中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 223-235.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00043
张悦仪1( ), 迟云平1,2(
), 迟云平1,2( ), 谢远云1,2, 康春国3, 刘若男1, 孙磊1, 吴鹏1, 魏振宇1
), 谢远云1,2, 康春国3, 刘若男1, 孙磊1, 吴鹏1, 魏振宇1
收稿日期:2024-02-07
修回日期:2024-04-15
出版日期:2024-07-20
发布日期:2024-08-29
通讯作者:
迟云平
作者简介:迟云平(E-mail: 1982cyp@163.com)基金资助:
Yueyi Zhang1( ), Yunping Chi1,2(
), Yunping Chi1,2( ), Yuanyun Xie1,2, Chunguo Kang3, Ruonan Liu1, Lei Sun1, Peng Wu1, Zhenyu Wei1
), Yuanyun Xie1,2, Chunguo Kang3, Ruonan Liu1, Lei Sun1, Peng Wu1, Zhenyu Wei1
Received:2024-02-07
Revised:2024-04-15
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-08-29
Contact:
Yunping Chi
摘要:
沙漠作为干旱气候的产物,记录着气候与环境变迁的丰富信息,在不同区域条件下沙漠风成沉积物特征指示的气候环境存在差异。本研究在科尔沁沙地自东向西共选取25个样点,进行色度、漫反射光谱和磁化率分析,探讨沙地地表风成沉积物的空间变化特征,并结合区域的现代气候因子探讨各代用指标的气候意义。结果表明:科尔沁沙地地表风成沉积物的色度特征与区域降水关系密切,亮度(L*)、红度(a*)与黄度红度比(b*/a*)能够作为指示区域气候的代用指标;地表沉积物中针铁矿(Gt)和赤铁矿(Hm)的相对含量均处于较低水平,Gt/Hm的变化能够指示气候干湿条件的总体趋向;地表风成沉积物的χfd%值能够作为区域降水情况的代用指标,沉积物的磁性增强主要源于降水强度增加导致的风化成壤作用加强,进而产生大量细颗粒亚铁磁性矿物。总体而言,科尔沁沙地地表风成沉积物色度、磁化率和Gt/Hm能够有效指示区域气候环境。
中图分类号:
张悦仪, 迟云平, 谢远云, 康春国, 刘若男, 孙磊, 吴鹏, 魏振宇. 科尔沁沙地地表沉积物特征及其气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 223-235.
Yueyi Zhang, Yunping Chi, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Ruonan Liu, Lei Sun, Peng Wu, Zhenyu Wei. Characteristics and climate significance of surface sediments in the Horqin Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 223-235.
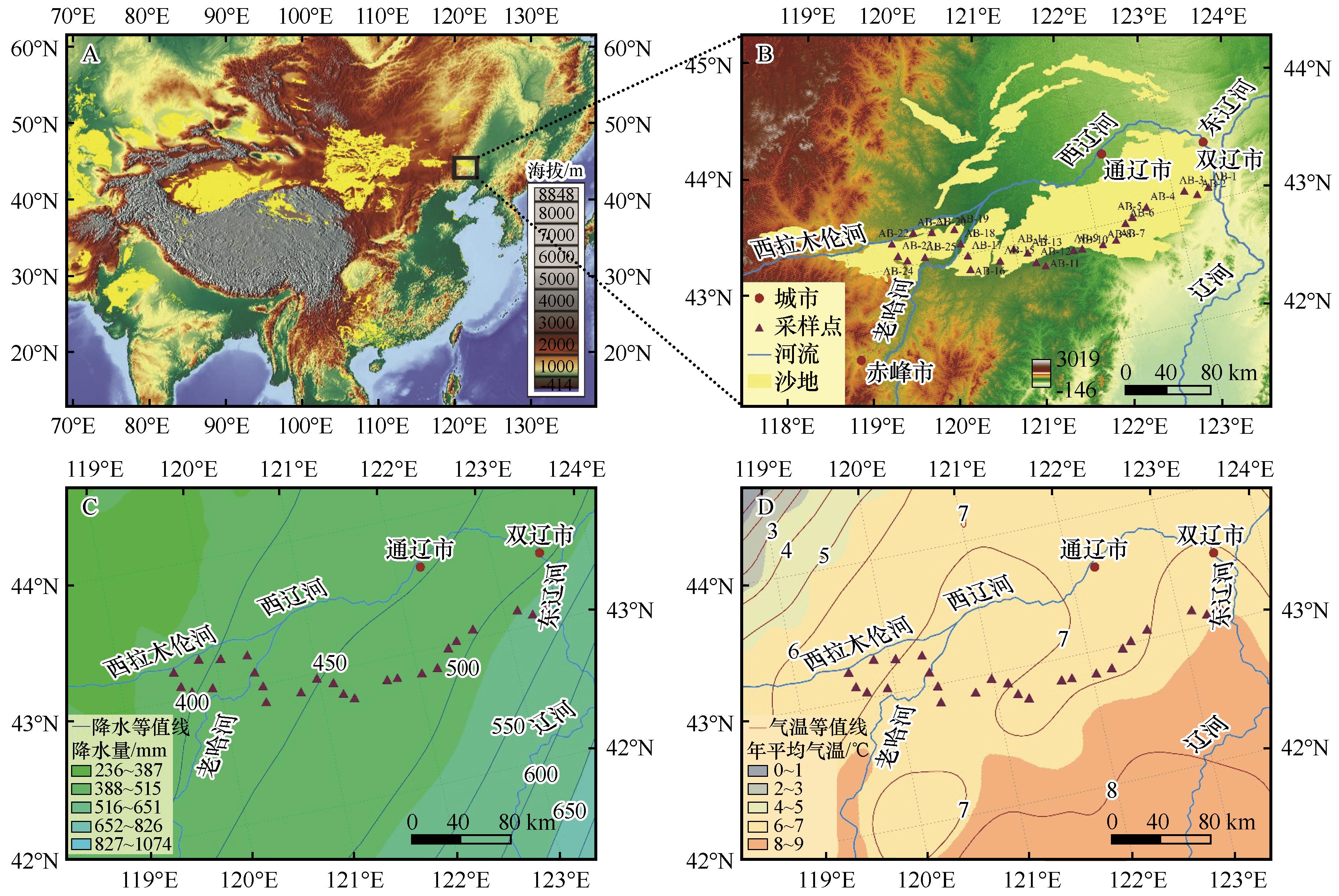
图1 (A)东亚地区DEM图;(B)科尔沁沙地DEM图;(C)年降水量;(D)年平均气温
Fig.1 (A) DEM map of East Asia; (B) Horqin Sandy Land DEM map; (C) Annual precipitation; (D) Annual mean temperature
| 样品 | 亮度L* | 红度a* | 黄度b* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | |
| 全样 | 74.01 | 80.37 | 55.19 | 3.18 | 5.30 | 1.93 | 11.02 | 13.00 | 8.36 |
| <63 μm | 56.91 | 63.30 | 52.58 | 5.04 | 6.19 | 3.65 | 13.81 | 16.22 | 10.29 |
| 42°—43°N | 73.91 | 79.38 | 55.20 | 3.24 | 5.30 | 3.24 | 11.20 | 12.44 | 11.20 |
| 43°—44°N | 74.10 | 80.37 | 56.10 | 3.12 | 4.02 | 3.12 | 10.85 | 13.00 | 10.85 |
| 119°—121°E | 76.62 | 80.37 | 72.24 | 2.96 | 3.26 | 2.96 | 10.84 | 11.81 | 10.84 |
| 121°—124°E | 71.60 | 79.38 | 55.20 | 3.38 | 5.30 | 3.38 | 11.19 | 13.00 | 11.19 |
表1 科尔沁沙地风成沉积物颜色参数
Table 1 The color parameters of wind-sand sediments in Horqin Sandy Land
| 样品 | 亮度L* | 红度a* | 黄度b* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | |
| 全样 | 74.01 | 80.37 | 55.19 | 3.18 | 5.30 | 1.93 | 11.02 | 13.00 | 8.36 |
| <63 μm | 56.91 | 63.30 | 52.58 | 5.04 | 6.19 | 3.65 | 13.81 | 16.22 | 10.29 |
| 42°—43°N | 73.91 | 79.38 | 55.20 | 3.24 | 5.30 | 3.24 | 11.20 | 12.44 | 11.20 |
| 43°—44°N | 74.10 | 80.37 | 56.10 | 3.12 | 4.02 | 3.12 | 10.85 | 13.00 | 10.85 |
| 119°—121°E | 76.62 | 80.37 | 72.24 | 2.96 | 3.26 | 2.96 | 10.84 | 11.81 | 10.84 |
| 121°—124°E | 71.60 | 79.38 | 55.20 | 3.38 | 5.30 | 3.38 | 11.19 | 13.00 | 11.19 |
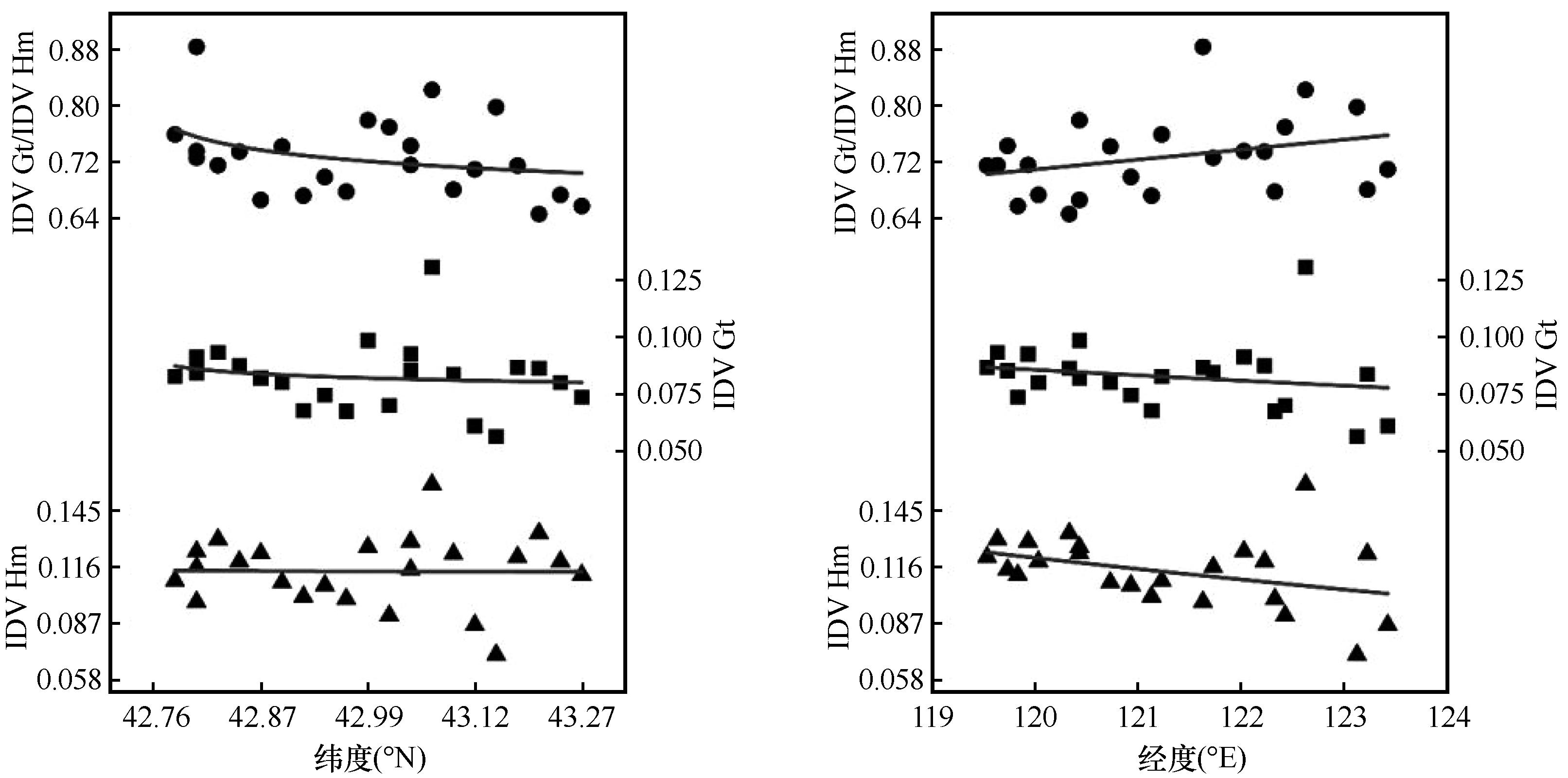
图4 科尔沁沙地风成砂样品针铁矿(Gt)和赤铁矿(Hm)一阶导数(IDV)特征峰分布曲线
Fig.4 Characteristic peak distribution curve of first derivative of goethite and hematite in eolian sand samples from Horqin Sandy Land
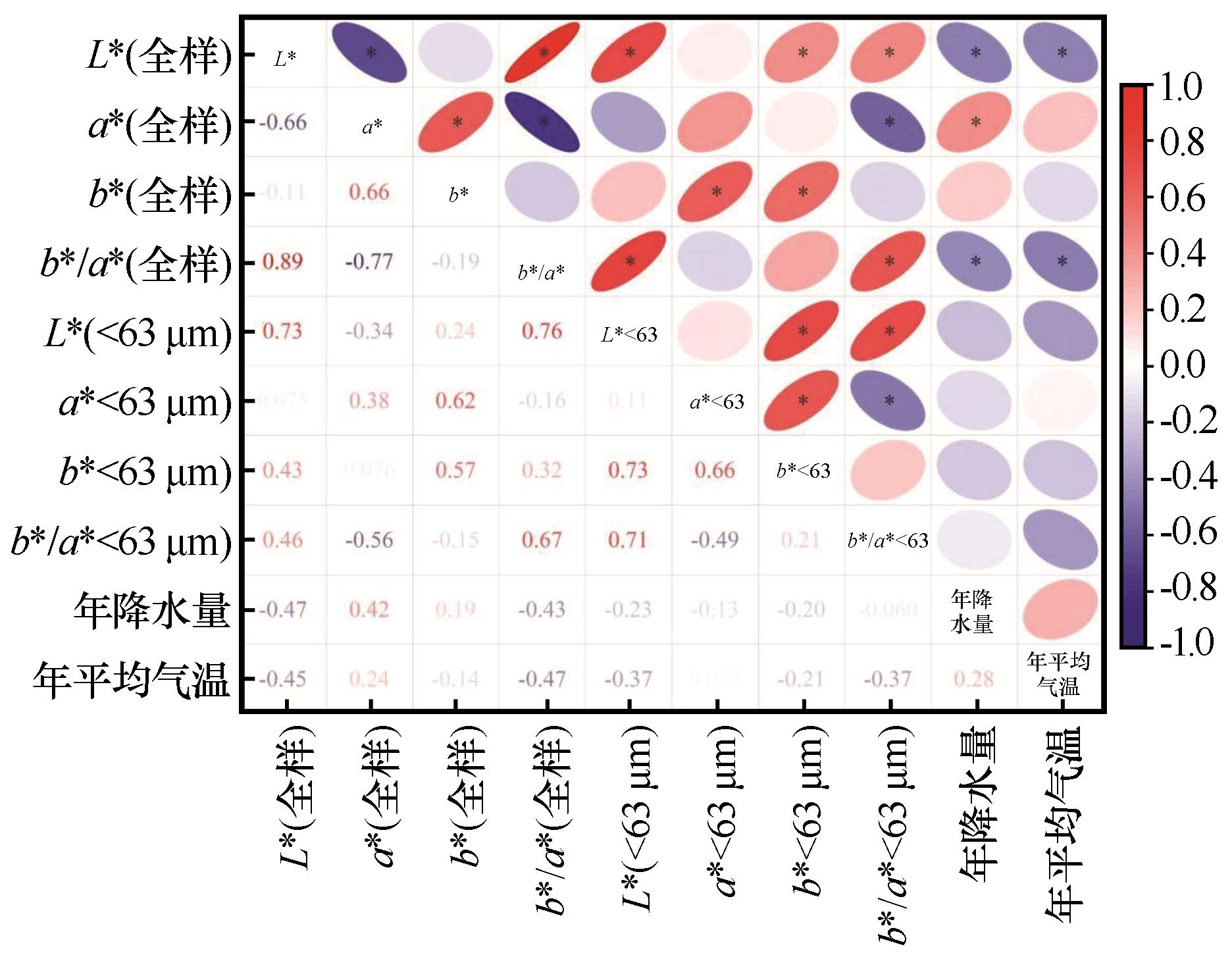
图6 科尔沁沙地风成砂色度参数与气候因子相关系数注:*,P≤0.05
Fig.6 Indicative diagram of correlation coefficients between chromaticity parameters and climate factors of aeolian sand in Horqin Sandy Land [*P≤0.05]
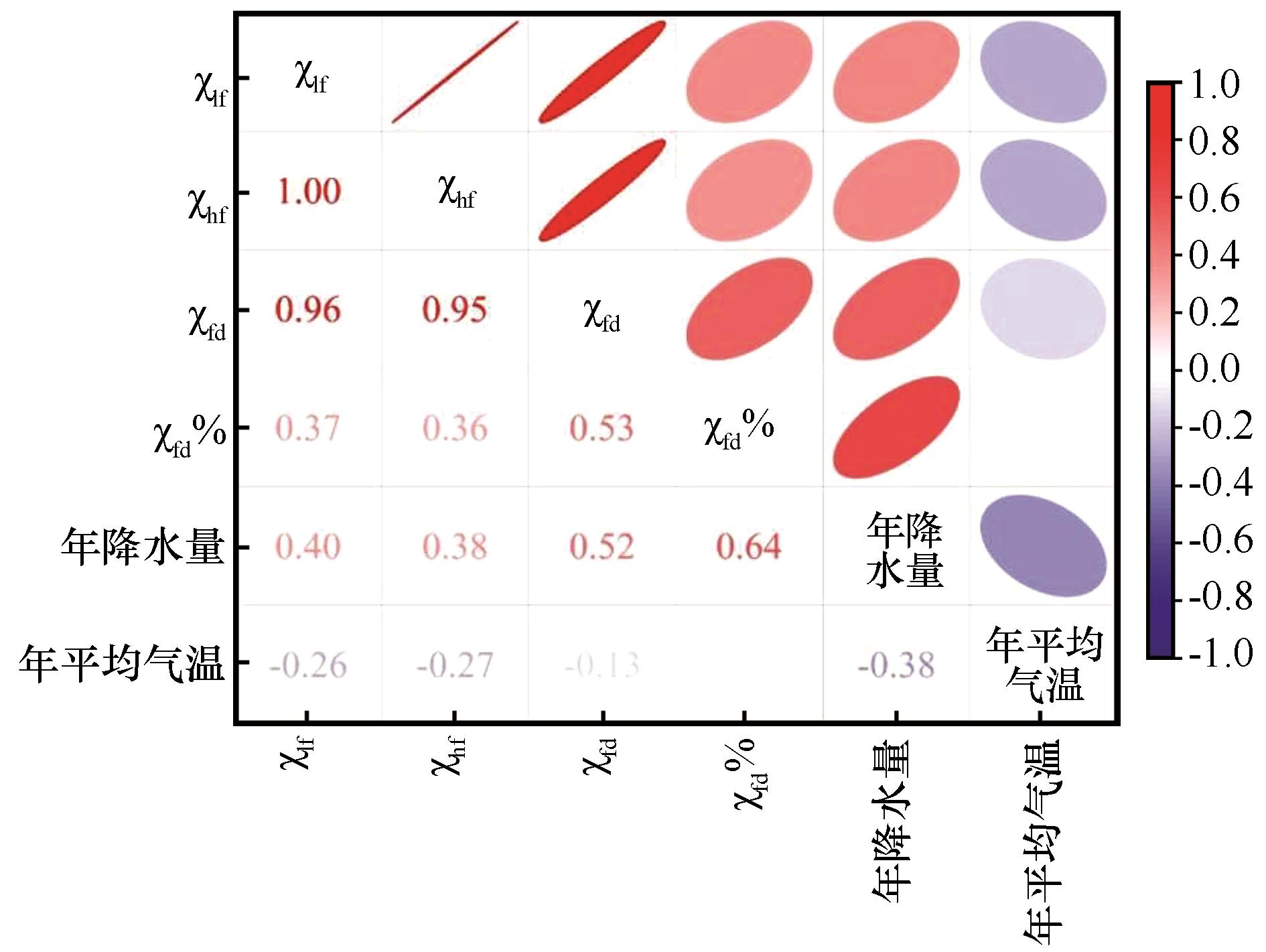
图9 科尔沁沙地风成砂磁化率参数与气候因子相关系数指示图
Fig.9 Correlation coefficient diagram between magnetic susceptibility parameters and climatic factors of aeolian sand in Horqin Sandy Land
| 1 | 鹿化煜,李郎平,弋双文,等.中国北方沙漠-黄土体系的沉积和侵蚀过程与未来趋向探析[J].地学前缘,2010,17(5):336-344. |
| 2 | 鹿化煜,周亚利, Mason J,等.中国北方晚第四纪气候变化的沙漠与黄土记录:以光释光年代为基础的直接对比[J].第四纪研究,2006,26(6):888-894. |
| 3 | 杨利荣,岳乐平.光释光测年揭示的科尔沁沙地末次晚冰期-全新世沙漠空间格局变化[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):260-268. |
| 4 | 王涛.我国沙漠化研究的若干问题:2.沙漠化的研究内容[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(5):1-6. |
| 5 | 花婷,王训明,次珍,等.中国干旱、半干旱区近千年来沙漠化对气候变化的响应[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(3):618-624. |
| 6 | 董治宝.中国风沙物理研究五十年(Ⅰ)[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(3):293-305. |
| 7 | Lancaster N, Yang X, Thomas D.Spatial and temporal complexity in Quaternary desert datasets:implications for interpreting past dryland dynamics and understanding potential future changes[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2013,78:301-302. |
| 8 | 钱广强,董治宝,罗万银,等.巴丹吉林沙漠地表沉积物粒度特征及区域差异[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(6):1357-1364. |
| 9 | Liu D, Sun J.Expansion and contraction of Chinese deserts during the Quaternary[J].Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences,2002,45(1):91-101. |
| 10 | Wei G, Zhang C, Li Q,et al.Characterization of geochemical elements in surface sediments from Chinese deserts[J].Catena,2023,220:106637. |
| 11 | 吴艳宏,李世杰.湖泊沉积物色度在短尺度古气候研究中的应用[J].地球科学进展,2004(5):789-792. |
| 12 | 杨胜利,方小敏,李吉均,等.表土颜色和气候定性至半定量关系研究[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2001():175-181. |
| 13 | 李星耀,李志文,朱志军,等.南昌市厚田剖面末次冰期沉积的色度特征及其古环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2023,43(1):170-179. |
| 14 | Liang X, Wang X, Zhai X,et al.Color changes in yardang strata sediment in the Dunhuang Yardang National Geopark,Northwest China:controlling factors and significance for sedimentary environments[J].Frontiers in Earth Science,2023,10:1107213. |
| 15 | Blundell A, Dearing J A, Boyle J F,et al.Controlling factors for the spatial variability of soil magnetic susceptibility across England and Wales[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2009,95(3/4):158-188. |
| 16 | Blundell A, Hannam J A, Dearing J A,et al.Detecting atmospheric pollution in surface soils using magnetic measurements:a reappraisal using an England and Wales database[J].Environmental Pollution,2009,157(10):2878-2890. |
| 17 | Jia J, Xia D, Wang B,et al.The investigation of magnetic susceptibility variation mechanism of Tien Mountains modern loess:Pedogenic or wind intensity model?[J].Quaternary International,2013,296:141-148. |
| 18 | Zan J, Fang X, Yan M,et al.Magnetic variations in surface soils in the NE Tibetan Plateau indicating the climatic boundary between the Westerly and East Asian summer monsoon regimes in NW China[J].Global and Planetary Change,2015,130:1-6. |
| 19 | Zan J, Fang X, Kang J,et al.Spatial and altitudinal variations in the magnetic properties of eolian deposits in the northern Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent regions:implications for delineating the climatic boundary[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2020,208:103271. |
| 20 | Deaton B C, Balsam W L.Visible spectroscopy:a rapid method for determining hematite and goethite concentration in geological materials[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1991,61(4):628-632. |
| 21 | Scheinost A C, Chavernas A, Barrón V,et al.Use and limitations of second-derivative diffuse reflectance spectroscopy in the visible to near-infrared range to identify and quantify Fe oxide minerals in soils[J].Clays and Clay Minerals,1998,46:528-536. |
| 22 | Cornell R M, Schwertmann U.The Iron Oxides:Structure,Properties,Reactions,Occurrences,and Uses[M].Weinheim,Germany:Wiley-vch,2003. |
| 23 | 季峻峰,陈骏, Balsam W,等.黄土剖面中赤铁矿和针铁矿的定量分析与气候干湿变化研究[J].第四纪研究,2007,27(2):221-229. |
| 24 | Jiang Z, Liu Q, Roberts A P,et al.The magnetic and color reflectance properties of hematite:from Earth to Mars[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2022,60(1):e2020RG000698. |
| 25 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980:46-55. |
| 26 | 李晓岚,张宏升.内蒙古科尔沁沙地临界起沙阈值的范围确定[J].气象学报,2016,74(1):76-88. |
| 27 | 弋双文,鹿化煜,曾琳,等.末次盛冰期以来科尔沁沙地古气候变化及其边界重建[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):206-217. |
| 28 | Balsam W, Ji J, Renock D,et al.Determining hematite content from NUV/Vis/NIR spectra:limits of detection[J].American Mineralogist,2014,99(11/12):2280-2291. |
| 29 | Yang S, Fang X, Li J,et al.Transformation functions of soil color and climate[J].Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences,2001,44:218-226. |
| 30 | 李越,宋友桂,王千锁.新疆昭苏黄土剖面色度变化特征及古气候意义[J].地球环境学报,2014,5(2):67-75. |
| 31 | 刘荔昀,鲁瑞洁,刘小槺.风成沉积物色度记录的毛乌素沙漠全新世以来气候变化[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):83-89. |
| 32 | Hu X, Du Y, Guan C,et al.Color variations of the Quaternary Red Clay in southern China and its paleoclimatic implications[J].Sedimentary Geology,2014,303:15-25. |
| 33 | Ding Z, Lu R, Wang L,et al.Early-Mid Holocene climatic changes inferred from colors of eolian deposits in the Mu Us Desert[J].Geoderma,2021,401:115172. |
| 34 | Tang J, Lü B, Liu X,et al.Chromaticity characteristics of soil profiles in the coastal areas of Fujian and Guangdong,southern China and their climatic significance[J].Quaternary International,2023,649:38-45. |
| 35 | 苗运法,杨胜利,卓世新,等.我国西北干旱区现代地表沉积物颜色指标与降水关系[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(4):77-85. |
| 36 | 宋瑞卿,朱芸,吕镔,等.青藏高原表土的色度特征及其环境意义[J].亚热带资源与环境学报,2016,11(1):14-20. |
| 37 | 严永耀,安聪荣,苗运法,等.新疆青海地区现代地表沉积物颜色指标与气候参数关系[J].干旱区地理,2017,40(2):355-364. |
| 38 | Nagao S, Nakashima S.The factors controlling vertical color variations of North Atlantic Madeira Abyssal Plain sediments[J].Marine Geology,1992,109(1/2):83-94. |
| 39 | Liu H, Youbin S, Zhisheng A.Changing color of Chinese loess:controlling factors and paleocliamtic significances[J].Geochimica,2010,39(5):447-455. |
| 40 | 高铭君,李育,张占森,等.祁连山周边内流区湖泊沉积物与人类活动研究[J].地理学报,2023,78(5):1192-1212. |
| 41 | 杜兰,李志文,杜丁丁,等.烟台芝罘黄土剖面末次间冰期沉积物色度特征及其古环境意义[J].热带地理,2021,41(2):423-430. |
| 42 | 石培宏,杨太保,田庆春,等.靖远黄土-古土壤色度变化特征分析及古气候意义[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(2):15-23. |
| 43 | 胡梦珺,吉天琪,郑登友,等.9.4 ka 以来青藏高原东北部风成沉积物色度参数变化特征及其环境演变[J].现代地质,2022,36(2):439. |
| 44 | Schwertmann U.The effect of pedogenic environments on iron oxide minerals[J].Advances in Soil Science,1985,1:171-200. |
| 45 | Wondafrash T T, Sancho M I, Miguel G V,et al.Relationship between soil color and temperature in the surface horizon of Mediterranean soils:a laboratory study[J].Soil Science,2005,170(7):495-503. |
| 46 | 姬红利,周文君,张一平,等.云南土壤色度与海拔及气候的关系研究[J].云南大学学报(自然科学版),2013,35():352-358. |
| 47 | 王海燕,庞奖励,黄春长,等.郧西县庹家湾黄土剖面色度参数特征及其古气候重建[J].水土保持学报,2017,31(2):151-156. |
| 48 | 杨丹,庞奖励,周亚利,等.汉中盆地军王村黄土-古土壤剖面的色度特征及机理[J].中山大学学报:自然科学版,2018,57(1):93-101. |
| 49 | 郑兴芬,吕镔,陈梓炫,等.不同空间范围土壤色度的纬向变化特征及其气候意义[J].土壤学报,2020,57(5):1186-1196. |
| 50 | 陈梓炫,吕镔,郑兴芬,等.基于漫反射光谱和色度的土壤中赤铁矿和针铁矿半定量探讨[J].土壤,2020,52(5):1083-1091. |
| 51 | 孙磊,谢远云,康春国,等.呼伦贝尔沙地重矿物,Sr-Nd 同位素组成及其对亚洲风尘系统的指示[J].中国地质,2021,48(6):1965-1974. |
| 52 | 彭淑贞,郭正堂.西峰晚第三纪红土记录的亮度学特征[J].第四纪研究,2003,23(1):110. |
| 53 | Zhang Y G, Ji J, Balsam W L,et al.High resolution hematite and goethite records from ODP 1143,South China Sea:co-evolution of monsoonal precipitation and El Niño over the past 600,000 years[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2007,264(1/2):136-150. |
| 54 | Jiang Z, Liu Q, Colombo C,et al.Quantification of Al-goethite from diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and magnetic methods[J].Geophysical Journal International,2014,196(1):131-144. |
| 55 | 姜兆霞,刘青松.赤铁矿的定量化及其气候意义[J].第四纪研究,2016,36(3):676-689. |
| 56 | 程婷.中国东部嵊山岛黄土赤铁矿、针铁矿含量与东亚季风演化[D].上海:华东师范大学,2021. |
| 57 | 李香钰,方小敏,杨一博,等.3 Ma 以来黄土高原朝那黄土-红粘土序列赤铁矿记录及其古气候意义[J].第四纪研究,2012,32(4):700-708. |
| 58 | 杨云淇,殷科,王朝文,等.漫反射光谱赤铁矿和针铁矿定量研究进展[J].矿物学报,2020,40(1):92-100. |
| 59 | Torrent J, Barrón V.The visible diffuse reflectance spectrum in relation to the color and crystal properties of hematite[J].Clays and Clay Minerals,2003,51(3):309-317. |
| 60 | Barron V, Torrent J.Influence of aluminum substitution on the color of synthetic hematites[J].Clays and Clay Minerals,1984,32:157-158. |
| 61 | Schwertmann U, Friedl J, Stanjek H,et al.The effect of Al on Fe oxides.XIX.Formation of Al-substituted hematite from ferrihydrite at 25 C and pH 4 to 7[J].Clays and Clay Minerals,2000,48:159-172. |
| 62 | 朱梦园,吕镔,郭滢.不同气候带风成沉积中赤铁矿和针铁矿含量对比:基于漫反射光谱和色度方法[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2022,42(6):1684-1690. |
| 63 | Jordanova D, Jordanova N.Updating the significance and paleoclimate implications of magnetic susceptibility of Holocene loessic soils[J].Geoderma,2021,391:114982. |
| 64 | 武力,李隆威,王汝建,等.晚第四纪东南极普里兹湾外沉积物磁化率特征及其古环境意义[J].广东海洋大学学报,2023,43(3):107-116. |
| 65 | Liu X, Lu R, Lü Z,et al.Magnetic susceptibility of surface soils in the Mu Us Desert and its environmental significance[J].Aeolian Research,2017,25:127-134. |
| 66 | Collinson,D W.Methods in Rock Magnetism and Palaeomagnetism[M].London,UK:Chapman and Hall,1983:21-33. |
| 67 | Liu Q, Roberts A P, Larrasoaña J C,et al.Environmental magnetism:principles and applications[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2012,50(4):RG4002. |
| 68 | Maher B A.Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,154:23-84. |
| 69 | 韩瑞,苏志珠,李想,等.粒度和磁化率记录的毛乌素沙地东缘全新世气候变化[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(2):105-114. |
| 70 | Yang L W, Jia J.Temperature dependence of pedogenic magnetic mineral formation in loess deposits[J].Quaternary International,2021,580:95-99. |
| 71 | 周晶,戴雪荣,付苗苗.沉积物磁性特征对物源指示作用的探讨[J].土壤通报,2008,39(5):1169-1172. |
| 72 | 胡凯程,贾佳,胡忠行,等.湿润气候条件下温度对土壤磁化率影响的再认识[J].第四纪研究,2022,42(2):461-471. |
| 73 | 吕厚远,韩家懋,吴乃琴,等.中国现代土壤磁化率分析及其古气候意义[J].中国科学(B辑 化学 生命科学 地学),1994,(12):1290-1297. |
| 74 | 谷永建,李玉梅,韩龙,等.中国东部表土磁化率与现代气候因子的关系及其环境意义[J].中国科学院大学学报,2019,36(4):498. |
| 75 | Long X, Ji J, Barrón V,et al.Climatic thresholds for pedogenic iron oxides under aerobic conditions:processes and their significance in paleoclimate reconstruction[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,150:264-277. |
| 76 | 龚亚玲,胡忠行,李文,等.浙江玄武岩风化壳红土磁性特征及其对成土过程的响应[J].第四纪研究,2021,41(1):51-62. |
| 77 | 夏敦胜,马剑英,王冠,等.环境磁学及其在西北干旱区环境研究中的问题[J].地学前缘,2006,13(3):168-179. |
| 78 | 刘青松,邓成龙.磁化率及其环境意义[J].地球物理学报,2009,52(4):1041-1048. |
| 79 | 昝金波,宁文晓,杨胜利,等.表土磁学特征揭示的青藏高原及其周边地区的气候边界[J].地球科学进展,2022,37(1):14. |
| 80 | 吕镔,刘秀铭,赵国永,等.新疆博乐黄土岩石磁学特征及环境意义[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(5):1-8. |
| 81 | Deng C, Zhu R, Jackson M J,et al.Variability of the temperature-dependent susceptibility of the Holocene eolian deposits in the Chinese loess plateau:a pedogenesis indicator[J].Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy,2001,26(11/12):873-878. |
| 82 | Torrent J, Barrón V, Liu Q S.Magnetic enhancement is linked to and precedes hematite formation in aerobic soil[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2006,33(2):L02401. |
| 83 | 邓成龙,刘青松,潘永信,等.中国黄土环境磁学[J].第四纪研究,2007,27(2):193-209. |
| [1] | 杨宇哲, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 刘怡婷, 李嘉宁, 杨天宇. 毛乌素沙地东南缘L3 、S3 黄土-古土壤色度特征及古气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 176-186. |
| [2] | 毛学刚, 赵丽娟. 沙漠、戈壁和黄土表土岩石磁学特征及其对黄土磁化率机制的意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 183-193. |
| [3] | 刘荔昀, 鲁瑞洁, 刘小槺. 风成沉积物色度记录的毛乌素沙漠全新世以来气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 83-89. |
| [4] | 韩瑞, 苏志珠, 李想, 柳苗苗, 马义娟. 粒度和磁化率记录的毛乌素沙地东缘全新世气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(2): 105-114. |
| [5] | 杨帆, 靳鹤龄, 李孝泽, 耿建伟, 刘冰. 中晚全新世毛乌素沙地东南部气候变化过程[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3): 431-438. |
| [6] | 田丽慧, 张登山, 彭继平, 吴汪洋, 张佩. 高寒沙地人工植被恢复区地表沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(1): 32-39. |
| [7] | 徐莉, 李艳红, 杨甲全. 罗布泊盐湖表层土地球化学及沉积特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(6): 1552-1557. |
| [8] | 赵国永1, 刘秀铭1,2,3, 吕 镔2, 陈 渠4, 李平原1, 郭 晖1, 刘 植1. 红黏土磁化率增强机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(3): 673-681. |
| [9] | 杨萍果. 山西襄汾农田土壤磁化率和养分空间变异性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(3): 813-818. |
| [10] | 王君兰, 李晖, 邓伟, 郭小燕, 李双, 张家武. 内蒙古嘎顺诺尔湖泊沉积物磁化率与粒度的古环境意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(3): 661-668. |
| [11] | 刘 冰;靳鹤龄;孙 忠. 近6 ka以来科尔沁沙地东部气候变化记录[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6): 1398-1405. |
| [12] | 贾 佳;夏敦胜;魏海涛;金 明;刘现彬;王 博. 阿西克剖面记录的西天山地区黄土磁学性质及古气候意义初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6): 1406-1415. |
| [13] | 邓少福;杨太保*;秦宏毅;曾 彪;朱锡芬;鄂崇毅. 新疆塔城黄土古土壤磁化率特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(4): 848-854. |
| [14] | 徐树建;王 涛. 蓬莱黄土剖面光释光年代学及其沉积特征研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(2): 295-301. |
| [15] | 蔡茂堂;魏明建. 洛川地区倒数第二次间冰期气候变化研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(3): 536-543. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
