中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 200-210.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00093
• • 上一篇
苏万红1( ), 詹瑾2(
), 詹瑾2( ), 李亚2, 纪永福2, 李玉霖3, 丛安琪3, 张雯2, 付贵全2, 王曰军4
), 李亚2, 纪永福2, 李玉霖3, 丛安琪3, 张雯2, 付贵全2, 王曰军4
收稿日期:2025-05-11
修回日期:2025-07-08
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-18
通讯作者:
詹瑾
作者简介:苏万红(1970—),男,甘肃景泰人,工程师,主要从事干旱区恢复生态学研究。E-mail: 1250626183@qq.com
基金资助:
Wanhong Su1( ), Jin Zhan2(
), Jin Zhan2( ), Ya Li2, Yongfu Ji2, Yulin Li3, Anqi Cong3, Wen Zhang2, Guiquan Fu2, Yuejun Wang4
), Ya Li2, Yongfu Ji2, Yulin Li3, Anqi Cong3, Wen Zhang2, Guiquan Fu2, Yuejun Wang4
Received:2025-05-11
Revised:2025-07-08
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
Jin Zhan
摘要:
地上凋落物和地下根系输入是土壤碳库的重要植物来源,探讨地上凋落物和地下根系去除对沙质草地表层土壤碳组分的影响,有利于深入理解该生态系统土壤碳库的积累机制。本研究依托科尔沁沙地西南部国家野外科学观测研究站建立的长期凋落物去除实验(对照、地上凋落物去除、地下根系去除、地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除),比较凋落物去除处理对沙质草地表层土壤碳组分的影响,并分析了土壤碳库活度变化的驱动因素。结果显示:(1)地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除显著增加了土壤容重(P<0.05),使土壤全碳、活性碳含量分别显著降低了23.78%、23.49%(P<0.05);与地上凋落物去除相比,该处理显著降低了土壤活性碳含量(P<0.05);(2)地上凋落物去除使土壤微生物生物量碳含量从0.032 g·kg-1显著降低至0.016 g·kg-1(P<0.05);(3)地下根系去除使土壤碳库活度从0.46显著降低至0.30(P<0.05);(4)Pearson相关性分析表明土壤碳组分与土壤容重、含水量、电导率、pH存在显著相关性。结构方程模型分析结果显示,土壤容重、含水量、电导率、pH和土壤碳组分共同解释了土壤碳库活度变化的92%,土壤理化性质可通过影响土壤碳组分来调控土壤碳库活度。
中图分类号:
苏万红, 詹瑾, 李亚, 纪永福, 李玉霖, 丛安琪, 张雯, 付贵全, 王曰军. 凋落物去除对沙质草地表层土壤碳组分的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 200-210.
Wanhong Su, Jin Zhan, Ya Li, Yongfu Ji, Yulin Li, Anqi Cong, Wen Zhang, Guiquan Fu, Yuejun Wang. Effects of litter removal on top soil carbon components in the sandy grassland[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(4): 200-210.
| 处理 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 对照(CK) | 在自然状态下不做任何处理 |
| 地上凋落物去除(-L) | 每年11月清除样方内地上现存的枯落物 |
| 地下根系去除(-R) | 采用壕沟法,在每块样地内布置边长为1.5 m×1.5 m的小样方,在不干扰其他土壤的基础上,在每个小样方四周挖60 cm深的壕沟,小样方内原有根系保留,在沟内内衬铝制铁皮阻隔小样方外根系入侵,并回填土壤。整个试验期间不定期拔除小样方内地表生长的植物,以消除地下根系输入的干扰 |
| 地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除(-L-R) | 清除掉样方内地上现存的枯落物,同时采用壕沟法,在1.5 m×1.5 m小样方四周挖60 cm深的壕沟,小样方内原有根系保留,在沟内内衬铝制铁皮阻隔小样方外根系入侵,并回填土壤。整个试验期间不定期拔除小样方内地表生长的植物,以消除地下根系输入的干扰 |
表1 沙质草地凋落物去除实验处理描述
Table 1 Description of experimental treatment for litter removal in sandy grassland
| 处理 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 对照(CK) | 在自然状态下不做任何处理 |
| 地上凋落物去除(-L) | 每年11月清除样方内地上现存的枯落物 |
| 地下根系去除(-R) | 采用壕沟法,在每块样地内布置边长为1.5 m×1.5 m的小样方,在不干扰其他土壤的基础上,在每个小样方四周挖60 cm深的壕沟,小样方内原有根系保留,在沟内内衬铝制铁皮阻隔小样方外根系入侵,并回填土壤。整个试验期间不定期拔除小样方内地表生长的植物,以消除地下根系输入的干扰 |
| 地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除(-L-R) | 清除掉样方内地上现存的枯落物,同时采用壕沟法,在1.5 m×1.5 m小样方四周挖60 cm深的壕沟,小样方内原有根系保留,在沟内内衬铝制铁皮阻隔小样方外根系入侵,并回填土壤。整个试验期间不定期拔除小样方内地表生长的植物,以消除地下根系输入的干扰 |
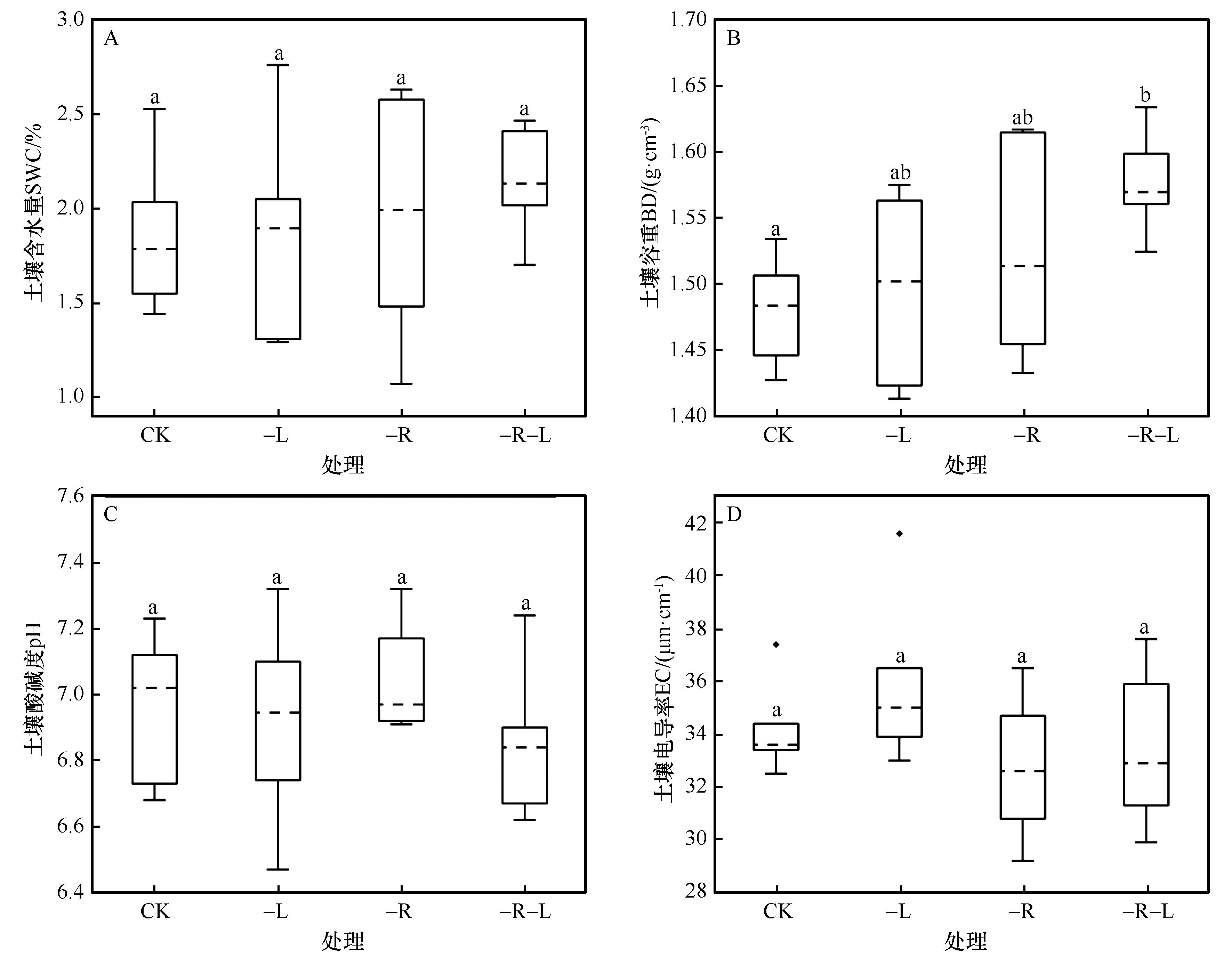
图2 凋落物去除下沙质草地土壤理化性质特征注:CK:对照;-L:地上凋落物去除;-R:地下根系去除;-L-R:地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除;小写字母表示不同凋落物去除处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.2 Soil physical and chemical properties under litter removal treatment
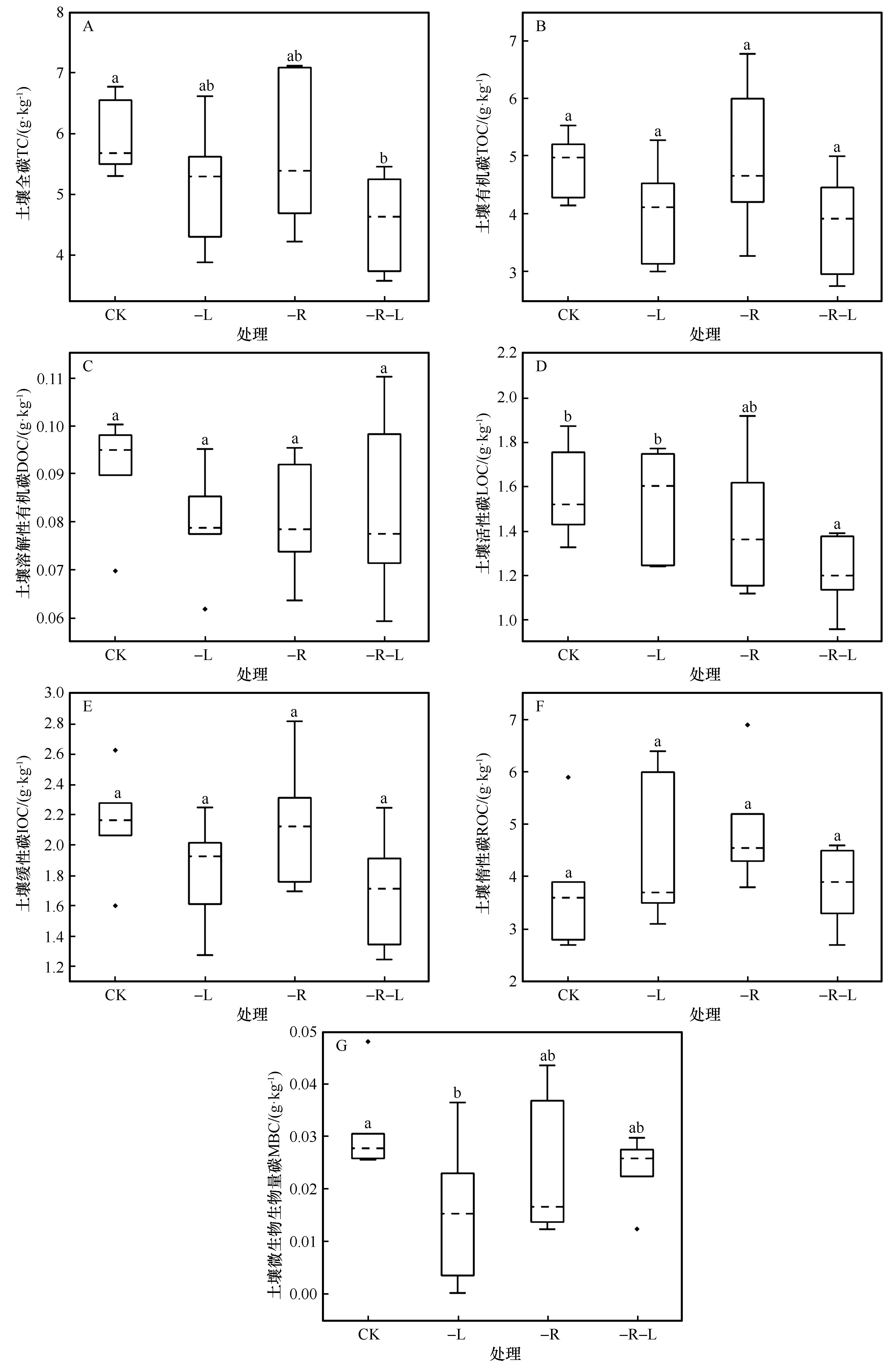
图3 凋落物去除下沙质草地土壤碳组分特征注:CK:对照;-L:地上凋落物去除;-R:地下根系去除;-L-R:地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除;不同小写字母表示不同凋落物去除处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.3 Characterization of soil carbon components under litter removal treatment
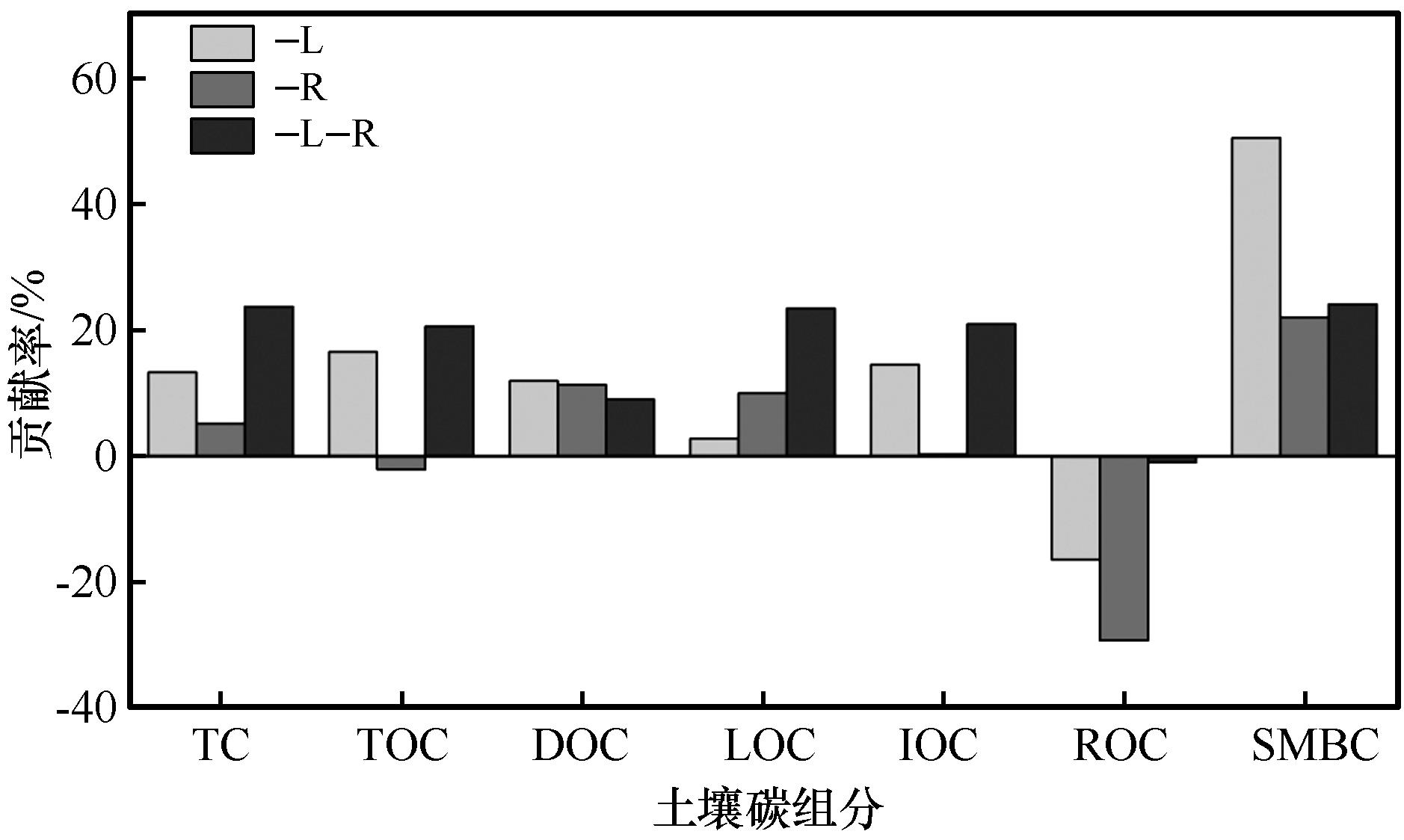
图4 地上凋落物和地下根系对土壤不同碳组分的贡献率注:-L:地上凋落物去除;-R:地下根系去除;-L-R:地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除;TC:土壤全碳含量;TOC:土壤总有机碳含量;DOC:土壤溶解性有机碳含量;LOC:活性碳;IOC:缓性碳;ROC:惰性碳含量;SMBC:土壤微生物生物量碳
Fig.4 Contribution of contributions of aboveground litter and belowground root to different soil carbon components
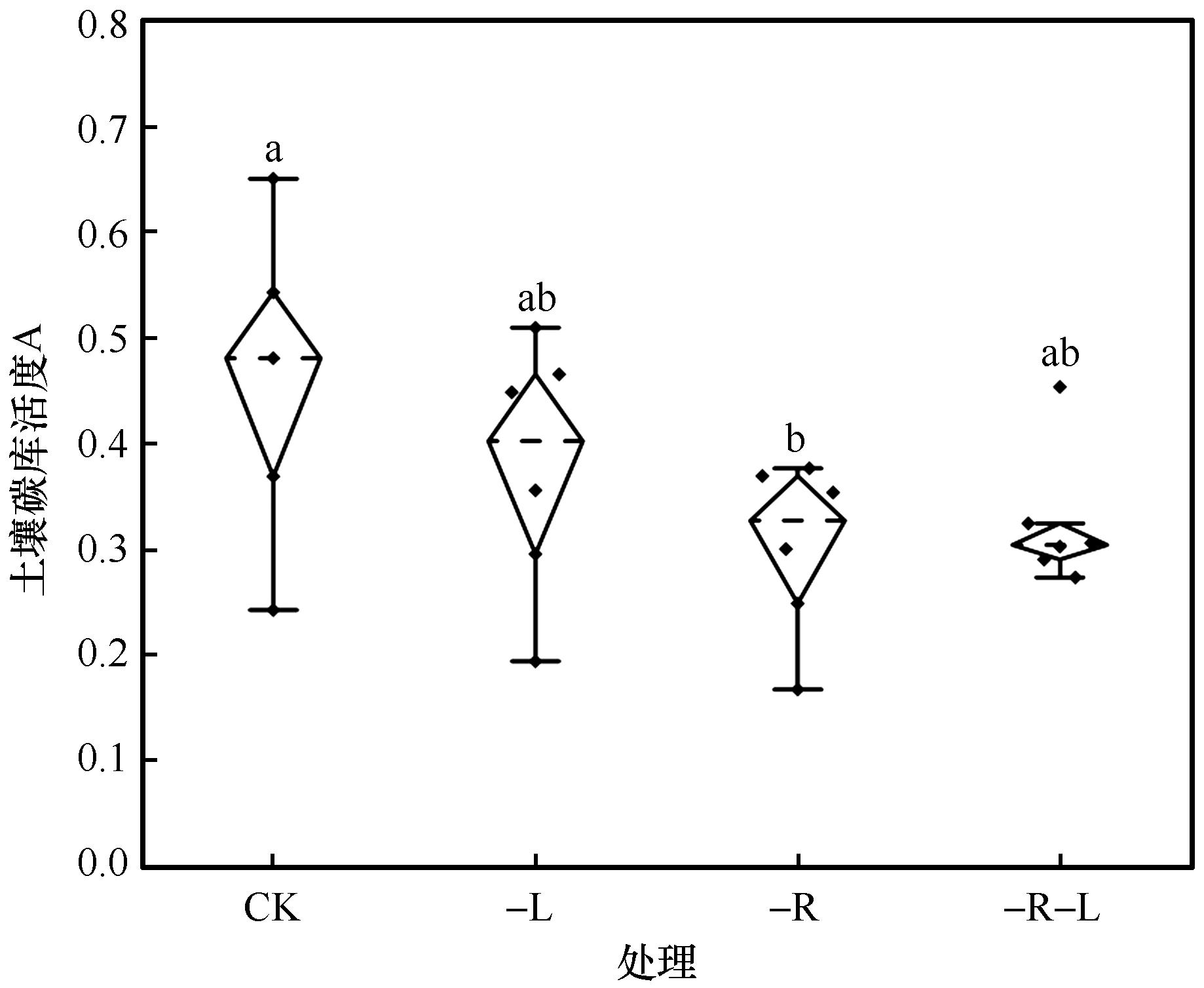
图5 凋落物去除下沙质草地土壤碳库活度特征注:CK:对照;-L:地上凋落物去除;-R:地下根系去除;-L-R:地上凋落物和地下根系同时去除;不同小写字母表示不同凋落物去除处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.5 Characterization of soil carbon pool activity under litter removal treatment
| 指标 | SWC | BD | pH | EC | TC | TOC | DOC | LOC | IOC | ROC | MBC | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWC | 1 | |||||||||||
| BD | -0.307 | 1 | ||||||||||
| pH | 0.027 | -0.020 | 1 | |||||||||
| EC | 0.207 | -0.281 | 0.376 | 1 | ||||||||
| TC | 0.161 | -0.643** | 0.140 | 0.363 | 1 | |||||||
| TOC | 0.363 | -0.638** | 0.037 | 0.276 | 0.897** | 1 | ||||||
| DOC | -0.517* | 0.222 | 0.153 | -0.012 | -0.021 | -0.308 | 1 | |||||
| LOC | 0.185 | -0.663** | 0.294 | 0.564** | 0.694** | 0.651** | -0.034 | 1 | ||||
| IOC | 0.170 | -0.532** | 0.008 | 0.142 | 0.879** | 0.823** | -0.236 | 0.342 | 1 | |||
| ROC | 0.163 | -0.113 | -0.469* | -0.075 | 0.106 | 0.280 | -0.504* | -0.027 | 0.273 | 1 | ||
| SMBC | 0.217 | 0.141 | 0.178 | 0.085 | 0.164 | 0.149 | 0.238 | -0.032 | 0.163 | -0.051 | 1 | |
| A | -0.075 | -0.316 | 0.540** | 0.347 | 0.210 | 0.042 | 0.394 | 0.578** | -0.122 | -0.774** | 0.074 | 1 |
表2 土壤碳组分与土壤理化性质的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between soil carbon components and soil physical and chemical properties
| 指标 | SWC | BD | pH | EC | TC | TOC | DOC | LOC | IOC | ROC | MBC | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWC | 1 | |||||||||||
| BD | -0.307 | 1 | ||||||||||
| pH | 0.027 | -0.020 | 1 | |||||||||
| EC | 0.207 | -0.281 | 0.376 | 1 | ||||||||
| TC | 0.161 | -0.643** | 0.140 | 0.363 | 1 | |||||||
| TOC | 0.363 | -0.638** | 0.037 | 0.276 | 0.897** | 1 | ||||||
| DOC | -0.517* | 0.222 | 0.153 | -0.012 | -0.021 | -0.308 | 1 | |||||
| LOC | 0.185 | -0.663** | 0.294 | 0.564** | 0.694** | 0.651** | -0.034 | 1 | ||||
| IOC | 0.170 | -0.532** | 0.008 | 0.142 | 0.879** | 0.823** | -0.236 | 0.342 | 1 | |||
| ROC | 0.163 | -0.113 | -0.469* | -0.075 | 0.106 | 0.280 | -0.504* | -0.027 | 0.273 | 1 | ||
| SMBC | 0.217 | 0.141 | 0.178 | 0.085 | 0.164 | 0.149 | 0.238 | -0.032 | 0.163 | -0.051 | 1 | |
| A | -0.075 | -0.316 | 0.540** | 0.347 | 0.210 | 0.042 | 0.394 | 0.578** | -0.122 | -0.774** | 0.074 | 1 |
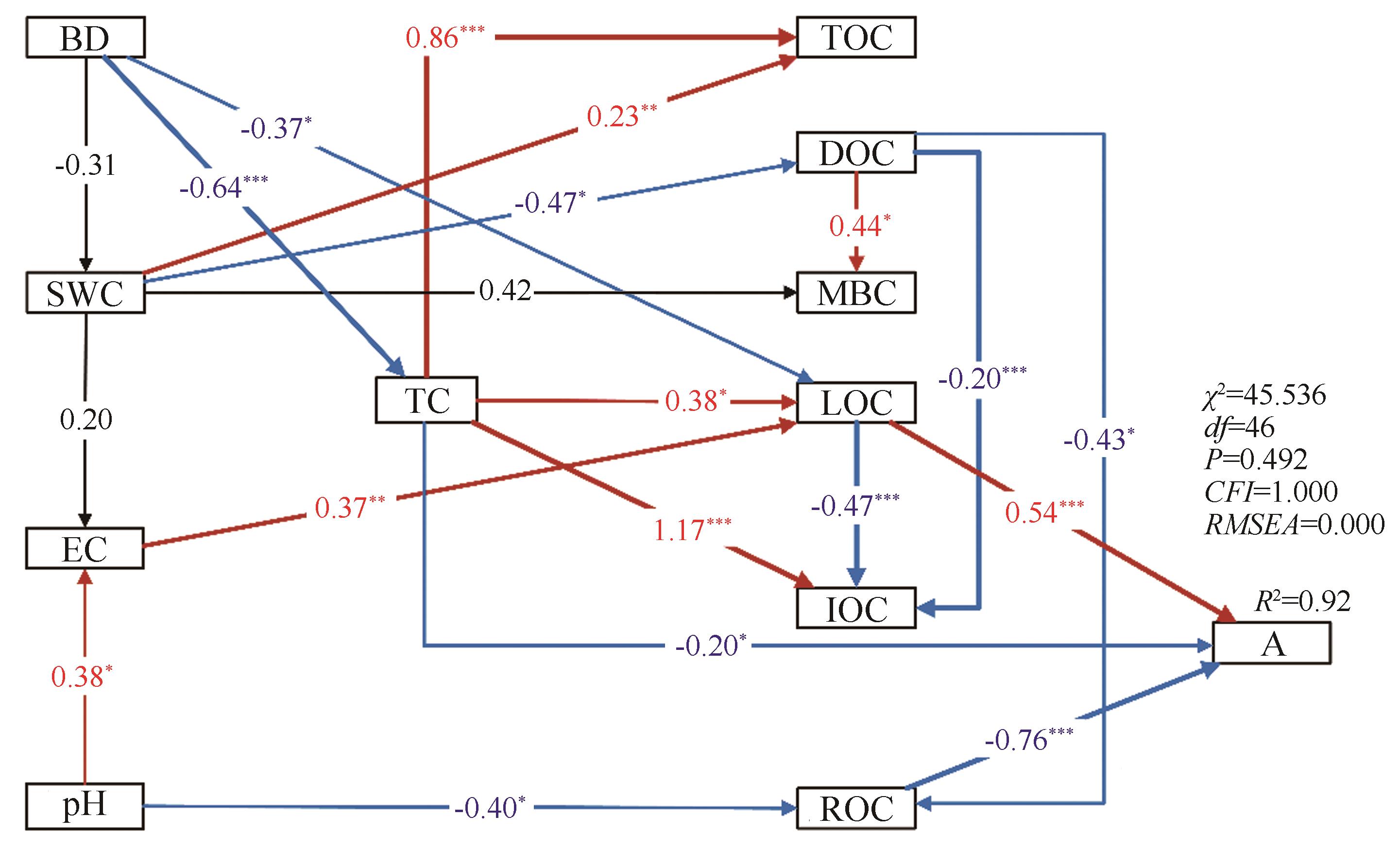
图6 土壤碳库活度影响因子的结构方程模型注:SWC:土壤含水量;BD:土壤容重;pH:土壤pH;EC:电导率;TC:土壤全碳含量;TOC:土壤总有机碳含量;DOC:土壤溶解性有机碳含量;LOC:活性碳;IOC:缓性碳;ROC:惰性碳含量;SMBC:土壤微生物生物量碳;A:土壤碳库活度;χ2表示卡方最小差异值,df表示自由度,P表示显著性,CFI表示拟合优度指数,RMSEA表示近似误差均方根,箭头上的数字表示标准化的路径系数,表明两两之间关联的效应强度;红色箭头和蓝色箭头分别表示正向关系和负向关系,箭头宽度与关系强度成正比。*、**、***分别表示在P<0.05、P<0.01和P<0.001时具有统计学意义的路径
Fig.6 Structural equation model to predict the influence factors of soil carbon pool activity
| [1] | 陈甜.亚热带典型森林凋落物添加对土壤有机碳周转和稳定性影响[D].福州:福建农林大学,2022. |
| [2] | Lal R.Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security[J].Science,2004,304(5677):1623-1627. |
| [3] | Schulze E D, Freibauer A.Carbon unlocked from soils[J].Nature,2005,437(7056):205-206. |
| [4] | 王清奎.碳输入方式对森林土壤碳库和碳循环的影响研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2011,22(4):1075-1081. |
| [5] | Boris S, Wernervon B, Alice B,et al.Resilience of Amazon Forests emerges from plant trait diversity[J].Nature Climate Change,2016,6(11):1032-1036. |
| [6] | 史吉平,张林葆.长期施肥对土壤有机质及生物学特性的影响[J].土壤肥料,1998(3):7-11. |
| [7] | 冼海英,肖波,姚小萌,等.黄土高原生物结皮覆盖下表层土壤有机碳组分对模拟气候暖湿化的响应[J].应用生态学报,2025,36(1):132-140. |
| [8] | Xia S W, Chen J, Schaefer D,et al.Scale-dependent soil macronutrient heterogeneity reveals effects of litterfall in a tropical rainforest[J].Plant and Soil,2015,391(1/2):51-61. |
| [9] | 张娟娟,李星志,王亚楠,等.太阳辐射对陆地生态系统凋落物分解影响的研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2024,35(9):2463-2472. |
| [10] | Huang W, Spohn M.Effects of long-term litter manipulation on soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in a temperate deciduous forest[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2015,83:12-18. |
| [11] | 谭红妍,陈宝瑞,闫瑞瑞,等.草地土壤微生物特性及其对人为干扰响应的研究进展[J].草地学报,2014,22(6):1163-1170. |
| [12] | Hyvonen R, Agren G I, Linder S,et al.The likely impact of elevated CO2,nitrogen deposition,increased temperature and management on carbon sequestration in temperate and boreal forest ecosystems:a literature review[J].New Phytologist,2007,173(3):463-480. |
| [13] | Thiessen S, Gleixner G, Wutzler T,et al.Both priming and temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition depend on microbial biomass:an incubation study[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2013,57:739-748. |
| [14] | Prescott C E, Vesterdal L.Decomposition and transformations along the continuum from litter to soil organic matter in forest soils[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2021,498:119522. |
| [15] | Bolinder M A, Angers D A, Gregorich E G,et al.The response of soil quality indicators to conservation management[J].Canadian Journal of Soil Science,1999,79(1):37-45. |
| [16] | 韩尚君,韩海荣,程小琴,等.改变凋落物输入对不同林龄油松林土壤呼吸的影响[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(11):3576-3587. |
| [17] | 汪金松,赵秀海,张春雨,等.改变C源输入对油松人工林土壤呼吸的影响[J].生态学报,2012,32(9):2768-2777. |
| [18] | Busse M D, Sanchez F G, Ratcliff A W,et al.Soil carbon sequestration and changes in fungal and bacterial biomass following incorporation of forest residues[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2009,41(2):220-227. |
| [19] | Sokol N W, Kuebbing S E, Karlsen-Ayala E,et al.Evidence for the primacy of living root inputs, not root or shoot litter, in forming soil organic carbon[J].New Phytologist,2019,221(1):233-246. |
| [20] | Rasse D P, Rumpel C, Dignac M F.Is soil carbon mostly root carbon?Mechanisms for a specific stabilisation[J].Plant and Soil,2005,269(1/2):341-356. |
| [21] | Xia M, Talhelm A F, Pregitzer K S.Fine roots are the dominant source of recalcitrant plant litter in sugar maple-dominated northern hardwood forests[J].New Phytologist,2015,208(3):715-726. |
| [22] | Veres Z, Kotroczo Z, Fekete I,et al.Soil extracellular enzyme activities are sensitive indicators of detrital inputs and carbon availability[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2015,92:18-23. |
| [23] | Zhang Y, Tang Z, You Y,et al.Differential effects of forest-floor litter and roots on soil organic carbon formation in a temperate oak forest[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2023,180:109017. |
| [24] | Wang Q, Yu Y, He T,et al.Aboveground and belowground litter have equal contributions to soil CO2 emission:an evidence from a 4-year measurement in a subtropical forest[J].Plant and Soil,2017,421(1/2):7-17. |
| [25] | Feng J, He K, Zhang Q,et al.Changes in plant inputs alter soil carbon and microbial communities in forest ecosystems[J].Global Change Biology,2022,28(10):3426-3440. |
| [26] | Wu Q, Wu F, Zhu J,et al.Leaf and root inputs additively contribute to soil organic carbon formation in various forest types[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments,2023,23(3):1135-1145. |
| [27] | Sayer E J.Using experimental manipulation to assess the roles of leaf litter in the functioning of forest ecosystems[J].Biological Reviews,2006,81(1):1-31. |
| [28] | Feng X, Wang S.Plant influences on soil microbial carbon pump efficiency[J].Global Change Biology,2023,29(14):3854-3856. |
| [29] | Ma N, Ji Y, Yue K,et al.Effect of the seasonal precipitation regime on shrub litter decomposition in a subtropical forest[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2023,548:121423. |
| [30] | Craine J M, Ocheltree T W, Nippert J B,et al.Global diversity of drought tolerance and grassland climate-change resilience[J].Nature Climate Change,2013,3(1):63-67. |
| [31] | 李玉强,赵哈林,赵学勇,等.不同强度放牧后自然恢复的沙质草地土壤呼吸、碳平衡与碳储量[J].草业学报,2006,15(5):25-31. |
| [32] | 陈银萍,李晓辉,罗永清,等.科尔沁不同沙地类型植被动态特征及其与凋落物的关系研究[J].草地学报,2021,29(1):114. |
| [33] | 赵珍珍.基于多源数据的科尔沁沙地生态环境变化研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2017. |
| [34] | 赵哈林,苏永中,周瑞莲.我国北方沙区退化植被的恢复机理[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(3):323-328. |
| [35] | Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, Wang S K,et al.Influence of dune stabilization on relationship between plant diversity and productivity in Horqin Sand Land, Northern China[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2012,67(5):1547-1556. |
| [36] | Zhao H L, Okuro T, Li Y L,et al.Effects of human activities and climate changes on plant diversity in Horqin sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia[J].Acta Prataculturae Sinica,2008,17(5):1-8. |
| [37] | Zuo X A, Zhao X Y, Zhao H L,et al.Scale dependent effects of environmental factors on vegetation pattern and composition in Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China[J].Geoderma,2012,173:1-9. |
| [38] | Nadelhoffer K J, Boone R D, Bowden R D,et al.The DIRT experiment:litter and root influences on forest soil organic matter stocks and function[M]//Forest Landscape Dynamics in New England:Ecosystem Structure and Function as a Consequence of 5000 Years of Change.2004. |
| [39] | Belay T, Zhou X, Su B, et al. Labile,recalcitrant, and microbial carbon and nitrogen pools of a tallgrass prairie soil in the US Great Plains subjected to experimental warming and clipping[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2009,41(1):110-116. |
| [40] | Xu G, Chen J, Berninger F,et al.Labile, recalcitrant, microbial carbon and nitrogen and the microbial community composition at two Abies faxoniana forest elevations under elevated temperatures[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2015,91:1-13. |
| [41] | 徐明岗,于荣,孙小凤,等.长期施肥对我国典型土壤活性有机质及碳库管理指数的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2006,12(4):459-465. |
| [42] | 毛馨月,沈育伊,褚俊智,等.模拟氮沉降对中亚热带桉树人工林土壤有机碳组分及碳库管理指数的影响[J].环境科学,2025,46(2):1032-1045. |
| [43] | Gessner M O, Swan C M, Dang C K,et al.Diversity meets decomposition[J].Trends in Ecology and Evolution,2010,25(6):372-380. |
| [44] | Bowden R D, Deem L, Plante A F,et al.Litter input controls on soil carbon in a temperate deciduous forest[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,2014,78:S66-S75. |
| [45] | Dai G, Zhu S, Cai Y,et al.Plant-derived lipids play a crucial role in forest soil carbon accumulation[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2022,168:108645. |
| [46] | Bird J A, Kleber M, Torn M S. 13C and 15N stabilization dynamics in soil organic matter fractions during needle and fine root decomposition[J].Organic Geochemistry,2008,39(4): 465-477. |
| [47] | Sun T, Hobbie S E, Berg B,et al.Contrasting dynamics and trait controls in first-order root compared with leaf litter decomposition[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2018,115(41):10392-10397. |
| [48] | 牛喜妹,李佳南,王平,等.羊草地上不同性状凋落物分解对土壤碳组分的影响[J].环境生态学,2022,4(9):54-60. |
| [49] | 田思惠,柳鑫,金宝成,等.三工河流域琵琶柴群落凋落物对土壤有机碳固定的影响[J].生态学报,2019,39(14):5339-5347. |
| [50] | Zhan J, Li Y L, Cheng L,et al.Effect of N addition and litter manipulation on plant community productivity in the semiarid sandy grassland[J].Ecological Engineering,2024,201:107191. |
| [51] | 周莉,李保国,周广胜.土壤有机碳的主导影响因子及其研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2005,20(1):99-105. |
| [52] | Zhou G, Wang Y, Jiang Y,et al.Conversion of terrestrial ecosystems and carbon cycling[J].Acta Phytoecologica Sinica,2002,26(2):250-254. |
| [53] | Lu Y H, Watanabe A, Kimura M.Carbon dynamics of rhizodeposits, root-and shoot-residues in a rice soil[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2003,35(9):1223-1230. |
| [54] | Gude A, Kandeler E, Gleixner G.Input related microbial carbon dynamic of soil organic matter in particle size fractions[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2012,47:209-219. |
| [55] | 彭思瑞,张慧玲,孙兆林,等.长期凋落物去除对亚热带杉木林土壤有机碳及其组分的影响[J].植物生态学报,2024,48(8):1078-1088. |
| [56] | Bailey V L, Pries C H, Lajtha K.What do we know about soil carbon destabilization?[J].Environmental Research Letters,2019,14(8):083004. |
| [57] | 刘红梅,张海芳,赵建宁,等.氮添加对贝加尔针茅草原土壤活性有机碳和碳库管理指数的影响[J].草业学报,2020,29(8):18-26. |
| [58] | 詹瑾,丛安琪,李玉霖,等.长期氮沉降和地上凋落物处理对半干旱区沙质草地表层土壤碳氮组分的影响[J].水土保持学报,2023,37(4):227-234. |
| [59] | Sequeira C H, Wills S A, Seybold C A,et al.Predicting soil bulk density for incomplete databases[J].Geoderma,2014,213:64-73. |
| [60] | 彭璞,贾剑波,陆佳,等.生草栽培对油茶林土壤肥力及活性碳组分的影响[J].应用生态学报,2025,36(2):504-512. |
| [61] | 张亚杰,邓少虹,李伏生,等.喀斯特地区春玉米套作夏大豆下作物产量和农田碳贮量对有机肥与化肥配施的响应[J].南方农业学报,2015,46(9):1584-1590. |
| [62] | 张一清,王文娥,胡明宇,等.容重及含水率对土壤电导率的影响研究[J].干旱地区农业研究,2022,40(3):162-169. |
| [63] | 苏永中,赵哈林,张铜会.几种灌木、半灌木对沙地土壤肥力影响机制的研究[J].应用生态学报,2002,13(7):802-806. |
| [64] | 解雪峰,刘艳英,阮妤楠,等.天目山森林土壤碳组分沿海拔梯度变化特征及影响因素[J].环境科学,2025:1-11.. |
| [65] | Xing G, Wang X, Jiang Y,et al.Variations and influencing factors of soil organic carbon during the tropical forest succession from plantation to secondary and old-growth forest[J].Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution,2023,10. |
| [1] | 朱远忠, 黄文达, 于海伦, 何远政, 王怀海, 史尚彬, 寇志强. 科尔沁沙质草地不同水热梯度植物群落叶功能性状特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 143-150. |
| [2] | 包天玲, 刘继亮, 苑峰, 李寅龙, 贾振宇, 潘成臣. 科尔沁沙质草地植物群落对增温的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 151-160. |
| [3] | 张晶, 左小安, 吕朋. 土壤水分和养分对沙质草地优势植物叶片氮回收效率的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 161-169. |
| [4] | 王怀海, 黄文达, 何远政, 牛亚毅, 朱远忠. 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 274-281. |
| [5] | 赵啸龙, 谢玉鸿, 马旭君, 王少昆. 科尔沁沙质草地不同恢复年限草本层群落结构及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [6] | 王明明, 刘新平, 李玉霖, 车力木格, 罗永清, 孙珊珊, 魏静. 不同植被盖度沙质草地生长季土壤水分动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(5): 54-61. |
| [7] | 熊炳桥, 赵丽娅, 高丹丹. 围封对退化沙质草地植物群落的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 324-328. |
| [8] | 张建鹏, 李玉强, 赵学勇, 张铜会, 佘倩楠, 刘敏, 魏水莲. 围封对沙漠化草地土壤理化性质和固碳潜力恢复的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3): 491-499. |
| [9] | 孙殿超, 李玉霖, 赵学勇, 罗亚勇, 毕京东. 围封和放牧对科尔沁沙质草地净生态系统碳交换量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 93-102. |
| [10] | 毛伟, 李玉霖, 孙殿超, 王少昆. 养分和水分添加后沙质草地不同功能群植物地上生物量变化对群落生产力的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 27-33. |
| [11] | 孙殿超, 李玉霖, 赵学勇, 毛伟, 岳祥飞. 放牧及围封对科尔沁沙质草地土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(6): 1620-1627. |
| [12] | 王少昆, 赵学勇, 黄文达, 李玉强, 岳祥飞, 张腊梅. 科尔沁沙质草地纤维素分解菌的筛选、鉴定及其分解能力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(6): 1584-1591. |
| [13] | 李玉霖, 陈 静, 崔 夺, 王新源, 赵学勇. 不同湿度条件下模拟增温对科尔沁沙质草地土壤氮矿化的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(6): 1775-1781. |
| [14] | 胡尔查1,2, 王晓江1, 张文军1, 刘永宏1, 海 龙1, 张 雷1, 苏楞高娃3. 基于ALOS数据的浑善达克沙质草地风蚀坑空间格局及特征分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(3): 662-667. |
| [15] | 左小安, 赵学勇, 张铜会, 王少昆, 罗亚勇, 周 欣. 沙质草地放牧和封育下物种丰富度和生物量关系的季节变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 501-507. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
