中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 122-134.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00094
史利江1( ), 李前锦1, 高杉1, 李永宁1, 姚晓军2, 张晓龙1, 张殷波1, 高峰1
), 李前锦1, 高杉1, 李永宁1, 姚晓军2, 张晓龙1, 张殷波1, 高峰1
收稿日期:2024-04-30
修回日期:2024-07-22
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-12-06
作者简介:史利江(1978—),男,山西阳泉人,博士,副教授,研究方向为区域经济与区域可持续发展。E-mail: slj19972@126.com
基金资助:
Lijiang Shi1( ), Qianjin Li1, Shan Gao1, Yongning Li1, Xiaojun Yao2, Xiaolong Zhang1, Yinbo Zhang1, Feng Gao1
), Qianjin Li1, Shan Gao1, Yongning Li1, Xiaojun Yao2, Xiaolong Zhang1, Yinbo Zhang1, Feng Gao1
Received:2024-04-30
Revised:2024-07-22
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-06
摘要:
基于DPSIR模型构建了黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力的综合评价指标体系,利用熵值法、泰尔指数、空间自相关、引力模型以及地理探测器等方法分析了2010―2020年黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力的时空格局演变、影响因素以及空间关联网络特征。结果表明:(1)黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力呈逐年上升趋势,四大城市群间绿色技术创新能力的非均衡性逐步减小,但各城市间绿色技术创新能力的非均衡性逐渐增大。(2)绿色技术创新能力的空间分布形成了多“核心-边缘”的空间格局,4个省会城市的绿色技术创新能力优势明显,而黄土高原东西两侧、关中平原西部及中原城市群东南部的城市绿色技术创新能力偏低;空间自相关在全局上随机性较强,在局部也仅有个别城市存在高-低、低-高的集聚现象,没有形成明显的空间集聚特征。(3)绿色技术创新能力的空间关联网络格局趋于复杂,形成了郑州-新乡-西安强空间引力的小三角区和郑州-西安-太原强空间引力的大三角区。(4)社会经济基础、创新资源、创新环境以及产业结构等因素通过与其他因子的交互作用,成为影响黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力空间分异的主要驱动因素。
中图分类号:
史利江, 李前锦, 高杉, 李永宁, 姚晓军, 张晓龙, 张殷波, 高峰. 黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力的时空演变与影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 122-134.
Lijiang Shi, Qianjin Li, Shan Gao, Yongning Li, Xiaojun Yao, Xiaolong Zhang, Yinbo Zhang, Feng Gao. Analysis on the spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of green technology innovation capability of urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 122-134.
| 城市群名称 | 城市构成 |
|---|---|
| 中原城市群 | 郑州、开封、洛阳、南阳、安阳、商丘、新乡、平顶山、许昌、焦作、信阳、鹤壁、濮阳、漯河、三门峡、周口、驻马店、长治、晋城 |
| 关中平原城市群 | 西安、宝鸡、铜川、渭南、咸阳、延安、商洛、天水、平凉、庆阳、运城、临汾 |
| 山西中部城市群 | 太原、晋中、忻州、阳泉、吕梁 |
| 呼包鄂榆城市群 | 呼和浩特、包头、鄂尔多斯、榆林 |
表1 黄河中游城市群范围内地级市统计
Table 1 Statistical table of prefecture level cities within the urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yellow River
| 城市群名称 | 城市构成 |
|---|---|
| 中原城市群 | 郑州、开封、洛阳、南阳、安阳、商丘、新乡、平顶山、许昌、焦作、信阳、鹤壁、濮阳、漯河、三门峡、周口、驻马店、长治、晋城 |
| 关中平原城市群 | 西安、宝鸡、铜川、渭南、咸阳、延安、商洛、天水、平凉、庆阳、运城、临汾 |
| 山西中部城市群 | 太原、晋中、忻州、阳泉、吕梁 |
| 呼包鄂榆城市群 | 呼和浩特、包头、鄂尔多斯、榆林 |
| 目标层 | 准则层 | 要素层 | 指标层 | 属性 | 权重/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绿色 技术 创新 | 驱动D | 经济发展 | 人均GDP(元) | + | 3.25 |
| 社会生活 | 城镇居民人均可支配收入(元) | + | 1.46 | ||
| 在岗职工平均工资(元) | + | 1.74 | |||
| 教育水平 | 高等院校数量(所) | + | 11.43 | ||
| 压力P | 环境压力 | 单位GDP工业废水排放量(t/万元) | - | 0.22 | |
| 单位GDP工业二氧化硫排放量(t/亿元) | - | 0.14 | |||
| 社会压力 | 年末城镇登记失业人员数占年末单位从业人员数(%) | - | 0.06 | ||
| 状态S | 绿色技术创新投入 | 教育支出/地方一般公共预算支出(%) | + | 1.05 | |
| 科学研究、技术服务和地质勘查行业从业人数/年末单位从业人员数(%) | + | 3.59 | |||
| 水利、环境和公共设施管理业行业从业人员数/年末单位从业人员数(%) | + | 3.99 | |||
| 绿色技术创新环境 | 人均道路面积(m2) | + | 3.46 | ||
| 万人国际互联网接入用户数(户) | + | 3.82 | |||
| 百人均图书馆藏书量(册) | + | 6.69 | |||
| 外商投资企业数(个) | + | 5.53 | |||
| 影响I | 绿色技术创新产出 | 绿色发明专利授权量(件) | + | 16.52 | |
| 绿色实用新型专利授权量(件) | + | 13.11 | |||
| 专利申请量(件) | + | 13.28 | |||
| 响应R | 经济响应 | 单位GDP全社会固定资产投资总额(%) | + | 1.92 | |
| 环境响应 | 工业固体废物综合利用率(%) | + | 0.87 | ||
| 生活垃圾无害化处理率(%) | + | 0.34 | |||
| 人均公园绿地面积(hm2/万人) | + | 4.47 | |||
| 科技响应 | 科学技术支出/地方一般公共预算支出(%) | + | 3.06 |
表2 黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力评价指标体系
Table 2 Evaluation index system for green technology innovation capability of urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yellow River
| 目标层 | 准则层 | 要素层 | 指标层 | 属性 | 权重/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绿色 技术 创新 | 驱动D | 经济发展 | 人均GDP(元) | + | 3.25 |
| 社会生活 | 城镇居民人均可支配收入(元) | + | 1.46 | ||
| 在岗职工平均工资(元) | + | 1.74 | |||
| 教育水平 | 高等院校数量(所) | + | 11.43 | ||
| 压力P | 环境压力 | 单位GDP工业废水排放量(t/万元) | - | 0.22 | |
| 单位GDP工业二氧化硫排放量(t/亿元) | - | 0.14 | |||
| 社会压力 | 年末城镇登记失业人员数占年末单位从业人员数(%) | - | 0.06 | ||
| 状态S | 绿色技术创新投入 | 教育支出/地方一般公共预算支出(%) | + | 1.05 | |
| 科学研究、技术服务和地质勘查行业从业人数/年末单位从业人员数(%) | + | 3.59 | |||
| 水利、环境和公共设施管理业行业从业人员数/年末单位从业人员数(%) | + | 3.99 | |||
| 绿色技术创新环境 | 人均道路面积(m2) | + | 3.46 | ||
| 万人国际互联网接入用户数(户) | + | 3.82 | |||
| 百人均图书馆藏书量(册) | + | 6.69 | |||
| 外商投资企业数(个) | + | 5.53 | |||
| 影响I | 绿色技术创新产出 | 绿色发明专利授权量(件) | + | 16.52 | |
| 绿色实用新型专利授权量(件) | + | 13.11 | |||
| 专利申请量(件) | + | 13.28 | |||
| 响应R | 经济响应 | 单位GDP全社会固定资产投资总额(%) | + | 1.92 | |
| 环境响应 | 工业固体废物综合利用率(%) | + | 0.87 | ||
| 生活垃圾无害化处理率(%) | + | 0.34 | |||
| 人均公园绿地面积(hm2/万人) | + | 4.47 | |||
| 科技响应 | 科学技术支出/地方一般公共预算支出(%) | + | 3.06 |
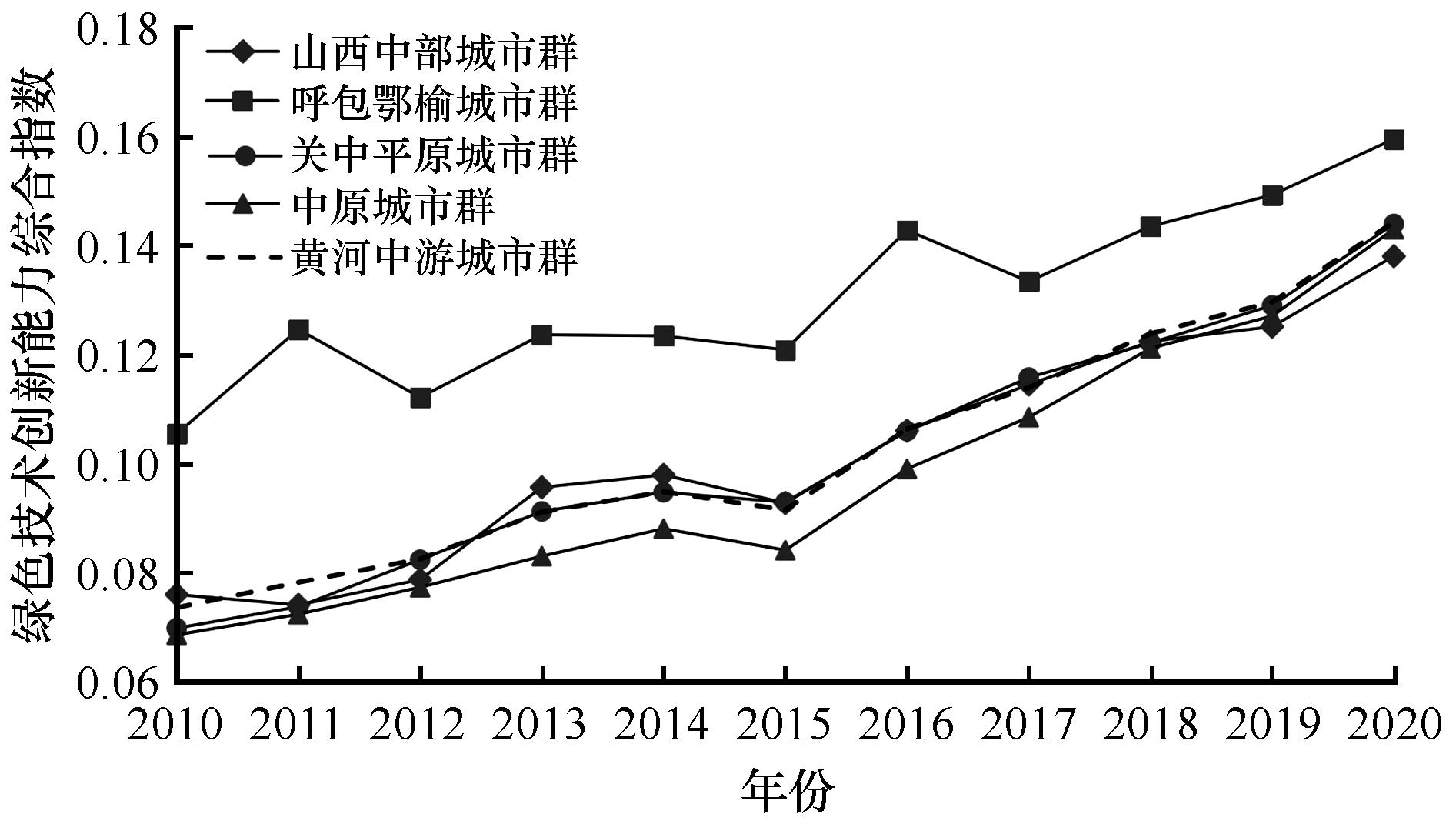
图2 2010—2020年黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力变化
Fig.2 Changes in green technology innovation capability of urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
| 年份 | 泰尔指数T | 组间差异 | 组内差异 | 山西中部城市群 | 呼包鄂榆城市群 | 关中平原城市群 | 中原城市群 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.150 | 0.010 | 0.140 | 0.172 | 0.019 | 0.246 | 0.103 |
| 2011 | 0.188 | 0.017 | 0.171 | 0.236 | 0.064 | 0.320 | 0.097 |
| 2012 | 0.175 | 0.007 | 0.168 | 0.220 | 0.032 | 0.309 | 0.101 |
| 2013 | 0.180 | 0.008 | 0.172 | 0.167 | 0.036 | 0.340 | 0.100 |
| 2014 | 0.172 | 0.005 | 0.167 | 0.177 | 0.020 | 0.315 | 0.106 |
| 2015 | 0.217 | 0.006 | 0.211 | 0.203 | 0.039 | 0.394 | 0.137 |
| 2016 | 0.180 | 0.006 | 0.174 | 0.147 | 0.046 | 0.317 | 0.123 |
| 2017 | 0.199 | 0.002 | 0.197 | 0.166 | 0.032 | 0.348 | 0.147 |
| 2018 | 0.203 | 0.001 | 0.202 | 0.180 | 0.032 | 0.341 | 0.161 |
| 2019 | 0.197 | 0.001 | 0.196 | 0.171 | 0.028 | 0.342 | 0.150 |
| 2020 | 0.226 | 0.001 | 0.225 | 0.196 | 0.032 | 0.377 | 0.181 |
表3 2010—2020年黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力的泰尔指数
Table 3 Theil index statistics of green technology innovation capability of urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
| 年份 | 泰尔指数T | 组间差异 | 组内差异 | 山西中部城市群 | 呼包鄂榆城市群 | 关中平原城市群 | 中原城市群 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.150 | 0.010 | 0.140 | 0.172 | 0.019 | 0.246 | 0.103 |
| 2011 | 0.188 | 0.017 | 0.171 | 0.236 | 0.064 | 0.320 | 0.097 |
| 2012 | 0.175 | 0.007 | 0.168 | 0.220 | 0.032 | 0.309 | 0.101 |
| 2013 | 0.180 | 0.008 | 0.172 | 0.167 | 0.036 | 0.340 | 0.100 |
| 2014 | 0.172 | 0.005 | 0.167 | 0.177 | 0.020 | 0.315 | 0.106 |
| 2015 | 0.217 | 0.006 | 0.211 | 0.203 | 0.039 | 0.394 | 0.137 |
| 2016 | 0.180 | 0.006 | 0.174 | 0.147 | 0.046 | 0.317 | 0.123 |
| 2017 | 0.199 | 0.002 | 0.197 | 0.166 | 0.032 | 0.348 | 0.147 |
| 2018 | 0.203 | 0.001 | 0.202 | 0.180 | 0.032 | 0.341 | 0.161 |
| 2019 | 0.197 | 0.001 | 0.196 | 0.171 | 0.028 | 0.342 | 0.150 |
| 2020 | 0.226 | 0.001 | 0.225 | 0.196 | 0.032 | 0.377 | 0.181 |
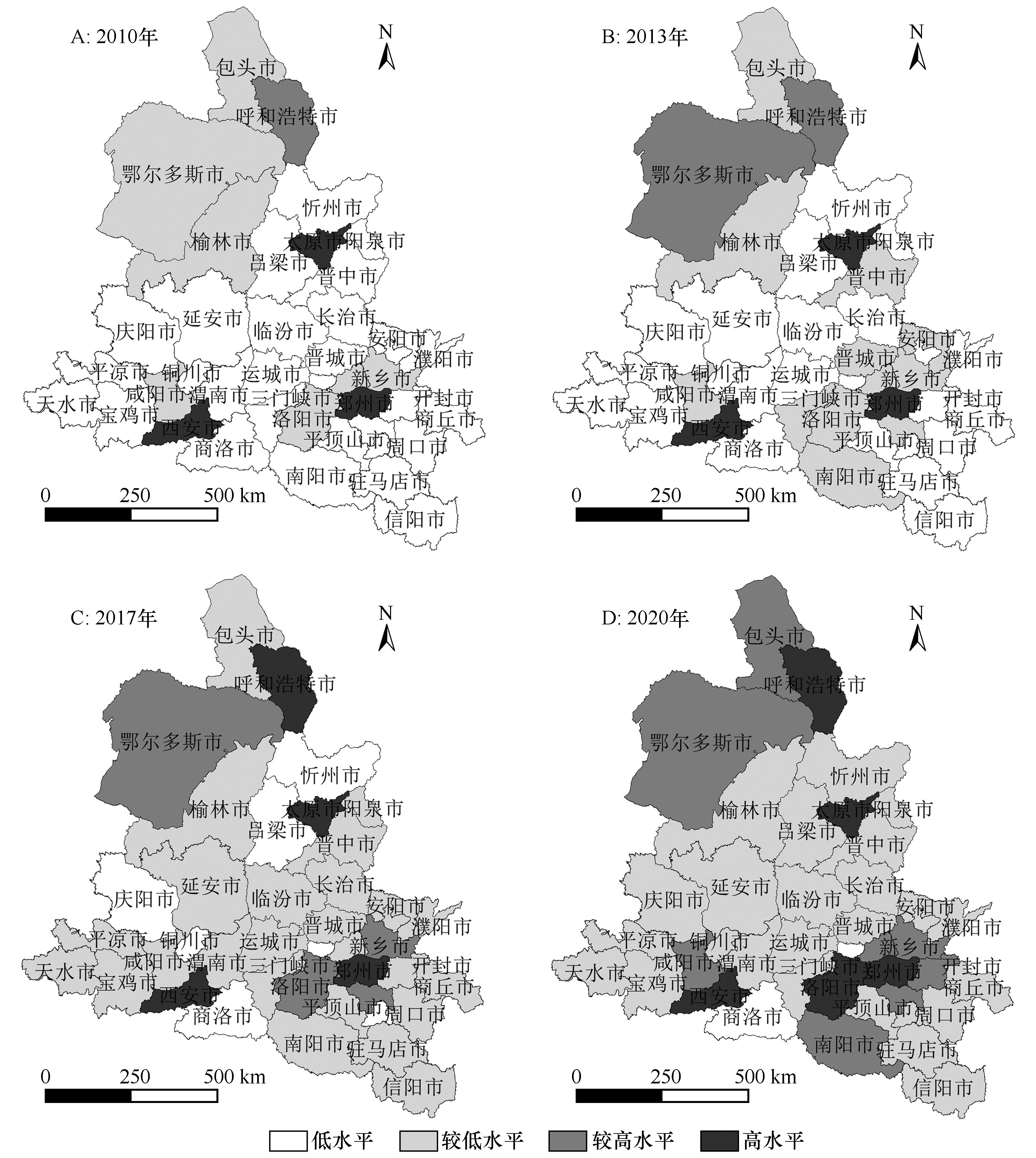
图3 黄河中游城市群地级市绿色技术创新能力空间格局注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2020)4619 号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.3 Spatial pattern of green technology innovation capability of prefecture level cities in urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
| 年份 | Moran's I | P | Z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | -0.006 | 0.833 | 0.211 |
| 2011 | 0.009 | 0.706 | 0.377 |
| 2012 | -0.021 | 0.961 | 0.049 |
| 2013 | -0.029 | 0.973 | -0.034 |
| 2014 | -0.028 | 0.980 | -0.026 |
| 2015 | -0.024 | 0.988 | 0.015 |
| 2016 | -0.019 | 0.935 | 0.081 |
| 2017 | -0.041 | 0.855 | -0.183 |
| 2018 | -0.033 | 0.934 | -0.082 |
| 2019 | -0.043 | 0.834 | -0.210 |
| 2020 | -0.044 | 0.827 | -0.218 |
表4 2010—2020年黄河中游城市群地级市绿色技术创新能力的莫兰指数值
Table 4 Statistical table of Moran index values for green technology innovation capability of prefectural cities in urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
| 年份 | Moran's I | P | Z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | -0.006 | 0.833 | 0.211 |
| 2011 | 0.009 | 0.706 | 0.377 |
| 2012 | -0.021 | 0.961 | 0.049 |
| 2013 | -0.029 | 0.973 | -0.034 |
| 2014 | -0.028 | 0.980 | -0.026 |
| 2015 | -0.024 | 0.988 | 0.015 |
| 2016 | -0.019 | 0.935 | 0.081 |
| 2017 | -0.041 | 0.855 | -0.183 |
| 2018 | -0.033 | 0.934 | -0.082 |
| 2019 | -0.043 | 0.834 | -0.210 |
| 2020 | -0.044 | 0.827 | -0.218 |
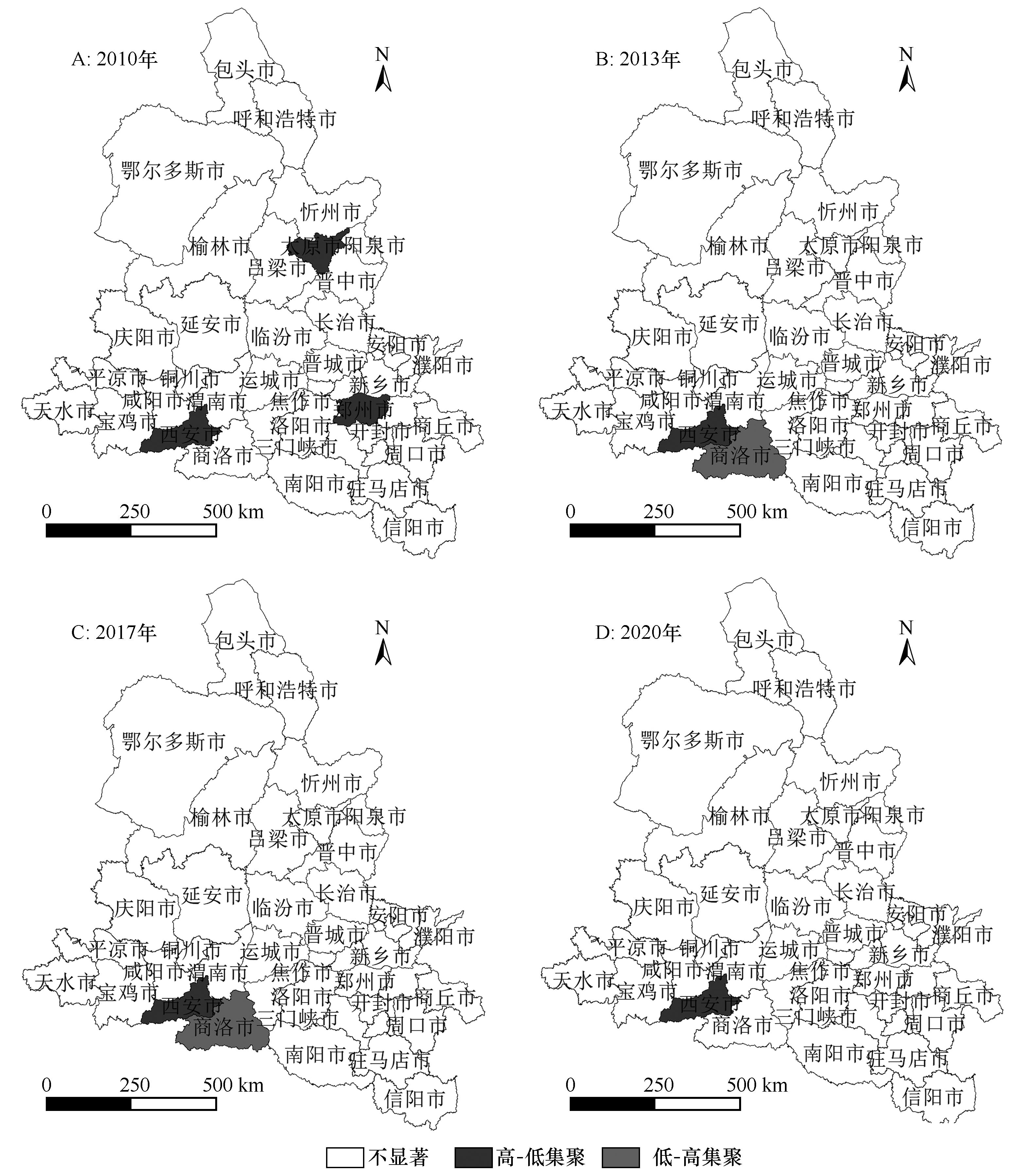
图4 黄河中游城市群地级市绿色技术创新能力的LISA集聚图注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2020)4619 号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.4 LISA cluster map of green technology innovation capability of prefecture-level cities in urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
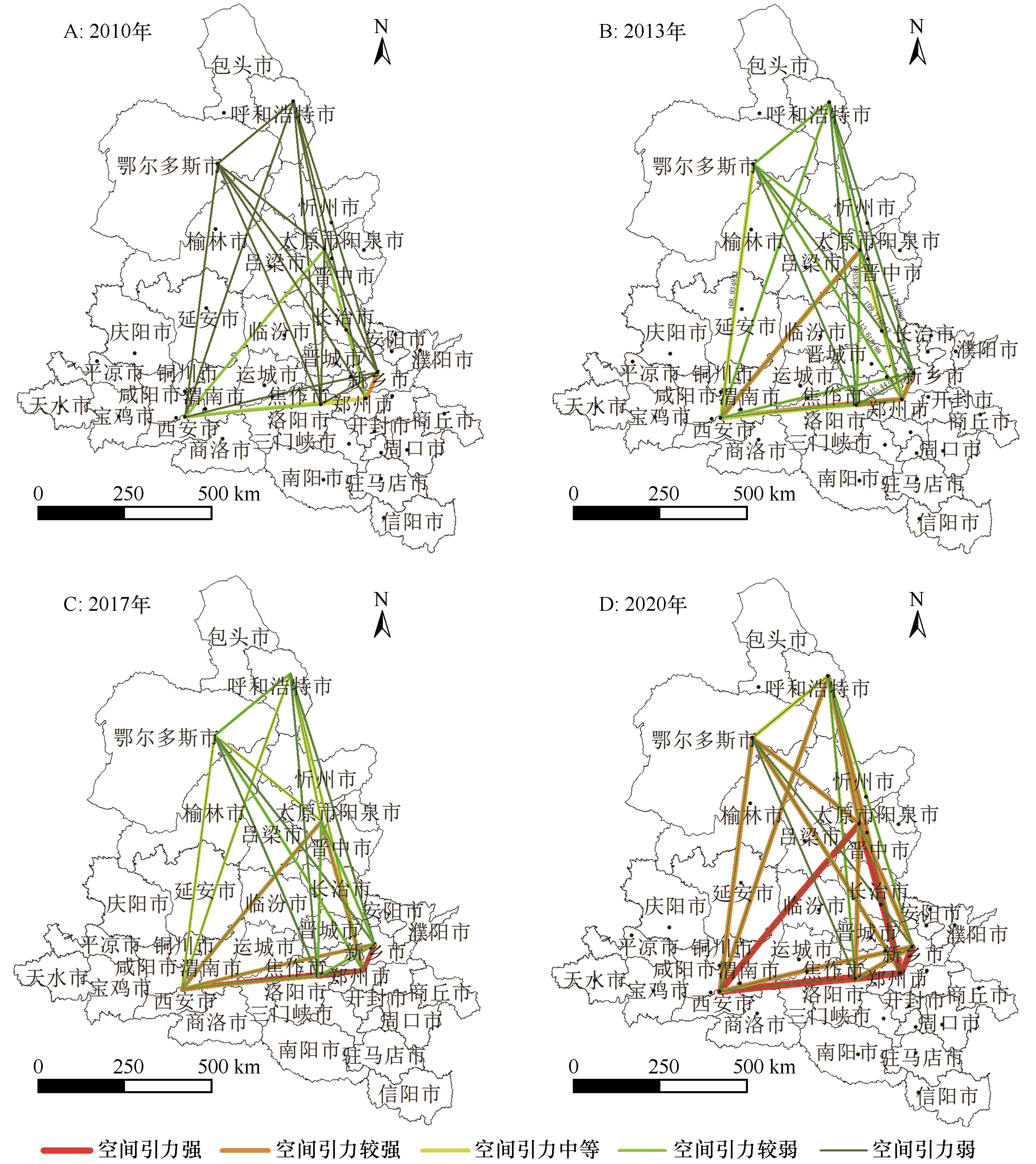
图5 黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力较高城市的空间关联网络注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2020)4619 号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.5 Spatial association network of cities with high green technology innovation capability in urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
| 等级 | 年份 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2013 | 2017 | 2020 | |
| 弱 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| 较弱 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| 中等 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 |
| 较强 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 10 |
| 强 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
表5 2010—2020年黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力较高城市间空间引力等级
Table 5 Statistical table of spatial gravity levels between cities with high green technology innovation capability in urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River from 2010 to 2020
| 等级 | 年份 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2013 | 2017 | 2020 | |
| 弱 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 2 |
| 较弱 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| 中等 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 |
| 较强 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 10 |
| 强 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| 指标 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | 0.918 | 0.453 | 0.440 | 0.887 | 0.955 | 0.066 | 0.069 | 0.125 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.042 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.672 | 0.698 | 0.432 |
表6 黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力空间分异的驱动因子探测结果
Table 6 Exploration results of driving factors for spatial differentiation of green technology innovation capability in the urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River
| 指标 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q | 0.918 | 0.453 | 0.440 | 0.887 | 0.955 | 0.066 | 0.069 | 0.125 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.042 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.672 | 0.698 | 0.432 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.918 | |||||||
| X2 | 0.974 | 0.453 | ||||||
| X3 | 0.989 | 0.529 | 0.440 | |||||
| X4 | 0.935 | 0.957 | 0.978 | 0.887 | ||||
| X5 | 0.977 | 0.971 | 0.977 | 0.964 | 0.955 | |||
| X6 | 0.953 | 0.628 | 0.702 | 0.913 | 0.961 | 0.066 | ||
| X7 | 0.982 | 0.549 | 0.705 | 0.915 | 0.974 | 0.170 | 0.069 | |
| X8 | 0.977 | 0.667 | 0.650 | 0.935 | 0.974 | 0.341 | 0.358 | 0.125 |
表7 黄河中游城市群绿色技术创新能力空间分异驱动因子的交互作用探测结果
Table 7 Exploration results of the interaction of driving factors for the spatial differentiation of green technology innovation capability in the urban agglomeration of the middle reaches of the Yellow River
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.918 | |||||||
| X2 | 0.974 | 0.453 | ||||||
| X3 | 0.989 | 0.529 | 0.440 | |||||
| X4 | 0.935 | 0.957 | 0.978 | 0.887 | ||||
| X5 | 0.977 | 0.971 | 0.977 | 0.964 | 0.955 | |||
| X6 | 0.953 | 0.628 | 0.702 | 0.913 | 0.961 | 0.066 | ||
| X7 | 0.982 | 0.549 | 0.705 | 0.915 | 0.974 | 0.170 | 0.069 | |
| X8 | 0.977 | 0.667 | 0.650 | 0.935 | 0.974 | 0.341 | 0.358 | 0.125 |
| 1 | 郝春旭,邵超峰,董战峰,等.2020年全球环境绩效指数报告分析[J].环境保护,2020,48(16):68-72. |
| 2 | 杨阳,曾刚,葛世帅,等.国内外绿色创新研究进展与展望[J].经济地理,2022,42(3):10-21. |
| 3 | Bernauer T, Engel S, Kammerer D,et al.Explaining green innovation:ten years after porter's win-win proposition:how to study the effects of regulation on corporate environmental innovation?[J].Environmental Science,Business Environmental Law Policy eJournal,2006(1):1-16. |
| 4 | 周衍平,尹意,陈会英.外商直接投资对绿色专利产出的影响:基于中国省际面板数据的实证分析[J].科学与管理,2022,42(1):34-42. |
| 5 | 孙中瑞,樊杰,孙勇,等.中国绿色科技创新效率空间关联网络结构特征及影响因素[J].经济地理,2022,42(3):33-43. |
| 6 | 齐绍洲,林屾,崔静波.环境权益交易市场能否诱发绿色创新?:基于中国上市公司绿色专利数据的证据[J].经济研究,2018,53(12):129-143. |
| 7 | 盛馥来,诸大建.绿色经济:联合国视野中的理论、方法与案例[M].北京:中国财政经济出版社,2015. |
| 8 | 黄晶.绿色创新经济:理论与方法[M].北京:社会科学文献出版社,2020. |
| 9 | 薛宝琪.黄河流域城市创新能力时空格局及影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(6):116-124. |
| 10 | 段德忠,夏启繁,张杨,等.长江经济带环境创新的时空特征及其影响因素[J].地理科学,2021,41(7):1158-1167. |
| 11 | 周福礼,海盼盼,王雪妮.黄河流域绿色发展效率时空演进:基于多周期两阶段DEA模型[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):95-104. |
| 12 | 李魁明,王晓燕,姚罗兰.黄河流域农业绿色发展水平区域差异及影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):85-94. |
| 13 | 彭文斌,苏欣怡,杨胜苏,等.环境规制视角下城市绿色创新时空演变及溢出效应[J].地理科学,2023,43(1):41-49. |
| 14 | Karakaya E, Hidalgo A, Nuur C.Diffusion of eco-innovations:a review[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2014,33:392-399. |
| 15 | Schiederig T, Tietze F, Herstatt C.Green innovation in technology and innovation management:an exploratory literature review[J].RD Management,2012,42(2):180-192. |
| 16 | 罗万云,王福博,孙慧.黄河流域高质量绿色发展水平与空间格局演化特征[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):11-20. |
| 17 | 曾刚,胡森林.技术创新对黄河流域城市绿色发展的影响研究[J].地理科学,2021,41(8):1314-1323. |
| 18 | 苗长虹,张佰发.黄河流域高质量发展分区分级分类调控策略研究[J].经济地理,2021,41(10):143-153. |
| 19 | 赵雪雁,杜昱璇,李花 等.黄河中游城镇化与生态系统服务耦合关系的时空变化[J].自然资源学报,2021,36(1):131-147. |
| 20 | 孙永鹏.黄河中游城市群经济增长的空间溢出效应研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2021. |
| 21 | 方创琳.新发展格局下的中国城市群与都市圈建设[J].经济地理,2021,41(4):1-7. |
| 22 | 任保平,杜宇翔.黄河中游地区生态保护和高质量发展战略研究[J].人民黄河,2021,43(2):1-5. |
| 23 | 段德忠,杜德斌.中国城市绿色技术创新的时空分布特征及影响因素[J].地理学报,2022,77(12):3125-3145. |
| 24 | 孙博文.新质生产力背景下中国绿色创新能力评价:基于绿色技术创新能力、绿色技术创新辐射力和绿色创新制度支撑力的“三力”评价体系研究[J/OL].生态经济:1-19[2024-06-29]. |
| 25 | 陈佳佳,郑雅男,张伟兰,等.黄河流域产业绿色化与生态环境绿色化耦合协调度时空演变[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):1-10. |
| 26 | 王雅洁,张嘉颖.城市群协同创新动态评价[J].统计与决策,2022,38(8):168-173. |
| 27 | 周亮,车磊,周成虎.中国城市绿色发展效率时空演变特征及影响因素[J].地理学报,2019,74(10):2027-2044. |
| 28 | 刘建华,李伟.基于修正引力模型的中原城市群创新空间联系研究[J].地域研究与开发,2019,38(5):63-68. |
| 29 | 张书豪,吴艳婷,于海生.基于改进引力模型和社会网络分析法的山东省城市创新关联网络研究[J].鲁东大学学报(自然科学版),2022,38(4):342-349. |
| 30 | 彭英,余小莉.基于改进引力模型的江苏省城市创新空间关联及其影响因素[J].科技管理研究,2021,41(24):81-86. |
| 31 | 周正柱,杨静,张泽安.长三角城市群创新联系网络时空演变分析[J].江苏大学学报(社会科学版),2022,24(5):85-96. |
| 32 | 王劲峰,徐成东.地理探测器:原理与展望[J].地理学报,2017,72(1):116-134. |
| 33 | 李璐.黄河流域城市绿色创新效率及影响因素研究[D].太原:山西财经大学,2022. |
| 34 | 李大鹏.长江中游城市群绿色创新能力的时空特征及影响因素研究[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2021. |
| 35 | Porter M E, Linde C V.Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship[J].Journal of Economic Perspectives,1995,9(4):97-118. |
| [1] | 罗君, 张学斌, 石培基. 兰州-西宁城市群国土空间演化特征及分区优化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 182-193. |
| [2] | 王录仓, 屈艳琦, 武潼. 城市群空间结构对城市群空间扩张模式与形态的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 63-74. |
| [3] | 徐晨曦, 万红莲, 何若楠, 殷鹏, 倪敬峰, 黄敏, 王晓利. 关中平原城市群脆弱性时空演变与驱动因子[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 111-120. |
| [4] | 迟文峰, 王月甜, 党晓宏, 吴晓光, 罗前程. 黄河流域土壤侵蚀时空演变与格局特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 305-317. |
| [5] | 孙国军, 方昤璇, 刘海军. 甘肃省文化产业发展时空特征及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 75-82. |
| [6] | 谢磊, 何仁伟, 史文涛, 蒲红铮. 黄河流域城乡融合发展时空演变和动力机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 31-40. |
| [7] | 赵明, 周春晓, 李崇, 刘硕, 赵胡笳. 1960—2020年辽宁沙尘强度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 113-120. |
| [8] | 杨洁, 谢保鹏, 张德罡. 黄河流域生境质量时空演变及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 12-22. |
| [9] | 李光勤, 方徐兵. 黄河流域绿色发展水平时空演变特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 129-139. |
| [10] | 王旭洋, 李玉霖, 连杰, 段育龙, 王立龙. 半干旱典型风沙区植被覆盖度演变与气候变化的关系及其对生态建设的意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 183-194. |
| [11] | 卓静, 朱延年, 王娟, 何慧娟, 邹继业. 红碱淖面积时空演变规律及保护措施成效[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(4): 195-203. |
| [12] | 程广斌, 申立敬. 天山北坡城市群城市综合承载力评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(5): 1371-1375. |
| [13] | 段翰晨1,2, 王 涛1, 薛 娴1, 孙家欢1,2, 杨林海1. 基于RS与GIS的科尔沁沙地沙漠化时空演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 470-477. |
| [14] | 谢 霞1,2, 塔西甫拉提·特依拜2,3. 艾比湖流域绿洲化与荒漠化过程时空演变研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(1): 38-45. |
| [15] | 李玲萍, 李岩瑛, 刘明春. 石羊河流域1961—2005年蒸发皿蒸发量变化趋势及原因初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(3): 832-841. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
