中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 17-30.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00156
收稿日期:2022-10-25
修回日期:2022-11-24
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-08-14
通讯作者:
杨林海
作者简介:杨林海(E-mail: ylh@snnu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Xueyang Guo( ), Linhai Yang(
), Linhai Yang( ), Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu
), Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu
Received:2022-10-25
Revised:2022-11-24
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Linhai Yang
摘要:
酒东沙地位于河西走廊中段的张掖绿洲和酒泉绿洲之间,其风沙环境的变化对周边的人类活动至关重要。与其他沙区相比,该沙地的研究基础相对薄弱。对酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物的粒度、化学元素和矿物特征进行了研究,并探讨了其环境指示意义。结果表明:酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物平均粒径218~308 μm,以中沙和细沙为主,分选性良好,偏度近对称,峰度中等;沉积物粒径总体上由北向南逐渐变细;在近东西向的两条断面上,位于沙地腹地的表层风沙沉积物自西向东逐渐变细,而沙地南缘则呈现相反的规律;酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物中跃移组分含量最高,其次为短距离悬移组分、蠕移组分和长距离悬移组分。常量元素以SiO2为主,CaO和MgO含量存在顺主导风向减少的规律;微量元素除Cr、Ni和Co表现出明显的富集特征外,其余元素均出现不同程度的亏损。矿物以硬矿物石英和长石为主,其次是白云石,其他矿物含量极少;矿物成分成熟度指数Q/TF较低。酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物处于基本未受或遭受了较弱的化学风化的初期,以物理风化过程为主,推测其形成于干冷、弱化学风化和弱成壤环境下。
中图分类号:
郭雪阳, 杨林海, 程良清, 胡光印, 胡菁菁. 河西走廊酒东沙地风沙沉积物理化特征及其环境意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 17-30.
Xueyang Guo, Linhai Yang, Liangqing Cheng, Guangyin Hu, Jingjing Hu. Physical and chemical characteristics of aeolian sands in Jiudong Sandy Land of Hexi Corridor and its environmental significance[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 17-30.
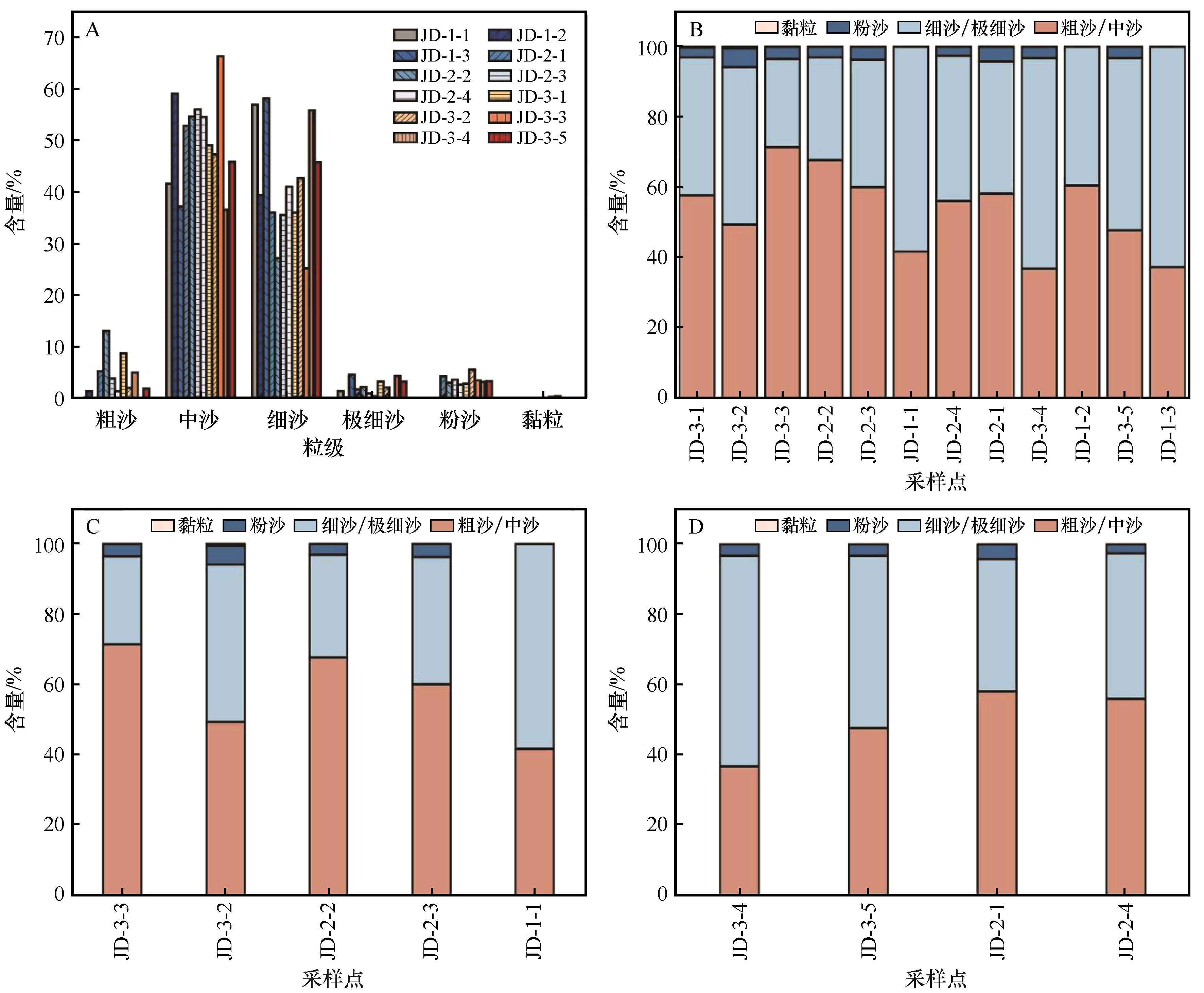
图2 酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物粒级级配(A)及自北向南(B)和自西向东(C:沙地腹地,D:沙地南缘)的粒度变化特征
Fig.2 Gradation of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land (A), grain size variation characteristics from north to south (B) and from west to east (C: hinterland of the sandy land, D: south edge of the sandy land)
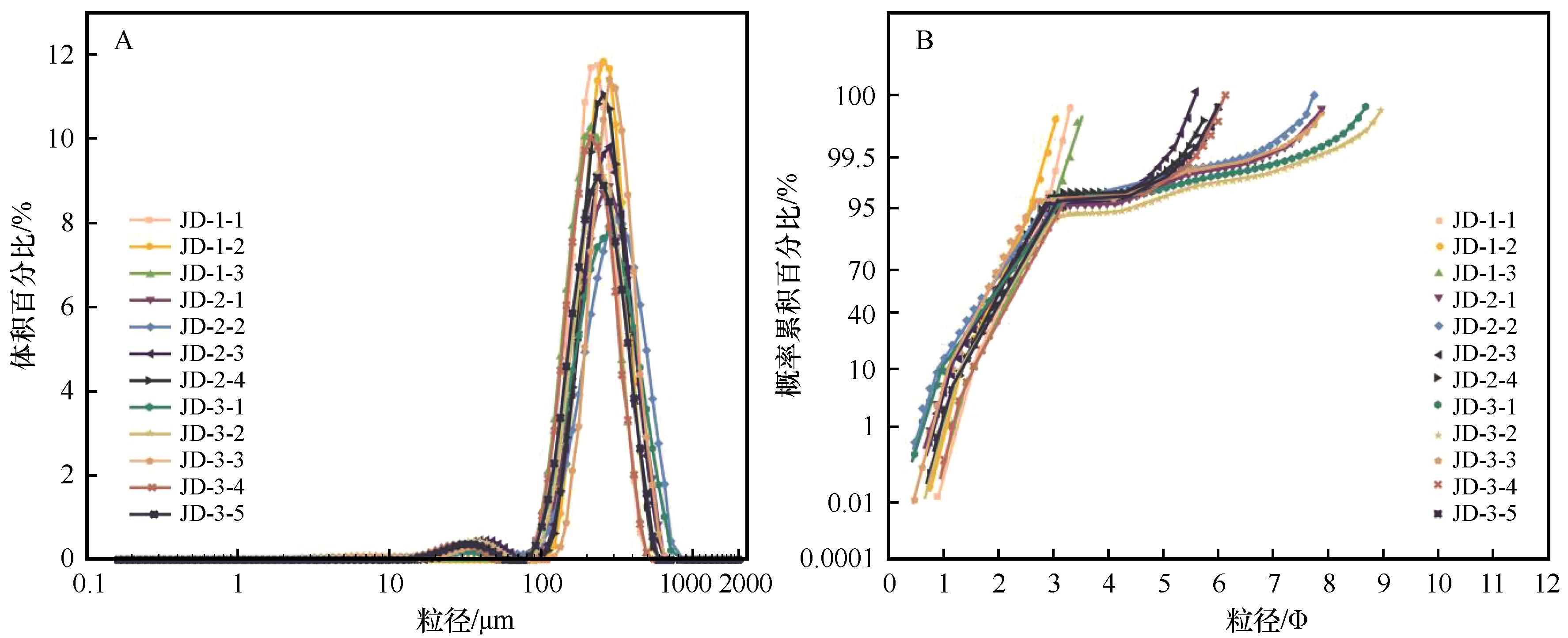
图4 酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物频率分布曲线(A)和概率累积曲线(B)
Fig.4 Frequency distribution curves (A) and probability accμmulation curves (B) of the aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land
| 采样点 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 68.92 | 6.9 | 2.22 | 1.36 | 2.80 | 1.86 | 1.53 |
| JD-1-2 | 66.95 | 7.28 | 2.61 | 1.59 | 3.65 | 1.95 | 1.57 |
| JD-1-3 | 68.52 | 7.06 | 2.36 | 1.51 | 3.30 | 1.86 | 1.59 |
| JD-2-1 | 60.21 | 7.91 | 4.09 | 2.59 | 6.58 | 2.06 | 1.45 |
| JD-2-2 | 71.83 | 7.26 | 2.06 | 1.48 | 3.21 | 2.07 | 1.64 |
| JD-2-3 | 64.30 | 7.15 | 2.62 | 1.96 | 4.61 | 2.06 | 1.47 |
| JD-2-4 | 60.69 | 7.52 | 3.13 | 2.43 | 6.06 | 2.02 | 1.41 |
| JD-3-1 | 69.23 | 7.4 | 2.41 | 1.53 | 3.56 | 2.09 | 1.63 |
| JD-3-2 | 63.09 | 7.53 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 5.93 | 1.99 | 1.47 |
| JD-3-3 | 62.12 | 7.59 | 2.85 | 1.92 | 4.95 | 2.18 | 1.54 |
| JD-3-4 | 61.65 | 7.95 | 3.16 | 2.22 | 5.64 | 2.05 | 1.64 |
| JD-3-5 | 66.96 | 7.87 | 2.80 | 1.71 | 3.87 | 2.02 | 1.77 |
| 变化范围 | 60.21~71.83 | 6.9~7.95 | 2.06~4.09 | 1.36~2.59 | 2.8~6.58 | 1.86~2.18 | 1.41~1.77 |
| 平均值 | 65.37 | 7.45 | 2.80 | 1.89 | 4.51 | 2.02 | 1.56 |
| 标准差 | 3.85 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 1.29 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 变异系数 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| 上部陆壳 | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 2.20 | 4.20 | 3.90 | 3.40 |
| 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 80.27 | 7.78 | 1.93 | 1.19 | 2.06 | 1.90 | 2.00 |
| 腾格里沙漠 | 80.94 | 8.26 | 1.96 | 1.12 | 1.30 | 1.88 | 2.25 |
| 塔克拉玛干沙漠 | 62.05 | 10.18 | 2.36 | 1.58 | 7.30 | 2.33 | 2.40 |
表1 酒东沙地及中国主要沙漠表层风沙沉积物常量元素含量(%)
Table 1 Major element contents of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land and other deserts in China (%)
| 采样点 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 68.92 | 6.9 | 2.22 | 1.36 | 2.80 | 1.86 | 1.53 |
| JD-1-2 | 66.95 | 7.28 | 2.61 | 1.59 | 3.65 | 1.95 | 1.57 |
| JD-1-3 | 68.52 | 7.06 | 2.36 | 1.51 | 3.30 | 1.86 | 1.59 |
| JD-2-1 | 60.21 | 7.91 | 4.09 | 2.59 | 6.58 | 2.06 | 1.45 |
| JD-2-2 | 71.83 | 7.26 | 2.06 | 1.48 | 3.21 | 2.07 | 1.64 |
| JD-2-3 | 64.30 | 7.15 | 2.62 | 1.96 | 4.61 | 2.06 | 1.47 |
| JD-2-4 | 60.69 | 7.52 | 3.13 | 2.43 | 6.06 | 2.02 | 1.41 |
| JD-3-1 | 69.23 | 7.4 | 2.41 | 1.53 | 3.56 | 2.09 | 1.63 |
| JD-3-2 | 63.09 | 7.53 | 3.29 | 2.34 | 5.93 | 1.99 | 1.47 |
| JD-3-3 | 62.12 | 7.59 | 2.85 | 1.92 | 4.95 | 2.18 | 1.54 |
| JD-3-4 | 61.65 | 7.95 | 3.16 | 2.22 | 5.64 | 2.05 | 1.64 |
| JD-3-5 | 66.96 | 7.87 | 2.80 | 1.71 | 3.87 | 2.02 | 1.77 |
| 变化范围 | 60.21~71.83 | 6.9~7.95 | 2.06~4.09 | 1.36~2.59 | 2.8~6.58 | 1.86~2.18 | 1.41~1.77 |
| 平均值 | 65.37 | 7.45 | 2.80 | 1.89 | 4.51 | 2.02 | 1.56 |
| 标准差 | 3.85 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 1.29 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| 变异系数 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| 上部陆壳 | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 2.20 | 4.20 | 3.90 | 3.40 |
| 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 80.27 | 7.78 | 1.93 | 1.19 | 2.06 | 1.90 | 2.00 |
| 腾格里沙漠 | 80.94 | 8.26 | 1.96 | 1.12 | 1.30 | 1.88 | 2.25 |
| 塔克拉玛干沙漠 | 62.05 | 10.18 | 2.36 | 1.58 | 7.30 | 2.33 | 2.40 |
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值 | 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 腾格里沙漠 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 458.2~507.4 | 474.3 | 13.8 | 0.03 | 550.0 | 544.5 | 619.61 |
| Sr | 136.1~196.0 | 165.3 | 20.0 | 0.12 | 350.0 | 168.1 | 171.77 |
| Cr | 40.2~356.8 | 175.8 | 91.9 | 0.52 | 35.0 | 105.1 | 95.53 |
| Zr | 72.9~147.9 | 93.6 | 22.2 | 0.24 | 190.0 | 89.5 | 105.13 |
| Rb | 51.4~66.1 | 57.7 | 4.4 | 0.08 | 112.0 | 62.8 | 70.69 |
| V | 38.9~76.2 | 52.0 | 10.5 | 0.20 | 60.0 | — | — |
| Co | 4.1~107.3 | 29.8 | 37.5 | 1.26 | 10.0 | 124.1 | 121.23 |
| Zn | 21.6~39.0 | 29.4 | 5.1 | 0.17 | 71.0 | — | — |
| La | 11.0~26.0 | 16.5 | 4.3 | 0.26 | 30.0 | — | — |
| Pb | 11.6~13.7 | 12.8 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 15.0 | — | — |
| Cu | 11.6~16.4 | 13.6 | 1.5 | 0.11 | 25.0 | 13.8 | 12.67 |
| Y | 12.1~18.7 | 14.4 | 2.1 | 0.15 | 22.0 | — | — |
| Ga | 8.9~10.7 | 9.7 | 0.7 | 0.07 | 17.0 | 10.7 | 11.13 |
| Ni | 18.9~37.4 | 26.6 | 5.0 | 0.19 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 16.65 |
| Nb | 6.3~11.1 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 0.19 | 25.0 | — | — |
| Bi | 5.8~5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 | — | — |
表2 酒东沙地及邻近沙漠表层风沙沉积物微量元素含量(μg·g-1 )
Table 2 Trace element contents of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land and adjacent deserts in China (μg·g-1 )
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值 | 巴丹吉林沙漠 | 腾格里沙漠 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 458.2~507.4 | 474.3 | 13.8 | 0.03 | 550.0 | 544.5 | 619.61 |
| Sr | 136.1~196.0 | 165.3 | 20.0 | 0.12 | 350.0 | 168.1 | 171.77 |
| Cr | 40.2~356.8 | 175.8 | 91.9 | 0.52 | 35.0 | 105.1 | 95.53 |
| Zr | 72.9~147.9 | 93.6 | 22.2 | 0.24 | 190.0 | 89.5 | 105.13 |
| Rb | 51.4~66.1 | 57.7 | 4.4 | 0.08 | 112.0 | 62.8 | 70.69 |
| V | 38.9~76.2 | 52.0 | 10.5 | 0.20 | 60.0 | — | — |
| Co | 4.1~107.3 | 29.8 | 37.5 | 1.26 | 10.0 | 124.1 | 121.23 |
| Zn | 21.6~39.0 | 29.4 | 5.1 | 0.17 | 71.0 | — | — |
| La | 11.0~26.0 | 16.5 | 4.3 | 0.26 | 30.0 | — | — |
| Pb | 11.6~13.7 | 12.8 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 15.0 | — | — |
| Cu | 11.6~16.4 | 13.6 | 1.5 | 0.11 | 25.0 | 13.8 | 12.67 |
| Y | 12.1~18.7 | 14.4 | 2.1 | 0.15 | 22.0 | — | — |
| Ga | 8.9~10.7 | 9.7 | 0.7 | 0.07 | 17.0 | 10.7 | 11.13 |
| Ni | 18.9~37.4 | 26.6 | 5.0 | 0.19 | 20.0 | 18.2 | 16.65 |
| Nb | 6.3~11.1 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 0.19 | 25.0 | — | — |
| Bi | 5.8~5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 | — | — |
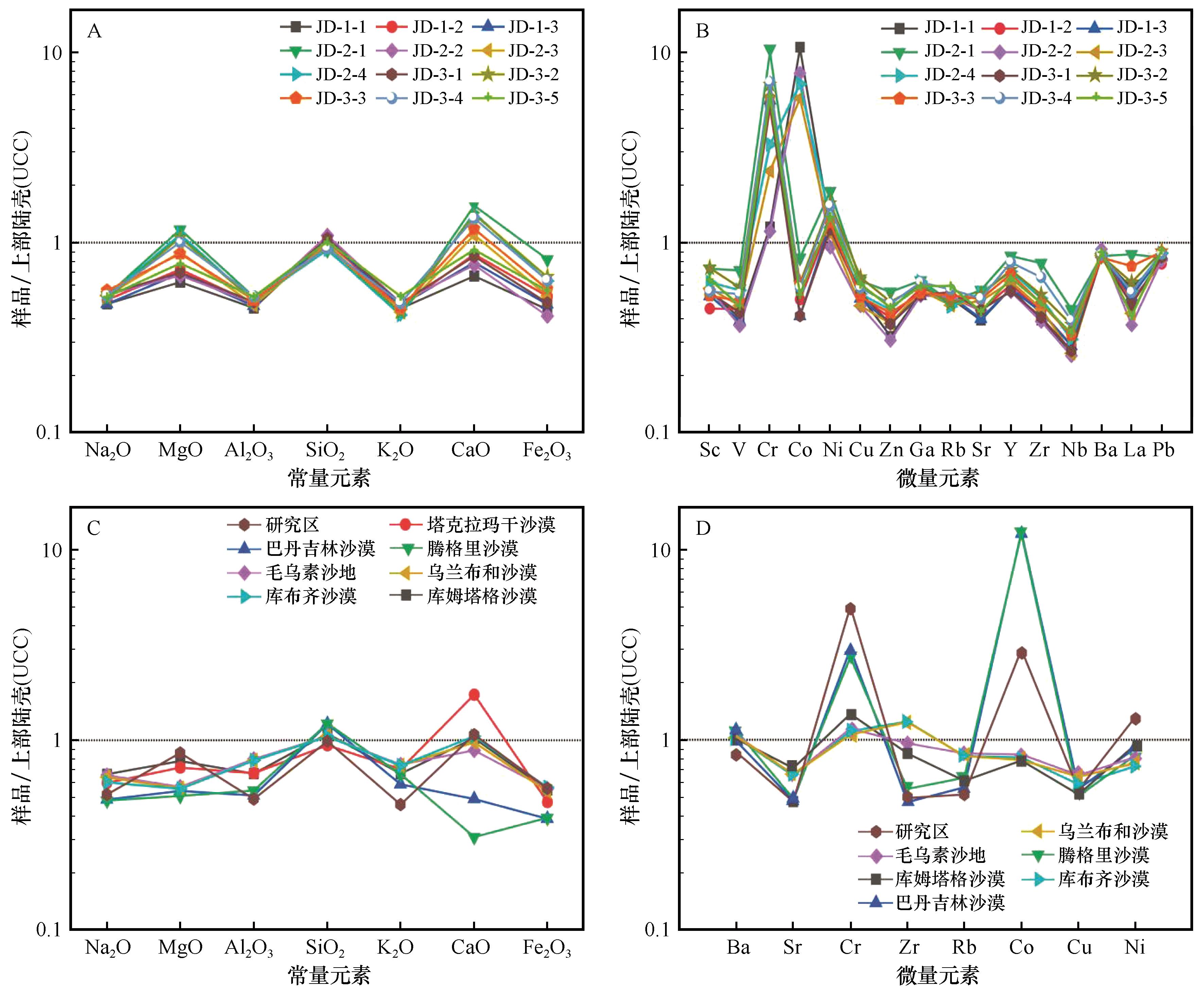
图6 酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物地球化学元素UCC标准化值及其与其他沙漠和沙地的对比
Fig.6 Distribution of UCC standardized values of geochemical elements in aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land (the values of other deserts are shown for comparison)
| 指数 | JD-1-1 | JD-1-2 | JD-1-3 | JD-2-1 | JD-2-2 | JD-2-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rb/Sr | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.30 |
| 淋溶系数 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 0.95 | 1.14 |
| CIA | 45.98 | 46.24 | 46.35 | 47.58 | 44.77 | 45.00 |
| 指数 | JD-2-4 | JD-3-1 | JD-3-2 | JD-3-3 | JD-3-4 | JD-3-5 |
| Rb/Sr | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.44 |
| 淋溶系数 | 1.26 | 0.98 | 1.25 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 0.97 |
| CIA | 46.85 | 45.08 | 46.99 | 45.13 | 47.22 | 46.86 |
表3 酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物的化学风化程度
Table 3 Chemical weathering degree of the aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land
| 指数 | JD-1-1 | JD-1-2 | JD-1-3 | JD-2-1 | JD-2-2 | JD-2-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rb/Sr | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.30 |
| 淋溶系数 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 0.95 | 1.14 |
| CIA | 45.98 | 46.24 | 46.35 | 47.58 | 44.77 | 45.00 |
| 指数 | JD-2-4 | JD-3-1 | JD-3-2 | JD-3-3 | JD-3-4 | JD-3-5 |
| Rb/Sr | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.44 |
| 淋溶系数 | 1.26 | 0.98 | 1.25 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 0.97 |
| CIA | 46.85 | 45.08 | 46.99 | 45.13 | 47.22 | 46.86 |
| 采样点 | 石英 | 长石 | 白云石 | 磷酸钠 铍石 | 铁锂 云母 | Q/TF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 75 | 25 | 3.00 | |||
| JD-1-2 | 69 | 31 | 2.23 | |||
| JD-1-3 | 68 | 30 | 2 | 2.27 | ||
| JD-2-1 | 63 | 33 | 4 | 1.91 | ||
| JD-2-2 | 69 | 28 | 2 | 2.46 | ||
| JD-2-3 | 65 | 32 | 3 | 2.03 | ||
| JD-2-4 | 63 | 32 | 5 | 1.97 | ||
| JD-3-1 | 66 | 32 | 2 | 2.06 | ||
| JD-3-2 | 65 | 29 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2.24 |
| JD-3-3 | 60 | 36 | 4 | 1 | 1.67 | |
| JD-3-4 | 61 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 2.03 | |
| JD-3-5 | 65 | 34 | 1 | 1.91 |
表4 酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物矿物平均含量及成熟度指数
Table 4 Average mineral content and maturity index of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land
| 采样点 | 石英 | 长石 | 白云石 | 磷酸钠 铍石 | 铁锂 云母 | Q/TF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD-1-1 | 75 | 25 | 3.00 | |||
| JD-1-2 | 69 | 31 | 2.23 | |||
| JD-1-3 | 68 | 30 | 2 | 2.27 | ||
| JD-2-1 | 63 | 33 | 4 | 1.91 | ||
| JD-2-2 | 69 | 28 | 2 | 2.46 | ||
| JD-2-3 | 65 | 32 | 3 | 2.03 | ||
| JD-2-4 | 63 | 32 | 5 | 1.97 | ||
| JD-3-1 | 66 | 32 | 2 | 2.06 | ||
| JD-3-2 | 65 | 29 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2.24 |
| JD-3-3 | 60 | 36 | 4 | 1 | 1.67 | |
| JD-3-4 | 61 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 2.03 | |
| JD-3-5 | 65 | 34 | 1 | 1.91 |
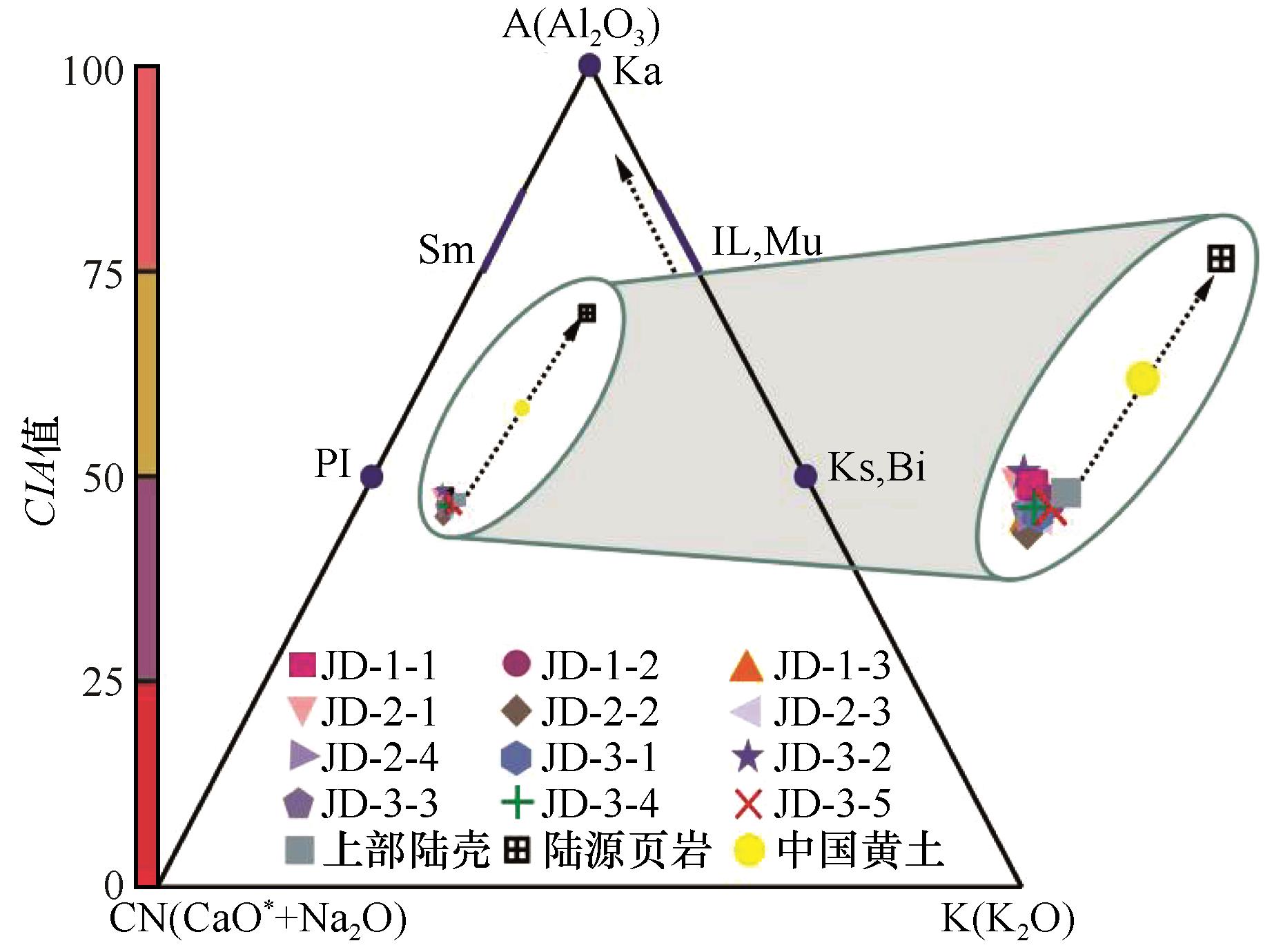
图7 酒东沙地表层风沙沉积物A-CN-K三角图(长虚线箭头表示早期大陆风化趋势;短虚线箭头表示中期大陆风化趋势;Ka=高岭石、Sm=蒙脱石、PI=斜长石、IL=伊利石、Mu=白云母、Bi=黑云母、Ks=钾长石)
Fig.7 A-CN-K triangle diagram of aeolian sand sediments on the surface of Jiudong Sandy Land (Long dashed arrows indicate early continental weathering trends; Short dashed arrows indicate the mediμm-term continental weathering trends; Ka= kaolinite,Sm=montmorillonite,PI=plagioclase,IL=Illite,Mu=muscovite,Bi=black mica,Ks=potassiμm feldspar)
| 1 | 董治宝,吕萍.70年来中国风沙地貌学的发展[J].地理学报,2020,75(3):509-528. |
| 2 | 吴正.风沙地貌学[M].北京:科学出版社,1987:1-18. |
| 3 | 朱秉启.中纬度荒漠区河西走廊沙丘地貌的演化特征及其环境指示[J].地理学报,2021,76(11):2710-2729. |
| 4 | 马建军.1988-2017年西藏定结地区风沙地貌格局变化及其对气候的响应[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2019. |
| 5 | Thomas D S G, Wiggs G F S.Aeolian system responses to global change:challenges of scale,process and temporal integration[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2008,33(9):1396-1418. |
| 6 | 陈国祥.毛乌素沙地风成沉积物沉积学特征[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2019. |
| 7 | 钱亦兵,吴兆宁,石井武政,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠沙物质成分特征及其来源[J].中国沙漠,1993,13(4):32-38. |
| 8 | 徐志伟,鹿化煜,赵存法,等.库姆塔格沙漠地表物质组成、来源和风化过程[J].地理学报,2010,65(1):53-64. |
| 9 | Liu B, Qu J, Ning D,et al.Grain-size study of aeolian sediments found east of Kumtagh Desert[J].Aeolian Research,2014,13:1-6. |
| 10 | 崔徐甲,孙虎,董治宝,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山沉积物地球化学元素组成及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(1):17-25. |
| 11 | Ren X Z.Major and trace elemental geochemistry of dune surface sands in the southeastern margin of the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Quaternary International,2012,279/280:399-399. |
| 12 | Wen Y L, Wu Y Q, Tan L H,et al.End-member modeling of the grain size record of loess in the Mu Us Desert and implications for dust sources[J].Quaternary International,2019,532:87-97. |
| 13 | Yang L H, Wang T, Long H,et al.Late Holocene dune mobilization in the Horqin dunefield of northern China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,138:136-147. |
| 14 | 程弘毅.河西地区历史时期沙漠化研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2007. |
| 15 | Chen D B, Pan B T, Hu X F,et al.Formation age of Jiudong Sandy Land,in the western Hexi Corridor,NW China[J].Quaternary International,2019,513:47-55. |
| 16 | 张正偲,董治宝.黑河流域中游沙漠风能环境与风沙地貌[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(2):332-341. |
| 17 | Zhang Z C, Dong Z B.Grain size characteristics in the Hexi Corridor Desert[J].Aeolian research,2015,18:55-67. |
| 18 | Zhang Z C, Pan K J, Zhang C X,et al.Geochemical characteristics and the provenance of aeolian material in the Hexi Corridor Desert,China[J].Catena,2020,190:1-10. |
| 19 | Xu Z W, Zhao C F, Wang X Y,et al.Composition,origin and weathering process of surface sediment in Kumtagh Desert,Northwest China[J].Geograpjical Sciences,2011,21(6):1062-1076. |
| 20 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K,et al.Grain-size distribution function of polygonal sediments in hydraulic and environments,and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J].Sedimentary Geology,2002,152:263-277. |
| 21 | Yang X P, Zhang F, Fu X D,et al.Oxygen isotopic compositions of quartz in the sand seas and sandy lands of northern China and their implications for understanding the provenances of aeolian sands[J].Geomorphology,2008,102:278-285. |
| 22 | 马金凤.河西走廊酒东盆地 1.7Ma以来的沉积物粘土矿物特征及其古环境意义[D].兰州:兰州大学,2018. |
| 23 | 常兆丰,张剑挥,王强强,等.新月形沙丘及新月形沙丘链存在的环境条件:以甘肃河西沙区为例[J].干旱区资源与环境,2016,30(11):167-173. |
| 24 | 潘凯佳,张正偲,董治宝,等.河西走廊新月形沙丘表层沉积物的理化性质[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(1):44-51. |
| 25 | Zhang C X, Wang X M, Dong Z B,et al.Aeolian process of the dried-up riverbeds of the Hexi Corridor,China:a wind tunnel experiment[J].Environmental Monitoring & Assessment,2017,189(8):419. |
| 26 | Li X D, Liu T, Zhao C L,et al.Land use drives the spatial variability of soil phosphorus in the Hexi Corridor,China[J].Biogeochemistry,2021,155:59-75. |
| 27 | Lancaster N.The Namib Sand Sea:Dunes Forms,Processes and Sediments[M].Rotterdam,Nertherlands:Balkema,1989. |
| 28 | Zhao H, Li G, Sheng Y,et al.Early-middle Holocene lake-desert evolution in northern Ulan Buh desert,China[J].Palaeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2012,331:31-38. |
| 29 | 董治宝,胡光印,颜长珍,等.江河源区沙漠化[M].北京:科学出版社,2013. |
| 30 | Dasch E J.Strontium isotopes in weathering profiles,deep-sea sediments,and sedimentary rocks[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1969,33(12):1521-1552. |
| 31 | 陈秋洁.巴丹吉林沙漠地表风成沉积物的元素组成特征与环境指示意义[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| 32 | Lancaster N.Aeolian processes[M]//Elias S A.Reference Module in Earth Systems and Enviromental Sciences.New York,USA:Elsevier,2014:1-17. |
| 33 | 王晓枝,董治宝,南维鸽,等.拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘沉积物特征[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):22-31. |
| 34 | Visher G.Grain size distributions and depositional processes[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1969,39(3):1074-1106. |
| 35 | 冯铄,刘志飞, Sompongchaiyakul P,等.泰国湾表层沉积物陆源碎屑的粒度特征及其展现的沉积动力环境[J].地学前缘,2022,29(4):211-220. |
| 36 | 徐树建,倪志超,丁新潮.山东平阴黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2016,35(2):353-359. |
| 37 | Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continenal Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M].Boston,USA:Blackwell Scientific,1985. |
| 38 | 李恩菊.巴丹吉林沙漠与腾格里沙漠沉积物特征的对比研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2011. |
| 39 | 赵万苍,刘连文,陈骏,等.中国沙漠元素地球化学区域特征及其对黄土物源的指示意义[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(9):1425-1438. |
| 40 | 李继彦,周玲,刘益,等.晋西北地区表层土壤粒度与地球化学元素组成[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):155-162. |
| 41 | 柳本立,屈建军,杨根生,等.库姆塔格沙漠东部复杂地貌地表沉积物化学元素组成初步研究[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(5):1194-1199. |
| 42 | 赵杰.古尔班通古特沙漠风成沉积物特征研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2020. |
| 43 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoric climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,229:715-717. |
| 44 | Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J].Geology,1995,23(10):921-924. |
| 45 | Pettijohn F J, Paul E P, Raymond S.Sand and Sandstone[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer Verlag,1973. |
| 46 | 宁凯,李卓仑,王乃昂,等.巴丹吉林沙漠地表风积砂粒度空间分布及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(3):642-648. |
| 47 | 宋洁,春喜,白雪梅,等.中国沙漠粒度分析研究综述[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(3):597-603. |
| 48 | 张余,张克存,安志山,等.敦煌沙漠绿洲过渡带地表沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境[J].水土保持通报,2017,37(4):69-73. |
| 49 | 何清,杨兴华,霍文,等.库姆塔格沙漠粒度分布特征及环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(1):18-22. |
| 50 | 吉启慧.粒度分析在塔克拉玛干沙漠研究中的应用[J].中国沙漠,1996,16(2):173-179. |
| 51 | 李超,董治宝,崔徐甲.腾格里沙漠东南缘不同发育阶段横向沙丘粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(1):129-135. |
| 52 | 舒培仙,牛东风,李保生,等.毛乌素沙地现代沙丘沙的粒度特征及其意义[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(1):158-166. |
| 53 | Lancaster D.Grain size characteristics of linear dunes in the southwestern Kalahari[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1986,56(3):395-400. |
| 54 | Mischke S.New evidence for origin of Badain Jaran Desert of lnner Mongolia from granulometry and thermoluminescence dating[J].Journal of Palaeogeography,2005,7(1):79-97. |
| 55 | 李玲萍,李岩瑛,李晓京,等.河西走廊不同强度冷锋型沙尘暴环流和动力特征[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(5):219-228. |
| 56 | Pye K.Aeolian Dust and Dust Deposits[M].London,UK:Academic Press,1987:1-256. |
| 57 | Sun D H, Su R X, Bloemendal J,et al.Grain-size and accumulation rate records from Late Cenozoic aeolian sequences in Northern China:implication for variations in the East Asian winter monsoon and westerly atmospheric circulation [J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2008,264(1/2):39-53. |
| 58 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K,et al.Bimodal grain-size distribution of Chinese loess,and its palaeoclimatic implications[J].Catena,2004,55(3):325-340. |
| 59 | Vandenberghe J.Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:a powerful proxy for process identification[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2013,121:18-30. |
| 60 | 孔凡彪,陈海涛,徐树建,等.山东章丘黄土粒度指示的粉尘堆积过程及古气候意义[J].地理学报,2021,76(5):1163-1176. |
| 61 | Nottebaum V, Stauch G, Hartmann K,et al.Unmixed loess grain size populations along the northern Qilian Shan (China):relationships between geomorphologic,sedimentologic and climatic controls[J].Quaternary International,2015,372:151-166. |
| 62 | 梁爱民,屈建军,董治宝,等.库姆塔格沙漠沉积物粒度端元特征及其物源启示[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(2):33-42. |
| 63 | Wang X M, Dong Z B, Zhang J W,et al.Grain size characteristics of dune sand in the central Taklimakan Sand Sea[J].Sedimentary Geology,2003,16:1-4. |
| 64 | 唐进年.库姆塔格沙漠沉积物特征与沉积环境研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2018. |
| 65 | 王立强.河西走廊及其毗邻地区地表沉积与亚洲粉尘源区示踪[D].兰州:兰州大学,2011. |
| 66 | 罗万银,董治宝,钱广强,等.戈壁表层沉积物地球化学元素组成及其沉积意义[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1441-1453. |
| 67 | 胡观冠,李保生,温小浩,等.毛乌素沙地现代流动沙丘沙的矿物成分[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1454-1460. |
| 68 | 王祎.青藏高原东北缘尖扎盆地沉积物矿物特征及其古环境意义[D].西安:长安大学,2019. |
| [1] | 孟庆爽, 左合君, 闫敏, 王海兵, 席成. 库布齐沙漠地表沉积物常量元素与粒度的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 107-117. |
| [2] | 李琦炜, 龚志军, 罗明, 彭花明, 王瀚, 王威. 鄱阳湖沙山两处具有平行层理砂层的粒度分析及其对沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 152-159. |
| [3] | 范亚伟, 杜鹤强, 卢善龙, 韩致文, 刘秀帆, 刘欣雷. 长江源卓乃湖流域地表沉积物粒度分布与风沙流结构[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 47-56. |
| [4] | 胡梦珺, 庄静, 孙文丽, 郑登友, 吉天琪, 许澳康. 青藏高原东北部全新世常量元素地球化学特征及环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 11-20. |
| [5] | 黄日辉, 张立婷, 冯淼彦, 刘铮瑶, 李健熙, 陈韵琪, 张志浩, 王璟. 广东省东海岛大岭剖面沉积物粒度、微形态特征与沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 121-129. |
| [6] | 张正偲, 潘凯佳, 张焱, 韩兰英. 中国西北戈壁区沙尘暴过程中近地层风沙运动特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 130-138. |
| [7] | 陈京平, 余子莹, 杨帆, 王蜜, 胡涵, 倪观忠, 高鑫, 王鑫. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地沙尘暴和地表沙物质粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [8] | 李静芸, 傅天阳, 申玉龙, 王立辉, 伍永秋. 毛乌素沙地新月形和抛物线形沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 226-232. |
| [9] | 张雯, 杜丁丁, 李志文, 吴汪洋, 李向洁, 白永会. 鄱阳湖沙地沉积物粒度特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 122-132. |
| [10] | 古拉依赛木·艾拜都拉, 张峰, 吴枫, 吴世新, 郑江华, 孙涛. 腾格里沙漠沙丘沉积物粒度特征及其空间差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 133-145. |
| [11] | 王蒙, 逯军峰, 付鹏, 董治宝. 巴丹吉林沙漠周边地区土壤养分和粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 232-244. |
| [12] | 汪进秋, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 孙磊, 吴鹏, 魏振宇. 中更新世以来的哈尔滨黄土物源变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 25-35. |
| [13] | 庞红丽, 高红山, 李富强, 张连科. 黄河宁蒙段沉积物地球化学元素组成及分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 44-53. |
| [14] | 姜吴彬, 张德国, 杨小平. 沙丘形态及表沙粒度特征对风况和地表植被变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 120-129. |
| [15] | 王晓枝, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 李超, 高冲, 张欣. 拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 22-31. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
