
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 34-44.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zeyu Teng1,3( ), Shengchun Xiao1, Xiaohong Chen2, Chao Han1,3
), Shengchun Xiao1, Xiaohong Chen2, Chao Han1,3
Received:2020-11-21
Revised:2021-02-04
Online:2021-07-27
Published:2021-07-27
CLC Number:
Zeyu Teng, Shengchun Xiao, Xiaohong Chen, Chao Han. The soil bacterial condition beneath five shrub species in the central Alxa[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 34-44.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00023
| 植物 | 高度 /m | 地径 /cm | 冠幅(长轴) /m | 冠幅(短轴) /m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红砂 | 0.13±0.01 | 0.52±0.10 | 0.27±0.02 | 0.21±0.02 |
| 沙冬青 | 0.52±0.09 | 0.65±0.11 | 0.69±0.18 | 0.63±0.17 |
| 绵刺 | 0.25±0.01 | 0.92±0.13 | 0.58±0.18 | 0.50±0.19 |
| 霸王 | 0.40±0.03 | 1.43±0.61 | 1.13±0.31 | 0.87±0.14 |
| 白刺 | 0.33±0.02 | 0.90±0.18 | 2.23±1.01 | 1.23±0.24 |
Table 1 Morphological indicators for sampling shrubs
| 植物 | 高度 /m | 地径 /cm | 冠幅(长轴) /m | 冠幅(短轴) /m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红砂 | 0.13±0.01 | 0.52±0.10 | 0.27±0.02 | 0.21±0.02 |
| 沙冬青 | 0.52±0.09 | 0.65±0.11 | 0.69±0.18 | 0.63±0.17 |
| 绵刺 | 0.25±0.01 | 0.92±0.13 | 0.58±0.18 | 0.50±0.19 |
| 霸王 | 0.40±0.03 | 1.43±0.61 | 1.13±0.31 | 0.87±0.14 |
| 白刺 | 0.33±0.02 | 0.90±0.18 | 2.23±1.01 | 1.23±0.24 |
| 对比组 | F | P |
|---|---|---|
| 红砂-白刺 | 3.348 | <0.001 |
| 红砂-霸王 | 2.737 | <0.001 |
| 红砂-沙冬青 | 2.858 | 0.002 |
| 红砂-绵刺 | 2.328 | 0.021 |
| 绵刺-白刺 | 1.859 | 0.076 |
| 绵刺-霸王 | 1.578 | 0.084 |
| 绵刺-沙冬青 | 1.488 | 0.098 |
| 沙冬青-霸王 | 1.239 | 0.173 |
| 沙冬青-白刺 | 1.281 | 0.154 |
| 霸王-白刺 | 1.680 | 0.055 |
| (0—10 cm)-(10—20 cm) | 30.278 | <0.001 |
| 全部 | 1.969 | <0.001 |
Table 2 The AMOVA (analysis of molecular variance) results of soil bacterial community structure between different shrubs
| 对比组 | F | P |
|---|---|---|
| 红砂-白刺 | 3.348 | <0.001 |
| 红砂-霸王 | 2.737 | <0.001 |
| 红砂-沙冬青 | 2.858 | 0.002 |
| 红砂-绵刺 | 2.328 | 0.021 |
| 绵刺-白刺 | 1.859 | 0.076 |
| 绵刺-霸王 | 1.578 | 0.084 |
| 绵刺-沙冬青 | 1.488 | 0.098 |
| 沙冬青-霸王 | 1.239 | 0.173 |
| 沙冬青-白刺 | 1.281 | 0.154 |
| 霸王-白刺 | 1.680 | 0.055 |
| (0—10 cm)-(10—20 cm) | 30.278 | <0.001 |
| 全部 | 1.969 | <0.001 |
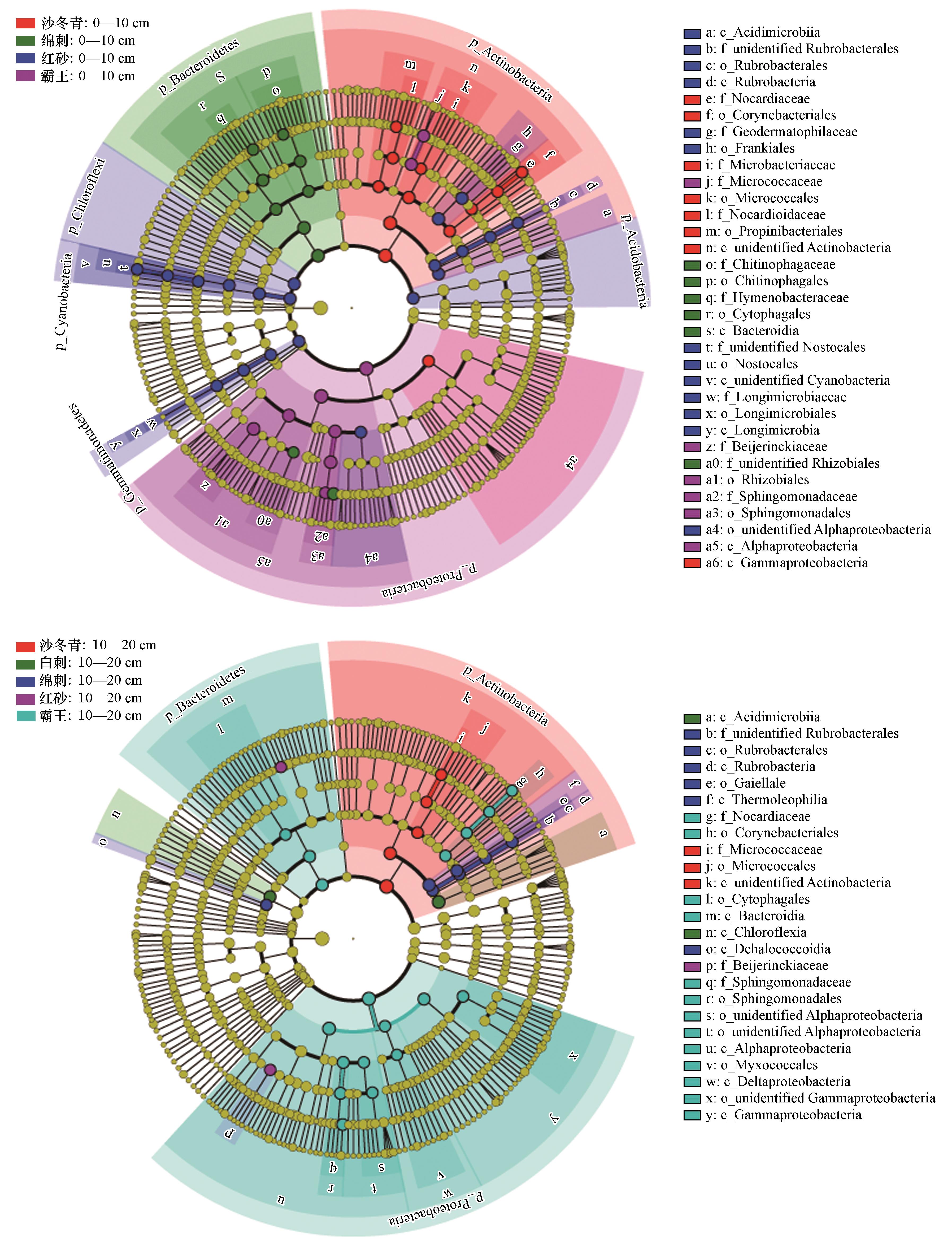
Fig.2 The result of Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) of soil bacterial community structure among shrubs in surface layer (A, upper) and subsurface layer (B, lower), the biomarkers indicates that the difference of their abundance among shrubs was statistically significant (LDA≥4)
| 土层 | 植物 | Chao1指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 | PD whole tree指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 cm | 红砂 | 2009.12±87.04ab | 8.68±0.05c | 0.9927±0.0004c | 127.15±1.98b |
| 绵刺 | 1768.74±62.49b | 8.45±0.11cd | 0.9895±0.0012d | 121.00±2.08b | |
| 沙冬青 | 1514.74±370.49bc | 8.39±0.36b | 0.9899±0.0021d | 113.68±23.49b | |
| 霸王 | 1765.50±190.19b | 8.19±0.08de | 0.9877±0.0011d | 127.57±15.16b | |
| 白刺 | 1538.73±303.53bc | 8.54±0.15e | 0.9906±0.0008cd | 110.63±14.21b | |
| 10—20 cm | 红砂 | 2201.70±291.70a | 9.10±0.03b | 0.9932±0.0006bc | 147.80±5.92a |
| 绵刺 | 2138.18±143.00a | 9.25±0.10a | 0.9962±0.0003a | 142.81±5.46a | |
| 沙冬青 | 1837.21±46.73b | 9.08±0.03b | 0.9951±0.0004ab | 130.48±3.82ab | |
| 霸王 | 1275.719±348.13c | 8.69±0.44ab | 0.9942±0.0002b | 104.78±22.00b | |
| 白刺 | 1781.79±103.30b | 8.75±0.05cd | 0.9936±0.0004b | 129.81±6.54ab | |
| 0—20 cm | 红砂 | 2105.39±219.52a | 8.89±0.23a | 0.9929±0.0006a | 137.47±11.97a |
| 绵刺 | 1953.46±225.14a | 8.85±0.45a | 0.9928±0.0037a | 131.91±12.51ab | |
| 沙冬青 | 1675.97±294.90b | 8.73±0.44ab | 0.9925±0.0031a | 122.08±17.64ab | |
| 霸王 | 1520.61±367.31b | 8.44±0.40b | 0.9910±0.0038a | 116.18±21.01b | |
| 白刺 | 1660.26±242.58b | 8.64±0.15ab | 0.9921±0.0017a | 120.22±14.43ab | |
| 10 cm | 1719.37±272.96a | 8.45±0.23b | 0.9901±0.0020b | 120.01±13.87b | |
| 20 cm | 1846.91±387.58a | 8.97±0.28a | 0.9945±0.0013a | 131.13±18.02a |
Table 3 Statistical table of Alpha diversities among different shrubs and soil layers
| 土层 | 植物 | Chao1指数 | Shannon指数 | Simpson指数 | PD whole tree指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 cm | 红砂 | 2009.12±87.04ab | 8.68±0.05c | 0.9927±0.0004c | 127.15±1.98b |
| 绵刺 | 1768.74±62.49b | 8.45±0.11cd | 0.9895±0.0012d | 121.00±2.08b | |
| 沙冬青 | 1514.74±370.49bc | 8.39±0.36b | 0.9899±0.0021d | 113.68±23.49b | |
| 霸王 | 1765.50±190.19b | 8.19±0.08de | 0.9877±0.0011d | 127.57±15.16b | |
| 白刺 | 1538.73±303.53bc | 8.54±0.15e | 0.9906±0.0008cd | 110.63±14.21b | |
| 10—20 cm | 红砂 | 2201.70±291.70a | 9.10±0.03b | 0.9932±0.0006bc | 147.80±5.92a |
| 绵刺 | 2138.18±143.00a | 9.25±0.10a | 0.9962±0.0003a | 142.81±5.46a | |
| 沙冬青 | 1837.21±46.73b | 9.08±0.03b | 0.9951±0.0004ab | 130.48±3.82ab | |
| 霸王 | 1275.719±348.13c | 8.69±0.44ab | 0.9942±0.0002b | 104.78±22.00b | |
| 白刺 | 1781.79±103.30b | 8.75±0.05cd | 0.9936±0.0004b | 129.81±6.54ab | |
| 0—20 cm | 红砂 | 2105.39±219.52a | 8.89±0.23a | 0.9929±0.0006a | 137.47±11.97a |
| 绵刺 | 1953.46±225.14a | 8.85±0.45a | 0.9928±0.0037a | 131.91±12.51ab | |
| 沙冬青 | 1675.97±294.90b | 8.73±0.44ab | 0.9925±0.0031a | 122.08±17.64ab | |
| 霸王 | 1520.61±367.31b | 8.44±0.40b | 0.9910±0.0038a | 116.18±21.01b | |
| 白刺 | 1660.26±242.58b | 8.64±0.15ab | 0.9921±0.0017a | 120.22±14.43ab | |
| 10 cm | 1719.37±272.96a | 8.45±0.23b | 0.9901±0.0020b | 120.01±13.87b | |
| 20 cm | 1846.91±387.58a | 8.97±0.28a | 0.9945±0.0013a | 131.13±18.02a |
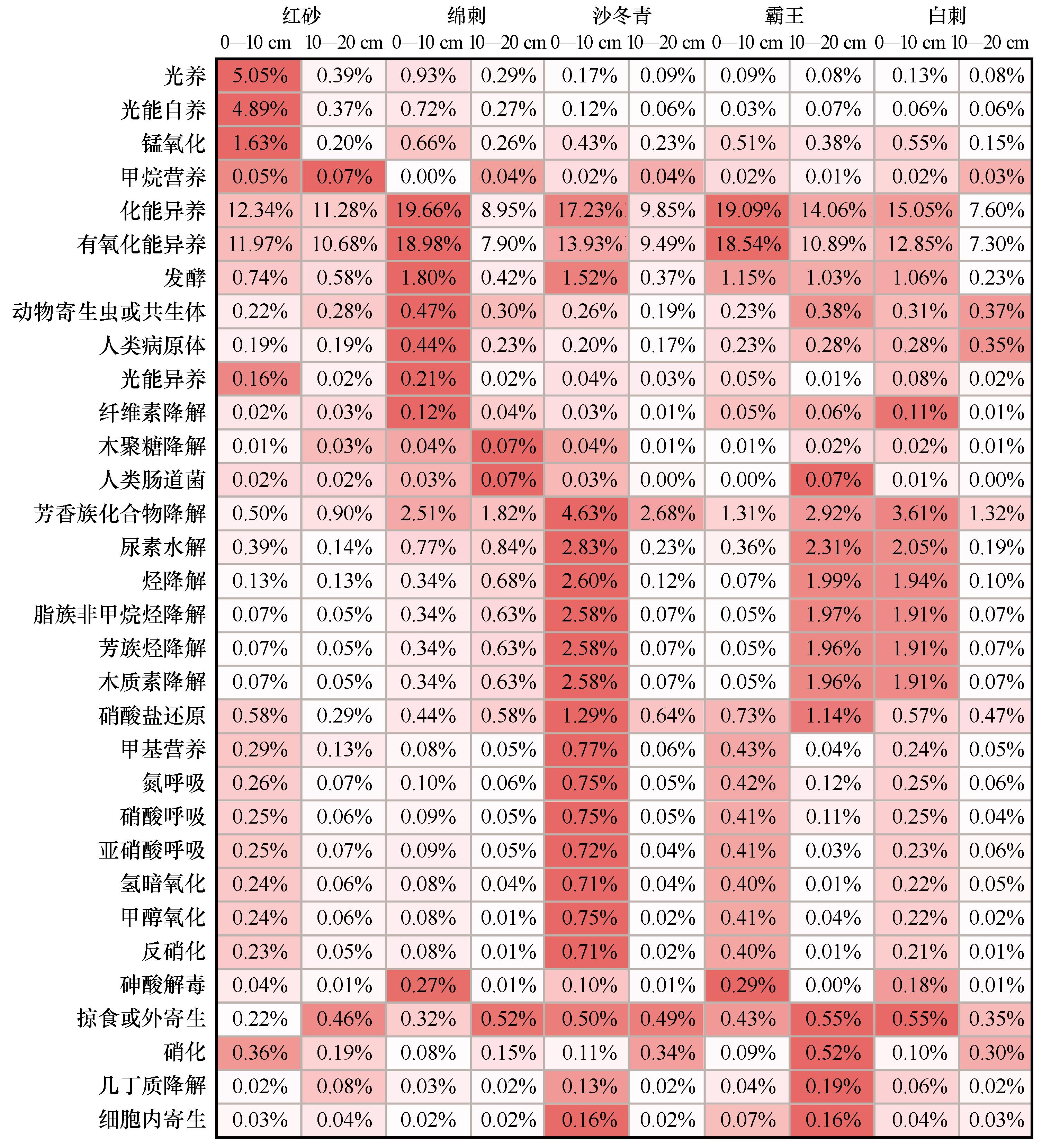
Fig.3 The functional annotation heat map based on Functional Annotation of Prokaryotic Taxa (FAPROTAX), the data is the sum of the bacterial average abundance with this function
| 环境因子 | 红砂 | 绵刺 | 沙冬青 | 霸王 | 白刺 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | |||||
| MBC/(mg·kg-1) | 65.99±12.66 | 58.42±11.38 | 80.51±15.14 | 65.11±10.36 | 45.79±8.11 | 38.12±6.93 | 84.02±17.21 | 62.09±11.44 | 57.70±9.91 | 45.77±8.36 | ||||
| MBN/(mg·kg-1) | 9.11±1.02 | 7.99±0.86 | 12.95±1.17 | 8.88±0.99 | 5.96±0.41 | 5.19±0.39 | 12.18±1.33 | 9.58±0.81 | 8.94±0.75 | 6.52±0.55 | ||||
| TC/(g·kg-1) | 5.56±0.27 | 4.71±0.21 | 4.94±0.39 | 7.28±0.44 | 2.91±0.13 | 8.38±0.47 | 4.96±0.35 | 6.82±0.37 | 2.93±0.11 | 8.07±0.42 | ||||
| TN/(g·kg-1) | 0.19±0.01 | 0.18±0.00 | 0.29±0.02 | 0.22±0.01 | 0.11±0.00 | 0.13±0.00 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.09±0.01 | 0.14±0.00 | ||||
| TP/(g·kg-1) | 0.35±0.03 | 0.37±0.04 | 0.30±0.03 | 0.34±0.04 | 0.24±0.02 | 0.30±0.02 | 0.30±0.03 | 0.34±0.03 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.24±0.03 | ||||
| SOC/(g·kg-1) | 2.15±0.19 | 2.22±0.21 | 3.83±0.33 | 3.02±0.32 | 1.29±0.10 | 1.55±0.14 | 2.45±0.23 | 2.13±0.22 | 1.18±0.11 | 1.74±0.14 | ||||
| AN/(mg·kg-1) | 10.53±2.76 | 6.27±2.28 | 19.29±3.92 | 10.17±3.13 | 3.04±1.04 | 12.84±3.06 | 15.97±3.47 | 11.86±3.36 | 8.19±2.11 | 3.72±1.17 | ||||
| AP/(mg·kg-1) | 1.28±0.20 | 2.03±0.42 | 3.80±0.57 | 0.96±0.21 | 0.84±0.19 | 0.85±0.21 | 1.87±0.24 | 1.19±0.17 | 0.63±0.07 | 1.08±0.18 | ||||
| Cl-/(mg·kg-1) | 116.53±3.41 | 118.07±3.37 | 27.68±1.03 | 30.55±1.24 | 25.14±1.08 | 36.26±1.42 | 113.78±3.03 | 93.06±2.94 | 33.06±1.38 | 49.66±1.90 | ||||
| HCO | 75.68±1.36 | 81.38±1.42 | 50.62±0.93 | 68.76±1.44 | 44.24±0.52 | 88.29±2.04 | 50.54±0.88 | 73.5±1.82 | 48.88±0.47 | 68.98±1.96 | ||||
| SO | 134.55±9.38 | 55.99±5.03 | 38.88±4.02 | 41.21±4.50 | 154.40±11.66 | 149.58±12.05 | 193.77±15.44 | 85.09±6.14 | 43.64±4.16 | 39.02±4.42 | ||||
| Ca2+/(mg·kg-1) | 35.79±2.84 | 36.10±2.55 | 66.98±5.72 | 84.23±6.11 | 56.86±4.06 | 77.8±5.30 | 75.14±5.22 | 68.63±4.93 | 63.27±5.71 | 86.44±6.16 | ||||
| K+/(mg·kg-1) | 33.58±1.09 | 25.62±1.26 | 24.92±1.07 | 22.29±0.94 | 22.29±1.23 | 22.27±1.10 | 36.51±1.24 | 30.33±1.37 | 16.77±0.77 | 25.85±1.45 | ||||
| Mg2+/(mg·kg-1) | 10.15±0.98 | 13.20±1.52 | 11.39±1.07 | 15.80±1.39 | 11.75±1.25 | 15.46±1.41 | 12.91±1.35 | 18.6±1.83 | 11.01±1.22 | 18.08±2.00 | ||||
| Na+/(mg·kg-1) | 186.78±20.03 | 221.38±19.37 | 34.78±2.94 | 33.46±3.44 | 22.05±2.19 | 80.11±9.92 | 95.84±12.56 | 122.68±15.34 | 13.57±0.84 | 28.7±3.24 | ||||
| EC/(μS·cm-1) | 217.67±2.06 | 248.10±1.55 | 106.33±1.07 | 140.67±1.24 | 100.17±0.82 | 171.90±0.64 | 231.00±2.55 | 202.10±1.29 | 100.23±0.71 | 143..83±0.70 | ||||
| MOI/% | 0.87±0.06 | 1.65±0.09 | 1.68±0.42 | 1.48±0.08 | 1.07±0.06 | 1.78±0.07 | 2.07±0.51 | 1.96±0.10 | 1.69±0.10 | 1.83±0.06 | ||||
| pH | 8.98±0.05 | 9.20±0.06 | 8.33±0.04 | 8.61±0.03 | 8.28±0.04 | 8.55±0.04 | 7.87±0.04 | 8.77±0.04 | 8.65±0.05 | 8.58±0.05 | ||||
Table 4 Statistical table of microbial biomass and environmental factors between groups
| 环境因子 | 红砂 | 绵刺 | 沙冬青 | 霸王 | 白刺 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | |||||
| MBC/(mg·kg-1) | 65.99±12.66 | 58.42±11.38 | 80.51±15.14 | 65.11±10.36 | 45.79±8.11 | 38.12±6.93 | 84.02±17.21 | 62.09±11.44 | 57.70±9.91 | 45.77±8.36 | ||||
| MBN/(mg·kg-1) | 9.11±1.02 | 7.99±0.86 | 12.95±1.17 | 8.88±0.99 | 5.96±0.41 | 5.19±0.39 | 12.18±1.33 | 9.58±0.81 | 8.94±0.75 | 6.52±0.55 | ||||
| TC/(g·kg-1) | 5.56±0.27 | 4.71±0.21 | 4.94±0.39 | 7.28±0.44 | 2.91±0.13 | 8.38±0.47 | 4.96±0.35 | 6.82±0.37 | 2.93±0.11 | 8.07±0.42 | ||||
| TN/(g·kg-1) | 0.19±0.01 | 0.18±0.00 | 0.29±0.02 | 0.22±0.01 | 0.11±0.00 | 0.13±0.00 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.09±0.01 | 0.14±0.00 | ||||
| TP/(g·kg-1) | 0.35±0.03 | 0.37±0.04 | 0.30±0.03 | 0.34±0.04 | 0.24±0.02 | 0.30±0.02 | 0.30±0.03 | 0.34±0.03 | 0.19±0.01 | 0.24±0.03 | ||||
| SOC/(g·kg-1) | 2.15±0.19 | 2.22±0.21 | 3.83±0.33 | 3.02±0.32 | 1.29±0.10 | 1.55±0.14 | 2.45±0.23 | 2.13±0.22 | 1.18±0.11 | 1.74±0.14 | ||||
| AN/(mg·kg-1) | 10.53±2.76 | 6.27±2.28 | 19.29±3.92 | 10.17±3.13 | 3.04±1.04 | 12.84±3.06 | 15.97±3.47 | 11.86±3.36 | 8.19±2.11 | 3.72±1.17 | ||||
| AP/(mg·kg-1) | 1.28±0.20 | 2.03±0.42 | 3.80±0.57 | 0.96±0.21 | 0.84±0.19 | 0.85±0.21 | 1.87±0.24 | 1.19±0.17 | 0.63±0.07 | 1.08±0.18 | ||||
| Cl-/(mg·kg-1) | 116.53±3.41 | 118.07±3.37 | 27.68±1.03 | 30.55±1.24 | 25.14±1.08 | 36.26±1.42 | 113.78±3.03 | 93.06±2.94 | 33.06±1.38 | 49.66±1.90 | ||||
| HCO | 75.68±1.36 | 81.38±1.42 | 50.62±0.93 | 68.76±1.44 | 44.24±0.52 | 88.29±2.04 | 50.54±0.88 | 73.5±1.82 | 48.88±0.47 | 68.98±1.96 | ||||
| SO | 134.55±9.38 | 55.99±5.03 | 38.88±4.02 | 41.21±4.50 | 154.40±11.66 | 149.58±12.05 | 193.77±15.44 | 85.09±6.14 | 43.64±4.16 | 39.02±4.42 | ||||
| Ca2+/(mg·kg-1) | 35.79±2.84 | 36.10±2.55 | 66.98±5.72 | 84.23±6.11 | 56.86±4.06 | 77.8±5.30 | 75.14±5.22 | 68.63±4.93 | 63.27±5.71 | 86.44±6.16 | ||||
| K+/(mg·kg-1) | 33.58±1.09 | 25.62±1.26 | 24.92±1.07 | 22.29±0.94 | 22.29±1.23 | 22.27±1.10 | 36.51±1.24 | 30.33±1.37 | 16.77±0.77 | 25.85±1.45 | ||||
| Mg2+/(mg·kg-1) | 10.15±0.98 | 13.20±1.52 | 11.39±1.07 | 15.80±1.39 | 11.75±1.25 | 15.46±1.41 | 12.91±1.35 | 18.6±1.83 | 11.01±1.22 | 18.08±2.00 | ||||
| Na+/(mg·kg-1) | 186.78±20.03 | 221.38±19.37 | 34.78±2.94 | 33.46±3.44 | 22.05±2.19 | 80.11±9.92 | 95.84±12.56 | 122.68±15.34 | 13.57±0.84 | 28.7±3.24 | ||||
| EC/(μS·cm-1) | 217.67±2.06 | 248.10±1.55 | 106.33±1.07 | 140.67±1.24 | 100.17±0.82 | 171.90±0.64 | 231.00±2.55 | 202.10±1.29 | 100.23±0.71 | 143..83±0.70 | ||||
| MOI/% | 0.87±0.06 | 1.65±0.09 | 1.68±0.42 | 1.48±0.08 | 1.07±0.06 | 1.78±0.07 | 2.07±0.51 | 1.96±0.10 | 1.69±0.10 | 1.83±0.06 | ||||
| pH | 8.98±0.05 | 9.20±0.06 | 8.33±0.04 | 8.61±0.03 | 8.28±0.04 | 8.55±0.04 | 7.87±0.04 | 8.77±0.04 | 8.65±0.05 | 8.58±0.05 | ||||
| 环境因子 | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| Mg2+ | 0.7084 | <0.001 |
| TC | 0.5294 | <0.001 |
| HCO | 0.4575 | <0.001 |
| Ca2+ | 0.2455 | 0.002 |
| pH | 0.1806 | 0.007 |
| MOI | 0.1779 | 0.008 |
| EC | 0.1539 | 0.011 |
| SOC | 0.1529 | 0.013 |
| TN | 0.1371 | 0.018 |
Table 5 The nine environmental factors most associated with soil bacterial community by Mantel test
| 环境因子 | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| Mg2+ | 0.7084 | <0.001 |
| TC | 0.5294 | <0.001 |
| HCO | 0.4575 | <0.001 |
| Ca2+ | 0.2455 | 0.002 |
| pH | 0.1806 | 0.007 |
| MOI | 0.1779 | 0.008 |
| EC | 0.1539 | 0.011 |
| SOC | 0.1529 | 0.013 |
| TN | 0.1371 | 0.018 |
| 1 | 李骁,王迎春.土壤微生物多样性与植物多样性[J].内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版),2006,37(6):708-713. |
| 2 | 鲁海燕,徐艾诗,曹靖.微生物多样性对植物群落影响的研究进展[J].长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2010,33(3):103-106. |
| 3 | 毕江涛,贺达汉.植物对土壤微生物多样性的影响研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2009,25(9):244-250. |
| 4 | Wardle D A,Bardgett R D,Klironomos J N,et al.Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota[J].Science,2004,304:1629-1633. |
| 5 | Berg G,Smalla K.Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere[J].FEMS Microbiology Ecology,2009,68:1-13. |
| 6 | Leloup J,Baude M,Nunan N,et al.Unravelling the effects of plant species diversity and aboveground litter input on soil bacterial communities[J].Geoderma,2018,317:1-7. |
| 7 | Barness G,Zaragoza S R,Shmueli I,et al.Vertical distribution of a soil microbial community as affected by plant ecophysiological adaptation in a desert system[J].Microbial Ecology,2009,57:36-49. |
| 8 | Sherman C,Marais E,Maggs-Kölling G,et al.Abiotic and plant gender effects on the structure and function of soil microbial communities associated with Acanthosicyos horridus (Nara) in the Namibian sand-dune desert ecosystem[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2019,163:50-58. |
| 9 | Li H,Xu Z,Yan Q,et al.Soil microbial beta-diversity is linked with compositional variation in aboveground plant biomass in a semi-arid grassland[J].Plant and Soil,2018,423:465-480. |
| 10 | 陈广生,曾德慧,陈伏生,等.干旱和半干旱地区灌木下土壤“肥岛”研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2003(12):2295-2300. |
| 11 | Dunbar J,Barns S M,Ticknor L O,et al.Empirical and theoretical bacterial diversity in four Arizona soils[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2002,68(6):3035-3045. |
| 12 | Huang J,Yu H,Guan X,et al.Accelerated dryland expansion under climate change[J].Nature Climate Change,2015,6(2):2837-2842. |
| 13 | Yi C,Wei S,Hendrey G.Warming climate extends dryness-controlled areas of terrestrial carbon sequestration[J].Scientific Reports,2014,4:5472-5477. |
| 14 | Zhou Z Y,Yan S Y,Qin Y,et al.The characters of shrub by diversity of Alxa arid desert region[J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2009,23(9):146-150. |
| 15 | 胡亚林,汪思龙,颜绍馗.影响土壤微生物活性与群落结构因素研究进展[J].土壤通报,2006,37(1):170-176. |
| 16 | Pointing S B,Belnap J.Microbial colonization and controls in dryland systems[J].Nature Reviews Microbiology,2012,10:551-562. |
| 17 | Kennedy A C,Smith K L.Soil microbial diversity and the sustainability of agricultural soils[J].Plant & Soil,1995,170:75-86. |
| 18 | Somova L A,Pechurkin N S.Functional,regulatory and indicator features of microorganisms in man-made ecosystems[J].Advances in Space Research,2001,27(9):1563-1570. |
| 19 | 肖生春,陈小红,丁爱军.近现代阿拉善荒漠气候变化与环境演变机制研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(6):1102-1110. |
| 20 | 乌仁塔娜,王玉霞,高润宏.阿拉善荒漠功能灌木群分布格局[J].中国农学通报,2013,29(19):79-83. |
| 21 | 卢琦,王继和,褚建民,等.中国荒漠植物图鉴[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2012:206-369. |
| 22 | 孙艳霞,杨九艳,乔宜青,等.阿拉善高原红砂(Reaumuria songarica)种群空间分布格局[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):105-115. |
| 23 | 周航宇,包爱科,杜宝强,等.荒漠植物红砂响应高浓度NaCl的生理机制[J].草业科学,2012,29(1):77-81. |
| 24 | 王继和,吴春荣.甘肃荒漠区濒危植物绵刺生理生态学特性的研究[J].中国沙漠,2000,20(4):397-403. |
| 25 | 肖星卉,高润宏,王树森,等.西鄂尔多斯古地中海孑遗植物干旱胁迫与保护酶响应研究[J].内蒙古科技与经济,2018(12):58-60. |
| 26 | 郭丁,裴世芳,俞斌华,等.阿拉善荒漠草地几种灌木对土壤有效态养分的影响[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(1):95-100. |
| 27 | 王彦阁,杨晓晖,于春堂,等.白刺属植物现状、生态功能及保护策略[J].水土保持研究,2007,14(3):74-79. |
| 28 | 杨鑫光,傅华,李晓东.干旱胁迫对霸王水分生理特征及细胞膜透性的影响[J].西北植物学报,2009,29(10):2076-2083. |
| 29 | 王静娅,王明亮,张凤华.干旱区典型盐生植物群落下土壤微生物群落特征[J].生态学报,2016,36(8):2363-2372. |
| 30 | 李欣玫,左易灵,薛子可,等.不同荒漠植物根际土壤微生物群落结构特征[J].生态学报,2018,38(8):2855-2863. |
| 31 | 席军强,杨自辉,郭树江,等.民勤绿洲-沙漠过渡带土壤微生物数量特征[J].干旱区资源与环境,2015,29(7):116-121. |
| 32 | 裴浩,朱宗元,梁存柱,等.阿拉善荒漠区生态环境特征与环境保护[M].北京:气象出版社,2011:15-16. |
| 33 | Zhou J,Bruns M V,Tiedje J M.DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1996,62:316-322. |
| 34 | Michelsen C F,Pedas P,Glaring M A,et al.Bacterial diversity in Greenlandic soils as affected by potato cropping and inorganic versus organic fertilization[J].Polar Biology,2014,37:61-71. |
| 35 | Martin M.Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads[J].Embnet Journal,2011,17:10-12. |
| 36 | Edgar R C,Haas B J,Clemente J C,et al.UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection[J].Bioinformatics,2011,27:2194-2200. |
| 37 | Vance E D,Brooks P C,Jenkinson D S.An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C[J].Soil Biology & Biochemistry,1987,19(6):703-707. |
| 38 | 李月飞,陈林,李学斌,等.荒漠草原灌丛沃岛的结构特征和生态效应[J].草业科学,2018,35(10):2327-2335. |
| 39 | 尹传华,董积忠,石秋梅,等.不同生境下盐生灌木盐岛效应的变化及生态学意义[J].土壤学报,2012,49(2):289-295. |
| 40 | Lozupone C,Lladser M E,Knights D,et al.UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison[J].The ISME Journal,2011,5:169-172. |
| 41 | Angiosperm Phylogeny Group.An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants:APG IV[J].Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society,2016,181(1):1-20. |
| 42 | Jones P,Garcia B J,Furches A,et al.Plant host-associated mechanisms for microbial selection[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2019,10:862. |
| 43 | Chen M Y,Wu S H,Lin G H,et al.Rubrobacter taiwanensis sp.nov.a novel thermophilic,radiation-resistant species isolated from hot springs[J].International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology,2004,54(5):1849-1855. |
| 44 | Sun H M,Zhang T,Yu L Y,et al.Ubiquity,diversity and physiological characteristics of Geodermatophilaceae in Shapotou National Desert Ecological Reserve[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2015,6:Article1059. |
| 45 | Yoshida N,Inaba S,Takagi H.Utilization of atmospheric ammonia by an extremely oligotrophic bacterium,Rhodococcus erythropolis N9T-4[J].Journal of Bioence & Bioengineering,2014,117(1):28-32. |
| 46 | Wang S M,Wan C G,Wang Y R,et al.The characteristics of Na+,K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert,China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2004,56:525-539. |
| 47 | Duval C,Thomazeau S,Drelin Y,et al.Phylogeny and salt-tolerance of freshwater Nostocales strains: contribution to their systematics and evolution[J].Harmful Algae,2018,73:58-71. |
| 48 | Gilbert P,Rickard A H.Adhaeribacter[M]//Whitman W B.Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria.Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons,Inc,2015. |
| 49 | 刘光琇,陈拓,李师翁,等.极端环境微生物学[M].北京:科学出版社,2016:34-36. |
| [1] | Liuwen Dong, Jialong Han, Wenzhi Zhao, Jiliang Liu, Yibin Ba. Comparison of ground arthropod community between Lake Wetland and adjacent sand dune in Heihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 250-258. |
| [2] | Rentao Liu, Anning Zhang. Short-term effect of afforested shrub plantations on ground-active arthropod communities in desertified regions [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 190-199. |
| [3] | Ziyuan Zhou, Minghan Yu, Guodong Ding, Guanglei Gao, Yingying He. Diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizocompartments of Caragana in the Mu Us Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 128-137. |
| [4] | Delu Li, Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Xinrong Li, Hongbo Yuan, Linyuan Wei, Haotian Yang, Zhong Zhang. Vegetation characteristics of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| [5] | Wang Yu, Liu Juanjuan, Feng Qi, Liu Xiande, Wang Zhijun, Guo Yamin, Kong Dexing. Community structure and biodiversity of zoobenthos in Heihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 125-135. |
| [6] | Xiong Bingqiao, Zhao Liya, Gao Dandan. Effect of Enclosure on the Structure of Plant Community in Degraded Sandy Grasslands of Eastern Inner Mongolia [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2018, 38(2): 324-328. |
| [7] | Li Ting, Zhang Wei, Liu Guangxiu, Chen Tuo. Advances in the Study of Microbial Ecology in Desert Soil [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2018, 38(2): 329-338. |
| [8] | Liu Rentao, Xi Weihua, Liu Jia'nan, Zhao Juan, Chang Haotao. Spatial Distribution of Arthropod Community between Caragana Shrub Microhabitats [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2018, 38(1): 117-125. |
| [9] | Xiao Shengchun, Chen Xiaohong, Ding Aijun. Study Process of Climate Changes, Environment Evolution and Its Driving Mechanism in the Last Two Centuries in the Alxa Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(6): 1102-1110. |
| [10] | Wang Shaokun, Zhao Xueyong, Jia Kunfeng, Gao Baolan, Qu Hao, Mao Wei, Lian Jie, Chen Min, Zhu Yangchun. Soil Bacterial Diversity and Its Vertical Distribution in Stipa klemenzii Community of Urad Desert Steppe [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(6): 1564-1570. |
| [11] | LI Xiao-xiong1, LIU Xian-de1,2, ZHAO Wei-jun2. Community Structure of a Dynamical Plot of Picea crassifolia Forest in Qilian Mountains, China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(1): 94-100. |
| [12] | LIU Ren-tao1,2, ZHAO Ha-lin2, ZHAO Xue-yong2. Community Structure of the Soil Fauna under or outside the Caragana microphylla Canopy in Shifting Sandy Land [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(1): 167-173. |
| [13] | ZHENG Tian;LI Wei-hong;LI Jian-gui;WAN Jiang-hui;. Characters of Community Diversity in the Oasis-desert Transition Zone in Lower Reaches of Tarim River [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2009, 29(2): 241-247. |
| [14] | JIANG Li-xue;LI Yan. Comparison on Architecture Characteristics of Root Systems and Leaf Traits for Three Desert Shrubs Adapted to Arid Habitat [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2008, 28(6): 1118-1124. |
| [15] | ZHANG Dao-yuan;MA Wen-bao;SHI Xiang;WANG Jian-cheng;WANG Xi-yong. Distribution and Bio-ecological Characteristics of Eremosparton songoricum, a Rare Plant in Gurbantunggut Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2008, 28(3): 430-436. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech