克沙地榆树疏林退化的影响[J].生态学报,2020,40(5):163-171. |
| 54 | 杨利民,周广胜,王国宏,等.人类活动对榆树疏林土壤环境和植物多样性的影响[J].应用生态学报,2003,14(3):321-325. |
| 55 | 左小安,赵学勇,张铜会,等.科尔沁沙地榆树疏林草地物种多样性及乔木种群空间格局[J].干旱区资源与环境,2005,19(4):63-68. |
| 56 | 丁威,王玉冰,向官海,等.小叶锦鸡儿灌丛化对典型草原群落结构与生态系统功能的影响[J].植物生态学报,2020,44(1):33-43. |
| 57 | Brown J H.Two decades of homage to Santa Rosalia:toward a general theory of diversity[J].American Zoologist,1981,21(4):877-888. |
| 58 | Wright D H.Species-energy theory:an extension of species-area theory[J].Oikos,1983,41(3):496-506. |
| 59 | O’Brien E M.Climatic gradients in woody plant species richness:towards an explanation based on an analysis of southern Africa’s woody flora[J].Journal of Biogeography,1993,20(2):181-198. |
| 60 | Hawkins B A,Porter E E,Felizola D F.Productivity and history as predictors of the latitudinal diversity gradient of terrestrial birds[J].Ecology,2003,84(6):1608-1623. |
| 61 | 孙小丽,康萨如拉,张庆,等.荒漠草原物种多样性、生产力与气候因子和土壤养分之间关系的研究[J].草业学报,2015,24(12):10-19. |
| 62 | Bai Y F,Wu J G,Xing Q,et al.Primary production and rain use efficiency across a precipitation gradient on the Mongolia Plateau[J].Ecology,2008,89(8):2140-2153. |
| 63 | Collins S L,Koerner S E,Plaut J A,et al.Stability of tallgrass prairie during a 19-year increase in growing season precipitation[J].Functional Ecology,2012,26(6):1450-1459. |
| 64 | Volder A,Briske D D,Tjoelker M G.Climate warming and precipitation redistribution modify tree grass interactions and tree species establishment in a warm temperate savanna[J].Global Change Biology,2013,19(3):843-857. |
| 65 | Francis A P,Currie D J.A globally consistent richness-climate relationship for angiosperms[J].The American Naturalist,2003,161(4):523-536. |
| 66 | 刘先华,李凌浩,陈佐忠.内蒙古锡林河流域植被多样性特点及其与气候因子的关系[J].植物生态学报,1998,22(5):466-472. |
| 67 | 白永飞,李凌浩,王其兵,等.锡林河流域草原群落植物多样性和初级生产力沿水热梯度变化的样带研究[J].植物生态学报,2000,24(6):667-673. |
| 68 | Zhang Q,Wu J,Buyantuev A,et al.Plant species diversity is correlated with climatic factors differently at the community and the functional group levels:a case study of desert steppe in Inner Mongolia,China[J].Giornale Botanico Italiano,2016,150(1):121-123. |
| 69 | Currie D J.Energy and large-scale patterns of animal and plant-species richness[J].The American Naturalist,1991,137(1):27-49. |
| 70 | 山丹,朱媛君,王百竹,等.呼伦贝尔沙地北部沙带植物群落分布格局与土壤特性的关系[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1) :145-155. |
| 71 | 朱媛君,张璞进,牛明丽,等.毛乌素沙地丘间低地主要植物群落土壤酶活性[J].生态学杂志,2016,35(8):2014-2021. |
| 72 | 杨雪梅,杨太保,刘海猛,等.气候变暖背景下近30a北半球植被变化研究综述[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(2):379-391. |
| 73 | Perroni Y,Montana C,Garcia F.Relationship between soil nutrient availability and plant species richness in a tropical semi-arid environment[J].Journal of Vegetation Science,2006,17(6):719-728. |
| 74 | Cornwell W K,Grubb P J.Regional and local patterns in plant species richness with respect to resource availability[J].Oikos,2003,100(3):417-428. |
| 75 | Zhang J Q,Qi L I,Ren Z W,et al.Effects of nitrogen addition on species richness and relationship between species richness and aboveground productivity of alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology,2010,23(1):33-38. |
| 76 | Bai Y F,Wu J G,Clark C M,et al.Trade offs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning:evidence from Inner Mongolia Grasslands[J].Global Change Biology,2010,16(1):358-372. |
| 77 | Jouany C,Cruz P,Daufresne T,et al.Biological phosphorus cycling in grasslands:interactions with nitrogen[M]//Bunemann E K,Oberson A,Frossard E.Phosphorus in Action:Biological Processes in Soil Phosphorus Cycling.Berlin,Germany:Springer,2011:275-294. |
| 78 | Perroni Y,Garcia-Oliva F,Souza V.Plant species identity and soil P forms in an oligotrophic grassland-desert scrub system[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2014,108(9):29-37. |
| 79 | 王艳芬,陈佐忠,Tieszen LT.人类活动对锡林郭勒地区主要草原土壤有机碳分布的影响[J].植物生态学报,1998,22(6):66-72. |
| 80 | Zuo X A,Zhao X Y,Zhao H L,et al.Changes of species diversity and productivity in relation to soil properties in sandy grassland in Horqin sand land[J].Environmental Science,2007,28(5):945-951. |
| 81 | 沙威,董世魁,刘世梁,等.阿尔金山自然保护区植物群落生物量和物种多样性的空间格局及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志,2016,35(2):330-337. |
| [1] | 马永桃, 任孝宗, 胡慧芳, 刘敏, 孟琪. 基于地理探测器的浑善达克沙地植被变化定量归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 195-204. |
| [2] | 齐丹卉, 杨洪晓, 卢琦, 甘红豪, 褚建民. 浑善达克沙地植物群落主要类型与特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 23-33. |
| [3] | 张亦然, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 王昕. 基于U型神经网络的沙丘-草甸相间地区无人机影像植被覆盖度提取及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 16-24. |
| [4] | 何远政, 黄文达, 赵昕, 吕朋, 王怀海. 气候变化对植物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [5] | 赵媛媛, 武海岩, 丁国栋, 高广磊, 屠文竹. 浑善达克沙地土地沙漠化研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 101-111. |
| [6] | 苏郎嘎, 田桂泉, 红霞. 浑善达克沙地苔藓物种多样性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 51-59. |
| [7] | 山丹, 朱媛君, 王百竹, 刘艳书, 时忠杰, 杨晓晖. 呼伦贝尔沙地北部沙带植物群落分布格局与土壤特性的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 145-155. |
| [8] | 董雪, 辛智鸣, 李永华, 郝玉光, 纪署光, 段瑞兵, 张冉浩, 黄雅茹. 沙冬青(Ammopiptanthus mongolicus)叶性状对环境因子的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 126-134. |
| [9] | 詹瑾, 李玉霖, 韩丹, 杨红玲. 放牧对浑善达克沙地丘间低地植被群落及土壤的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 184-191. |
| [10] | 侍瑞, 苏培玺, 周紫鹃, 丁新景. 高寒植物群落优势种光合日变化及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(4): 46-53. |
| [11] | 曹红芳, 秦伟, 胡永宁, 黄荣凤, 秦艳, 纪磊, 张娜. 榆树年轮记录的浑善达克沙地春季平均最高气温[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(6): 1313-1320. |
| [12] | 汪勇, 闻志彬, 张宏祥, 张明理. 中国假木贼属(Anabasis)的地理分布及潜在分布区预测[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(5): 1033-1040. |
| [13] | 赵鹏, 屈建军, 韩庆杰, 徐先英, 姜生秀, 付贵全. 敦煌绿洲边缘植物群落与土壤养分互馈关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(4): 791-799. |
| [14] | 曹瑞, 刘果厚, 兰庆, 刘冠志, 慕宗杰, 桂荣, 刘利红, 王健. 浑善达克沙地飞播区植被动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 535-544. |
| [15] | 田桂泉, 韩淑美, 苏日古嘎. 大青沟国家自然保护区地面苔藓植物分布格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 545-552. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
