中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 289-300.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00126
收稿日期:2025-04-14
修回日期:2025-06-16
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-27
通讯作者:
陈克龙
作者简介:王明宇(2001—),男,江西抚州人,硕士研究生,主要从事自然地理与生态环境过程的研究。E-mail: king_qhnu@163.com
基金资助:
Mingyu Wang1( ), Chengyong Wu2,3, Kelong Chen1,2(
), Chengyong Wu2,3, Kelong Chen1,2( )
)
Received:2025-04-14
Revised:2025-06-16
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-27
Contact:
Kelong Chen
摘要:
为探究青海湖流域植被绿度时空变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应,基于2000—2023年MODIS归一化植被指数(NDVI)数据、气象数据,通过Sen+Mann-Kendall趋势分析、Hurst指数、相关分析以及残差分析等方法,分析青海湖流域植被绿度的时空变化规律和未来发展趋势,并评估气候变化与人类活动对植被绿度影响程度。结果显示:(1)2000—2023年青海湖流域NDVI年均值为0.45,时间上呈显著上升趋势,年变化速率为0.0022,改善区占研究区的86.22%,呈显著上升趋势,空间异质性明显。(2)植被绿度总体变化相对稳定,变异系数为0~1.7,平均值为0.08,展现出积极发展态势。(3)青海湖流域植被绿度与降水和气温均正相关,且与降水(r=0.196,P<0.05)的相关性强于气温(r=0.07,P<0.05),85.5%区域以降水驱动为主。(4)青海湖流域63.6%区域植被绿度受气候变化和人类活动双重影响,其中人类活动的相对贡献率为85.02%,
中图分类号:
王明宇, 吴成永, 陈克龙. 青海湖流域植被绿度时空变化及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 289-300.
Mingyu Wang, Chengyong Wu, Kelong Chen. Spatiotemporal changes of vegetation greenness and their influencing factors in the Qinghai Lake Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 289-300.
| 变异系数 | Cv<0.05 | 0.05≤Cv<0.10 | 0.10≤Cv<0.15 | 0.15≤Cv<0.20 | Cv≥0.20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稳定性 | 低波动 | 中低波动 | 中波动 | 中高波动 | 高波动 |
表1 植被绿度稳定性变异系数判定标准
Table 1 Criteria for determining the coefficient of variation of vegetation greenness
| 变异系数 | Cv<0.05 | 0.05≤Cv<0.10 | 0.10≤Cv<0.15 | 0.15≤Cv<0.20 | Cv≥0.20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稳定性 | 低波动 | 中低波动 | 中波动 | 中高波动 | 高波动 |
| Slope(NDVIobs) | 驱动因素 | 驱动因素判定标准 | 驱动因素的贡献率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope(NDVICC) | Slope(NDVIHA) | 气候变化 | 人类活动 | ||
| >0 | CC&HA | >0 | >0 | ||
| CC | >0 | <0 | 100 | 0 | |
| HA | <0 | >0 | 0 | 100 | |
| <0 | CC&HA | <0 | <0 | ||
| CC | <0 | >0 | 100 | 0 | |
| HA | >0 | <0 | 0 | 100 | |
表2 植被绿度驱动因素判定标准及贡献率
Table 2 Criteria and contribution rates of the driving factors for vegetation greenness
| Slope(NDVIobs) | 驱动因素 | 驱动因素判定标准 | 驱动因素的贡献率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope(NDVICC) | Slope(NDVIHA) | 气候变化 | 人类活动 | ||
| >0 | CC&HA | >0 | >0 | ||
| CC | >0 | <0 | 100 | 0 | |
| HA | <0 | >0 | 0 | 100 | |
| <0 | CC&HA | <0 | <0 | ||
| CC | <0 | >0 | 100 | 0 | |
| HA | >0 | <0 | 0 | 100 | |
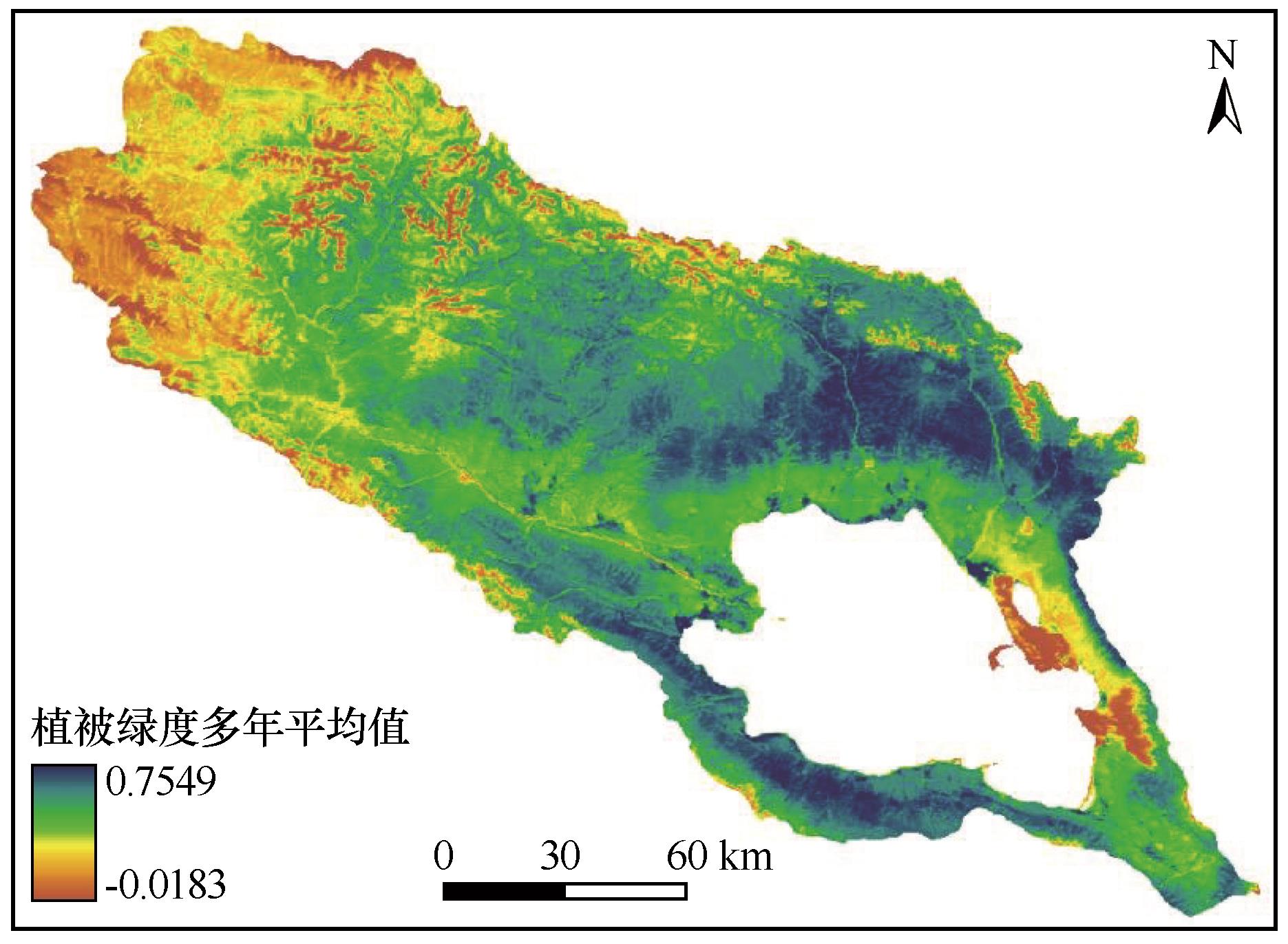
图3 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度多年平均值空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.3 Spatial distribution of the multi-year average vegetation greenness in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
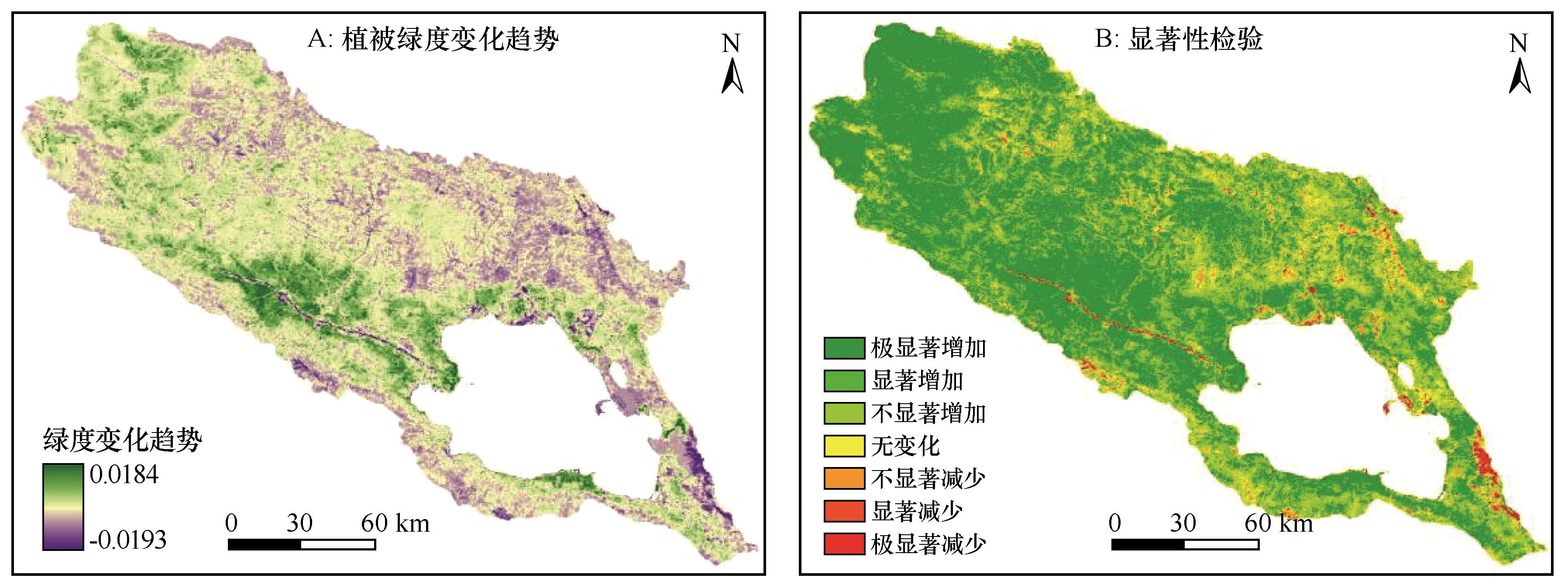
图4 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度变化趋势及显著性检验空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.4 Spatial distribution of the vegetation greenness change trend and its significance test in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
| 变化趋势Slope | 显著性水平P | 变化趋势 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.0005 | <0.01 | 极显著减少 | 3 957 | 0.97 |
| 0.01~0.05 | 显著减少 | 55 | 0.01 | |
| ≥0.05 | 不显著减少 | 11 622 | 3 | |
| -0.005~0.0005 | ≥0.05 | 无变化 | 39 226 | 9.8 |
| >0.0005 | ≥0.05 | 不显著增加 | 120 304 | 30 |
| 0.01~0.05 | 显著增加 | 900 | 0.22 | |
| <0.01 | 极显著增加 | 224 374 | 56 |
表3 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度变化趋势显著性检验
Table 3 Significance test of the vegetation greenness change trend in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
| 变化趋势Slope | 显著性水平P | 变化趋势 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.0005 | <0.01 | 极显著减少 | 3 957 | 0.97 |
| 0.01~0.05 | 显著减少 | 55 | 0.01 | |
| ≥0.05 | 不显著减少 | 11 622 | 3 | |
| -0.005~0.0005 | ≥0.05 | 无变化 | 39 226 | 9.8 |
| >0.0005 | ≥0.05 | 不显著增加 | 120 304 | 30 |
| 0.01~0.05 | 显著增加 | 900 | 0.22 | |
| <0.01 | 极显著增加 | 224 374 | 56 |
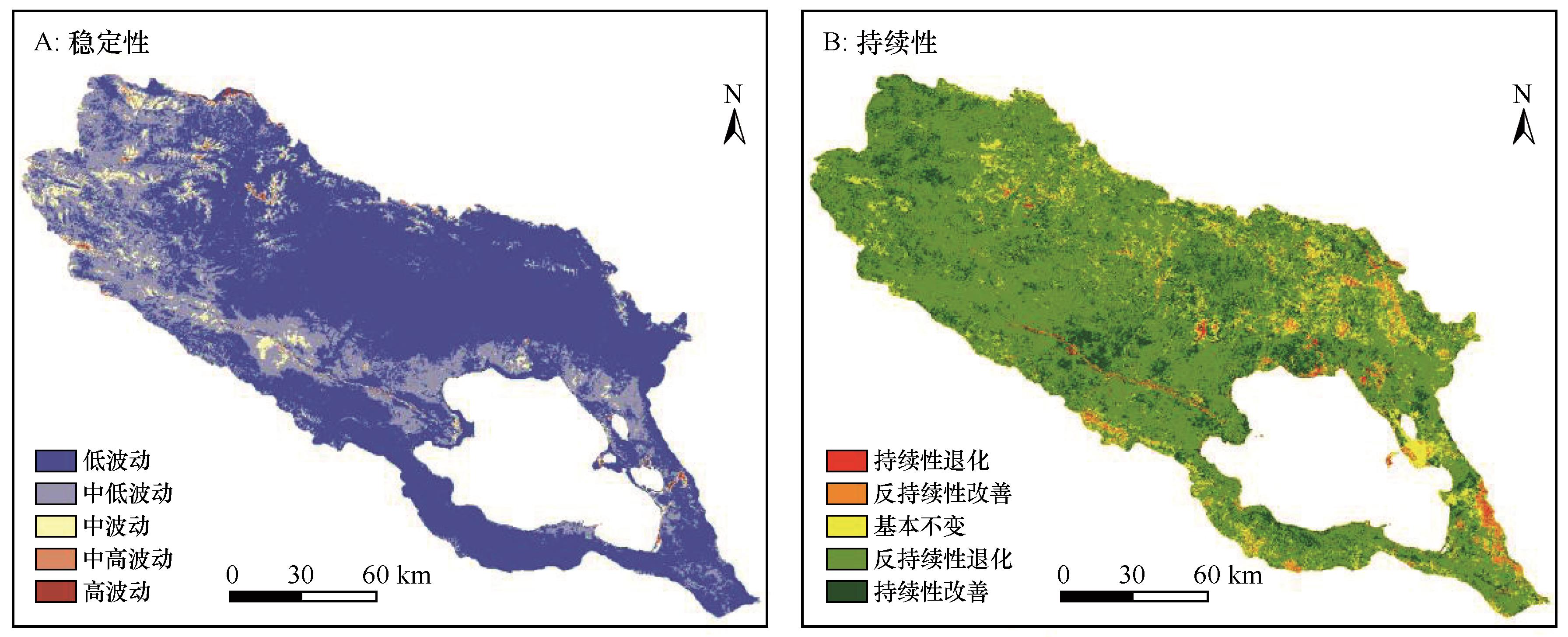
图5 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度稳定性与持续性注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.5 Vegetation greenness stability and sustainability in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
| 变化趋势值slope | Hurst指数 | 未来变化趋势 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.0005 | 0.5~1 | 持续性退化 | 4 018 | 1 |
| 0~0.5 | 反持续性退化(改善) | 285 864 | 71.34 | |
| -0.0005~0.0005 | 0~1 | 基本不变 | 40 182 | 10 |
| >0.0005 | 0~0.5 | 反持续性改善(退化) | 11 563 | 2.98 |
| 0.5~1 | 持续性改善 | 58 811 | 14.68 |
表4 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度变化持续性
Table 4 Persistence of vegetation greenness changes in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
| 变化趋势值slope | Hurst指数 | 未来变化趋势 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.0005 | 0.5~1 | 持续性退化 | 4 018 | 1 |
| 0~0.5 | 反持续性退化(改善) | 285 864 | 71.34 | |
| -0.0005~0.0005 | 0~1 | 基本不变 | 40 182 | 10 |
| >0.0005 | 0~0.5 | 反持续性改善(退化) | 11 563 | 2.98 |
| 0.5~1 | 持续性改善 | 58 811 | 14.68 |
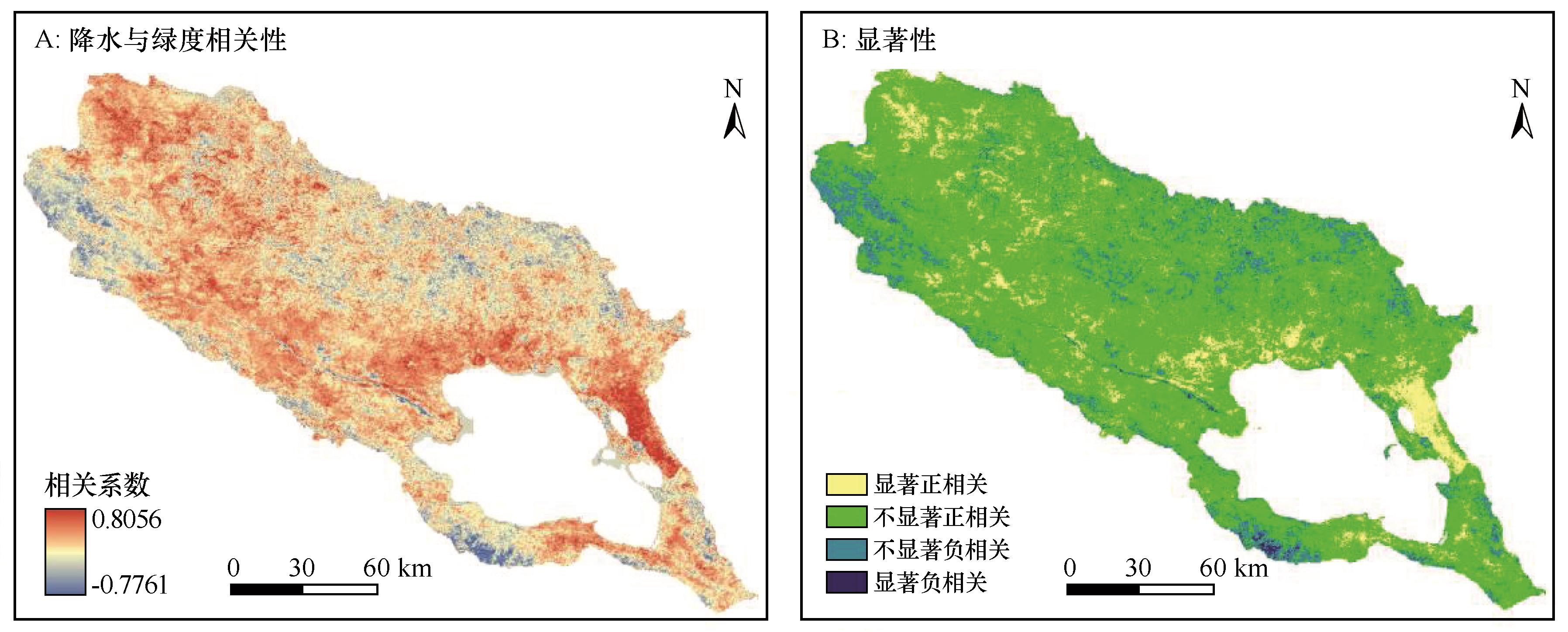
图6 植被绿度与降水相关性及显著性注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.6 Results of correlation and significance test between vegetation greenness and precipitation
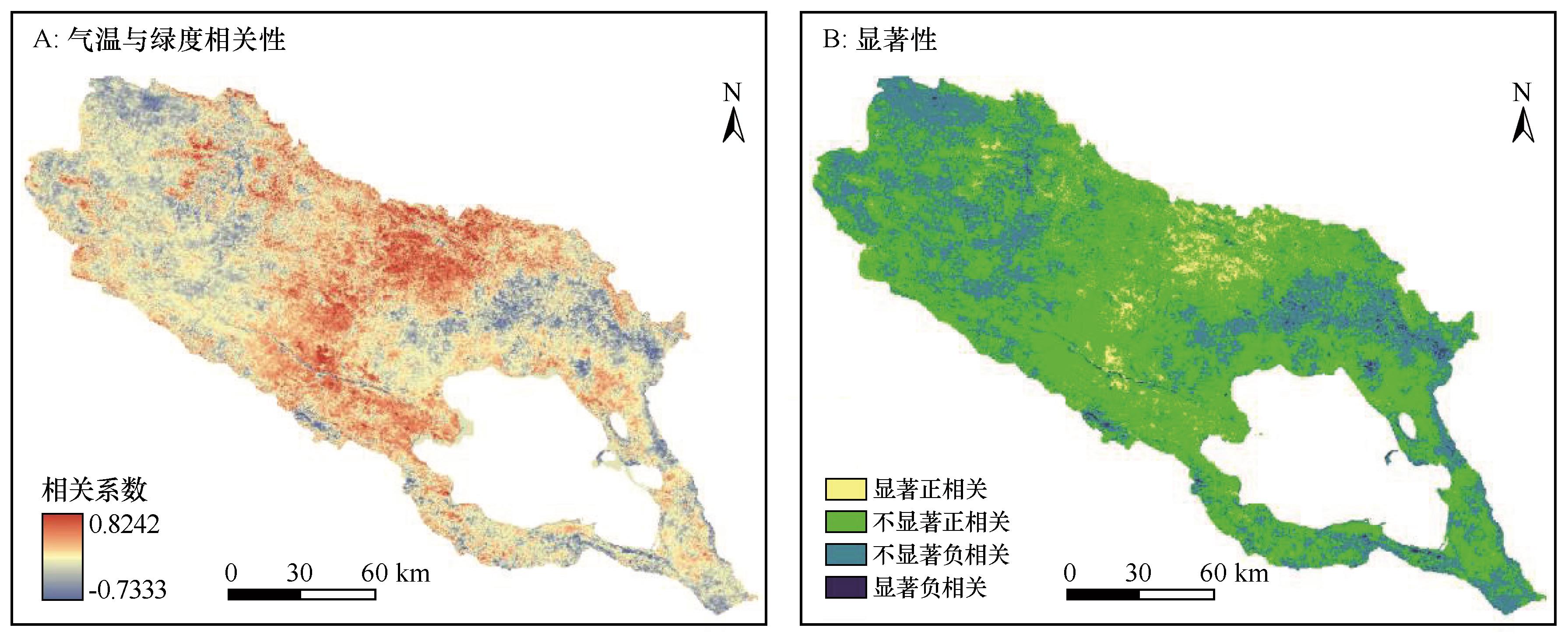
图7 植被绿度与气温相关性及显著性注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.7 Results of correlation and significance test between vegetation greenness and air temperature
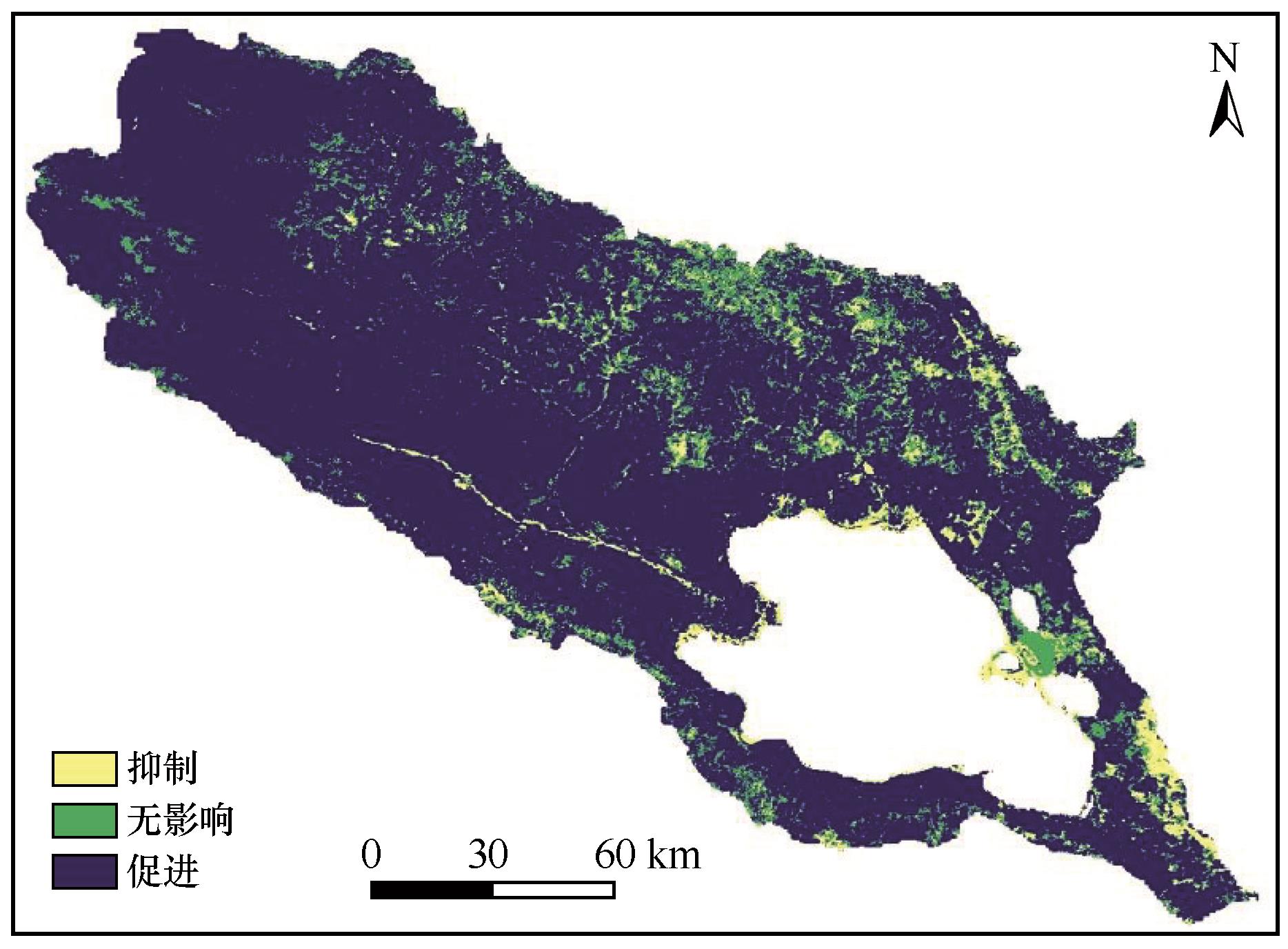
图8 青海湖流域植被绿度残差变化趋势空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.8 Spatial distribution of the residual variation trend of vegetation greenness in the Qinghai Lake Basin
| 残差趋势值Sr | 人类活动影响 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.0005 | 抑制 | 22 401 | 5.8 |
| -0.0005~0.0005 | 无影响 | 45 342 | 11.4 |
| >0.0005 | 促进 | 332 665 | 82.8 |
表5 残差趋势统计
Table 5 Residual trend statistics
| 残差趋势值Sr | 人类活动影响 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| <-0.0005 | 抑制 | 22 401 | 5.8 |
| -0.0005~0.0005 | 无影响 | 45 342 | 11.4 |
| >0.0005 | 促进 | 332 665 | 82.8 |
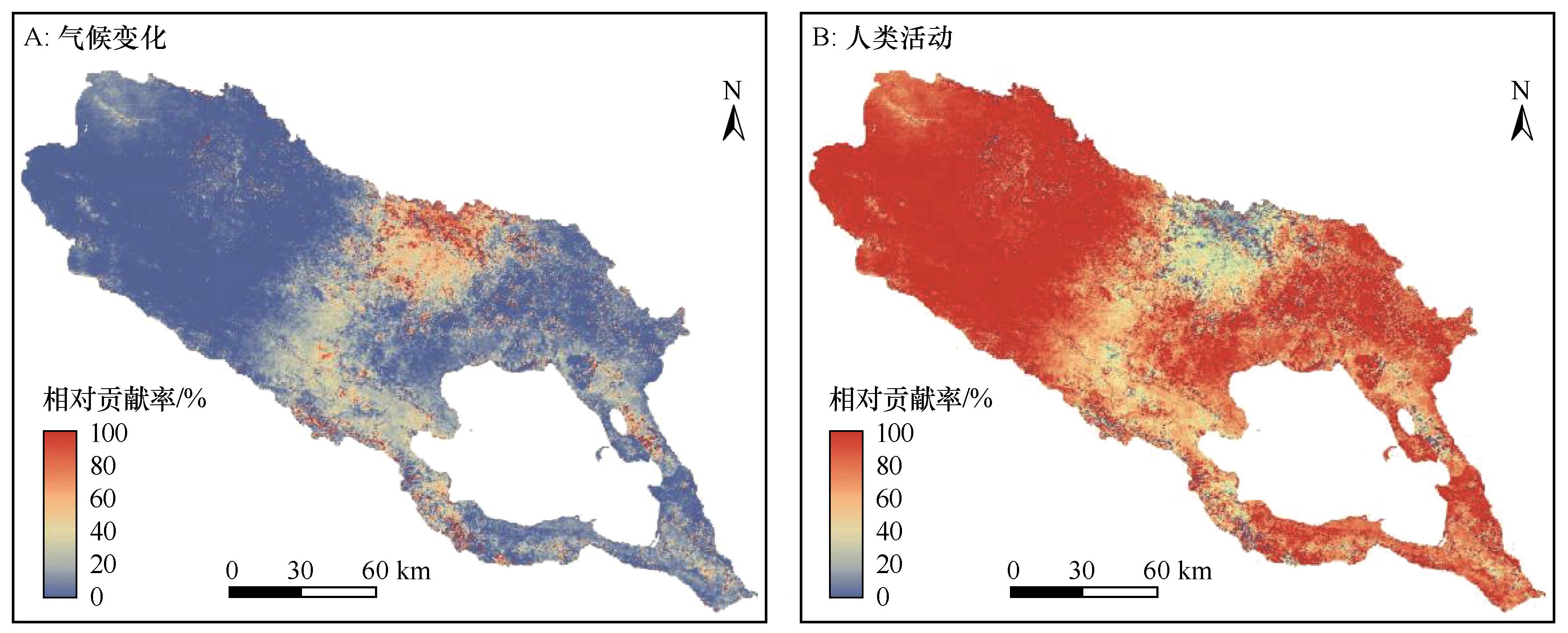
图9 气候变化与人类活动对植被绿度变化的贡献率注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.9 The contribution rates of climate change and human activities to vegetation greenness change
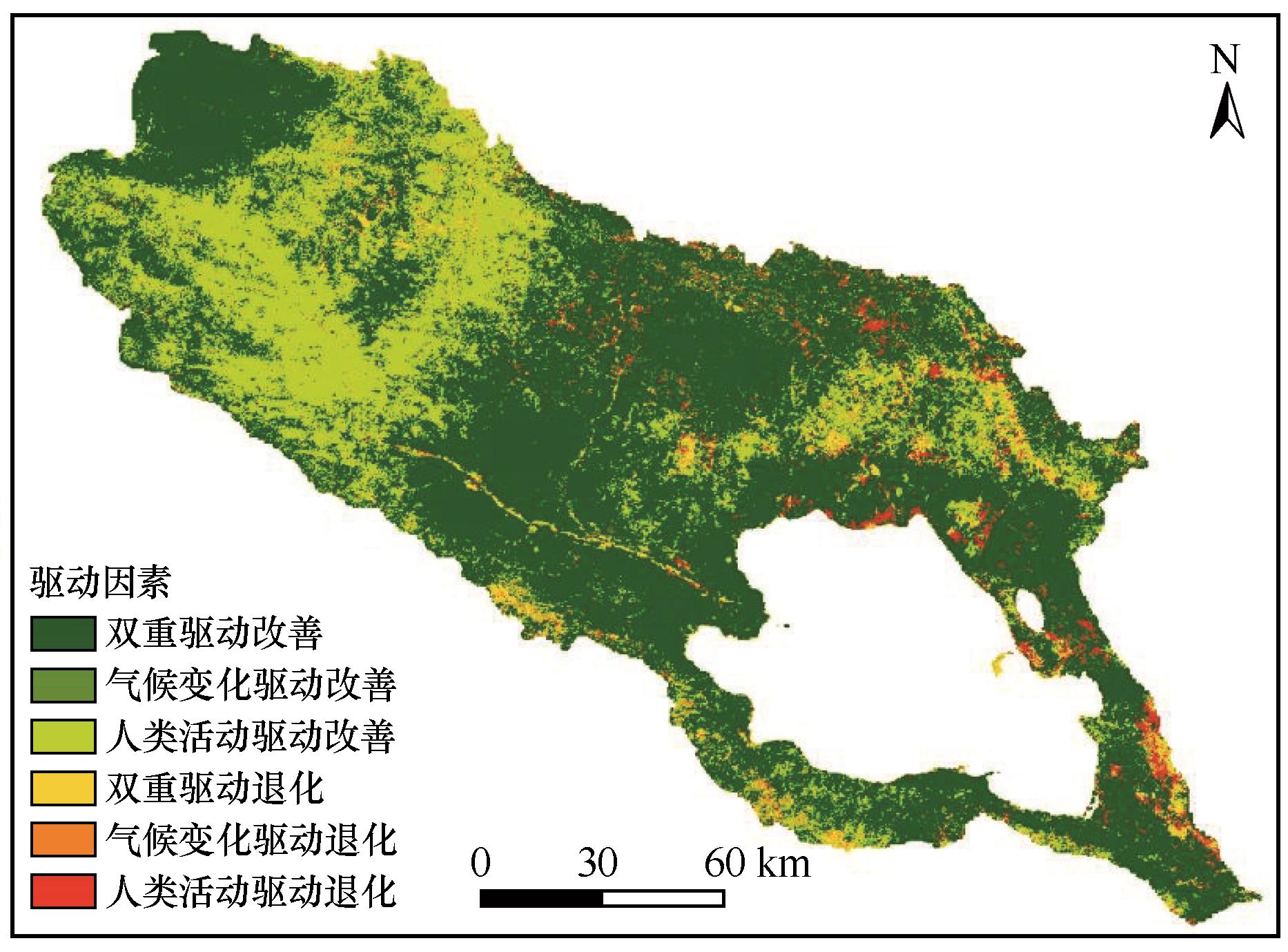
图10 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度变化驱动因素空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2023)2767号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.10 Spatial distribution of driving factors for vegetation greenness changes in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
| Slope (NDVIobs) | 驱动因素 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| >0 | 气候变化和人类活动 | 253 592 | 63.6 |
| 气候变化 | 6 320 | 1.5 | |
| 人类活动 | 111 006 | 27.8 | |
| <0 | 气候变化和人类活动 | 14 169 | 3.4 |
| 气候变化 | 3 317 | 0.7 | |
| 人类活动 | 12 034 | 3.0 |
表6 2000—2023年青海湖流域植被绿度变化的驱动因素统计
Table 6 Statistics of driving factors for vegetation greenness changes in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2023
| Slope (NDVIobs) | 驱动因素 | 像元数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| >0 | 气候变化和人类活动 | 253 592 | 63.6 |
| 气候变化 | 6 320 | 1.5 | |
| 人类活动 | 111 006 | 27.8 | |
| <0 | 气候变化和人类活动 | 14 169 | 3.4 |
| 气候变化 | 3 317 | 0.7 | |
| 人类活动 | 12 034 | 3.0 |
| [1] | Qiu B, Yan X, Chen C,et al.The impact of indicator selection on assessment of global greening[J].GIScience & Remote Sensing,2021,58(3):1-14. |
| [2] | Zhang Y, Song C, Band L E,et al.Reanalysis of global terrestrial vegetation trends from MODIS products:browning or greening?[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2017,191:145-155. |
| [3] | Cong N, Wang T, Nan H,et al.Changes in satellite‐derived spring vegetation green‐up date and its linkage to climate in China from 1982 to 2010:a multimethod analysis[J].Global Change Biology,2013,19(3):881-891. |
| [4] | 曹永强,周姝含,杨雪婷.近20年辽宁省植被动态特征及其对气候变化的响应[J].生态学报,2022,42(14):5966-5979. |
| [5] | 刘爽,宫鹏.2000-2010年中国地表植被绿度变化[J].科学通报,2012,57(16):1423-1434. |
| [6] | 梁顺林,白瑞,陈晓娜,等.2019年中国陆表定量遥感发展综述[J].遥感学报,2020,24(6):618-671. |
| [7] | 章钊华,赵书河,丛佃敏,等.基于遥感的泰山地区植被绿度趋势变化研究[J].地理空间信息,2018,16(7):65-68. |
| [8] | 刘海,刘凤,郑粮.气候变化及人类活动对黄河流域植被覆盖变化的影响[J].水土保持学报,2021,35(4):143-151. |
| [9] | 张志强,刘欢,左其亭,等.2000-2019年黄河流域植被覆盖度时空变化[J].资源科学,2021,43(4):849-858. |
| [10] | 杨达,易桂花,张廷斌,等.青藏高原植被生长季NDVI时空变化与影响因素[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(4):1361-1372. |
| [11] | 金凯.中国植被覆盖时空变化及其与气候和人类活动的关系[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2019. |
| [12] | 余志巍,刘强,张宇阳,等.内蒙古不同草地NDVI变化及其驱动要素[J].生态学报,2024,44(22):10068-10082. |
| [13] | 李双双,段生勇,胡佳岚,等.黄土高原植被变化主导空间模态及其影响因素[J].地理学报,2024,79(7):1768-1786. |
| [14] | 张江,袁旻舒,张婧,等.近30年来青藏高原高寒草地NDVI动态变化对自然及人为因子的响应[J].生态学报,2020,40(18):6269-6281. |
| [15] | 钟诗瑶,李传华,乔鹏飞.2000-2020年干旱梯度下西北干旱半干旱区植被突变及归因[J].中国沙漠,2025,45(2):275-283. |
| [16] | 任涵玉,温仲明,刘洋洋,等.我国北方草地净初级生产力时空动态特征及其与水热因子的关系[J].草地学报,2021,29(8):1779-1792. |
| [17] | 涂又,姜亮亮,刘睿,等.1982-2015年中国植被NDVI时空变化特征及其驱动分析[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(22):75-84. |
| [18] | 刘慧丽,陈浩,董廷旭,等.川渝地区NDVI动态特征及其对气候变化的响应[J].生态学报,2023,43(16):6743-6757. |
| [19] | Liu Y, Li Y, Li S,et al.Spatial and temporal patterns of global NDVI trends:correlations with climate and human factors[J].Remote Sensing,2015,7(10):13233-13250. |
| [20] | 路建兵,鞠珂,廖伟斌.2000-2020年甘肃省植被覆盖特征及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(4):118-127. |
| [21] | 燕丹妮,武心悦,王博恒,等.1982-2015年黄土高原植被变化特征及归因[J].生态学报,2023,43(23):9794-9804. |
| [22] | 朱士华,方霞,杭鑫,等.中亚草地植被指数(NDVI)对气候变化及人类活动的响应[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):229-241. |
| [23] | 张倩,曹广超,张乐乐,等.祁连山南坡植被绿度时空变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J].干旱区研究,2024,41(12):2143-2153. |
| [24] | Sun Y, Yang Y, Zhang L,et al.The relative roles of climate variations and human activities in vegetation change in North China[J].Physics and Chemistry of the Earth,2015,87-88:12. |
| [25] | 陶洁怡,章锦河,郭丽佳,等.三江源国家公园水源涵养服务时空演变特征及其驱动因素[J].生态学报,2025,45(3):1226-1238. |
| [26] | 徐晓梅,王军农.青海湖流域水文要素初步分析[J].科学技术与工程,2012,12(29):7669-7673. |
| [27] | Chen H, Zhu Q, Peng C,et al.The impacts of climate change and human activities on biogeochemical cycles on the Qinghai‐Tibetan Plateau[J].Global Change Biology,2013,19(10):2940-2955. |
| [28] | 杨元合,朴世龙.青藏高原草地植被覆盖变化及其与气候因子的关系[J].植物生态学报,2006,30(1):1-8. |
| [29] | 吴恒飞,陈克龙,张乐乐,等.增温对青海湖流域高寒沼泽草甸主要温室气体通量的影响[J].草原与草坪,2021,41(4):1-9. |
| [30] | 李星玥,杜岩功,陈克龙,等.青海湖流域南岸温性草原CO2排放特征对模拟降雨变化的响应[J].草地学报,2023,31(8):2496-2504. |
| [31] | 韩艳莉,陈克龙,于德永.土地利用变化对青海湖流域生境质量的影响[J].生态环境学报,2019,28(10):2035-2044. |
| [32] | 陈克龙.基于生态健康的青海湖流域植被生态补偿标准研究[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2016. |
| [33] | 拓进宝.2000-2016年青海湖流域NDVI时空变化及其与环境因子的关系[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2019. |
| [34] | 张乐乐,高黎明,陈克龙.高分辨率遥感降水资料在青海湖流域及周边区域的适用性评价[J].水文,2020,40(5):15-21. |
| [35] | 刘芙梅,吴成永,陈克龙.青海湖流域植被覆盖时空变化特征及驱动力分析[J].草原与草坪,2024,44(1):1-12. |
| [36] | 陈亚荣,李星玥,陈克龙.布哈河流域不同水体稳定同位素特征分析[J].水文,2025,45(1):83-89. |
| [37] | 高小红,王一谋,冯毓荪,等.基于遥感与GIS的青海湖地区土地利用变化及其对生态环境影响的研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2002(6):304-309. |
| [38] | Sen P K.Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's Tau[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association,1968,63:324. |
| [39] | 刘智源,李继红.2000-2020年黑龙江省植被时空变化对气候因子响应[J].森林工程,2024,40(1):85-97. |
| [40] | 孙锐,陈少辉,苏红波.2000-2016年黄土高原不同土地覆盖类型植被NDVI时空变化[J].地理科学进展,2019,38(8):1248-1258. |
| [41] | 牟禹恒,黄义忠,梁睿,等.基于MODIS NDVI的文山州植被覆盖度及景观格局分析[J].西北林学院学报,2023,38(1):174-180. |
| [42] | 秦格霞,芦倩,孟治元,等.1982-2015年中国北方草地NDVI时空动态及其对气候变化的响应[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(1):101-108. |
| [43] | Jiang W, Yuan L, Wang W,et al.Spatio‐temporal analysis of vegetation variation in the Yellow River Basin[J].Ecological Indicators,2015,51:117-126. |
| [44] | 陈怡洁,陈瑜.黄河流域甘肃段NDVI时空变化及其影响因素分析[J].测绘与空间地理信息,2024,47(3):89-92. |
| [45] | 岳萌,耿广坡,王涛,等.2000-2019年黄河流域陕西段植被NDVI时空变化及其驱动因素分析[J].水土保持研究,2023,30(2):238-246. |
| [46] | 程兀杰,孟妮娜,蔡昕楠,等.陕西省NDVI时空变化及其对气候和人类活动的响应[J].人民黄河,2023,45(4):28-34. |
| [47] | 刘芙梅.青海湖流域地表绿度变化特征及其驱动力分析[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2023. |
| [48] | 陈昀琳.基于Landsat和MODIS NDVI时序数据的青海湖流域植被覆盖度提取及其变化分析[D].北京:中国地质大学,2019. |
| [49] | 杨亮,刘丽男,孙少波.1982-2015年青藏高原植被变化的主导环境因子[J].生态学报,2023,43(2):744-755. |
| [50] | 韩艳莉.气候与景观格局变化对青海湖流域生态系统服务的影响[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2021. |
| [51] | 陈克龙,韩艳丽,曹生奎.青海湖流域植被生态补偿标准初探[J].青海师范大学学报(自然科学版),2012,28(1):21-24. |
| [52] | 王逸玮.青藏高原沱沱河源多年冻土区NDVI时空变化及影响因素分析[D].南京:南京信息工程大学,2024. |
| [53] | 卓嘎,陈思蓉,周兵.青藏高原植被覆盖时空变化及其对气候因子的响应[J].生态学报,2018,38(9):3208-3218. |
| [54] | 潘虹,顾海敏,史建桥,等.基于RS和GIS的青海湖流域植被覆盖度变化与驱动因子研究[J].资源开发与市场,2016,32(7):827-831. |
| [55] | 李焱.2000-2020年藏西南高原植被覆盖时空变化及其影响因素[D].兰州:兰州大学,2022. |
| [56] | 李永格,李宗省,冯起,等.基于生态红线划定的祁连山生态保护性开发研究[J].生态学报,2019,39(7):2343-2352. |
| [57] | 杜凯,康宇坤,张德罡,等.放牧模式对祁连山东缘高寒草甸植被特征的影响[J].草原与草坪,2021,41(3):9-18. |
| [58] | 马昊翔,陈长成,宋英强,等.青海省近10年草地植被覆盖动态变化及其驱动因素分析[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(6):137-145. |
| [59] | 田海静.非气候因素引起的中国植被变化遥感诊断[D].北京:中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所,2017. |
| [1] | 邓心茹, 别强, 黄春林, 石莹, 李欣璋. 干旱区典型绿洲景观格局的冷岛效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(6): 12-25. |
| [2] | 管悦汝, 白俊武, 李一琼, 杨朝辉, 时浩南. 2001—2020年毛乌素沙地植被净初级生产力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(6): 258-268. |
| [3] | 姜志伟, 杨智博, 杨清, 胡洁, 刘茜雅, 于玲玲, 张红红, 淡照晶, 田磊. 2000—2022年库布齐沙漠植被覆盖度时空变化及其驱动因子[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 124-133. |
| [4] | 方海富, 李玉霖, 李衍青, 莫雨茵, 詹瑾, 罗志佳. 科尔沁沙地典型坨甸相间区景观格局变化及其驱动因子[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 285-294. |
| [5] | 白浩江, 罗永清, 程莉, 汪正蛟一. 差巴嘎蒿( Artemisia halodendron )和小叶锦鸡儿( Caragana microphylla )物候的气候响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 305-313. |
| [6] | 翟颖, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 查小春, 周亚利, 李瑜琴, 张玉柱, 孙雪晴, 赵晓康. 若尔盖盆地阿米欧拉-南剖面粒度端元特征及其记录的15 ka来气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 111-118. |
| [7] | 钟诗瑶, 李传华, 乔鹏飞. 2000—2020年干旱梯度下西北干旱半干旱区植被突变及归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 275-283. |
| [8] | 程星雨, 徐志伟, 俞妍, 张小啸. 卫星遥感揭示的2001年以来中蒙地区沙尘事件频次变化及其原因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 47-60. |
| [9] | 尹振良, 朱睿, 方春爽, 杨华庆, 陈泽霞. 基于Budyko假设的昌马河流域径流变化归因分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 110-121. |
| [10] | 李森, 杨宗英, 赵鸿雁, 那仁图雅null, 安桂香, 谢家丽, 贾晓鹏, 颜长珍. 1975—2020年黄河“几字弯”沙漠化时空变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 13-22. |
| [11] | 李晓燕, 曹广超, 陈宗颜, 袁杰, 孙子婷, 唐建亭. 2001―2022年祁连山南坡地表温度时空变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 84-94. |
| [12] | 申子傲, 吴静, 李纯斌. 2000—2020年河西内陆河流域植被覆盖时空变化特征及其驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 119-127. |
| [13] | 陈链璇, 曹生奎, 曹广超, 雷义珍, 赵浩然, 李文斌. 青海湖流域蒸散发对土壤水分的时空响应特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 202-212. |
| [14] | 杜佳瑜, 刘宪锋, 孙高鹏, 李双双. 2003—2018年黄土高原植被光学厚度时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 222-230. |
| [15] | 贺祯子, 徐冰鑫, 刘文静, 胡宜刚. 荒漠生物结皮碳交换对模拟增温和降雨变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 269-278. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
