中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 22-31.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00174
收稿日期:2021-09-30
修回日期:2021-11-17
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-08-29
通讯作者:
董治宝
作者简介:董治宝(E-mail: zbdong@snnu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Xiaozhi Wang( ), Zhibao Dong(
), Zhibao Dong( ), Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang
), Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang
Received:2021-09-30
Revised:2021-11-17
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-08-29
Contact:
Zhibao Dong
摘要:
分析了青藏高原拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘表层及不同深度沉积物的粒度和地球化学元素特征。结果表明:(1)爬坡沙丘表层沉积物以细沙为主,平均粒径为2.51Φ(细沙),分选中等,粒度分布曲线为正偏、窄峰。随海拔升高,表层沉积物逐渐变细;随深度增加,沉积物粒径逐渐变细。(2)爬坡沙丘沉积物常量元素中SiO2含量最高,微量元素中Ba含量最高。常量元素含量多随深度增加而减少,且在0—10 cm深度内变化幅度最大。与上部陆壳平均化学组成相比,除Na2O、MnO、Cr、Co、Mo、SiO2外,其余元素均处于亏损状态。拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘经历了中等的化学风化,处于大陆风化的早期阶段。
中图分类号:
王晓枝, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 李超, 高冲, 张欣. 拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 22-31.
Xiaozhi Wang, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang. Sediment characteristics of climbing dunes in Lhasa River Valley, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 22-31.
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.002 mm | 粉沙 0.002—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| P1 | 0.00 | 1.45 | 4.72 | 56.89 | 36.59 | 0.34 |
| P2 | 0.00 | 3.69 | 8.26 | 49.68 | 37.02 | 1.35 |
| P3 | 0.05 | 8.00 | 14.04 | 44.55 | 31.91 | 1.44 |
| P4 | 0.67 | 10.79 | 23.94 | 47.70 | 16.90 | 0.00 |
| P5 | 0.18 | 21.27 | 24.74 | 29.31 | 20.78 | 3.72 |
| P6 | 0.32 | 3.73 | 25.75 | 56.77 | 13.43 | 0.00 |
| P7 | 0.04 | 13.99 | 36.64 | 39.47 | 9.86 | 0.00 |
表1 爬坡沙丘表层沉积物粒级级配
Table 1 The surface sediment grain size composition of climbing dune
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.002 mm | 粉沙 0.002—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| P1 | 0.00 | 1.45 | 4.72 | 56.89 | 36.59 | 0.34 |
| P2 | 0.00 | 3.69 | 8.26 | 49.68 | 37.02 | 1.35 |
| P3 | 0.05 | 8.00 | 14.04 | 44.55 | 31.91 | 1.44 |
| P4 | 0.67 | 10.79 | 23.94 | 47.70 | 16.90 | 0.00 |
| P5 | 0.18 | 21.27 | 24.74 | 29.31 | 20.78 | 3.72 |
| P6 | 0.32 | 3.73 | 25.75 | 56.77 | 13.43 | 0.00 |
| P7 | 0.04 | 13.99 | 36.64 | 39.47 | 9.86 | 0.00 |
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.004 mm | 粉沙 0.004—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| 表层 | 0.18 | 8.99 | 19.73 | 46.34 | 23.78 | 0.98 |
| 4—10 cm | 1.18 | 13.39 | 20.63 | 42.58 | 21.88 | 0.33 |
| 10—40 cm | 0.75 | 12.89 | 21.09 | 43.76 | 21.26 | 0.28 |
| 40—60 cm | 1.03 | 14.83 | 21.66 | 42.06 | 20.07 | 0.36 |
表2 爬坡沙丘沉积物不同深度粒级级配
Table 2 The sediment grain size composition of climbing dune at different depths
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.004 mm | 粉沙 0.004—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| 表层 | 0.18 | 8.99 | 19.73 | 46.34 | 23.78 | 0.98 |
| 4—10 cm | 1.18 | 13.39 | 20.63 | 42.58 | 21.88 | 0.33 |
| 10—40 cm | 0.75 | 12.89 | 21.09 | 43.76 | 21.26 | 0.28 |
| 40—60 cm | 1.03 | 14.83 | 21.66 | 42.06 | 20.07 | 0.36 |
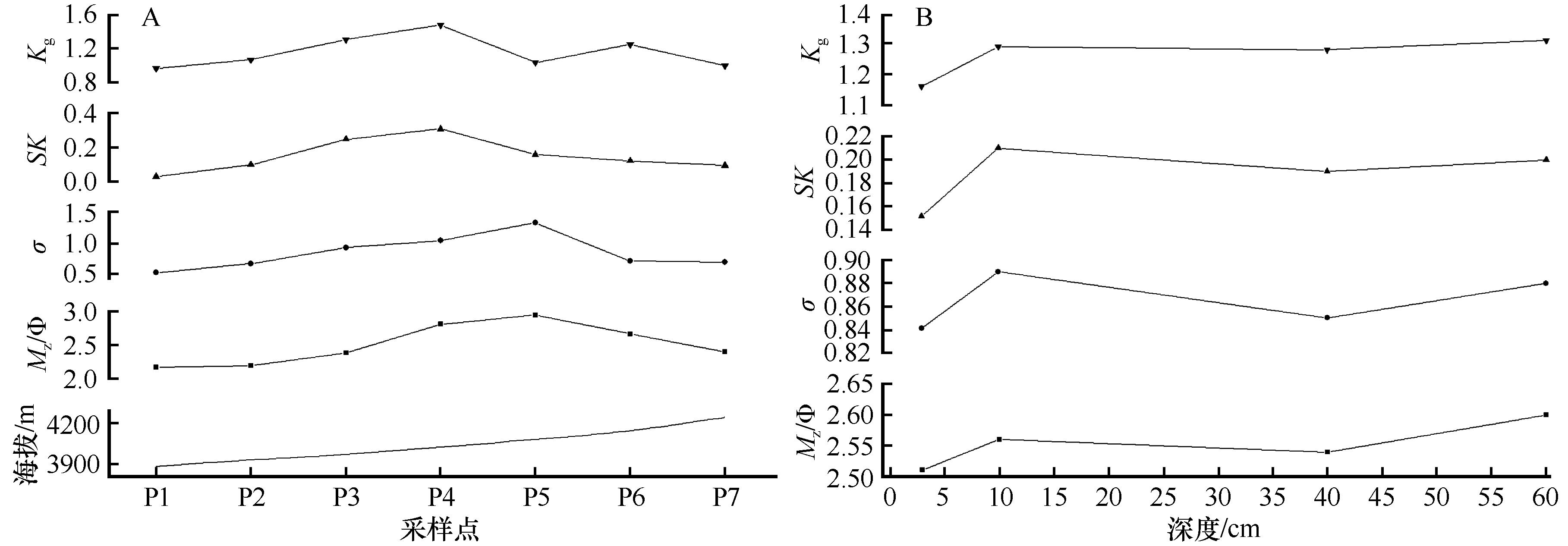
图3 爬坡沙丘沉积物粒度参数变化(A为表层沉积物,B为不同深度沉积物)
Fig.3 Grain size parameters of climbing dune deposition (A refers to surface sediments and B refers to sediments at different depths)
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 54.51—68.41 | 61.60 | 5.27 | 0.09 | 66.00 |
| Al2O3 | 8.69—14.03 | 11.02 | 1.47 | 0.13 | 15.20 |
| Na2O | 2.07—4.63 | 3.13 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 3.90 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.82—3.84 | 2.86 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 5.00 |
| K2O | 1.39—2.80 | 2.24 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 3.40 |
| CaO | 0.89—4.23 | 2.13 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 4.20 |
| MgO | 0.52—1.27 | 0.88 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 2.22 |
| TiO2 | 0.16—0.26 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.50 |
| P2O5 | 0.07—0.13 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.55 |
| MnO | 0.03—0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
表3 爬坡沙丘表层沉积物常量元素含量 (%)
Table 3 Major elements composition of climbing dune surface deposition
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 54.51—68.41 | 61.60 | 5.27 | 0.09 | 66.00 |
| Al2O3 | 8.69—14.03 | 11.02 | 1.47 | 0.13 | 15.20 |
| Na2O | 2.07—4.63 | 3.13 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 3.90 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.82—3.84 | 2.86 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 5.00 |
| K2O | 1.39—2.80 | 2.24 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 3.40 |
| CaO | 0.89—4.23 | 2.13 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 4.20 |
| MgO | 0.52—1.27 | 0.88 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 2.22 |
| TiO2 | 0.16—0.26 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.50 |
| P2O5 | 0.07—0.13 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.55 |
| MnO | 0.03—0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
| 项目 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常量元素含量 | 表层 | 61.93 | 11.18 | 3.10 | 3.02 | 2.24 | 2.18 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| 4—10 cm | 67.11 | 10.06 | 2.32 | 2.38 | 2.74 | 1.14 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 10—40 cm | 66.99 | 10.08 | 2.28 | 2.48 | 2.74 | 1.10 | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 40—60 cm | 67.14 | 9.9 | 2.32 | 2.53 | 2.69 | 1.11 | 0.67 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.03 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.20 | |
表4 爬坡沙丘沉积物不同深度常量元素含量 (%)
Table 4 Major elements composition of climbing dune at different depths
| 项目 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常量元素含量 | 表层 | 61.93 | 11.18 | 3.10 | 3.02 | 2.24 | 2.18 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| 4—10 cm | 67.11 | 10.06 | 2.32 | 2.38 | 2.74 | 1.14 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 10—40 cm | 66.99 | 10.08 | 2.28 | 2.48 | 2.74 | 1.10 | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 40—60 cm | 67.14 | 9.9 | 2.32 | 2.53 | 2.69 | 1.11 | 0.67 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.03 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.20 | |
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 321.8—581.5 | 404.6 | 59.1 | 0.15 | 550.0 |
| Sr | 135.7—440.0 | 264.5 | 101.6 | 0.38 | 350.0 |
| Cr | 16.9—288.8 | 125.0 | 95.8 | 0.77 | 35.0 |
| Zr | 62.8—175.4 | 118.7 | 29.4 | 0.25 | 190.0 |
| Rb | 35.7—141.7 | 93.4 | 38.9 | 0.42 | 112.0 |
| V | 33.8—78.3 | 57.6 | 16.2 | 0.28 | 60.0 |
| Co | 1.9—489.9 | 83.3 | 120.4 | 1.44 | 10.0 |
| Zn | 12.2—44.0 | 32.9 | 7.5 | 0.23 | 71.0 |
| La | 10.5—31.8 | 21.1 | 5.4 | 0.26 | 30.0 |
| Pb | 12.1—25.1 | 19.5 | 3.9 | 0.20 | 15.0 |
| Cu | 8.2—46.9 | 17.5 | 10.9 | 0.63 | 25.0 |
| Y | 11.6—19.5 | 14.8 | 2.3 | 0.15 | 22.0 |
| Ga | 11.4—16.2 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 0.08 | 17.0 |
| Ni | 2.5—15.5 | 9.3 | 3.3 | 0.36 | 20.0 |
| Nb | 2.5—10.2 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 0.35 | 25.0 |
| Bi | 5.8—5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 |
| Hf | 2.0—4.7 | 3.41 | 0.7 | 0.22 | 5.8 |
| Mo | 0.0—7.7 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 0.95 | 1.5 |
表5 爬坡沙丘表层沉积物微量元素含量 (μg·g-1)
Table 5 Trace elements composition of climbing dune surface deposition
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 321.8—581.5 | 404.6 | 59.1 | 0.15 | 550.0 |
| Sr | 135.7—440.0 | 264.5 | 101.6 | 0.38 | 350.0 |
| Cr | 16.9—288.8 | 125.0 | 95.8 | 0.77 | 35.0 |
| Zr | 62.8—175.4 | 118.7 | 29.4 | 0.25 | 190.0 |
| Rb | 35.7—141.7 | 93.4 | 38.9 | 0.42 | 112.0 |
| V | 33.8—78.3 | 57.6 | 16.2 | 0.28 | 60.0 |
| Co | 1.9—489.9 | 83.3 | 120.4 | 1.44 | 10.0 |
| Zn | 12.2—44.0 | 32.9 | 7.5 | 0.23 | 71.0 |
| La | 10.5—31.8 | 21.1 | 5.4 | 0.26 | 30.0 |
| Pb | 12.1—25.1 | 19.5 | 3.9 | 0.20 | 15.0 |
| Cu | 8.2—46.9 | 17.5 | 10.9 | 0.63 | 25.0 |
| Y | 11.6—19.5 | 14.8 | 2.3 | 0.15 | 22.0 |
| Ga | 11.4—16.2 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 0.08 | 17.0 |
| Ni | 2.5—15.5 | 9.3 | 3.3 | 0.36 | 20.0 |
| Nb | 2.5—10.2 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 0.35 | 25.0 |
| Bi | 5.8—5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 |
| Hf | 2.0—4.7 | 3.41 | 0.7 | 0.22 | 5.8 |
| Mo | 0.0—7.7 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 0.95 | 1.5 |
| 项目 | Ba | Sr | Cr | Zr | Rb | V | Co | Zn | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 396.7 | 259.7 | 136.7 | 127.9 | 96.7 | 59.5 | 52.5 | 36.2 | 21.6 |
| 4—10 cm | 384.2 | 172.8 | 70.6 | 142.5 | 132.5 | 42.5 | 97.6 | 31.2 | 22.4 | |
| 10—40 cm | 375.6 | 167.6 | 87.0 | 137.9 | 134.4 | 42.9 | 80.9 | 32.5 | 24.8 | |
| 40—60 cm | 380.3 | 170.2 | 199.4 | 136.05 | 131.8 | 44.5 | 4.1 | 34.7 | 25.5 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.08 | |
| 项目 | Pb | Cu | Y | Ga | Ni | Nb | Bi | Hf | Mo | |
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 15.5 | 13.9 | 10.5 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 3.5 |
| 4—10 cm | 23.0 | 10.6 | 17.0 | 13.3 | 11.1 | 8.4 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 1.2 | |
| 10—40 cm | 24.0 | 11.8 | 17.0 | 13.1 | 12.2 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 1.9 | |
| 40—60 cm | 22.5 | 12.2 | 16.7 | 12.9 | 13.5 | 8.3 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 5.2 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.60 | |
表6 爬坡沙丘沉积物不同深度微量元素含量 (μg·g-1)
Table 6 Trace elements composition of climbing dune at different depths
| 项目 | Ba | Sr | Cr | Zr | Rb | V | Co | Zn | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 396.7 | 259.7 | 136.7 | 127.9 | 96.7 | 59.5 | 52.5 | 36.2 | 21.6 |
| 4—10 cm | 384.2 | 172.8 | 70.6 | 142.5 | 132.5 | 42.5 | 97.6 | 31.2 | 22.4 | |
| 10—40 cm | 375.6 | 167.6 | 87.0 | 137.9 | 134.4 | 42.9 | 80.9 | 32.5 | 24.8 | |
| 40—60 cm | 380.3 | 170.2 | 199.4 | 136.05 | 131.8 | 44.5 | 4.1 | 34.7 | 25.5 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.08 | |
| 项目 | Pb | Cu | Y | Ga | Ni | Nb | Bi | Hf | Mo | |
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 15.5 | 13.9 | 10.5 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 3.5 |
| 4—10 cm | 23.0 | 10.6 | 17.0 | 13.3 | 11.1 | 8.4 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 1.2 | |
| 10—40 cm | 24.0 | 11.8 | 17.0 | 13.1 | 12.2 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 1.9 | |
| 40—60 cm | 22.5 | 12.2 | 16.7 | 12.9 | 13.5 | 8.3 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 5.2 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.60 | |
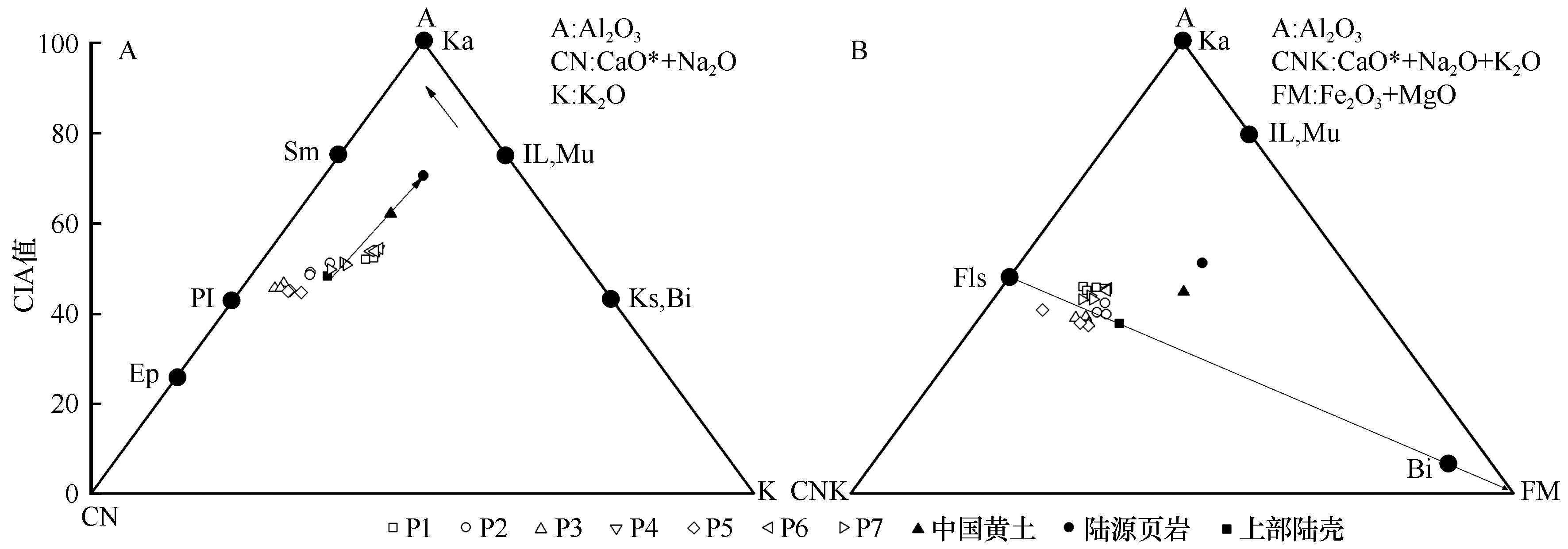
图5 爬坡沙丘表层沉积物A-CN-K (A)及A-CNK-FM (B)三角图解(长实箭头表示大陆风化趋势;Ka=高岭石、Sm=蒙脱石、PI=斜长石、Ep=绿帘石、IL=伊利石、Mu=白云母、Bi=黑云母、Ks=钾长石、Fls=长石)
Fig.5 A-CN-K (A) and A-CNK-FM (B) ternary plots of climbing dune surface deposition (The long solid arrows represent the weathering direction of the continent; Ka=kaokin、Sm=smectites、PI=plagioclase、Ep=epidote、IL=illite、Mu=Muscovite、Bi=biotite、Ks=K—feldspar、Fls=feldspar)
| 1 | 董玉祥.青藏高原沙漠化研究的进展与问题[J].中国沙漠,1999,19(3):251-255. |
| 2 | Dong M, Yan P, Liu B L,et al.Distribution patterns and morphological classification of climbing dunes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Aeolian Research,2018,35:58-68. |
| 3 | Dong Z B, Hu G Y, Qian G Q,et al.High-altitude aeolian research on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2017,55(4):864. |
| 4 | 安庆,安萍,徐汝汝,等.青藏高原不同地区沉积物的粒度特征与沉积环境判别公式适用性对比研究[J].聊城大学学报(自然科学版),2017(4):1-11. |
| 5 | 钟诚,何宗宜,刘淑珍.西藏生态环境稳定性评价研究[J].地理科学,2005,25 (5):573-578. |
| 6 | 张佩民,张振德,李晓琴,等.青藏高原荒漠化遥感信息提取及演变分析[J].干旱区地理,2006,29(5):710-717. |
| 7 | 陈涛,宋友桂,李云.柴达木盆地末次盛冰期与全新世大暖期风沙活动的对比研究[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(4):877-883. |
| 8 | 董治宝,胡光印,颜长珍,等.江河源区沙漠化[M].北京:科学出版社,2012:126-138. |
| 9 | 张登山,高尚玉,石蒙沂,等.青海高原土地沙漠化及其防治[M].北京:科学出版社,2009:18-38. |
| 10 | 李栓科.我国海拔最高的沙漠:库木库里沙漠形成时代的初步探讨[J].中国沙漠,1991,11(3):29-35. |
| 11 | 李森,杨萍,董玉祥,等.西藏土地沙漠化及其防治[M].北京:科学出版社,2010:24-51. |
| 12 | Livingstone I.Grain-size variation on a 'complex' linear dune in the Namib Desert[J].Geological Society London Special Publications,1987,35(1):281-291. |
| 13 | Wang X M, Dong Z B, Zhang J W,et al.Grain size characteristics of dune sands in the central Taklimakan Sand Sea[J].Sedimentary Geology,2003,161:1-14. |
| 14 | Friedman G M.Distinction between dune,beach,and river sands from their textural characteristics[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1961,31(4):514-529. |
| 15 | Ahlbrandt T S.Textural parameters of eolian deposits[M]//McKee E.A Study of Global Sand Seas.Washington,USA:U.S.Government Printing Office,1979:21-51. |
| 16 | 龙黎,董玉祥,孙忠.海岸沙丘表面现代风成沙地球化学元素分异的典型研究:以河北昌黎黄金海岸横向沙脊为例[J].沉积学报,2012,30(4):724-730. |
| 17 | 郜学敏,屈欣,王萌,等.柴达木盆地西北部长垄状雅丹沉积物地球化学元素组成及指示意义[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(3):127-136. |
| 18 | 徐志伟,鹿化煜,赵存法,等.库姆塔格沙漠地表物质组成、来源和风化过程[J].地理学报,2010,65(1):53-64. |
| 19 | 崔徐甲,孙虎,董治宝,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山沉积物地球化学元素组成及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(1):17-25. |
| 20 | Hack J T.Dunes of the Western Navajo County[J].Geographical Review,1941,31(2):240-263. |
| 21 | Smith R S U.Eolian sand on desert mountains[C]//Geological Society of America Annual Meeting Abstract,1954:102-103. |
| 22 | Evans J R.Falling and climbing sand dunes in the Cronese (“cat”) Mountain area,San Bernardino County,California[J].Journal of Geology,1962,70(1):107-113. |
| 23 | 全国科学技术名词审定委员会.地理学名词[M].北京:科学出版社,2007:96. |
| 24 | 孟小楠,严平,董苗.爬坡沙丘的研究进展[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018(3):391-396. |
| 25 | Lancaster N, Tchakerian V P.Geomorphology and sediments of sand ramps in the Mojave desert[J].Geomorphology,1996,17(1/3):151-165. |
| 26 | Bateman M D, Bryant R G, Foster I,et al.On the formation of sand ramps:a case study from the Mojave Desert[J].Geomorphology,2012,161/162:93-109. |
| 27 | White B R, Tsoar H.Slope effect on saltation over a climbing sand dune[J].Geomorphology,1998,22(2):159-180. |
| 28 | 李森,董光荣,申建友,等.雅鲁藏布江河谷风沙地貌形成机制与发育模式[J].中国科学D辑,1999,29(1):88-96. |
| 29 | 李森,王跃,哈斯,等.雅鲁藏布江河谷风沙地貌分类与发育问题[J].中国沙漠,1997,17(4):342. |
| 30 | Li S, Liu X W, Li H C,et al.A wind tunnel simulation of the dynamic processes involved in sand dune formation on the western coast of Hainan Island[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2007,7:453-459. |
| 31 | 赵子允.东昆仑山区风沙地貌的特征[J].中国沙漠,1983,3(3):35. |
| 32 | Chojnacki M, Burr D M, Moersch J E.Valles Marineris dune fields as compared with other martian populations:diversity of dune compositions,morphologies,and thermophysical properties[J].Icarus,2014,230:96-142. |
| 33 | 杨逸畴,高登义,李渤生.雅鲁藏布江下游河谷水汽通道初探[J].中国科学B辑,1987,17(8):893-902. |
| 34 | 成都地质学院陕北队.沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M].北京:科学出版社,1978. |
| 35 | 任明达,王乃梁.现代沉积环境概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1981:8-15. |
| 36 | Visher G.Grain size distribution and depositional process[J].Journal of Sediment Research,1969,39(3):1074-1106. |
| 37 | 陈渭南.塔克拉玛干沙漠84°E沿线沙物质的粒度特征[J].地理学报,1993,48(1):33-46. |
| 38 | 周娜,尤源,雷加强,等.毛里塔尼亚努瓦克肖特沙丘粒度分布特征及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(2):252-261. |
| 39 | 邵天杰,赵景波,董治宝.巴丹吉林沙漠沙山粒度组成与沙山地貌分带[J].山地学报,2013,31(4):434-441. |
| 40 | Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The continenal crust:its composition and evolution[M].Boston,USA:Blackwell Scientific,1985. |
| 41 | 陈国祥.毛乌素沙地风成沉积物沉积学特征[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2019. |
| 42 | 李恩菊.巴丹吉林沙漠与腾格里沙漠沉积物特征的对比研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2011. |
| 43 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoric climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,229:715-717. |
| 44 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles[J].The Journal of Geology,1989,97(2):129-147. |
| 45 | 董治宝.库姆塔格沙漠风沙地貌[M].北京:科学出版社,2011:116-117. |
| 46 | Cox R, Lowe D R, Cullers R L.The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1995,59:2919-2940. |
| 47 | Cullers R L.The geochemistry of shales,siltstones,and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age,Colorado,USA:implications for provenance and metamorphic studies[J].Lithos,2000,51:181-203. |
| 48 | Cullers R L.The source and origin of terrigenous sedimentary rocks in the Mesoproterozoic Ui group,southeastern Russia[J].Precambrian Research,2002,117:157-183. |
| 49 | 罗万银,董治宝,钱广强,等.戈壁表层沉积物地球化学元素组成及其沉积意义[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1441-1453. |
| 50 | 邵菁清,杨守业.化学蚀变指数(CIA)反映长江流域的硅酸盐岩化学风化与季风气候?[J].科学通报,2012,57(11):933-942. |
| 51 | 韩宗珠,张军强,邹昊,等.渤海湾北部底质沉积物中黏土矿物组成与物源研究[J].中国海洋大学学报,2011,41(11):95-102. |
| 52 | Horowitz A J.A Primer on Sediment-Trace Element Chemistry[M].Chelsea, Michigan,USA:Lewis Publishers,1991:136. |
| 53 | Jenne E A .Controls on Mn,Fe,Co,Ni,Cu,and Zn concentrations in soils and water:the significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides[M]//Baker R.Trace Inorganic in Water.1968:337-387. |
| 54 | Jenne E A, Kennedy V, Burchard J,et al.Sediment collection and processing for selective extraction and for total metal analysis[M]//Baker R.Contaminants and Sediments.1980:169-189. |
| 55 | 陈静生,王飞越,宋吉杰,等.中国东部河流沉积物中重金属含量与沉积物主要性质的关系[J].环境化学,1996,15(1):8-14. |
| [1] | 姜吴彬, 张德国, 杨小平. 沙丘形态及表沙粒度特征对风况和地表植被变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 120-129. |
| [2] | 高冲, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 刘铮瑶, 朱春鸣, 王晓枝, 肖南, 张欣. 古尔班通古特沙漠蜂窝状沙丘沉积物理化特征及沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 14-24. |
| [3] | 董苗, 严平, 王晓旭, 张国明, 孟小楠, 纪欣然, 王勇. 雅鲁藏布江山南宽谷段爬坡沙丘表层沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 153-163. |
| [4] | 颜明, 张应华, 贺莉, 程维明, 王随继, 许炯心. 无定河上游河道对沙漠化的阻截效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 62-68. |
| [5] | 周维鑫, 温小浩, 李保生, 王晨, 田梦圆, 邱明昆. 萨拉乌苏河流域干沟子剖面全新世湖相沉积的地球化学元素特征及其反映的物源变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 114-122. |
| [6] | 林永崇, 穆桂金, 陈丽玲, 吴楚娜, 徐立帅. 策勒绿洲近地表大气降尘粒度指示的分选特征及其意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 139-146. |
| [7] | 赵晖, 杨宏宇, 王兴繁, 汪克奇. 巴丹吉林沙漠典型沉积物年代学研究评述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 57-65. |
| [8] | 谢轲, 尹辉. 内蒙古额济纳盆地沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 111-119. |
| [9] | 潘美慧, 郝泽文, 齐宇涵, 杨安娜, 陈有桂, 李晨露. 西藏朋曲流域不同地貌部位流动沙丘粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 138-147. |
| [10] | 于海云, 张正偲, 王志军. 阿拉善高原东南部干涸湖盆沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 177-184. |
| [11] | 郜学敏, 屈欣, 王萌, 张思悦, 张姚姚, 李继彦. 柴达木盆地西北部长垄状雅丹沉积物地球化学元素组成及指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 127-136. |
| [12] | 张焱, 马鹏飞, 曾林, 梁爱民, 张正偲. 基于沉积物理化性质的雅鲁藏布江中游粉尘物源研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 92-100. |
| [13] | 朱春鸣, 董治宝, 刘铮瑶, 肖南, 杨军怀, 冯淼彦. 古尔班通古特沙漠树枝状沙丘沉积物粒度和微形态特征的空间分异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 9-18. |
| [14] | 李向洁, 李志文, 詹江振, 孙丽, 杜兰, 侯楚. 南昌厚田沙地沉积物的粒度特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 92-99. |
| [15] | 赵明珠, 俎瑞平, 王军战, 谭立海. 哈罗铁路沿线沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 19-27. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
