
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 18-30.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaofang Jiang1,3( ), Qingxia Xu4, Hanchen Duan1,2, Jie Liao1,2, Pinglin Guo1,3, Cuihua Huang1,2, Xian Xue1,2(
), Qingxia Xu4, Hanchen Duan1,2, Jie Liao1,2, Pinglin Guo1,3, Cuihua Huang1,2, Xian Xue1,2( )
)
Received:2023-02-06
Revised:2023-03-22
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
Xian Xue
CLC Number:
Xiaofang Jiang, Qingxia Xu, Hanchen Duan, Jie Liao, Pinglin Guo, Cuihua Huang, Xian Xue. Multi-model comparison on soil salinization inversion in Jingdian irrigation area of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 18-30.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00026
| 数据集 | 样品 数目 | 最大值 /(mS·cm-1) | 最小值 /(mS·cm-1) | 平均值 /(mS·cm-1) | 中位数 /(mS·cm-1) | 标准差 /(mS·cm-1) | 变异 系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 104 | 23.00 | 0.04 | 2.93 | 0.34 | 5.20 | 1.77 |
| 验证集 | 35 | 25.20 | 0.08 | 3.57 | 0.22 | 6.57 | 1.84 |
| 全部样品 | 139 | 25.20 | 0.04 | 3.09 | 0.28 | 5.56 | 1.80 |
Table 1 Statistical characteristics of soil samples
| 数据集 | 样品 数目 | 最大值 /(mS·cm-1) | 最小值 /(mS·cm-1) | 平均值 /(mS·cm-1) | 中位数 /(mS·cm-1) | 标准差 /(mS·cm-1) | 变异 系数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | 104 | 23.00 | 0.04 | 2.93 | 0.34 | 5.20 | 1.77 |
| 验证集 | 35 | 25.20 | 0.08 | 3.57 | 0.22 | 6.57 | 1.84 |
| 全部样品 | 139 | 25.20 | 0.04 | 3.09 | 0.28 | 5.56 | 1.80 |
| 波段数 | DNN | DRF | GBM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| 5 | 1.73 | 0.80 | 2.36 | 0.63 | 1.88 | 0.77 | ||
| 10 | 2.86 | 0.74 | 3.26 | 0.70 | 3.16 | 0.74 | ||
| 20 | 3.36 | 0.69 | 3.40 | 0.56 | 3.57 | 0.65 | ||
| 40 | 3.51 | 0.73 | 4.2 | 0.64 | 3.57 | 0.72 | ||
| 60 | 3.46 | 0.72 | 3.56 | 0.70 | 3.49 | 0.71 | ||
| 80 | 2.25 | 0.75 | 3.55 | 0.51 | 2.99 | 0.59 | ||
| 100 | 3.27 | 0.66 | 3.58 | 0.62 | 3.22 | 0.65 | ||
| 均值 | 2.92 | 0.73 | 3.42 | 0.62 | 3.13 | 0.79 | ||
Table 2 Modeling results of different band filtering number based on correlation reversed arrangement
| 波段数 | DNN | DRF | GBM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| 5 | 1.73 | 0.80 | 2.36 | 0.63 | 1.88 | 0.77 | ||
| 10 | 2.86 | 0.74 | 3.26 | 0.70 | 3.16 | 0.74 | ||
| 20 | 3.36 | 0.69 | 3.40 | 0.56 | 3.57 | 0.65 | ||
| 40 | 3.51 | 0.73 | 4.2 | 0.64 | 3.57 | 0.72 | ||
| 60 | 3.46 | 0.72 | 3.56 | 0.70 | 3.49 | 0.71 | ||
| 80 | 2.25 | 0.75 | 3.55 | 0.51 | 2.99 | 0.59 | ||
| 100 | 3.27 | 0.66 | 3.58 | 0.62 | 3.22 | 0.65 | ||
| 均值 | 2.92 | 0.73 | 3.42 | 0.62 | 3.13 | 0.79 | ||
| 数据 类型 | DNN | DRF | GBM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| SNR-5 dB | 4.87 | 0.51 | 5.88 | 0.24 | 5.61 | 0.31 | ||
| SNR-10 dB | 4.60 | 0.54 | 4.94 | 0.42 | 5.12 | 0.39 | ||
| SNR-20 dB | 2.30 | 0.75 | 1.82 | 0.81 | 2.04 | 0.75 | ||
| SNR-30 dB | 2.86 | 0.71 | 2.76 | 0.69 | 3.19 | 0.61 | ||
| SNR-40 dB | 3.62 | 0.61 | 2.99 | 0.62 | 2.96 | 0.66 | ||
| SNR-50 dB | 3.69 | 0.50 | 3.75 | 0.48 | 3.37 | 0.60 | ||
| 均值 | 3.66 | 0.60 | 3.69 | 0.54 | 3.72 | 0.55 | ||
Table 3 Modeling results of data source with different signal-to-noise ratio
| 数据 类型 | DNN | DRF | GBM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | |||
| SNR-5 dB | 4.87 | 0.51 | 5.88 | 0.24 | 5.61 | 0.31 | ||
| SNR-10 dB | 4.60 | 0.54 | 4.94 | 0.42 | 5.12 | 0.39 | ||
| SNR-20 dB | 2.30 | 0.75 | 1.82 | 0.81 | 2.04 | 0.75 | ||
| SNR-30 dB | 2.86 | 0.71 | 2.76 | 0.69 | 3.19 | 0.61 | ||
| SNR-40 dB | 3.62 | 0.61 | 2.99 | 0.62 | 2.96 | 0.66 | ||
| SNR-50 dB | 3.69 | 0.50 | 3.75 | 0.48 | 3.37 | 0.60 | ||
| 均值 | 3.66 | 0.60 | 3.69 | 0.54 | 3.72 | 0.55 | ||
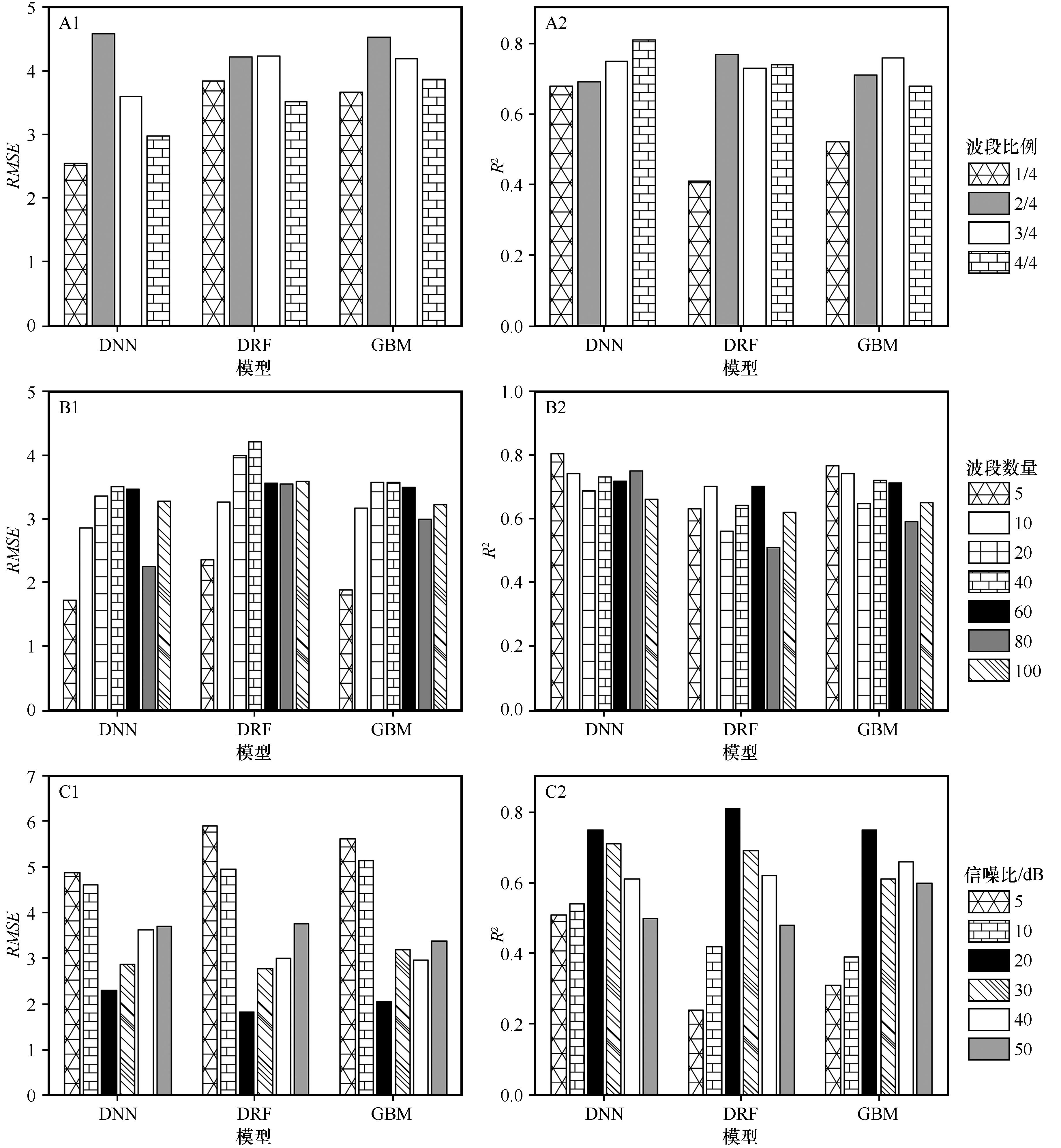
Fig.7 Modeling results of different data sources (A1, A2: modeling results of different bands proportion in all bands; B1, B2: modeling results of different band filtering number based on correlation reversed arrangement; C1, C2: modeling results of data source with different signal-to-noise ratio)
| 1 | Sidike A, Zhao S, Wen Y.Estimating soil salinity in Pingluo County of China using QuickBird data and soil reflectance spectra[J].International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2014,26:156-175. |
| 2 | Gorji T, Yildirim A, Hamzehpour N,et al.Soil salinity analysis of Urmia Lake Basin using Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2A based spectral indices and electrical conductivity measurements[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,112:106173. |
| 3 | Hopmans J W, Qureshi A S, Kisekka I,et al.Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity[M]//Sparks Donald L.Advances in Agronomy.Pittsburgh,USA:Academic Press,2021. |
| 4 | Allbed A, Kumar L, Aldakheel Y Y.Assessing soil salinity using soil salinity and vegetation indices derived from IKONOS high-spatial resolution imageries:applications in a date palm dominated region[J].Geoderma,2014,230:1-8. |
| 5 | Aldabaa A A A, Weindorf D C, Chakraborty S,et al.Combination of proximal and remote sensing methods for rapid soil salinity quantification[J].Geoderma,2015,239/240:34-46. |
| 6 | Corwin D L.Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas[J].European Journal of Soil Science,2021(2):13010. |
| 7 | Metternicht G I, Zinck J A.Remote sensing of soil salinity:potentials and constraints[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2003,85(1):1-20. |
| 8 | Guzinski R, Nieto H.Evaluating the feasibility of using Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 satellites for high-resolution evapotranspiration estimations[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2019,221:157-172. |
| 9 | Hong Y, Chen S, Chen Y,et al.Comparing laboratory and airborne hyperspectral data for the estimation and mapping of topsoil organic carbon:Feature selection coupled with random forest[J].Soil & Tillage Research,2020,199:104589. |
| 10 | Castaldi F, Palombo A, Santini F,et al.Evaluation of the potential of the current and forthcoming multispectral and hyperspectral imagers to estimate soil texture and organic carbon[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2016,179:54-65. |
| 11 | An D, Zhao G, Chang C,et al.Hyperspectral field estimation and remote-sensing inversion of salt content in coastal saline soils of the Yellow River Delta[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,2016,37(2):455-470. |
| 12 | Roy C M, Das S, Christopher J,et al.Improving biomass and grain yield prediction of wheat genotypes on sodic soil using integrated high-resolution multispectral,hyperspectral,3d point cloud,and machine learning techniques[J].Remote Sensing,2021,13(17):3482. |
| 13 | Zhu K, Sun Z, Zhao F,et al.Relating hyperspectral vegetation indices with soil salinity at different depths for the diagnosis of winter wheat salt stress[J].Remote Sensing,2021,13(2):250. |
| 14 | Gomez C, Adeline K, Bacha S,et al.Sensitivity of clay content prediction to spectral configuration of VNIR/SWIR imaging data,from multispectral to hyperspectral scenarios[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2018,204:18-30. |
| 15 | 唐海涛,孟祥添,苏循新,等.基于CARS算法的不同类型土壤有机质高光谱预测[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(2):105-113. |
| 16 | 钟亮,郭熙,国佳欣,等.基于不同卷积神经网络模型的红壤有机质高光谱估算[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(1):203-212. |
| 17 | Lu P, Wang L, Niu Z,et al.Prediction of soil properties using laboratory VIS-NIR spectroscopy and Hyperion imagery[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2013,132:26-33. |
| 18 | Peng J, Biswas A, Jiang Q,et al.Estimating soil salinity from remote sensing and terrain data in southern Xinjiang Province,China[J].Geoderma,2019,337:1309-1319. |
| 19 | Yang N, Yang S, Cui W,et al.Effect of spring irrigation on soil salinity monitoring with UAV-borne multispectral sensor[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,2021,23/24:1-18. |
| 20 | Zeraatpisheh M, Ayoubi S, Jafari A,et al.Digital mapping of soil properties using multiple machine learning in a semi-arid region,central Iran[J].Geoderma,2019,338:445-452. |
| 21 | Wang S J, Chen Y H, Wang M G,et al.Performance comparison of machine learning algorithms for estimating the soil salinity of salt-affected soil using field spectral data[J].Remote sensing,2019,11(22):2605. |
| 22 | Wang F, Shi Z, Biswas A,et al.Multi-algorithm comparison for predicting soil salinity[J].Geoderma,2020,365:114211. |
| 23 | Savitzky A, Golay M J.Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures[J].Analytical Chemistry,1964,36(8):1627-1639. |
| 24 | Wang F, Yang S, Wei Y,et al.Characterizing soil salinity at multiple depth using electromagnetic induction and remote sensing data with random forests:a case study in Tarim River Basin of southern Xinjiang,China[J].The Science of the Total Environment,2021,754:142030. |
| 25 | Gomez C, Lagacherie P, Coulouma G.Regional predictions of eight common soil properties and their spatial structures from hyperspectral Vis-NIR data[J].Geoderma,2012,189/190:176-185. |
| 26 | Ivushkin K, Bartholomeus H, Bregt A K,et al.Global mapping of soil salinity change[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2019,231:111260. |
| 27 | Rao B R M, Sharma R C, Ravi Sankar T,et al.Spectral behaviour of salt-affected soils[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,1995,16(12):2125-2136. |
| 28 | Bowers S A, Smith S J.Spectrophotometric determination of soil-water content[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,1972,36(6):978-980. |
| 29 | Camacho De Coca F, Baret F, Weiss M,et al.Comparison of physically-based and empirical methods for retrieval of LAI and FAPAR over specific and generic crops using Landsat-8 data[C]//Recent Advance in Quantitative Remote Sensing.Torrent,Valencia,Spain,2017. |
| 30 | Suo X, Jiang Y, Mei Y,et al.Artificial neural network to predict leaf population chlorophyll content from cotton plant images[J].Agricultural Sciences in China,2010,9(1):38-45. |
| 31 | Liu M, Liu X, Li M,et al.Neural-network model for estimating leaf chlorophyll concentration in rice under stress from heavy metals using four spectral indices[J].Biosystems Engineering,2010,106(3):223-233. |
| 32 | Kira O, Linker R, Gitelson A.Non-destructive estimation of foliar chlorophyll and carotenoid contents:focus on informative spectral bands[J].International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2015,38:251-260. |
| 33 | Sehgal V K, Chakraborty D, Sahoo R N.Inversion of radiative transfer model for retrieval of wheat biophysical parameters from broadband reflectance measurements[J].Information Processing in Agriculture,2016,3(2):107-118. |
| 34 | Verrelst J, Muñoz J, Alonso L,et al.Machine learning regression algorithms for biophysical parameter retrieval:opportunities for Sentinel-2 and-3[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2012,118:127-139. |
| 35 | Zhang Q, Li L, Sun R,et al.Retrieval of the soil salinity from Sentinel-1 dual-polarized sar data based on deep neural network regression[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,2022,19:1-5. |
| 36 | Farifteh J, Van der Meer F, Atzberger C,et al.Quantitative analysis of salt-affected soil reflectance spectra:a comparison of two adaptive methods (PLSR and ANN)[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2007,110(1):59-78. |
| 37 | Golden C E, Rothrock M J, Mishra A.Comparison between random forest and gradient boosting machine methods for predicting Listeria spp.prevalence in the environment of pastured poultry farms[J].Food Research International,2019,122:47-55. |
| 38 | Brillante L, Gaiotti F, Lovat L,et al.Investigating the use of gradient boosting machine,random forest and their ensemble to predict skin flavonoid content from berry physical-mechanical characteristics in wine grapes[J].Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2015,117:186-193. |
| 39 | Belgiu M, Drăguţ L.Random forest in remote sensing:a review of applications and future directions[J].ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2016,114:24-31. |
| 40 | Breiman L.Random forests[J].Machine Learning,2001,45(1):5-32. |
| 41 | Friedman J H.Stochastic gradient boosting[J].Computational Statistics & Data Analysis,2002,38(4):367-378. |
| 42 | Cutler D R, Edwards T C, Beard K H,et al.Random forests for classification in ecology[J].Ecology,2007,88(11):2783-2792. |
| 43 | Rodriguez-Galiano V F, Ghimire B, Rogan J,et al.An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification[J].ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2012,67:93-104. |
| 44 | Wang X, Gao X, Zhang Y,et al.Land-cover classification of coastal wetlands using the RF algorithm for Worldview-2 and Landsat 8 images[J].Remote Sensing,2019,11(16):1927. |
| 45 | Jang E, Kim Y J, Im J,et al.Global sea surface salinity via the synergistic use of SMAP satellite and HYCOM data based on machine learning[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2022,273:112980. |
| 46 | Nawar S, Mouazen A M.Comparison between random forests,artificial neural networks and gradient boosted machines methods of on-line VIS-NIR spectroscopy measurements of soil total nitrogen and total carbon[J].Sensors,2017,17:2428. |
| 47 | Sorenson P T, Small C, Tappert M C,et al.Monitoring organic carbon,total nitrogen,and pH for reclaimed soils using field reflectance spectroscopy[J].Canadian Journal of Soil Science,2017,97(2):241-248. |
| 48 | Quintano C, Fernandez-Manso A, Roberts D A.Enhanced burn severity estimation using fine resolution ET and MESMA fraction images with machine learning algorithm[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2020,244:111815. |
| 49 | Zhang T, Zeng S, Gao Y,et al.Using hyperspectral vegetation indices as a proxy to monitor soil salinity[J].Ecological Indicators,2011,11(6):1552-1562. |
| 50 | Ben-Dor E, Chabrillat S, Demattê J A M,et al.Using imaging spectroscopy to study soil properties[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2009,113:S38-S55. |
| 51 | Rossel R A V, Behrens T.Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra[J].Geoderma,2010,158(1/2):46-54. |
| 52 | Viscarra Rossel R A, Fouad Y, Walter C.Using a digital camera to measure soil organic carbon and iron contents[J].Biosystems Engineering,2008,100(2):149-159. |
| 53 | Melendez-Pastor I, Navarro-Pedreño J, Gómez I,et al.Identifying optimal spectral bands to assess soil properties with VNIR radiometry in semi-arid soils[J].Geoderma,2008,147(3/4):126-132. |
| 54 | 王爽,丁建丽,王璐,等.基于地表光谱建模的区域土壤盐渍化遥感监测研究[J].干旱区地理,2016,39(1):190-198. |
| 55 | Lobell D B, Asner G P.Moisture effects on soil reflectance[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,2002,66(3):722-727. |
| 56 | Guo L, Zhang H, Shi T,et al.Prediction of soil organic carbon stock by laboratory spectral data and airborne hyperspectral images[J].Geoderma,2019,337:32-41. |
| 57 | Ding J L, Yao Y, Wang F.Detecting soil salinization in arid regions using spectral feature space derived from remote sensing data[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2014,34(16):4620-4631. |
| 58 | Ding J, Yu D.Monitoring and evaluating spatial variability of soil salinity in dry and wet seasons in the Werigan-Kuqa Oasis,China,using remote sensing and electromagnetic induction instruments[J].Geoderma,2014,235/236:316-322. |
| 59 | Garajeh M K, Blaschke T, Haghi V H,et al.A comparison between Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 OLI satellite images for soil salinity distribution mapping using a deep learning convolutional neural network[J].Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing,2022,48(3):452-468. |
| [1] | Xinyue Zhao, Haiyang Xi, Jing Zhao, Kehua Ma, Wenju Cheng, Yuqing Chen. Inversion and spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in Alxa area, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 27-36. |
| [2] | Yang Aixia, Ding Jianli, Li Yanhong, Deng Kai, Wang Jinjie. Apparent Electronic Conductivity and Measured Spectral for Monitoring Soil salt Content in Arid Lakeside Wetland [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(5): 1365-1373. |
| [3] | Yuan Ze, Ding Jianli, Niu Zengyi, Li Yanhua. Soil Salinization Monitoring in the Ebinur Lake Region at A Field Scale Based on GF-1 Image [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(4): 1070-1078. |
| [4] | Ding Jianli, Niu Zengyi, Li Yanhua. Soil Salinization Disaster Warning in Arid Zones: A case study in the Ugan-Kuqa Oasis [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(4): 1079-1086. |
| [5] | Peng Fei, Huang Cuihua, Liao Jie, Xue Xian, Wang Tao. Effect of Kalidium foliatum Community on Soil Salinization [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(1): 90-93. |
| [6] | Pang Guojin, Wang Tao, Sun Jiahuan, Li Sen. Quantitative Analysis of Soil Salinity Content with Hyperspectra Data in Minqin, Gansu, China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(4): 1073-1079. |
| [7] | Yao Yuan, Ding Jianli, Zhang Fang, Jiang Hongnan, Lei Lei. Monitoring the Spatial Variability of Soil Salinity and Composite in Dry and Wet Seasons in North Tarim Basin monitored with Electromagnetic Induction Instruments [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(3): 765-772. |
| [8] | Zhang Huaishan, Dai Lilan, Zhao Guiqin, Wang Ping, Wang Chunmei. Comparison on Rhizospheric Microenvironment of Three Salt-tolerant Plants [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(1): 184-190. |
| [9] | Mamat·sawut1,2, Tashpolat·Tiyip1,2, DING Jian-li1,2, ZHANG fei1,2, SUN Qian1,2. Object-Oriented Information Extraction Method for Soil Salinization in Arid Area [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(5): 1586-1592. |
| [10] | LEI Lei, TIYIP Tashpolat, DING Jian-li, JIANG Hong-nan, ZHANG Fei, YAO Yuan, KELIMU Ardak. Soil Salinization Information Extraction by Using Hyperspectral Data of HJ-1A HSI: A case study in the Oasis of Ugan & Kuqa, Xinjiang, China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(4): 1104-1109. |
| [11] | YOU Quan-gang;XUE Xian;HUANG Cui-hua. Preliminary Study on the Effects of Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Salinization in Deep Groundwater Area: A case study of Minqin oasis [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(2): 302-308. |
| [12] | ZHAO Ha-lin;ZHAO Xue-yong;ZHANG Tong-hui;ZHANG Xiao-you;LI Yu-lin;LIU Li-chao. Desertification Process and Its Spatial Differentiation in Arid Areas of Northwest China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(1): 1-8. |
| [13] | WANG Yu-gang;XIAO Du-ning;LI Yan. Dynamics of Soil Salt Accumulation in Oasis at Lower Reaches of an Inland River Basin [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2009, 29(4): 604-610. |
| [14] | WANG Yu-gang;XIAO Du-ning;LI Yan. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Oasis Soil Salinization in Upper and Middle Reaches of Sangonghe River, Northwest China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2008, 28(3): 478-484. |
| [15] | WEN Xiao-hu;WU Yan-qing;SU Jian-ping;ZHANG Ying-hua;LIU Fa-min. Groundwater Salinization Characteristics and Mechanism in Ejin Basin [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2006, 26(5): 836-841. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech