中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 183-193.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00097
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2021-04-21
修回日期:2021-07-29
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-03-30
通讯作者:
赵丽娟
作者简介:赵丽娟(E-mail: zhaolijuan202010@163.com)基金资助:
Xuegang Mao1,2( ), Lijuan Zhao1(
), Lijuan Zhao1( )
)
Received:2021-04-21
Revised:2021-07-29
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-03-30
Contact:
Lijuan Zhao
摘要:
黄土高原黄土来自于其北部或西北部的沙漠和戈壁被广泛认可。本文选取西北地区典型的沙漠、戈壁和黄土表土样品,进行系统的岩石磁学研究。结果显示:沙漠和戈壁磁学特征相似,以磁铁矿占绝对优势,磁颗粒为多畴和假单畴,几乎不含超顺磁颗粒,磁性矿物总体含量高于黄土表土。黄土表土以磁铁矿为主,同时含有磁赤铁矿,磁颗粒以成壤过程中形成的超顺磁和单畴颗粒为主。虽然沙漠和戈壁细粒中亚铁磁性矿物相对比例明显高于粗粒,但粗粒组分含量大,对磁性稀释作用显著,全样总体表现为粗粒磁性特征。影响沙漠、戈壁和黄土磁化率的主导因素不同,沙漠和戈壁为磁性矿物含量主导型,磁性矿物总含量高,黄土表土为磁性矿物粒度主导型,超顺磁对磁化率贡献占主导。合理区分风速论和成土论两种磁化率机制,需准确判断成壤程度和氧化还原状态。因此,不同环境条件下磁化率的环境意义及古气候重建,需首先准确区分影响磁化率的主导因素。
中图分类号:
毛学刚, 赵丽娟. 沙漠、戈壁和黄土表土岩石磁学特征及其对黄土磁化率机制的意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 183-193.
Xuegang Mao, Lijuan Zhao. Rock magnetic properties of deserts, gobi and loess topsoils and their implications in models of magnetic susceptibility[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 183-193.
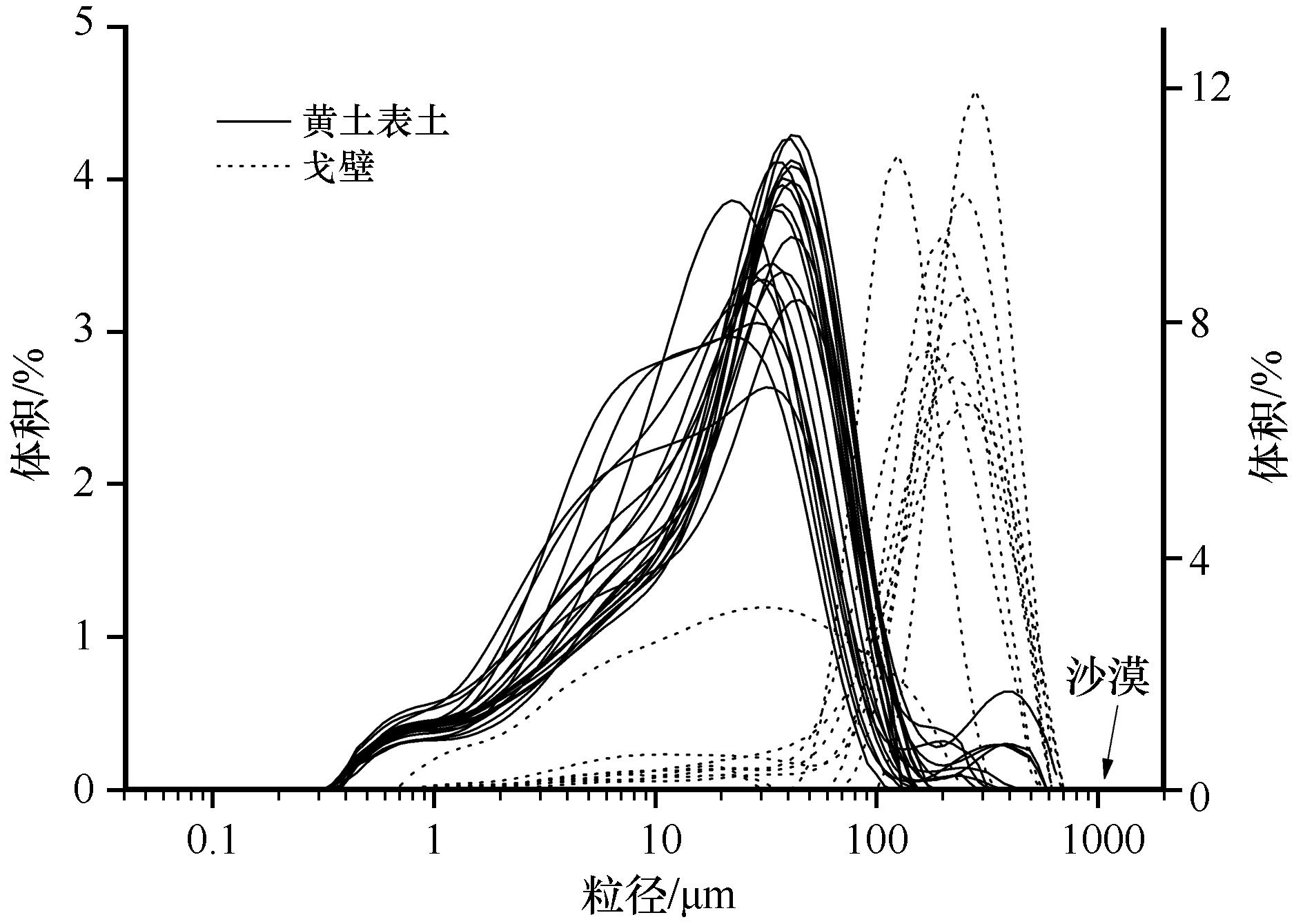
图2 戈壁和黄土表土粒度频率分布(沙漠粒度总体>1 000 μm,没有经过激光粒度仪测量)
Fig.2 The particle size distributions of Gobi and loess topsoil. The particle size of deserts is greater than 1 000 μm, not measured using Masters2000
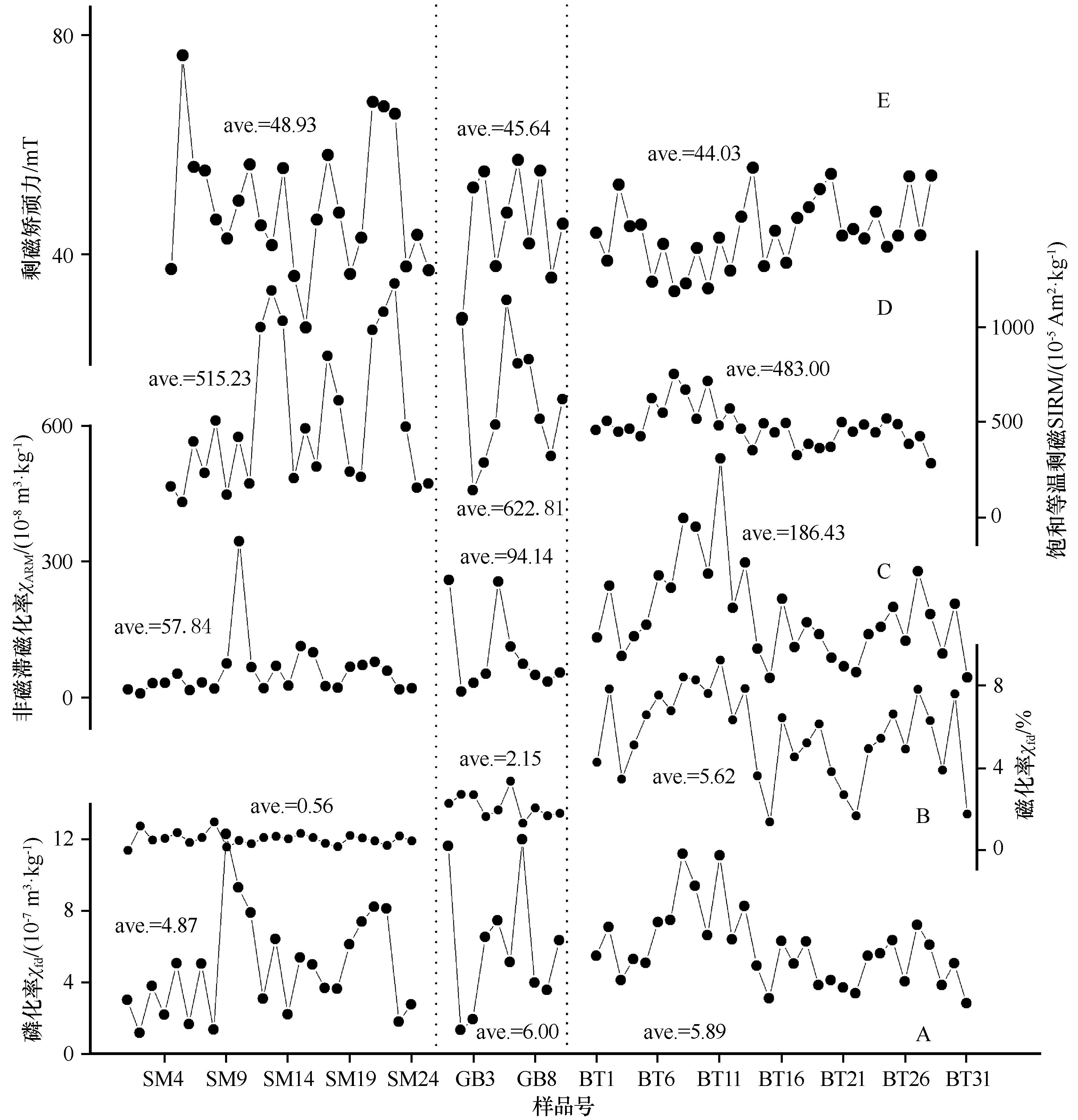
图3 沙漠、戈壁和现代黄土表土常温磁学参数图中两条虚线为三类样品的分界线,沙漠样品为SM1—SM24,戈壁样品为GB1—GB10,黄土表土样品为BT1—BT31,ave.指不同样品磁学参数的平均值
Fig. 3 Room temperature magnetic parameters of deserts, Gobi and loess topsoil. The dashed lines delimit the samples of desert, Gobi and loess. SM1-SM24 are desert samples. GB1-GB10 are Gobi samples. BT1-BT31 are loess samples. Ave. represents mean of magnetic parameters
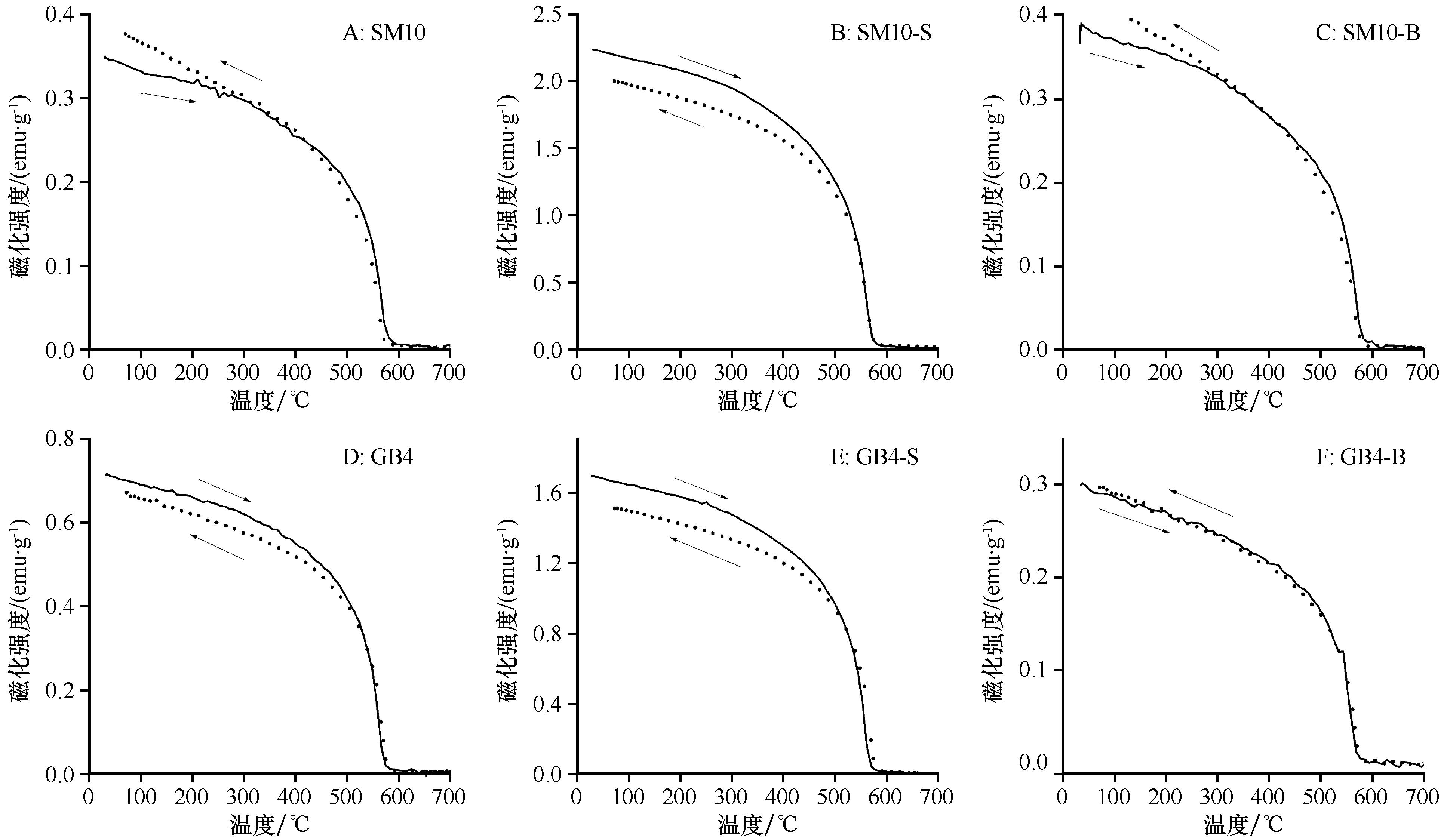
图5 沙漠(SM10)和戈壁(GB4)典型样品磁化强度随温度变化实线为加热曲线,点线为冷却曲线,左侧为全样样品,中间-S为对应样品<100 μm的细粒,右侧-B为对应样品>100 μm的粗粒
Fig.5 Thermomagnetic curves of typical desert sample (SM10) and gobi sample (GB4). The solid line is heating curve and the dashed line is cooling curve. The left panels are for bulk samples, middle panels (<100 μm) for fine subsamples and right panels for coarse (>100 μm) subsamples
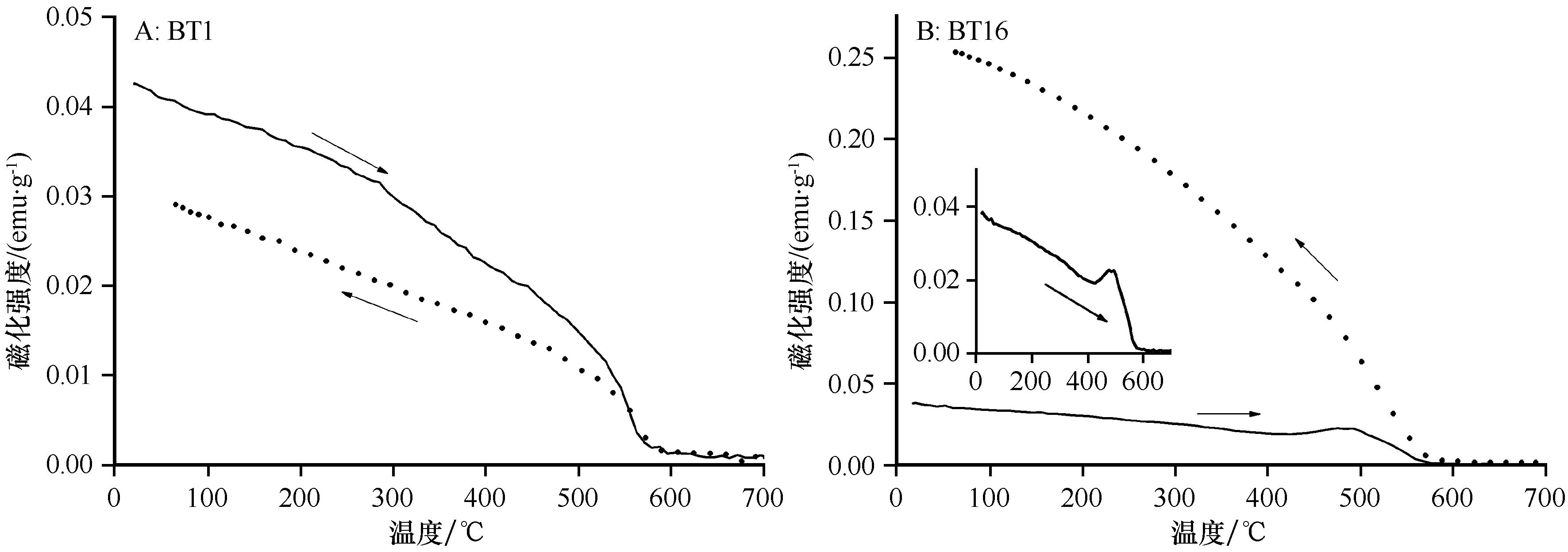
图6 黄土表土典型样品(BT1和BT16)磁化强度随温度变化实线为加热曲线,点线为冷却曲线
Fig.6 Thermomagnetic curves of typical loess topsoil samples (BT1 and BT16). The solid line is heating curve and dashed line is cooling curve
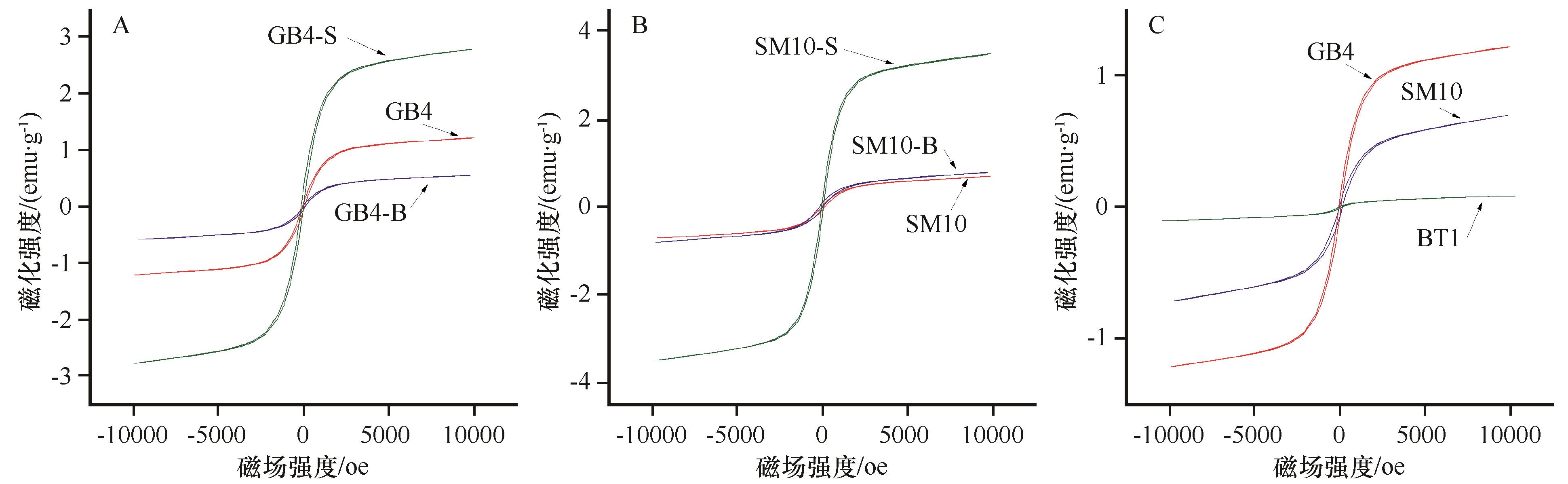
图7 戈壁(GB4)、沙漠(SM10)和黄土表土(BT1)典型样品的磁滞回线-S为对应样品<100 μm的细粒,-B为对应样品>100 μm的粗粒
Fig.7 Hysteresis loops of typical gobi (GB4), desert (SM10) and loess (BT1) samples. The-S represents fine (<100 μm) subsamples and -B represents coarse (>100 μm) subsamples
| 样品 编号 | 磁化强度 Ms /(10-3Am2/kg) | 剩余磁化 强度Mrs /(10-5Am2/kg) | 矫顽力 Bc/mT | 剩余 矫顽力 Bcr/mT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB4 | 1.02 | 6.68 | 6.48 | 37.80 |
| GB4-S | 2.42 | 15.80 | 7.16 | n.a. |
| GB4-B | 0.42 | 3.00 | 5.49 | n.a. |
| SM10 | 0.49 | 4.41 | 8.41 | 49.71 |
| SM10-S | 3.00 | 17.50 | 5.60 | n.a. |
| SM10-B | 0.53 | 6.31 | 10.98 | n.a. |
| BT1 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 8.25 | 43.87 |
表1 戈壁(GB4)、沙漠(SM10)和黄土表土(BT1)的磁滞参数
Table 1 Hysteretic parameters of typical Gobi (GB4), desert (SM10) and loess (BT1) samples. The-S represents fine (<100 μm) subsamples and-B represents coarse (>100 μm) subsamples
| 样品 编号 | 磁化强度 Ms /(10-3Am2/kg) | 剩余磁化 强度Mrs /(10-5Am2/kg) | 矫顽力 Bc/mT | 剩余 矫顽力 Bcr/mT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB4 | 1.02 | 6.68 | 6.48 | 37.80 |
| GB4-S | 2.42 | 15.80 | 7.16 | n.a. |
| GB4-B | 0.42 | 3.00 | 5.49 | n.a. |
| SM10 | 0.49 | 4.41 | 8.41 | 49.71 |
| SM10-S | 3.00 | 17.50 | 5.60 | n.a. |
| SM10-B | 0.53 | 6.31 | 10.98 | n.a. |
| BT1 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 8.25 | 43.87 |
| 1 | 刘东生 等.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社,1985. |
| 2 | Meijer N, Dupont-Nivet G, Licht A,et al.Identifying eolian dust in the geological record[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2020,211:102853. |
| 3 | Li Y, Shi W, Aydin A,et al.Loess genesis and worldwide distribution[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2020,201:102947. |
| 4 | Maher B A.Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,154:23-84. |
| 5 | Song Y, Yang S, Nie J,et al.Quaternary paleoclimate and paleoenvironmental changes in Central Asia[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2021,568:110319. |
| 6 | Sun Y, Yan Y, Nie J,et al.Source-to-sink fluctuations of Asian aeolian deposits since the late Oligocene[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2020,200:102963. |
| 7 | Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z,et al.Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J].Nature,2002,416(6877):159-163. |
| 8 | 杨杰东,李高军,戴澐,等.黄土高原黄土物源区的同位素证据[J].地学前缘,2009,16(6):195-206. |
| 9 | 李高军,车旭东,肖国桥,等.西宁黄土碎屑锆石年龄特征及其对黄土高原黄土物源的指示意义[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):345-350. |
| 10 | Jia J, Wang Y J, Xia D S,et al.Dust sources of Last Glacial Chinese loess based on the iron mineralogy of fractionated source samples[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2019,46(4):2103-2110. |
| 11 | 孙继敏.黄土沉积与地球圈层相互作用[J].第四纪研究,2020,40(1):1-7. |
| 12 | 张小曵.亚洲粉尘的源区分布释放、输送、沉降与黄土堆积[J].第四纪研究,2001,21(1):29-40. |
| 13 | 赵景波.西安刘家坡第1、第5层古土壤研究[J].地理研究,1991,10(4):51-58. |
| 14 | Chlachula J.The Siberian loess record and its significance for reconstruction of Pleistocene climate change in north-central Asia[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2003,22(18/19):1879-1906. |
| 15 | Begét J E, Stone D B, Hawkins D B.Paleoclimate forcing of magnetic susceptibility variations in Alaskan loess during the late Quaternary [J].Geology,1990,18(1):40-43. |
| 16 | 邓成龙,刘青松,潘永信,等.中国黄土环境磁学[J].第四纪研究,2007,27(2):193-209. |
| 17 | Liu Q, Deng C, Torrent J,et al.Review of recent developments in mineral magnetism of the Chinese loess[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2007,26(3/4):368-385. |
| 18 | Long X, Ji J, Barrón V,et al.Climatic thresholds for pedogenic iron oxides under aerobic conditions:processes and their significance in paleoclimate reconstruction[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,150:264-277. |
| 19 | 刘青松,邓成龙.磁化率及其环境意义[J].地球物理学报,2009,52(4):1041-1048. |
| 20 | Hu P, Liu Q, Torrent J,et al.Characterizing and quantifying iron oxides in Chinese loess / paleosols:implications for pedogenesis[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2013,369/370:271-283. |
| 21 | Long X, Ji J, Barrón V,et al.Climatic thresholds for pedogenic iron oxides under aerobic conditions:processes and their significance in paleoclimate reconstruction[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,150:264-277. |
| 22 | Balsam W L, Ellwood B B, Ji J,et al.Magnetic susceptibility as a proxy for rainfall:worldwide data from tropical and temperate climate[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2011,30(19/20):2732-2744. |
| 23 | Orgeira M J, Egli R, Compagnucci R H.A quantitative model of magnetic enhancement in loessic soils[M]//E.Petrovský E,Ivers D,Harinarayana E,et al.The Earth’s Magnetic Interior.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,2011:361-397. |
| 24 | Maher B A, Thompson R.Paleorainfall reconstructions from pedogenic magnetic susceptibility variations in the Chinese Loess and Paleosols[J].Quaternay Research,1995,44:383-391. |
| 25 | Zhou L P, Oldfield F, Wintle A G,et al.Partly pedogenic origin of magnetic variations in Chinese loess[J].Nature,1990,346(6286):737-739. |
| 26 | Heller F, Liu T.Magnetostratigraphical dating of loess deposits in China[J].Nature,1982,300(5891):431-433. |
| 27 | Begét J E, Hawkins D B.Influence of orbital parameters on Pleistocene loess deposition in central Alaska[J].Nature,1989,337(6203):151-153. |
| 28 | Chlachula J, Rutter N W, Evans M E.A late Quaternary loess-palaeosol record at Kurtak,southern Siberia[J].Canadian Journal of Earth Science,1997,34:679-686. |
| 29 | 刘秀铭,夏敦胜,刘东生,等.中国黄土和阿拉斯加黄土磁化率气候记录的两种模式探讨[J].第四纪研究,2007,27(2):210-220. |
| 30 | 刘秀铭,刘东生,夏敦胜,等.中国与西伯利亚黄土磁化率古气候记录:氧化和还原条件下的两种成土模式分析[J].中国科学(D辑),2007,37(10):1382-1391. |
| 31 | Seto Y, Stevens T.Magnetic susceptibility in the European Loess Belt:new and existing models of magnetic enhancement in loess[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2021,569:110329. |
| 32 | Bidegain J C, Evans M E, van Velzen A J.A magnetoclimatological investigation of Pampean loess,Argentina[J].Geophysical Journal International,2005,160(1):55-62. |
| 33 | Bidegain J C, van Velzen A J, Rico Y.The Brunhes/Matuyama boundary and magnetic parameters related to climatic changes in Quaternary sediments of Argentina[J].Journal of South American Earth Sciences,2007,23(1):17-29. |
| 34 | Kemp R A, Toms P S, King M,et al.The pedosedimentary evolution and chronology of Tortugas,a Late Quaternary type-site of the northern Pampa,Argentina[J].Quaternary International,2004,114(1):101-112. |
| 35 | 李平原,刘秀铭,郭雪莲,等.西北戈壁沙漠-黄土高原区表土磁化率特征及其意义[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):360-367. |
| 36 | 王涛,刘秀铭,吕镔,等.新疆尼勒克黄土岩石磁学特征及变化机制研究[J].第四纪研究,2014,34(3):491-503. |
| 37 | Sun D, Bloemendal J, Rea D,et al.Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments,and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J].Sedimentary Geology,2002,152(3/4):263-277. |
| 38 | Liu Q, Roberts A P, Larrasoaña J C,et al.Environmental magnetism:principles and applications[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2012,50(4):197-215. |
| 39 | Dunlop D J, Özdemir Ö.Rock Magnetism:Fundamentals and Frontiers[M].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University,1997. |
| 40 | Fine P, Singer M J, Verosub K L,et al.New evidence for the origin of ferrimagnetic minerals in loess from China[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,1993,57(6):1537-1542. |
| 41 | 段宗奇,高星,刘青松.非磁滞剩磁(ARM)及其在地学中的应用[J].地球物理学报,2012,27(5):1929-1938. |
| 42 | Dearing J A, Bird P M, Dann R J L,et al.Secondary ferrimagnetic minerals in Welsh soils:a comparison of mineral magnetic detection methods and implications for mineral formation[J].Geophysical Journal International,1997,130(3):727-736. |
| 43 | 刘秀铭, Shaw J,蒋建中,等.磁赤铁矿的几种类型与特点分析[J].中国科学(D辑),2010,40(5):592-602. |
| 44 | Deng C, Zhu R, Jackson M J,et al.Variability of the temperature-dependent susceptibility of the holocene eolian deposits in the Chinese loess plateau:a pedogenesis indicator[J].Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy,2001,26(11/12): 873-878. |
| 45 | Liu Q, Deng C, Yu Y,et al.Temperature dependence of magnetic susceptibility in an argon environment: implications for pedogenesis of Chinese loess/palaeosols[J].Geophysical Journal International,2005,161:102-112. |
| 46 | Fukuma K, Torii M.Variable shape of magnetic hysteresis loops in the Chinese loess-paleosol sequence[J].Earth,Planets and Space,1998,50(1):9-14. |
| 47 | 孙继敏,许立亮.8 Ma以来黄土高原风尘堆积的物源变化与上地壳演化的关系[J].第四纪研究,2007,27(2):187-192. |
| 48 | 陈渠,刘秀铭, Heller F,等.伊犁黄土磁化率的增减及其成因[J].科学通报,2012,57(24):2310-2321. |
| 49 | 吕镔,刘秀铭,赵国永,等.新疆博乐黄土岩石磁学特征及环境意义[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(5):1-8. |
| 50 | 宋友桂,史正涛,方小敏,等.伊犁黄土的磁学性质及其与黄土高原对比[J].中国科学(D辑),2010,40(1):61-72. |
| 51 | 贾佳,刘现彬,夏敦胜,等.坎苏剖面记录的西天山地区黄土磁学性质及其控制因素初探[J].干旱区地理,2011,34(1):124-132. |
| 52 | 叶玮.新疆伊犁地区自然环境特点与黄土形成条件[J].干旱区地理,1999,22(3):9-15. |
| 53 | 王勇,潘保田,管清玉,等.西北干旱区黄土-古土壤磁化率变化特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2008,28(1):111-114. |
| 54 | 刘秀铭,毛学刚,丁仲礼,等.黄土古气候变化趋势与青藏高原隆升关系初探[J].第四纪研究,2009,29(5):988-999. |
| 55 | 李平原,刘秀铭,刘植,等.腾格里沙漠边缘表土磁学性质及其意义[J].第四纪研究,2012,32(4):771-776. |
| 56 | Maher B A, Taylor R M.Formation of ultrafine-grained magnetite in soils[J].Nature,1988,336:368-370. |
| 57 | 刘秀铭,刘植,吕镔,等.塞尔维亚黄土的磁学性质及其环境意义[J].科学通报,2012,57(33):3173-3184. |
| 58 | Maher B A.Magnetic properties of modern soils and quaternary loessic paleosols:paleoclimatic implications[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,1998,137(1/2):25-54. |
| 59 | Jia J, Xia D, Wang B,et al.The investigation of magnetic susceptibility variation mechanism of Tien Mountains modern loess:Pedogenic or wind intensity model?[J].Quaternary International,2013,296:141-148. |
| 60 | Iriondo M H, Kröhling D M.Non-classical types of loess[J].Sedimentary Geology,2007,202(3):352-368. |
| 61 | 叶玮.新疆西风区黄土与古土壤磁化率变化特点[J].中国沙漠,2001,21(4):380-386. |
| [1] | 牛震敏, 王乃昂, 温鹏辉, 苏贤保, 于昕冉, 张文佳. 巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊对浅层沙含水量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 142-152. |
| [2] | 王涛. 中国防沙治沙实践与沙漠科学发展的70年——Ⅰ.初创篇[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 1-4. |
| [3] | 孙迎涛, 岳艳鹏, 成龙, 庞营军, 赵河聚, 费兵强, 修晓敏, 吴波, 赵雨兴, 石麟, 何金军, 贾晓红. 毛乌素沙地油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)生长及生物量分配对沙漠化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 123-133. |
| [4] | 贾晓鹏, 马启民, 龙银平, 王海兵. 以中型蒸渗仪监测的库布齐沙漠人工林土壤蒸发量[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 211-222. |
| [5] | 李志忠, 靳建辉, 刘瑞, 解锡豪, 邹晓君, 马运强, 谭典佳. 古尔班通古特沙漠风沙地貌研究进展评述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 41-47. |
| [6] | 赵文智, 白雪莲, 刘婵. 巴丹吉林沙漠南缘的植物固沙问题[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 5-11. |
| [7] | 赵晖, 杨宏宇, 王兴繁, 汪克奇. 巴丹吉林沙漠典型沉积物年代学研究评述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 57-65. |
| [8] | 曾方明, 薛红盼. 青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤元素组成数据集[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 262-264. |
| [9] | 王大刚, 于洋, 孙凌霄, 何婧, Ireneusz Malik, Malgorzata Wistuba, 姜逢清, 于瑞德. 塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘典型绿洲ET0模型适用性评价及修正[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 41-53. |
| [10] | 张小梅, 靳鹤龄, 刘冰. 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 81-93. |
| [11] | 肖建华, 司建华, 刘淳, 李学军, 席海洋, 鱼腾飞, 张成琦, 赵春彦, 朱猛, 贾冰. 沙漠能源生态圈概念、内涵及发展模式[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 11-20. |
| [12] | 乔荣荣, 韩艳, 季树新, 董春媛, 王傲洁, 常学礼. 基于地形指数的砒砂岩黄土区土壤侵蚀分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 175-182. |
| [13] | 马启民, 王海兵, 贾晓鹏. 库布齐沙漠人工柠条(Caragana korshinskii)林地表辐射特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 43-50. |
| [14] | 刘凯露, 吴新萍, 刘永强, 买买提艾力·买买提依明null, 杨帆, 何清. 基于多源遥感与再分析数据估算塔克拉玛干沙漠地表净辐射日变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 51-61. |
| [15] | 胡光印, 董治宝, 逯军峰, 杨林海, 南维鸽, 肖锋军. 黄河流域沙漠化空间格局与成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 213-224. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
