
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 330-341.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00152
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yu Xing1,2( ), Benli Liu1(
), Benli Liu1( ), Tao Ma3, Yimeng Wang1,2
), Tao Ma3, Yimeng Wang1,2
Received:2024-09-23
Revised:2024-11-05
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-06
Contact:
Benli Liu
CLC Number:
Yu Xing, Benli Liu, Tao Ma, Yimeng Wang. Wind erosion and dust emission in the core area of Hexi Corridor-Taklimakan Desert edge in 2000-2023[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 330-341.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00152
| 变量 | 时期 | 数据类型 | 时间/空间分辨率 | 变量用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 风速 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 1 h/0.25° | 用于估算风蚀量和PM10释放量,是风蚀和起尘的主要驱动力 |
| 土壤含水量 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 1 d/0.25° | |
| 土壤数据 | — | GeoTIFF | —/0.05° | 用于估算土壤的可蚀性和起尘能力 |
| NDVI | 2000—2023年 | HDF | 8 d/0.05° | 反映植被覆盖和健康状况,影响土壤表面抗风蚀能力 |
| EVI | ||||
| LAI | 2000—2023年 | GeoTIFF | 16 d/500 m | |
| 降水量 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 月/0.5° | 影响土壤湿度和植被生长,间接影响风蚀和PM10释放速率 |
| 温度 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 月/0.25° |
Table 1 Data sources
| 变量 | 时期 | 数据类型 | 时间/空间分辨率 | 变量用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 风速 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 1 h/0.25° | 用于估算风蚀量和PM10释放量,是风蚀和起尘的主要驱动力 |
| 土壤含水量 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 1 d/0.25° | |
| 土壤数据 | — | GeoTIFF | —/0.05° | 用于估算土壤的可蚀性和起尘能力 |
| NDVI | 2000—2023年 | HDF | 8 d/0.05° | 反映植被覆盖和健康状况,影响土壤表面抗风蚀能力 |
| EVI | ||||
| LAI | 2000—2023年 | GeoTIFF | 16 d/500 m | |
| 降水量 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 月/0.5° | 影响土壤湿度和植被生长,间接影响风蚀和PM10释放速率 |
| 温度 | 2000—2023年 | NetCDF | 月/0.25° |
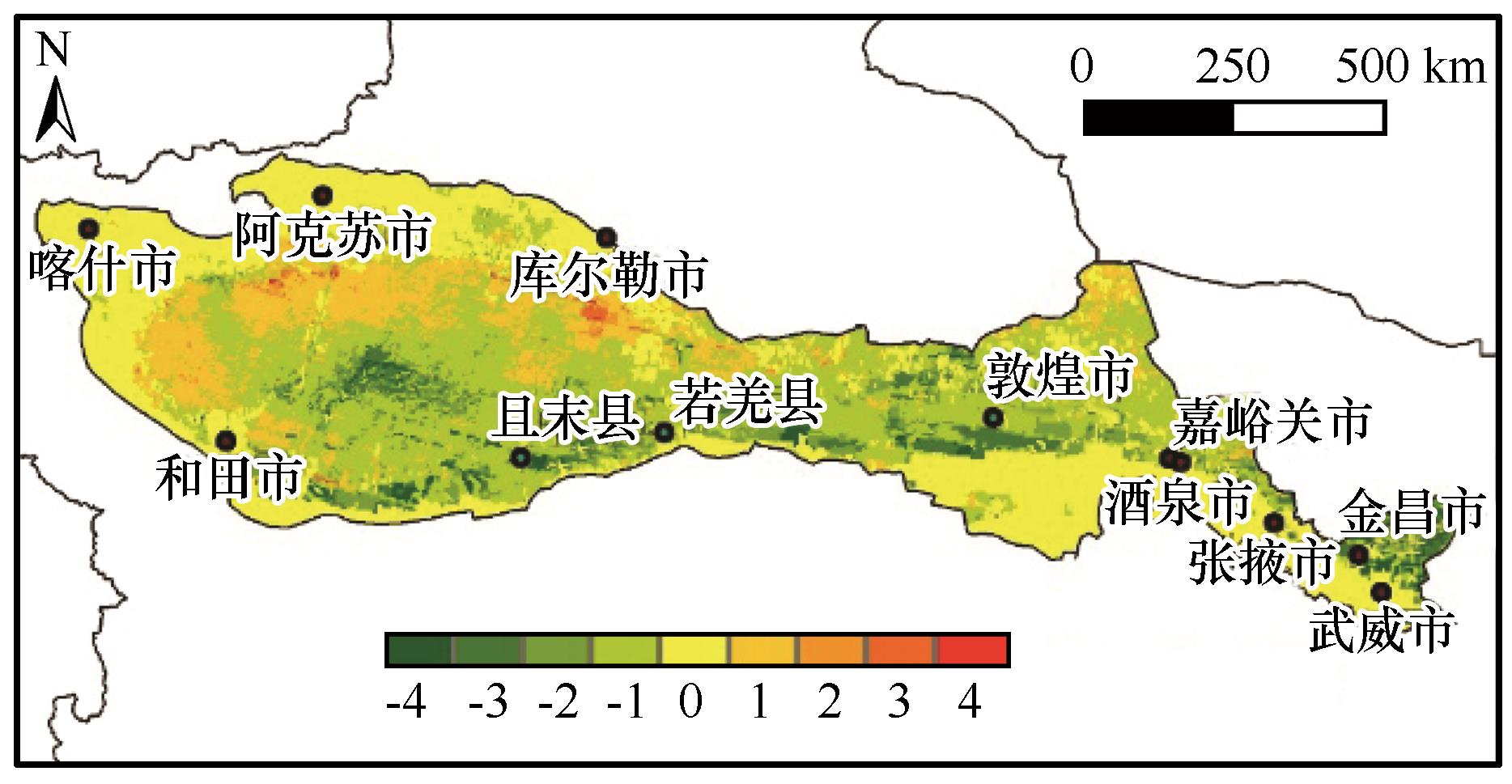
Fig.6 Spatial distribution of trends in wind erosion modulus changes in study area from 2000 to 2023 (Positive and negative values indicate increasing and decreasing trends, respectively. The absolute value of the numbers represents the degree of change, classified as extremely significant, significant, slight, and insignificant, in descending order)

Fig.10 Spatial distribution of correlation coefficients (Left) and partial correlation coefficients (Right) between wind erosion and influencing factors (wind speed, soil moisture, and NDVI) in study area from 2000 to 2023 (Asterisks indicate statistical significance at the 95% confidence level)
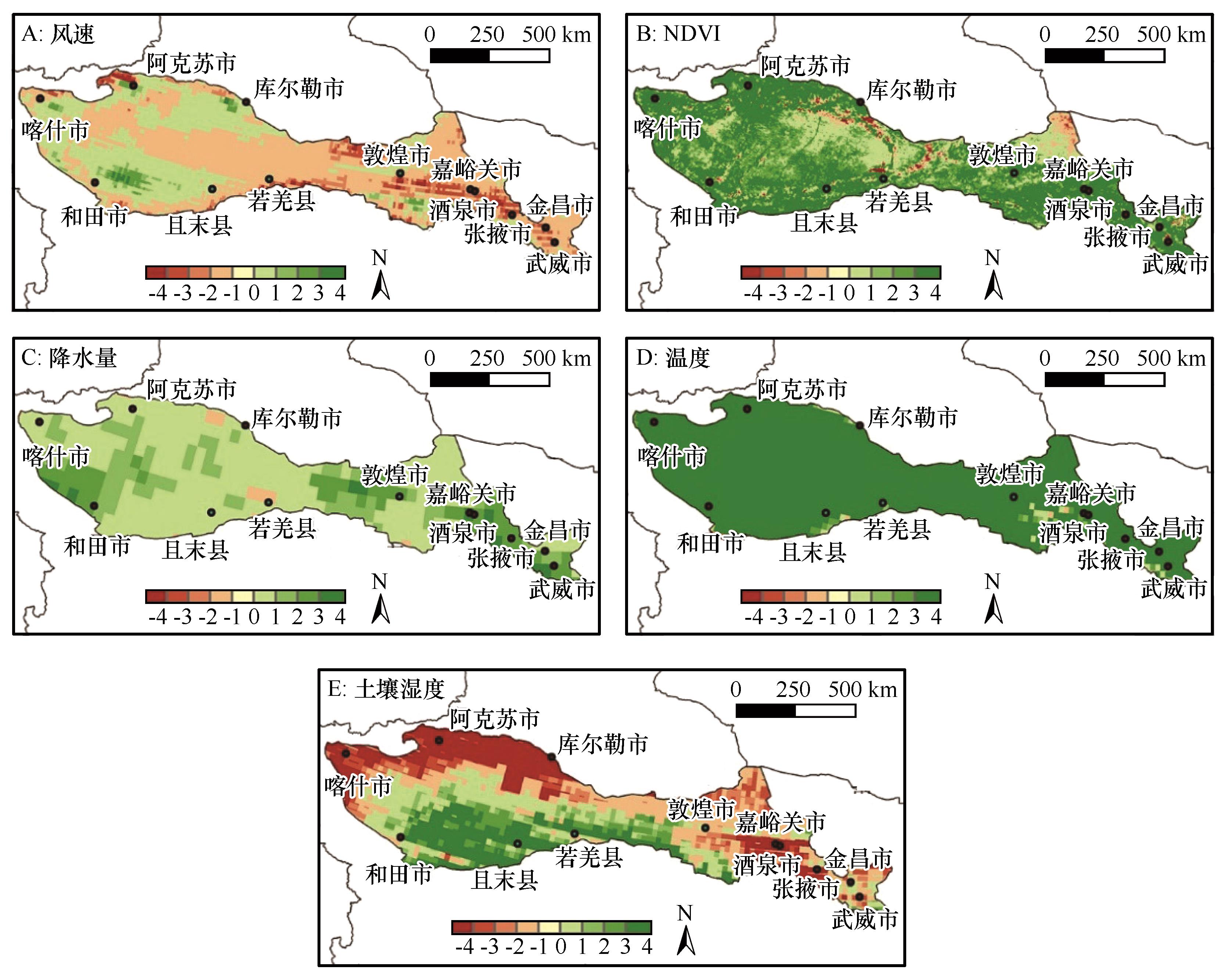
Fig.12 Trends of climatic factors in study area from 2000 to 2023(Positive and negative values indicate increasing and decreasing trends, respectively. The absolute value of the numbers represents the degree of change, classified as extremely significant, significant, slight, and insignificant, in descending order)
| 1 | 崔桂鹏,肖春蕾,雷加强,等.大国治理:中国荒漠化防治的战略选择与未来愿景[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(7):943-955. |
| 2 | 冯益明,卢琦,姚斌,等.河西走廊-塔克拉玛干沙漠边缘阻击战核心区现状、区划及任务[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(4):91-101. |
| 3 | 林锦阔.河西地区土壤侵蚀时空分异及其驱动因素[D].兰州:兰州大学,2021. |
| 4 | Hagen L J.A wind erosion prediction system to meet user needs[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,1991,46(2):106-111. |
| 5 | Warren S D, Mitasova H, Hohmann M G,et al.Validation of a 3-d enhancement of the universal soil loss equation for prediction of soil erosion and sediment deposition[J].Catena,2005,64(2/3):281-296. |
| 6 | Mayaud J.Development and testing of a coupled vegetation sediment-transport model for dryland environments[D].Oxford,UK:University of Oxford,2017. |
| 7 | Lu H, Shao Y P.Toward quantitative prediction of dust storms:an integrated wind erosion modelling system and its applications[J].Environmental Modelling Software,2001,16(3):233-249. |
| 8 | Ravi S, D'odorico P, Breshears D D,et al.Aeolian processes and the biosphere[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2011,49(3):RG3001. |
| 9 | Fryrear D W, Stout J E, Hagen L J,et al.Wind erosion-field measurement and analysis[J].Transactions of the ASAE,1991,34(1):155-160. |
| 10 | Meng Z J, Dang X H, Gao Y,et al.Interactive effects of wind speed,vegetation coverage and soil moisture in controlling wind erosion in a temperate desert steppe,Inner Mongolia of China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2018,10(4):534-547. |
| 11 | Zhang G F, Azorin-Molina C, Shi P J,et al.Impact of near-surface wind speed variability on wind erosion in the eastern agro-pastoral transitional zone of northern China,1982-2016[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2019,271:102-115. |
| 12 | Woodruff N P, Siddoway F H.A wind erosion equation[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,1965,29:602-608. |
| 13 | Fryrear D W, Saleh A, Bilbro J D,et al.Revised wind erosion equation[R].Lubbock,USA:USDA ARS,1998. |
| 14 | Jiang Y, Gao Y, Dong Z,et al.Simulations of wind erosion along the Qinghai-Tibet Railway in north-central Tibet[J].Aeolian Research,2018,32:192-201. |
| 15 | Guan Q, Sun X, Yang J,et al.Dust storms in northern china:long-term spatiotemporal characteristics and climate controls[J].Journal of Climate,2017,30(13):6683-6700. |
| 16 | Uwizeyimana D, Mureithi S M, Mvuyekure S M,et al.Modelling surface runoff using the soil conservation service-curve number method in a drought prone agro-ecological zone in Rwanda[J].International Soil and Water Conservation Research,2019,7(1):9-17. |
| 17 | 陆晓娟,李忆平,王劲松.中国北方干旱多发带极端春夏连旱的主要影响因子特征[J].高原气象:1-16. DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2024.00053 . |
| 18 | 雷加强,高鑫,赵永成,等.河西走廊-塔克拉玛干沙漠边缘阻击战:风沙形势与防治任务[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(7):966-977. |
| 19 | 王燕,王萍.风蚀预报系统(WEPS)在民勤荒漠地区的应用分析研究[J].干旱区地理,2013,36(1):109-117. |
| 20 | Rawls W J.Estimating soil bulk-density from particle-size analysis and organic-matter content[J].Soil Science,1983,135(2):123-125. |
| 21 | Barik G, Acharya P, Maiti A,et al.A synergy of linear model and wavelet analysis towards space-time characterization of aerosol optical depth (AOD) during pre-monsoon season (2007-2016) over Indian sub-continent[J].Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics,2020,211:105478. |
| 22 | 黄嘉佑.气象统计分析与预报方法[M].北京:气象出版社,1990. |
| 23 | 中华人民共和国水利部. 土壤侵蚀分类分级标准: [S].北京:中国水利水电出版社,2008. |
| 24 | Zender C S, Bian H S, Newman D.Mineral dust entrainment and deposition (dead) model:description and 1990s dust climatology[J].Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres,2003,108(D14):4416. |
| 25 | He Q, Yang X H, Mamtimin A,et al.Impact factors of soil wind erosion in the center of Taklimakan Desert[J].Journal of Arid Land,2011,3(1):9-14. |
| 26 | de Oro L A, Buschiazzo D E.Threshold wind velocity as an index of soil susceptibility to wind erosion under variable climatic conditions[J].Land Degradation Development,2009,20(1):14-21. |
| 27 | Chi W, Zhao Y, Kuang W,et al.Impacts of anthropogenic land use/cover changes on soil wind erosion in China[J].The Science of the Total Environment,2019,668:204-215. |
| 28 | Li X, Wu Z, Du Z,et al.Study on regional soil wind erosion and its influencing factors based on different wind erosion models-take Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region as an example[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2021,35(6):69-75. |
| 29 | Wang X, Cheng H, Che H,et al.Modern dust aerosol availability in northwestern China[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):8741. |
| 30 | Liu Y X, Teng Y, Liang S,et al.Establishment of pm10 and PM2.5 emission inventories from wind erosion source and simulation of its environmental impact based on WEPS-models3 in southern Xinjiang,China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2021,248:118222. |
| 31 | Li X L, Zhang H S.Seasonal variations in dust concentration and dust emission observed over Horqin Sandy Land area in China from December 2010 to November 2011[J].Atmospheric Environment,2012,61:56-65. |
| 32 | 霍文,杨青,何清,等.新疆大风区沙尘暴气候特征分析[J].干旱区地理,2011,34(5):753-761. |
| 33 | 马禹,肖开提,王旭.塔里木盆地沙尘天气的气候特征[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2006(6):784-790. |
| 34 | 赵兴梁.甘肃特大沙尘暴的危害与对策[J].中国沙漠,1993,13(3):4-10. |
| 35 | 张存杰 汤绪,李耀辉.河西走廊沙尘暴特征及气候成因分析[J].干旱气象,2003(4):18-22. |
| 36 | 宋敏红,钱正安,蔡英.19930505金昌特强沙尘暴爆发诱因再分析[J].高原气象,2020,39(5):1102-1109. |
| 37 | 黄麟,吴丹,孙朝阳.基于规划目标的京津风沙源治理区生态保护与修复效应[J].生态学报,2020,40(6):1923-1932. |
| 38 | 孙钦珂,周亮,唐相龙,等.干旱区绿洲城镇扩张对耕地空间影响及预测:以河西走廊区域为例[J].自然资源学报,2021,36(4):1008-1020. |
| 39 | 赵文智,任珩,杜军,等.河西走廊绿洲生态建设和农业发展的若干思考与建议[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(3):424-434. |
| 40 | Peng S, Chen A, Xu L,et al.Recent change of vegetation growth trend in China[J].Environmental Research Letters,2011,6(4):044027. |
| 41 | Tsoar H.Sand dunes mobility and stability in relation to climate[J].Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,2005,357(1):50-56. |
| 42 | 柳本立,彭婉月,刘树林,等.2021年3月中旬东亚中部沙尘天气地面起尘量及源区贡献率估算[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):79-86. |
| [1] | Yiming Feng, Qi Lu, Bin Yao, Lei Xi, Xiaoming Cao, Yongping Liu, Huseng Ning. Management regionalization and zoning management tasks of battle against desertification in the core area of Hexi Corridor-Taklimakan Desert edge [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 91-101. |
| [2] | Rende Wang, Hongjun Jiang, Qing Li, Gang Fu, Yuqiang Li, Yixiao Yuan, Chunping Chang, Zhongling Guo. Preliminary research on the relationship between soil dust emission ability and soil properties [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 43-49. |
| [3] | Wenfeng Chi, Yuetian Wang, Xiaohong Dang, Xiaoguang Wu, Qiancheng Luo. Temporal variation and spatial pattern of soil erosion in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 305-317. |
| [4] | Zhengcai Zhang, Kaijia Pan, Yan Zhang, Lanying Han. Sand transport characteristics above gobi surface during a dust storm in northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 130-138. |
| [5] | Rende Wang, Qing Li, Chunping Chang, Zhongling Guo, Jifeng Li, Xueyong Zou, Chunlai Zhang, Yixiao Yuan, Ying Liu, Na Zhou. Review of dust emission in soil wind erosion [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 85-103. |
| [6] | Lei Wang, Ruili Meng, Lei Cao, Fei Gao, Hao Chen, Yihui Li, Jiayin Zhang, Dongjie Yan, Xiao Liu, Tiantian Niu, Jing Ren. Influence of dust events on air quality of Shaanxi province from 2016 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 130-138. |
| [7] | Yue Zhang, Siyu Chen, Hongru Bi, Jiahui Cao, Yuan Luo, Yongqi Gong, Yu Chen. Characteristics and parameterization of farmland soil wind erosion in arid and semi-arid areas of China: progress and challenges [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 105-117. |
| [8] | Xiaoqin Yuan, Shengquan Liu, Feng Ai, Zheng Zhang, Qiang Li, Jinyu Jiang, Changchun Shi. Wind erosion resistance of litter of Salix psammophila community in the southeast edge of Mu Us Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 134-138. |
| [9] | Xiaoju Yang, Xueyong Zhao, Fasi Wu, Zhengmo Zhang, Ping Xue, Zhang Chen, Wanfu Wang, Guobin Zhang. Relationship of PM10 concentration in Mogao Grottoes to meteorological elements [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 54-64. |
| [10] | Lizhu Xing, Fangmin Zhang, Kaicheng Xing, Yunpeng Li, Qi Lu, Feifei Lu. Change of soil wind erosion and attribution in Bayannur, Inner Mongolia based on the Revised Wind Erosion Equation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 111-119. |
| [11] | Hanlin Li, Qing He, Quanwei Zhao. Transport pathways and potential source regions of PM10 in Kashgar, Xinjiang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 62-70. |
| [12] | Yahong Li, Chongfeng Bu, Qi Guo, Yingxin Wei. Ecological functions comparison of moss crust and algae crust in the Mu Us Sand Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 138-144. |
| [13] | Jun Liu, Zhongling Guo, Chunping Chang, Rende Wang, Jifeng Li, Qing Li, Xuyang Wang. Potential wind erosion simulation in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China using RWEQ and WEPS models [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 27-37. |
| [14] | Cen Songbo, Zhang Chunlai, Dai Yujie, Zhang Hui, Liu Xinyu, Li Qing, Huang Yuhu. Characteristics of PM10 emission from farmland during a wind erosion event [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 145-150. |
| [15] | Yang Caihong, Feng Fuxue, Chai Qiang, Geng Yanxiang, Fu Xingzhou. Soil Wind Erosion in Wheat/Maize Intercropping with Zero Tillage and Straw Retention [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 9-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech