中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 274-281.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00135
• • 上一篇
王怀海1,2( ), 黄文达1(
), 黄文达1( ), 何远政1,2, 牛亚毅1,2, 朱远忠1,2
), 何远政1,2, 牛亚毅1,2, 朱远忠1,2
收稿日期:2021-07-02
修回日期:2021-10-29
出版日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
黄文达
作者简介:黄文达(E-mail: huangwenda2008@163.com)基金资助:
Huaihai Wang1,2( ), Wenda Huang1(
), Wenda Huang1( ), Yuanzheng He1,2, Yayi Niu1,2, Yuanzhong Zhu1,2
), Yuanzheng He1,2, Yayi Niu1,2, Yuanzhong Zhu1,2
Received:2021-07-02
Revised:2021-10-29
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
Wenda Huang
摘要:
通过模拟气候变化,探究短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮及酶活性的影响,揭示沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性对短期气候变化的响应规律。结果表明:(1)短期增温和降水减少对土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性均产生显著影响。(2)在自然温度下,与自然降水相比,降水减少40%时土壤微生物量碳(MBC)和微生物氮(MBN)含量最高,增幅分别为87.9%和98.8%;降水减少60%时土壤碱性蛋白酶(S-ALPT)活性最低,降幅达32.8%。(3)在增温条件下,与自然降水相比,降水减少40%时土壤MBC和MBN含量最低,降幅分别为25.67%和48.16%,土壤脲酶(S-UE)活性最高,增幅20.42%。(4)土壤pH与3种土壤酶活性正相关,与土壤微生物量碳氮负相关。土壤微生物量碳氮与土壤纤维素酶(S-CL)活性负相关,与S-UE、S-ALPT活性正相关。
中图分类号:
王怀海, 黄文达, 何远政, 牛亚毅, 朱远忠. 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 274-281.
Huaihai Wang, Wenda Huang, Yuanzheng He, Yayi Niu, Yuanzhong Zhu. Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and enzyme activity in sandy grassland[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 274-281.
| 处理 | 土层 /cm | 土壤机械组成/% | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2—1 mm | 1—0.5 mm | 0.5—0.25 mm | 0.25—0.1 mm | 0.1—0.05 mm | <0.05 mm | |||
| T0×W0 | 0—10 | 0.21 ±0.14 | 0.34±0.11 | 28.47±1.22 | 55.68±2.85 | 10.14±1.69a | 4.78±1.38a | 8.04±0.25a |
| 10—20 | 0.19±0.04a | 0.36±0.07a | 28.44±1.16a | 55.92±3.58 | 10.32±2.90 | 4.50±1.06a | 7.78±0.22 | |
| T0×W20 | 0—10 | 0.21 ±0.06 | 0.38±0.92 | 27.30±0.91 | 56.58±0.93 | 12.31±1.39b | 3.26±0.87b | 7.74±0.27b |
| 10—20 | 0.06±0.01b | 0.25±0.05bc | 26.86±0.63b | 57.59±2.33 | 12.09±2.19 | 3.15±0.61b | 8.06±0.44 | |
| T0×W40 | 0—10 | 0.19±0.03 | 0.37±0.11 | 27.29±1.49 | 57.28±1.68 | 10.51±1.00ac | 4.25±0.65abc | 7.84±0.15ab |
| 10—20 | 0.07±0.03b | 0.31±0.07ac | 27.68±0.75abc | 57.53±1.67 | 11.21±0.73 | 3.33±0.39b | 8.13±0.34 | |
| T0×W60 | 0—10 | 0.20±0.05 | 0.42±0.10 | 27.83±1.63 | 56.21±1.25 | 10.58±1.11abc | 4.85±1.02ac | 7.69±0.11bc |
| 10—20 | 0.05±0.02b | 0.31±0.09ac | 28.61±1.47ac | 56.29±1.82 | 10.07±1.45 | 4.95±0.76a | 8.08±0.25 | |
| T×W0 | 0—10 | 0.23±0.04a | 0.40±0.08a | 28.77±2.14a | 54.60±2.25 | 11.26±0.30a | 4.38±0.29a | 7.90±0.19 |
| 10—20 | 0.66±0.03 | 0.29±0.07 | 29.06±1.45a | 55.77±1.59 | 10.77±0.90 | 3.92±0.14a | 8.21±0.29 | |
| T×W20 | 0—10 | 0.39±0.08ac | 0.33±0.09ac | 26.83±3.21ac | 54.69±2.43 | 13.20±1.07ac | 4.21±1.13a | 7.95±0.26 |
| 10—20 | 0.18±0.05 | 0.32±0.08 | 26.61±2.44ac | 56.15±1.48 | 12.78±1.99 | 3.78±0.71a | 8.19±0.33 | |
| T×W40 | 0—10 | 0.47±0.24bc | 0.25±0.51bc | 24.50±0.38bc | 54.55±4.09 | 11.80±2.27ac | 8.28±2.06b | 7.98±0.36 |
| 10—20 | 0.12±0.07 | 0.30±0.06 | 26.63±1.55ac | 54.78±2.86 | 12.65±2.54 | 5.12±0.64b | 8.20±0.32 | |
| T×W60 | 0—10 | 0.34±0.06abc | 0.31±0.04abc | 26.59±1.77abc | 54.52±2.06 | 14.11±3.08bc | 3.94±0.51a | 8.01±0.30 |
| 10—20 | 0.17±0.04 | 0.25±0.03 | 26.46±1.91bc | 56.38±1.16 | 13.12±2.09 | 3.28±0.31a | 8.16±0.40 | |
表1 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤理化性质的影响
Table 1 Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil physical and chemical properties in sandy grassland
| 处理 | 土层 /cm | 土壤机械组成/% | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2—1 mm | 1—0.5 mm | 0.5—0.25 mm | 0.25—0.1 mm | 0.1—0.05 mm | <0.05 mm | |||
| T0×W0 | 0—10 | 0.21 ±0.14 | 0.34±0.11 | 28.47±1.22 | 55.68±2.85 | 10.14±1.69a | 4.78±1.38a | 8.04±0.25a |
| 10—20 | 0.19±0.04a | 0.36±0.07a | 28.44±1.16a | 55.92±3.58 | 10.32±2.90 | 4.50±1.06a | 7.78±0.22 | |
| T0×W20 | 0—10 | 0.21 ±0.06 | 0.38±0.92 | 27.30±0.91 | 56.58±0.93 | 12.31±1.39b | 3.26±0.87b | 7.74±0.27b |
| 10—20 | 0.06±0.01b | 0.25±0.05bc | 26.86±0.63b | 57.59±2.33 | 12.09±2.19 | 3.15±0.61b | 8.06±0.44 | |
| T0×W40 | 0—10 | 0.19±0.03 | 0.37±0.11 | 27.29±1.49 | 57.28±1.68 | 10.51±1.00ac | 4.25±0.65abc | 7.84±0.15ab |
| 10—20 | 0.07±0.03b | 0.31±0.07ac | 27.68±0.75abc | 57.53±1.67 | 11.21±0.73 | 3.33±0.39b | 8.13±0.34 | |
| T0×W60 | 0—10 | 0.20±0.05 | 0.42±0.10 | 27.83±1.63 | 56.21±1.25 | 10.58±1.11abc | 4.85±1.02ac | 7.69±0.11bc |
| 10—20 | 0.05±0.02b | 0.31±0.09ac | 28.61±1.47ac | 56.29±1.82 | 10.07±1.45 | 4.95±0.76a | 8.08±0.25 | |
| T×W0 | 0—10 | 0.23±0.04a | 0.40±0.08a | 28.77±2.14a | 54.60±2.25 | 11.26±0.30a | 4.38±0.29a | 7.90±0.19 |
| 10—20 | 0.66±0.03 | 0.29±0.07 | 29.06±1.45a | 55.77±1.59 | 10.77±0.90 | 3.92±0.14a | 8.21±0.29 | |
| T×W20 | 0—10 | 0.39±0.08ac | 0.33±0.09ac | 26.83±3.21ac | 54.69±2.43 | 13.20±1.07ac | 4.21±1.13a | 7.95±0.26 |
| 10—20 | 0.18±0.05 | 0.32±0.08 | 26.61±2.44ac | 56.15±1.48 | 12.78±1.99 | 3.78±0.71a | 8.19±0.33 | |
| T×W40 | 0—10 | 0.47±0.24bc | 0.25±0.51bc | 24.50±0.38bc | 54.55±4.09 | 11.80±2.27ac | 8.28±2.06b | 7.98±0.36 |
| 10—20 | 0.12±0.07 | 0.30±0.06 | 26.63±1.55ac | 54.78±2.86 | 12.65±2.54 | 5.12±0.64b | 8.20±0.32 | |
| T×W60 | 0—10 | 0.34±0.06abc | 0.31±0.04abc | 26.59±1.77abc | 54.52±2.06 | 14.11±3.08bc | 3.94±0.51a | 8.01±0.30 |
| 10—20 | 0.17±0.04 | 0.25±0.03 | 26.46±1.91bc | 56.38±1.16 | 13.12±2.09 | 3.28±0.31a | 8.16±0.40 | |
| 处理 | df | MBC/(mg·kg-1) | MBN/(mg·kg-1) | MBC/MBN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| T | 1 | 9.040 | 0.008 | 5.033 | 0.039 | 16.713 | 0.001 |
| W | 3 | 1.597 | 0.229 | 6.398 | 0.005 | 4.576 | 0.017 |
| T×W | 3 | 13.521 | <0.001 | 14.336 | <0.001 | 0.627 | 0.068 |
表2 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物生物量碳MBC、微生物生物量氮MBN和MBC/MBN的影响
Table 2 The effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil MBC, MBN and MBC/MBN in sandy grassland
| 处理 | df | MBC/(mg·kg-1) | MBN/(mg·kg-1) | MBC/MBN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| T | 1 | 9.040 | 0.008 | 5.033 | 0.039 | 16.713 | 0.001 |
| W | 3 | 1.597 | 0.229 | 6.398 | 0.005 | 4.576 | 0.017 |
| T×W | 3 | 13.521 | <0.001 | 14.336 | <0.001 | 0.627 | 0.068 |
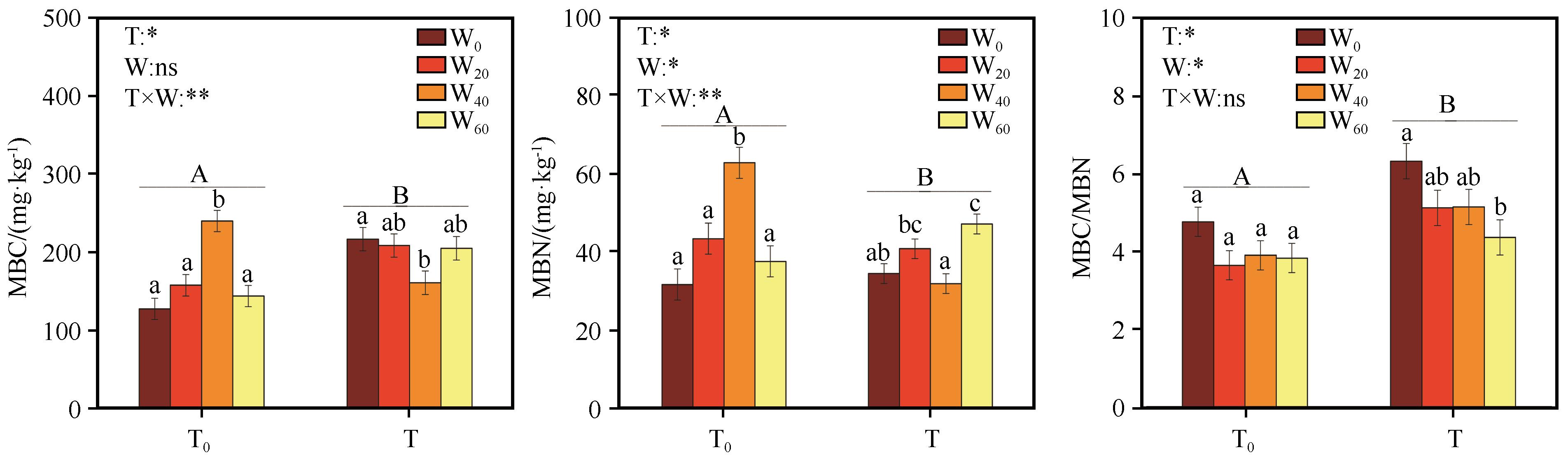
图2 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮的影响(T0表示自然温度;T表示增温;W0、W20、W40、W60分别表示降水减少0、20%、40%、60%。不同大写字母表示相同降水减少条件下增温处理之间的差异显著,小写字母表示相同温度条件下降水减少处理之间的差异显著,P<0.05;*,处理效应显著,P<0.05;**,处理效应极显著,P<0.01;ns,处理效应不显著)
Fig.2 Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil MBC, MBN and MBC/MBN in sandy grassland (T0, natural temperature; T, warming; W0, W20, W40 and W60, precipitation decreased by 0, 20%, 40% and 60%, Different capital letters indicate a significant difference between temperature treatments at the same precipitation conditions, and small letters show a significant differencebetween precipitation reduction treatments at the same temperature conditions, P<0.05)
| 处理 | df | S-UE/(U·g-1) | S-CL/(U·g-1) | S-ALPT/(U·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||||
| T | 1 | 13.981 | 0.001 | 7.539 | 0.001 | 8.205 | 0.007 | ||
| W | 3 | 9.972 | <0.001 | 0.701 | 0.558 | 13.309 | <0.001 | ||
| T×W | 3 | 1.962 | 0.139 | 1.231 | 0.315 | 16.432 | <0.001 | ||
表3 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤脲酶S-UE、纤维素酶S-CL和碱性蛋白酶S-ALPT的影响
Table 3 The effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on S-UE, S-CL and S-ALPT in sandy grassland
| 处理 | df | S-UE/(U·g-1) | S-CL/(U·g-1) | S-ALPT/(U·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||||
| T | 1 | 13.981 | 0.001 | 7.539 | 0.001 | 8.205 | 0.007 | ||
| W | 3 | 9.972 | <0.001 | 0.701 | 0.558 | 13.309 | <0.001 | ||
| T×W | 3 | 1.962 | 0.139 | 1.231 | 0.315 | 16.432 | <0.001 | ||
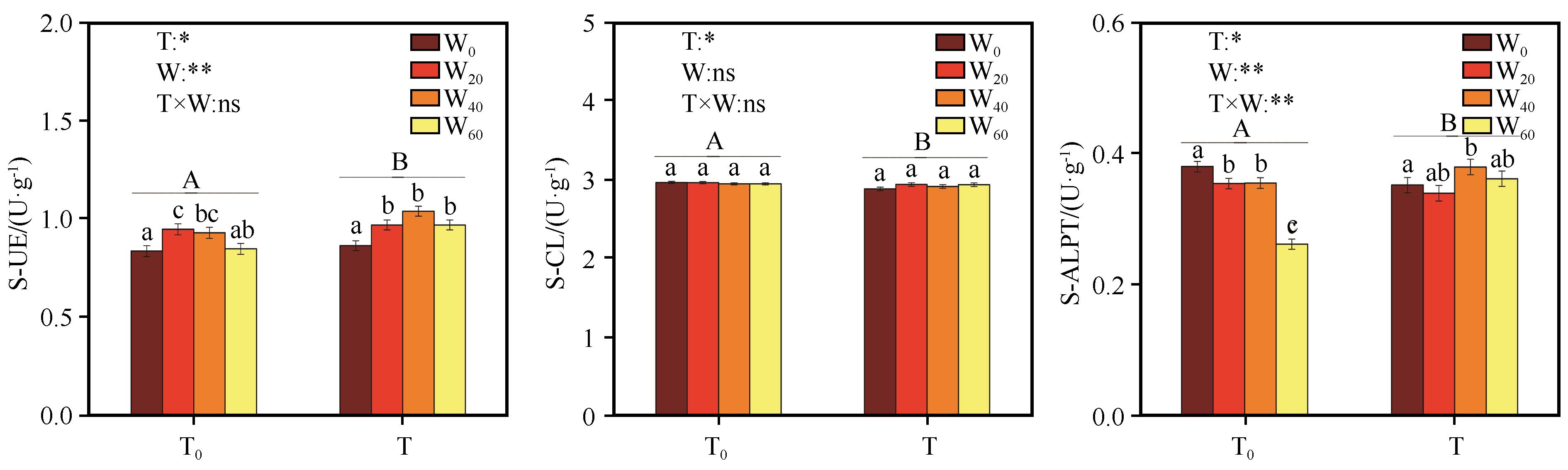
图3 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤酶活性的影响(T0表示自然温度;T表示增温;W0、W20、W40、W60分别表示降水减少0、20%、40%、60%。不同大写字母表示相同降水减少条件下增温处理之间的差异显著,小写字母表示相同温度条件下降水减少处理之间的差异显著,P<0.05;*,处理效应显著,P<0.05;**,处理效应极显著,P<0.01;ns,处理效应不显著)
Fig.3 Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil enzyme activities in sandy grassland (T0, natural temperature; T, warming; W0, W20, W40 and W60, precipitation decreased by 0, 20%, 40% and 60%, Different capital letters indicate a significant difference between temperature treatments at the same precipitation conditions, and small letters show a significant differencebetween precipitation reduction treatments at the same temperature conditions, P<0.05)
| 项目 | pH | MBC | MBN | S-UE | S-CL | S-ALPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC | -0.436* | |||||
| MBN | -0.194 | 0.155 | ||||
| S-UE | 0.252 | 0.099 | 0.146 | |||
| S-CL | 0.226 | -0.067 | -0.066 | -0.098 | ||
| S-ALPT | 0.143 | 0.065 | 0.383* | 0.182 | -0.230 | |
| MBC/MBN | -0.174 | 0.414* | -0.522** | -0.344 | -0.003 | -0.194 |
表4 土壤微生物生物量和酶活性之间的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between soil microbial biomass and soil enzyme activity
| 项目 | pH | MBC | MBN | S-UE | S-CL | S-ALPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC | -0.436* | |||||
| MBN | -0.194 | 0.155 | ||||
| S-UE | 0.252 | 0.099 | 0.146 | |||
| S-CL | 0.226 | -0.067 | -0.066 | -0.098 | ||
| S-ALPT | 0.143 | 0.065 | 0.383* | 0.182 | -0.230 | |
| MBC/MBN | -0.174 | 0.414* | -0.522** | -0.344 | -0.003 | -0.194 |
| 1 | Evgenia B, Yakov K.Active microorganisms in soil:critical review of estimation criteria and approaches[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2013,67:192-211. |
| 2 | 许淼平,任成杰,张伟,等.土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷与土壤酶化学计量对气候变化的响应机制[J].应用生态学报,2018,29(7):2445-2454. |
| 3 | Xiao W, Chen X, Jing X,et al.A meta-analysis of soil extracellular enzyme activities in response to global change[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2018,123:21-32. |
| 4 | 刘放,吴明辉,魏培洁,等.疏勒河源高寒草甸土壤微生物生物量碳氮变化特征[J].生态学报,2020,40(18):6416-6426. |
| 5 | 曾全超,李鑫,董扬红,等.黄土高原不同乔木林土壤微生物量碳氮和溶解性碳氮的特征[J].生态学报,2015,35(11):3598-3605. |
| 6 | 吴晓玲,张世熔,蒲玉琳,等.川西平原土壤微生物生物量碳氮磷含量特征及其影响因素分析[J].中国生态农业学报,2019,27(10):1607-1616. |
| 7 | 赵玉涛,韩士杰,李雪峰,等.模拟氮沉降增加对土壤微生物量的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2009(1):49-51. |
| 8 | 许华,何明珠,唐亮,等.荒漠土壤微生物量碳、氮变化对降水的响应[J].生态学报,2020,40(4):1295-1304. |
| 9 | Liu W X, Allison S D, Xia J Y,et al.Precipitation regime drives warming responses of microbial biomass and activity in temperate steppe soils[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2016,52:469-477. |
| 10 | 文小琴,舒英格,何欢.喀斯特山区土地不同利用方式的土壤养分及微生物特征[J].西南农业学报,2018,6:1227-1233. |
| 11 | 田耀武,和武宇恒,翟淑涵,等.陶湾流域草本植物土壤及土壤微生物量碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J].草地学报,2019,27(6):1643-1650. |
| 12 | Xu Z W, Yu G R, Zhang X Y,et al.Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the North-South Transect in eastern China (NSTEC)[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2017,104:152-163. |
| 13 | 江淼华,倪梦颖,周嘉聪,等.增温和降雨减少对杉木幼林土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(11):3210-3219. |
| 14 | Xu H W, Qu Q, Chen Y H,et al.Responses of soil enzyme activity and soil organic carbon stability over time after cropland abandonment in different vegetation zones of the Loess Plateau of China[J].Catena,2021,196:104812. |
| 15 | 解丽娜,贡璐,朱美玲,等.塔里木盆地南缘绿洲土壤酶活性与理化因子相关性[J].环境科学研究,2014(11):1306-1313. |
| 16 | 周际海,郜茹茹,魏倩,等.旱地红壤不同土地利用方式对土壤酶活性及微生物多样性的影响差异[J].水土保持学报,2020,34(1):327-332. |
| 17 | 莫雪,陈斐杰,游冲,等.黄河三角洲不同植物群落土壤酶活性特征及影响因子分析[J].环境科学,2020,41(2):895-904. |
| 18 | 钟泽坤,杨改河,任成杰,等.黄土丘陵区撂荒农田土壤酶活性及酶化学计量变化特征[J].环境科学,2021(1):411-421. |
| 19 | Zhang Y L, Chen L J, Chen X H,et al.Response of soil enzyme activity to long-term restoration of desertified land[J].Catena,2015,133:64-70. |
| 20 | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.Climate Change 2013:The Physical Science Basis[M].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press: 2014-06-15. |
| 21 | 卢静,刘金波,盛荣,等.短期落干对水稻反硝化微生物丰度和N2O释放的影响[J].应用生态学报,2014,10:2879-2884. |
| 22 | Daniel G, Rainer G J, Bernard L.Potential soil enzyme activities are decoupled from microbial activity in dry residue-amended soil[J].Pedobiologia-International Journal of Soil Biology,2012,55(5):253-261. |
| 23 | Tang S R, Cheng W G, Hu R G,et al.Five-year soil warming changes soil C and N dynamics in a single rice paddy field in Japan[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,756:143845. |
| 24 | Li G L, Kim S J, Han S H,et al.Precipitation affects soil microbial and extracellular enzymatic responses to warming[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2018,120:212-221. |
| 25 | 王涛.沙漠化研究进展[J].中国科学院院刊,2009,24:290-296. |
| 26 | 赵哈林,赵学勇,张铜会.科尔沁沙地沙漠化过程及其恢复机理[M].北京:海洋出版社,2003. |
| 27 | 陈新月,姚晓东,曾文静,等.北方农牧交错带草地土壤微生物量碳氮空间格局及驱动因素[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(2):250-260. |
| 28 | 王丽娜,罗久富,杨梅香,等.氮添加对退化高寒草地土壤微生物量碳氮的影响[J].草业学报,2019,28(7):38-48. |
| 29 | 李磊,王岩,胡姝娅,等.草甸草原土壤碳/氮矿化潜力及土壤微生物水分敏感性对极端干旱的响应[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(3):814-820. |
| 30 | 许华,何明珠,孙岩.干旱荒漠区土壤酶活性对降水调控的响应[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2018,54(6):790-797. |
| 31 | Li Y Q, Qing Y X, Lyu M K,et al.Effects of artificial warming on different soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools in a subtropical plantation[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2018,124:161-167. |
| 32 | Lin L, Zhu B, Chen C R,et al.Precipitation overrides warming in mediating soil nitrogen pools in an alpine grassland ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau [J].Scientific Reports,2016,6:31438. |
| 33 | 关松荫.土壤酶及其研究法[M].北京:农业出版社,1986. |
| 34 | Suseela V, Tharayil N, Xing B S,et al.Warming alters potential enzyme activity but precipitation regulates chemical transformations in grass litter exposed to simulated climatic changes[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2014,75:102-112. |
| 35 | Hueso S, Hernández T, García C.Resistance and resilience of the soil microbial biomass to severe drought in semiarid soils:the importance of organic amendments[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2011,50:27-36. |
| 36 | Li Y Y, Wang X X, Dong S K,et al.Effects of short-term and long-term warming on soil nutrients,microbial biomass and enzyme activities in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2014,76:140-142. |
| 37 | Yao X D, Zhang N L, Zeng H,et al.Effects of soil depth and plant-soil interaction on microbial community in temperate grasslands of northern China [J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,630:96-102. |
| 38 | Rousk J, Brookes P C, Bååth E.The microbial PLFA composition as affected by pH in an arable soil[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2010,42(3):516-520. |
| 39 | Bååth E, Anderson T H.Comparison of soil fungal/bacterial ratios in a pH gradient using physiological and PLFA-based techniques[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2003,35(7):955-963. |
| 40 | Keiblinger K M, Hall E K, Wanek W,et al.The effect of resource quantity and resource stoichiometry onmicrobial carbon-use-efficiency[J].FEMS Microbiology Ecology,2010,73(3):430-440. |
| 41 | Manzoni S, Taylor P, Richter A,et al.Environmentaland stoichiometric controlson microbial carbon-use efficiencyinsoils[J].New Phytologist,2012,196(1):79-91. |
| 42 | 王涵,王果,黄颖颖,等.pH变化对酸性土壤酶活性的影响[J].生态环境,2008,17(6):2401-2406. |
| 43 | 王杰,李刚,修伟明,等.氮素和水分对贝加尔针茅草原土壤酶活性和微生物量碳氮的影响[J].农业资源与环境学报,2014,31(3):237-245. |
| 44 | Cenini V L, Fornara D A, McMullan G,et al.Linkages between extracellular enzyme activities and the carbon and nitrogen content of grassland soils[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2016,96:198-206. |
| [1] | 赵啸龙, 谢玉鸿, 马旭君, 王少昆. 科尔沁沙质草地不同恢复年限草本层群落结构及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [2] | 苏天燕, 刘子涵, 丛安琪, 毛伟, 杨秋. 地下水埋深对半干旱区典型植物群落土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 185-194. |
| [3] | 韩丹, 李玉霖, 杨红玲, 宁志英, 张子谦. 模拟增温和改变降雨频率对干旱半干旱区土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 100-108. |
| [4] | 王明明, 刘新平, 李玉霖, 车力木格, 罗永清, 孙珊珊, 魏静. 不同植被盖度沙质草地生长季土壤水分动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(5): 54-61. |
| [5] | 刘艳梅, 杨航宇, 贾荣亮, 李宜轩. 人为踩踏生物土壤结皮对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(4): 54-63. |
| [6] | 李成阳, 薛娴, 赖炽敏, 尤全刚, 彭飞, 张文娟. 青藏高原退化高寒草甸生长季承载力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(6): 1330-1338. |
| [7] | 熊炳桥, 赵丽娅, 高丹丹. 围封对退化沙质草地植物群落的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 324-328. |
| [8] | 张建鹏, 李玉强, 赵学勇, 张铜会, 佘倩楠, 刘敏, 魏水莲. 围封对沙漠化草地土壤理化性质和固碳潜力恢复的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3): 491-499. |
| [9] | 毛伟, 李玉霖, 孙殿超, 王少昆. 养分和水分添加后沙质草地不同功能群植物地上生物量变化对群落生产力的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 27-33. |
| [10] | 陈静, 李玉霖, 冯静, 苏娜, 赵学勇. 温度和水分对科尔沁沙质草地土壤氮矿化的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 103-110. |
| [11] | 孙殿超, 李玉霖, 赵学勇, 罗亚勇, 毕京东. 围封和放牧对科尔沁沙质草地净生态系统碳交换量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 93-102. |
| [12] | 王少昆, 赵学勇, 黄文达, 李玉强, 岳祥飞, 张腊梅. 科尔沁沙质草地纤维素分解菌的筛选、鉴定及其分解能力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(6): 1584-1591. |
| [13] | 孙殿超, 李玉霖, 赵学勇, 毛伟, 岳祥飞. 放牧及围封对科尔沁沙质草地土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(6): 1620-1627. |
| [14] | 王永福, 赵学勇, 王少昆, 包哈森高娃. 科尔沁沙地两种固沙灌木林地土壤理化性质和酶活性比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(4): 937-941. |
| [15] | 彭飞, 薛娴, 尤全刚. 模拟增温对生态系统碳循环影响研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(5): 1285-1292. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
