
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 57-65.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00104
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiahui Cao( ), Siyu Chen(
), Siyu Chen( ), Chao Zhang, Lulu Lian, Dan Zhao, Shikang Du
), Chao Zhang, Lulu Lian, Dan Zhao, Shikang Du
Received:2023-06-16
Revised:2023-07-13
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Siyu Chen
CLC Number:
Jiahui Cao, Siyu Chen, Chao Zhang, Lulu Lian, Dan Zhao, Shikang Du. External contribution of the Tibetan Plateau dust[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 57-65.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00104
| 物理化学过程 | 设置 |
|---|---|
| 微物理方案 | Morrison two-moment scheme |
| 长波辐射方案 | RRTMG |
| 短波辐射方案 | RRTMG |
| 陆面方案 | Noah land-surface model |
| 积云参数化方案 | Grell 3D |
| 沙尘排放方案 | GOCART |
| 气溶胶方案 | MOSAIC-4Bin |
Table 1 WRF-Chem configuration options for physical and chemical parameterizations
| 物理化学过程 | 设置 |
|---|---|
| 微物理方案 | Morrison two-moment scheme |
| 长波辐射方案 | RRTMG |
| 短波辐射方案 | RRTMG |
| 陆面方案 | Noah land-surface model |
| 积云参数化方案 | Grell 3D |
| 沙尘排放方案 | GOCART |
| 气溶胶方案 | MOSAIC-4Bin |
| 试验设置 | 试验描述 |
|---|---|
| 标准试验 | 打开模拟区域内所有沙尘源 |
| 敏感性实验1 | 关闭塔克拉玛干沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验2 | 关闭塔尔沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验3 | 关闭戈壁沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验4 | 关闭古尔班通古特沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验5 | 关闭中亚沙漠沙源 |
Table 2 WRF-Chem experimental design
| 试验设置 | 试验描述 |
|---|---|
| 标准试验 | 打开模拟区域内所有沙尘源 |
| 敏感性实验1 | 关闭塔克拉玛干沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验2 | 关闭塔尔沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验3 | 关闭戈壁沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验4 | 关闭古尔班通古特沙漠沙源 |
| 敏感性实验5 | 关闭中亚沙漠沙源 |
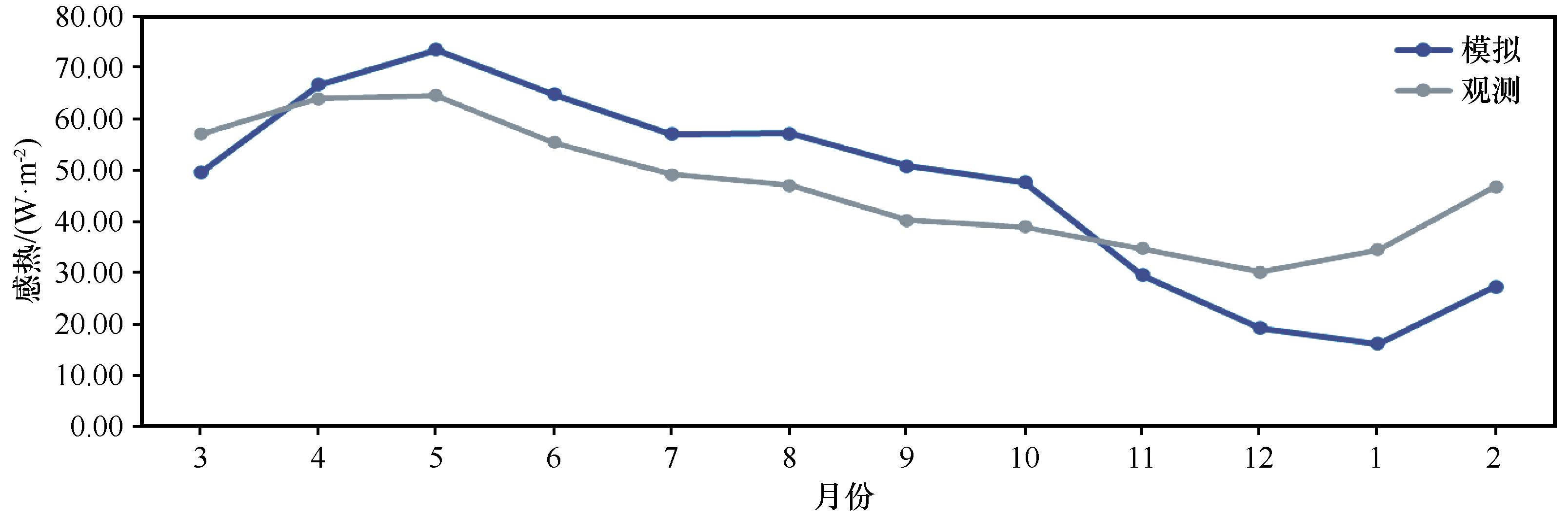
Fig.5 Comparison of the monthly mean sensible heat simulation results over the eastern Tibetan Plateau in 2018 with the multi-year monthly mean sensible heat from 32 observation stations located in the eastern Tibetan Plateau during 1960-2016
| 1 | Qiu J.The third pole[J].Nature,2008,454(7203):393-396. |
| 2 | Yang K, Chen Y, Qin J.Some practical notes on the land surface modeling in the Tibetan Plateau[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2009,13(5):687-701. |
| 3 | Cong Z, Kang S, Smirnov A,et al.Aerosol optical properties at NamCo,a remote site in central Tibetan Plateau[J].Atmospheric Research,2009,92(1):42-48. |
| 4 | Lau K, Kim K.Observational relationships between aerosol and Asian monsoon rainfall,and circulation[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2006,33:L21810. |
| 5 | Wu G, Duan A, Liu Y,et al.Tibetan Plateau climate dynamics:recent research progress and outlook[J].National Science Review,2015,2(1):100-116. |
| 6 | Huang J, Wang T, Wang W,et al.Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2014,119:11398-11416. |
| 7 | Wu C, Lin Z, Shao Y,et al.Drivers of recent decline in dust activity over East Asia[J].Nature Communications,2022,13:7105. |
| 8 | Kok J, Storelvmo T, Karydis V,et al.Mineral dust aerosol impacts on global climate and climate change[J].Nature Reviews Earth & Environment,2023,4(2):71-86. |
| 9 | Xu C, Ma Y, You C,et al.The regional distribution characteristics of aerosol optical depth over the Tibetan Plateau[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2015,15:12065-12078. |
| 10 | 延昊,张佳华,赵一平,等.青藏高原沙尘天气的遥感研究[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(6):932-934. |
| 11 | 韩永翔,奚晓霞,宋连春,等.青藏高原沙尘及其可能的气候意义[J].中国沙漠,2004,24(5):72-76. |
| 12 | Mao R, Gong D, Shao Y,et al.Numerical analysis for contribution of the Tibetan Plateau to dust aerosols in the atmosphere over the East Asia[J].Science China Earth Sciences,2013,56:301-310. |
| 13 | Dong Z, Brahney J, Kang S,et al.Aeolian dust transport, cycle and influences in high-elevation cryosphere of the Tibetan Plateau region:new evidences from alpine snow and ice[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2020,211:103408. |
| 14 | Chen S, Zhang R, Mao R,et al.Sources, characteristics and climate impact of light-absorbing aerosols over the Tibetan Plateau[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2022,232:104111. |
| 15 | Hu Z, Huang J, Zhao C,et al.Modeling dust sources,transport,and radiative effects at different altitudes over the Tibetan Plateau[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2020,20(3):1507-1529. |
| 16 | Wang T, Tang J, Sun M,et al.Identifying a transport mechanism of dust aerosols over South Asia to the Tibetan Plateau:a case study[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,758:143714. |
| 17 | Mao R, Hu Z, Zhao C,et al.The source contributions to the dust over the Tibetan Plateau:a modelling analysis[J].Atmospheric Environment,2019,214:116. |
| 18 | 张璐,李倩惠,孟露,等.深厚大气边界层演变与湍流运动、沙尘滞空的研究[J].地球科学进展,2022,37(10):991-1004. |
| 19 | 万云霞,张宇,张瑾文,等.感热变化对东亚地区大气边界层高度的影响[J].高原气象,2017,36(1):173-182. |
| 20 | Grell G, Peckham S, Schmitz R,et al.Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model[J].Atmospheric Environment,2005,39(37):6957-6975. |
| 21 | Ginoux P, Chin M, Tegen I,et al.Sources and distributions of dust aerosols simulated with the GOCART model[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2001,106(D17):20255-20273. |
| 22 | Zhao C, Liu X, Ruby L,et al.Radiative impact of mineral dust on monsoon precipitation variability over West Africa[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2011,11:1879-1893. |
| 23 | Zhao C, Liu X, Ruby L.Impact of the Desert dust on the summer monsoon system over Southwestern North America[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2012,12:3717-3731. |
| 24 | Chen S, Huang J, Kang L,et al.Emission,transport and radiative effects of mineral dust from Taklimakan and Gobi Deserts:comparison of measurements and model results[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2017,17(3):1-43. |
| 25 | Diner D, Beckert J, Reilly T,et al.Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument description and experiment overview[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,1998,36(4):1072-1087. |
| 26 | Monin A, Obukhov A.Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the atmosphere near the ground[J].TrAkad Nauk SSSR Geofiz Institute,1954,24:163-187. |
| 27 | Duan A, Li F, Wang M,et al.Persistent weakening trend in the spring sensible heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on the Asian summer monsoon[J].Journal of Climate,2011,24:5671-5682. |
| 28 | Duan A, Sun R, He J.Impact of surface sensible heating over the Tibetan Plateau on the western Pacific subtropical high:a landvair-sea interaction perspective[J].Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2017,34:157-168. |
| 29 | Duan A, Liu S, Zhao Y,et al.Atmospheric heat source/sink dataset over the Tibetan Plateau based on satellite and routine meteorological observations[J].Big Earth Data,2018,2(2):179-189. |
| 30 | Feng X, Mao R, Gong D,et al.Increased dust aerosols in the high troposphere over the Tibetan Plateau from 1990s to 2000s[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2020,125(13):e2020JD032807. |
| 31 | 叶笃正,罗四维,朱抱真.西藏高原及其附近的流场结构和对流层大气的热量平衡[J].气象学报,1957,28(2):108-121. |
| 32 | 李本涛,张镭,张云舒,等.青藏高原沙尘气溶胶时空变化及其来源地分析[J].高原气象,2023,42(3):564-574. |
| [1] | Haokun Mo, Guangyin Hu, Huicong Meng. Research progress on aeolian activity in the Qinghai Lake area, northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 197-209. |
| [2] | Zhulei Dong, Xuegong Jiang, Nana Yi, Zhili Xu, Yuehe Hang, Shuiyan Yu. Numerical simulation of the influence of wind speed and vegetation on dust weather in Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 29-39. |
| [3] | Mengjun Hu, Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Aokang Xu. Geochemical characteristics of major elements and environmental evolution in the Holocene in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 11-20. |
| [4] | Aihua Hao, Xian Xue, Quangang You, Chaoyang Gou. Review on precipitation change over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in recent 60 years [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 43-52. |
| [5] | Jingjing Hu, Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong. Particle size characteristics of aeolian desertified land in Madoi Basin of the source region of Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 242-252. |
| [6] | Siyu Chen, Yawen Guan, Dan Zhao, Gaotong Lou, Yu Chen. Influence of dust aerosol on land surface diurnal temperature range over East Asia Simulated with the WRF-Chem model [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 127-138. |
| [7] | Fangming Zeng, Hongpan Xue. The dataset of elemental compositions of the late Pleistocene loess-paleosol deposits on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 262-264. |
| [8] | Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong, Zhengcai Zhang, Ming Zhou, Lunyu Shang. The regime of sand driving wind and sand drift potential in Zoige Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 20-24. |
| [9] | Yi Nana, Jiang Xuegong, Dong Zhulei, Yu Shuiyan, Kang Shengwei. Numerical simulation of a dust process in Inner Mongolia of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 115-126. |
| [10] | Hua Cong, Liu Chao, Zhang Bihui. Comparative Analysis of Transport Characteristics of Two Dust Events Affecting Beijing [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 99-107. |
| [11] | Yao Huiru, Li Dongliang. The Gale Concentration Period and Degree over the Tibetan Plateau and Related Atmospheric Circulation during the Windy Period [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(2): 122-133. |
| [12] | Sun Yan, Wang Yibo, Sun Zhe, Liu Guohu, Gao Zeyong. Impact of Soil Organic Matter on Water Hold Capacity in Permafrost Active Layer in the Tibetan Plateau [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(2): 288-295. |
| [13] | Kang Litai, Chen Siyu. Numerical Modeling of a Dust Storm Process in Northern China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(2): 321-331. |
| [14] | Zu Ruiping, He Zhilin, Zong Yumei, Qu Jianjun, Niu Qinghe. Review on the Influences of Sand Accumulation on Permafrost in the Tibetan Plateau [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(5): 1208-1214. |
| [15] | YANG Xing-hua1,2, HE Qing1,2, Ali Mamtimin1,2, HUO Wen1,2, LIU Xin-chun1,2. Observational Study on Near-surface Horizontal Sand-dust Flux of Sandstorms in the Southeastern Fringe of the Taklimakan Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(5): 1299-1304. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech