中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 209-219.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00011
• • 上一篇
王融融1( ), 樊瑾1, 丛士翔1, 余海龙1(
), 樊瑾1, 丛士翔1, 余海龙1( ), 黄菊莹2
), 黄菊莹2
收稿日期:2022-10-21
修回日期:2023-02-20
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-08-14
通讯作者:
余海龙
作者简介:余海龙(E-mai: yhl@nxu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Rongrong Wang1( ), Jin Fan1, Shixiang Cong1, Hailong Yu1(
), Jin Fan1, Shixiang Cong1, Hailong Yu1( ), Juying Huang2
), Juying Huang2
Received:2022-10-21
Revised:2023-02-20
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Hailong Yu
摘要:
选取宁东能源化工基地典型火电厂周边广泛分布的3类生物结皮作为研究对象,探究工矿区生物结皮富集大气降尘重金属对酶活性的影响及其影响深度,在对比分析富集大气降尘过程中土壤理化性质、酶活性及重金属含量变化的基础上,采用相关分析、冗余分析方法探讨了生物结皮各层次土壤酶活性与土壤重金属含量和土壤理化性质之间的相关关系。结果表明:(1)沿藻结皮—混生结皮—藓结皮的演替方向,结皮层土壤有机碳(SOC)、全氮(TN)及全磷(TP)含量显著提升,土壤容重和pH降低;随土层深度增加,土壤理化性质变化不显著。(2)3类生物结皮对源自大气降尘的重金属元素均具有显著的表层富集作用,富集量藓结皮>混生结皮>藻结皮;结皮层重金属污染程度高于下层土壤。(3)4种土壤酶活性沿藻结皮—混生结皮—藓结皮的演替方向呈现一致的规律性,表现为藓结皮>混生结皮>藻结皮。(4)部分重金属元素Zn、Pb、Cd和土壤理化性质如容重、pH、SOC、TN等是影响土壤酶活性的主要因子,但相较于重金属元素,土壤理化性质对酶活性影响更大。
中图分类号:
王融融, 樊瑾, 丛士翔, 余海龙, 黄菊莹. 毛乌素沙地火电厂周边不同类型生物结皮酶活性及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 209-219.
Rongrong Wang, Jin Fan, Shixiang Cong, Hailong Yu, Juying Huang. Enzyme activity characteristics and their influencing factors of different biocrusts around thermal plant in Mu Us Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 209-219.
| 生物结皮类型 | 厚度/mm | 覆盖度/% | 优势种 | 生物量/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 4.50±0.31a | 82 | 具鞘微鞘藻(Microcolus vaginatus)、念珠藻(Nostoc commune Vauch)、隐头舟形藻(Navicula cryptocephala) | 11.23±0.05a |
| 混生结皮 | 5.53±0.34b | 86 | 具鞘微鞘藻、念珠藻、石果衣(Endocarpon pusillum)、糙聚盘衣(Glypholecia scabra) | 18.15±0.01b |
| 藓结皮 | 7.73±0.49c | 74 | 真藓(Bryum argenteum Hedw)、土生对齿藓(Didymodon vinealis)、盐土藓(Pterygoneurum subsessile)、厚肋流苏藓(Crossidium crassinerve) | 31.07±0.02c |
表1 研究区生物结皮基本概况
Table 1 Basic conditions of biocrusts in study area
| 生物结皮类型 | 厚度/mm | 覆盖度/% | 优势种 | 生物量/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 4.50±0.31a | 82 | 具鞘微鞘藻(Microcolus vaginatus)、念珠藻(Nostoc commune Vauch)、隐头舟形藻(Navicula cryptocephala) | 11.23±0.05a |
| 混生结皮 | 5.53±0.34b | 86 | 具鞘微鞘藻、念珠藻、石果衣(Endocarpon pusillum)、糙聚盘衣(Glypholecia scabra) | 18.15±0.01b |
| 藓结皮 | 7.73±0.49c | 74 | 真藓(Bryum argenteum Hedw)、土生对齿藓(Didymodon vinealis)、盐土藓(Pterygoneurum subsessile)、厚肋流苏藓(Crossidium crassinerve) | 31.07±0.02c |
| Igeo | <0 | 0~1 | 1~2 | 2~3 | 3~4 | 4~5 | 5~6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 污染等级 | 无 | 轻-中度 | 中度 | 中-强度 | 强度 | 强-极强度 | 极强 |
表2 地累积指数分级标准
Table 2 Classification criterions of geo-accumulation index
| Igeo | <0 | 0~1 | 1~2 | 2~3 | 3~4 | 4~5 | 5~6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 污染等级 | 无 | 轻-中度 | 中度 | 中-强度 | 强度 | 强-极强度 | 极强 |
| 样品 | 土层 | 黏粒 /% | 粉粒 /% | 砂粒 /% | 容重 /(g·cm-3) | 有机碳 /(g·kg-1) | 全氮 /(g·kg-1) | 全磷 /(g·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 结皮层 | 7.82±1.39Aa | 47.31±2.94Aa | 44.88±3.05ABa | 1.12±0.05Aa | 14.75±0.38Aa | 1.30±0.06Aa | 0.54±0.05Aa | 8.35±0.01Aa |
| 0~5 cm | 5.76±0.16Ba | 47.23±4.05Aa | 47.00±4.19ABa | 1.27±0.01Bab | 3.88±0.55Ba | 0.80±0.06Ba | 0.46±0.02ABa | 8.72±0.02Ba | |
| 5~10 cm | 4.55±0.29Ba | 44.30±0.41Aab | 51.15±0.53Aa | 1.39±0.05Ba | 3.68±0.27Ba | 0.77±0.04Ba | 0.39±0.02ABa | 8.82±0.06Ba | |
| 10~20 cm | 7.78±2.87Aa | 49.34±3.57Aa | 42.88±2.89Ba | 1.41±0.06Bb | 3.45±0.19Ba | 0.83±0.04Ba | 0.32±0.06Ba | 8.74±0.13Ba | |
| 混生结皮 | 结皮层 | 4.96±0.18Ab | 48.47±0.50ABa | 46.57±0.59Aa | 1.10±0.03Aa | 15.82±1.42Aa | 1.42±0.10Aa | 0.58±0.02Aa | 8.37±0.03Aa |
| 0~5 cm | 4.42±0.17Aa | 43.13±1.22Bab | 52.45±1.39Ba | 1.33±0.03Ba | 4.55±0.10Ba | 0.82±0.03Ba | 0.47±0.01Ba | 8.99±0.01Bb | |
| 5~10 cm | 4.34±0.18Aa | 46.83±1.46ABa | 48.84±1.47ABa | 1.30±0.05Bb | 4.64±0.42Ba | 0.77±0.07Ba | 0.40±0.01Ca | 9.03±0.04Bb | |
| 10~20 cm | 5.71±0.91Aa | 49.31±2.67Aa | 44.98±3.58Aa | 1.36±0.04Bb | 4.27±0.21Ba | 0.72±0.05Ba | 0.37±0.02Da | 8.84±0.05Ba | |
| 藓结皮 | 结皮层 | 3.97±0.22Ab | 46.98±0.43Aa | 49.05±0.54Aa | 1.05±0.01Aa | 23.67±2.64Ab | 1.89±0.21Aa | 0.79±0.01Ab | 8.22±0.09Ab |
| 0~5 cm | 5.50±0.91Aa | 41.32±0.78Ab | 53.19±1.45Aa | 1.18±0.04Bb | 4.80±0.25Ba | 0.95±0.05Ba | 0.51±0.05Ba | 8.83±0.09Bab | |
| 5~10 cm | 8.36±4.43ABb | 40.71±2.32Ab | 50.94±5.50Aa | 1.34±0.05Bb | 4.29±0.25Ba | 1.04±0.07Bb | 0.42±0.01BCa | 9.02±0.07Bb | |
| 10~20 cm | 14.17±8.85Bb | 46.46±3.70Aa | 39.38±5.94Ba | 1.37±0.06Bb | 4.68±0.68Ba | 0.88±0.05Ba | 0.36±0.03Ca | 8.95±0.13Ba |
表3 不同类型生物结皮土壤理化性质
Table 3 Soil physicochemical properties of different biocrusts
| 样品 | 土层 | 黏粒 /% | 粉粒 /% | 砂粒 /% | 容重 /(g·cm-3) | 有机碳 /(g·kg-1) | 全氮 /(g·kg-1) | 全磷 /(g·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 结皮层 | 7.82±1.39Aa | 47.31±2.94Aa | 44.88±3.05ABa | 1.12±0.05Aa | 14.75±0.38Aa | 1.30±0.06Aa | 0.54±0.05Aa | 8.35±0.01Aa |
| 0~5 cm | 5.76±0.16Ba | 47.23±4.05Aa | 47.00±4.19ABa | 1.27±0.01Bab | 3.88±0.55Ba | 0.80±0.06Ba | 0.46±0.02ABa | 8.72±0.02Ba | |
| 5~10 cm | 4.55±0.29Ba | 44.30±0.41Aab | 51.15±0.53Aa | 1.39±0.05Ba | 3.68±0.27Ba | 0.77±0.04Ba | 0.39±0.02ABa | 8.82±0.06Ba | |
| 10~20 cm | 7.78±2.87Aa | 49.34±3.57Aa | 42.88±2.89Ba | 1.41±0.06Bb | 3.45±0.19Ba | 0.83±0.04Ba | 0.32±0.06Ba | 8.74±0.13Ba | |
| 混生结皮 | 结皮层 | 4.96±0.18Ab | 48.47±0.50ABa | 46.57±0.59Aa | 1.10±0.03Aa | 15.82±1.42Aa | 1.42±0.10Aa | 0.58±0.02Aa | 8.37±0.03Aa |
| 0~5 cm | 4.42±0.17Aa | 43.13±1.22Bab | 52.45±1.39Ba | 1.33±0.03Ba | 4.55±0.10Ba | 0.82±0.03Ba | 0.47±0.01Ba | 8.99±0.01Bb | |
| 5~10 cm | 4.34±0.18Aa | 46.83±1.46ABa | 48.84±1.47ABa | 1.30±0.05Bb | 4.64±0.42Ba | 0.77±0.07Ba | 0.40±0.01Ca | 9.03±0.04Bb | |
| 10~20 cm | 5.71±0.91Aa | 49.31±2.67Aa | 44.98±3.58Aa | 1.36±0.04Bb | 4.27±0.21Ba | 0.72±0.05Ba | 0.37±0.02Da | 8.84±0.05Ba | |
| 藓结皮 | 结皮层 | 3.97±0.22Ab | 46.98±0.43Aa | 49.05±0.54Aa | 1.05±0.01Aa | 23.67±2.64Ab | 1.89±0.21Aa | 0.79±0.01Ab | 8.22±0.09Ab |
| 0~5 cm | 5.50±0.91Aa | 41.32±0.78Ab | 53.19±1.45Aa | 1.18±0.04Bb | 4.80±0.25Ba | 0.95±0.05Ba | 0.51±0.05Ba | 8.83±0.09Bab | |
| 5~10 cm | 8.36±4.43ABb | 40.71±2.32Ab | 50.94±5.50Aa | 1.34±0.05Bb | 4.29±0.25Ba | 1.04±0.07Bb | 0.42±0.01BCa | 9.02±0.07Bb | |
| 10~20 cm | 14.17±8.85Bb | 46.46±3.70Aa | 39.38±5.94Ba | 1.37±0.06Bb | 4.68±0.68Ba | 0.88±0.05Ba | 0.36±0.03Ca | 8.95±0.13Ba |
| 样品 | 土层 | Hg/(mg·kg-1) | Pb/(mg·kg-1) | As/(mg·kg-1) | Cd/(mg·kg-1) | Cr/(mg·kg-1) | Zn/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 结皮层 | 0.076±0.01ab | 16.200±0.32ab | 13.190±0.31ab | 0.281±0.02a | 52.732±1.96a | 39.507±0.97a |
| 0~5 cm | 0.072±0.01a | 13.332±0.68a | 12.802±0.41a | 0.131±0.02a | 52.566±2.07a | 32.086±0.71a | |
| 5~10 cm | 0.071±0.00a | 12.681±0.05a | 11.926±0.30a | 0.105±0.00a | 48.902±0.16a | 31.047±0.71a | |
| 10~20 cm | 0.070±0.00a | 12.713±0.33a | 11.543±0.28a | 0.103±0.00a | 50.147±2.35a | 31.040±0.60a | |
| 混生结皮 | 结皮层 | 0.079±0.01ab | 18.776±0.12b | 15.952±1.53a | 0.327±0.01a | 56.935±2.70a | 41.262±0.22ab |
| 0~5 cm | 0.078±0.01ab | 13.244±0.33a | 14.498±1.38a | 0.126±0.00a | 53.631±2.00a | 31.765±0.84a | |
| 5~10 cm | 0.070±0.00a | 12.701±0.24a | 12.766±0.34ab | 0.101±0.00a | 53.162±0.88a | 31.707±0.70a | |
| 10~20 cm | 0.074±0.00ab | 12.402±0.53a | 12.133±0.36a | 0.099±0.00a | 52.302±2.03a | 30.861±0.71a | |
| 藓结皮 | 结皮层 | 0.095±0.01a | 19.638±1.37b | 16.627±3.11a | 0.409±0.08a | 57.063±3.01a | 44.412±2.16b |
| 0~5 cm | 0.092±0.01b | 13.177±0.18a | 14.782±3.57a | 0.136±0.01a | 52.936±0.97a | 32.313±0.42a | |
| 5~10 cm | 0.080±0.04a | 11.663±0.52b | 14.063±0.51b | 0.105±0.00a | 49.778±1.53a | 30.041±0.48b | |
| 10~20 cm | 0.079±0.00b | 11.816±0.90a | 11.470±0.11a | 0.102±0.00a | 48.540±3.80a | 32.144±1.68a | |
| 风沙土背景值[ | 0.016 | 13.8 | 4.3 | 0.044 | 24.8 | 29.8 | |
| 宁夏土壤环境背景值[ | 0.021 | 20.6 | 11.9 | 0.112 | 60.0 | 58.8 | |
表4 不同类型生物结皮土壤重金属含量特征
Table 4 Characteristics of heavy metal contents of different biocrusts
| 样品 | 土层 | Hg/(mg·kg-1) | Pb/(mg·kg-1) | As/(mg·kg-1) | Cd/(mg·kg-1) | Cr/(mg·kg-1) | Zn/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 结皮层 | 0.076±0.01ab | 16.200±0.32ab | 13.190±0.31ab | 0.281±0.02a | 52.732±1.96a | 39.507±0.97a |
| 0~5 cm | 0.072±0.01a | 13.332±0.68a | 12.802±0.41a | 0.131±0.02a | 52.566±2.07a | 32.086±0.71a | |
| 5~10 cm | 0.071±0.00a | 12.681±0.05a | 11.926±0.30a | 0.105±0.00a | 48.902±0.16a | 31.047±0.71a | |
| 10~20 cm | 0.070±0.00a | 12.713±0.33a | 11.543±0.28a | 0.103±0.00a | 50.147±2.35a | 31.040±0.60a | |
| 混生结皮 | 结皮层 | 0.079±0.01ab | 18.776±0.12b | 15.952±1.53a | 0.327±0.01a | 56.935±2.70a | 41.262±0.22ab |
| 0~5 cm | 0.078±0.01ab | 13.244±0.33a | 14.498±1.38a | 0.126±0.00a | 53.631±2.00a | 31.765±0.84a | |
| 5~10 cm | 0.070±0.00a | 12.701±0.24a | 12.766±0.34ab | 0.101±0.00a | 53.162±0.88a | 31.707±0.70a | |
| 10~20 cm | 0.074±0.00ab | 12.402±0.53a | 12.133±0.36a | 0.099±0.00a | 52.302±2.03a | 30.861±0.71a | |
| 藓结皮 | 结皮层 | 0.095±0.01a | 19.638±1.37b | 16.627±3.11a | 0.409±0.08a | 57.063±3.01a | 44.412±2.16b |
| 0~5 cm | 0.092±0.01b | 13.177±0.18a | 14.782±3.57a | 0.136±0.01a | 52.936±0.97a | 32.313±0.42a | |
| 5~10 cm | 0.080±0.04a | 11.663±0.52b | 14.063±0.51b | 0.105±0.00a | 49.778±1.53a | 30.041±0.48b | |
| 10~20 cm | 0.079±0.00b | 11.816±0.90a | 11.470±0.11a | 0.102±0.00a | 48.540±3.80a | 32.144±1.68a | |
| 风沙土背景值[ | 0.016 | 13.8 | 4.3 | 0.044 | 24.8 | 29.8 | |
| 宁夏土壤环境背景值[ | 0.021 | 20.6 | 11.9 | 0.112 | 60.0 | 58.8 | |
| 样品 | 土层 | Hg | Pb | As | Cd | Cr | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 结皮层 | 1.657 | -0.354 | 1.032 | 2.091 | 0.503 | -0.178 |
| 0~5 cm | 1.583 | -0.635 | 0.989 | 0.985 | 0.499 | -0.478 | |
| 5~10 cm | 1.573 | -0.707 | 0.887 | 0.668 | 0.395 | -0.526 | |
| 10~20 cm | 1.537 | -0.703 | 0.840 | 0.636 | 0.431 | -0.526 | |
| 混生结皮 | 结皮层 | 1.722 | -0.141 | 1.306 | 2.309 | 0.614 | -0.115 |
| 0~5 cm | 1.701 | -0.644 | 1.168 | 0.937 | 0.528 | -0.493 | |
| 5~10 cm | 1.539 | -0.705 | 0.985 | 0.618 | 0.515 | -0.495 | |
| 10~20 cm | 1.616 | -0.739 | 0.912 | 0.584 | 0.492 | -0.534 | |
| 藓结皮 | 结皮层 | 1.988 | -0.076 | 1.366 | 2.632 | 0.617 | -0.009 |
| 0~5 cm | 1.941 | -0.652 | 1.196 | 1.047 | 0.509 | -0.468 | |
| 5~10 cm | 1.743 | -0.828 | 1.125 | 0.673 | 0.420 | -0.573 | |
| 10~20 cm | 1.716 | -0.809 | 0.831 | 0.632 | 0.384 | -0.476 |
表5 矿区不同类型生物结皮土壤重金属地累积指数
Table 5 The geoaccumulation index of different biocrusts in mining area
| 样品 | 土层 | Hg | Pb | As | Cd | Cr | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻结皮 | 结皮层 | 1.657 | -0.354 | 1.032 | 2.091 | 0.503 | -0.178 |
| 0~5 cm | 1.583 | -0.635 | 0.989 | 0.985 | 0.499 | -0.478 | |
| 5~10 cm | 1.573 | -0.707 | 0.887 | 0.668 | 0.395 | -0.526 | |
| 10~20 cm | 1.537 | -0.703 | 0.840 | 0.636 | 0.431 | -0.526 | |
| 混生结皮 | 结皮层 | 1.722 | -0.141 | 1.306 | 2.309 | 0.614 | -0.115 |
| 0~5 cm | 1.701 | -0.644 | 1.168 | 0.937 | 0.528 | -0.493 | |
| 5~10 cm | 1.539 | -0.705 | 0.985 | 0.618 | 0.515 | -0.495 | |
| 10~20 cm | 1.616 | -0.739 | 0.912 | 0.584 | 0.492 | -0.534 | |
| 藓结皮 | 结皮层 | 1.988 | -0.076 | 1.366 | 2.632 | 0.617 | -0.009 |
| 0~5 cm | 1.941 | -0.652 | 1.196 | 1.047 | 0.509 | -0.468 | |
| 5~10 cm | 1.743 | -0.828 | 1.125 | 0.673 | 0.420 | -0.573 | |
| 10~20 cm | 1.716 | -0.809 | 0.831 | 0.632 | 0.384 | -0.476 |
| 变异来源 | 自由度df | 碱性磷酸酶 | 蔗糖酶 | 过氧化氢酶 | 脲酶 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物结皮类型 | 2 | 41.845*** | 1.141 | 12.832*** | 23.079*** |
| 土壤深度 | 3 | 181.520*** | 62.026*** | 58.306*** | 76.540*** |
| 生物结皮类型×土壤深度 | 6 | 9.254*** | 0.982 | 3.259** | 14.289*** |
| 误差 | 54 |
表6 不同类型生物结皮酶活性的双因素方差分析
Table 6 Two-way ANOVA of enzyme activities of different biocrusts
| 变异来源 | 自由度df | 碱性磷酸酶 | 蔗糖酶 | 过氧化氢酶 | 脲酶 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生物结皮类型 | 2 | 41.845*** | 1.141 | 12.832*** | 23.079*** |
| 土壤深度 | 3 | 181.520*** | 62.026*** | 58.306*** | 76.540*** |
| 生物结皮类型×土壤深度 | 6 | 9.254*** | 0.982 | 3.259** | 14.289*** |
| 误差 | 54 |
| 酶活性 | 土壤性质 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | Pb | As | Cd | Cr | Zn | 容重 | 黏粒 | 粉粒 | 砂粒 | 土壤有机碳 | 全氮 | 全磷 | pH | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 0.275 | 0.851*** | 0.483** | 0.832*** | 0.559*** | 0.838*** | -0.675*** | -0.265 | 0.132 | 0.128 | 0.831*** | 0.710*** | 0.783*** | -0.565*** |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 0.352* | 0.838*** | 0.468** | 0.824*** | 0.496** | 0.844*** | -0.757*** | -0.158 | 0.081 | 0.075 | 0.826*** | 0.843*** | 0.810*** | -0.650*** |
| 脲酶 | 0.427** | 0.746*** | 0.422* | 0.784*** | 0.385* | 0.739*** | -0.651*** | -0.177 | -0.063 | 0.197 | 0.802*** | 0.756*** | 0.817*** | -0.608*** |
| 蔗糖酶 | 0.240 | 0.815*** | 0.311 | 0.786*** | 0.449** | 0.819*** | -0.748*** | -0.152 | 0.111 | 0.048 | 0.791*** | 0.796*** | 0.750*** | -0.645*** |
表7 生物结皮酶活性与土壤环境因子之间的相关性
Table 7 Correlation between enzyme activities of biocrusts and soil environment
| 酶活性 | 土壤性质 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | Pb | As | Cd | Cr | Zn | 容重 | 黏粒 | 粉粒 | 砂粒 | 土壤有机碳 | 全氮 | 全磷 | pH | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 0.275 | 0.851*** | 0.483** | 0.832*** | 0.559*** | 0.838*** | -0.675*** | -0.265 | 0.132 | 0.128 | 0.831*** | 0.710*** | 0.783*** | -0.565*** |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 0.352* | 0.838*** | 0.468** | 0.824*** | 0.496** | 0.844*** | -0.757*** | -0.158 | 0.081 | 0.075 | 0.826*** | 0.843*** | 0.810*** | -0.650*** |
| 脲酶 | 0.427** | 0.746*** | 0.422* | 0.784*** | 0.385* | 0.739*** | -0.651*** | -0.177 | -0.063 | 0.197 | 0.802*** | 0.756*** | 0.817*** | -0.608*** |
| 蔗糖酶 | 0.240 | 0.815*** | 0.311 | 0.786*** | 0.449** | 0.819*** | -0.748*** | -0.152 | 0.111 | 0.048 | 0.791*** | 0.796*** | 0.750*** | -0.645*** |
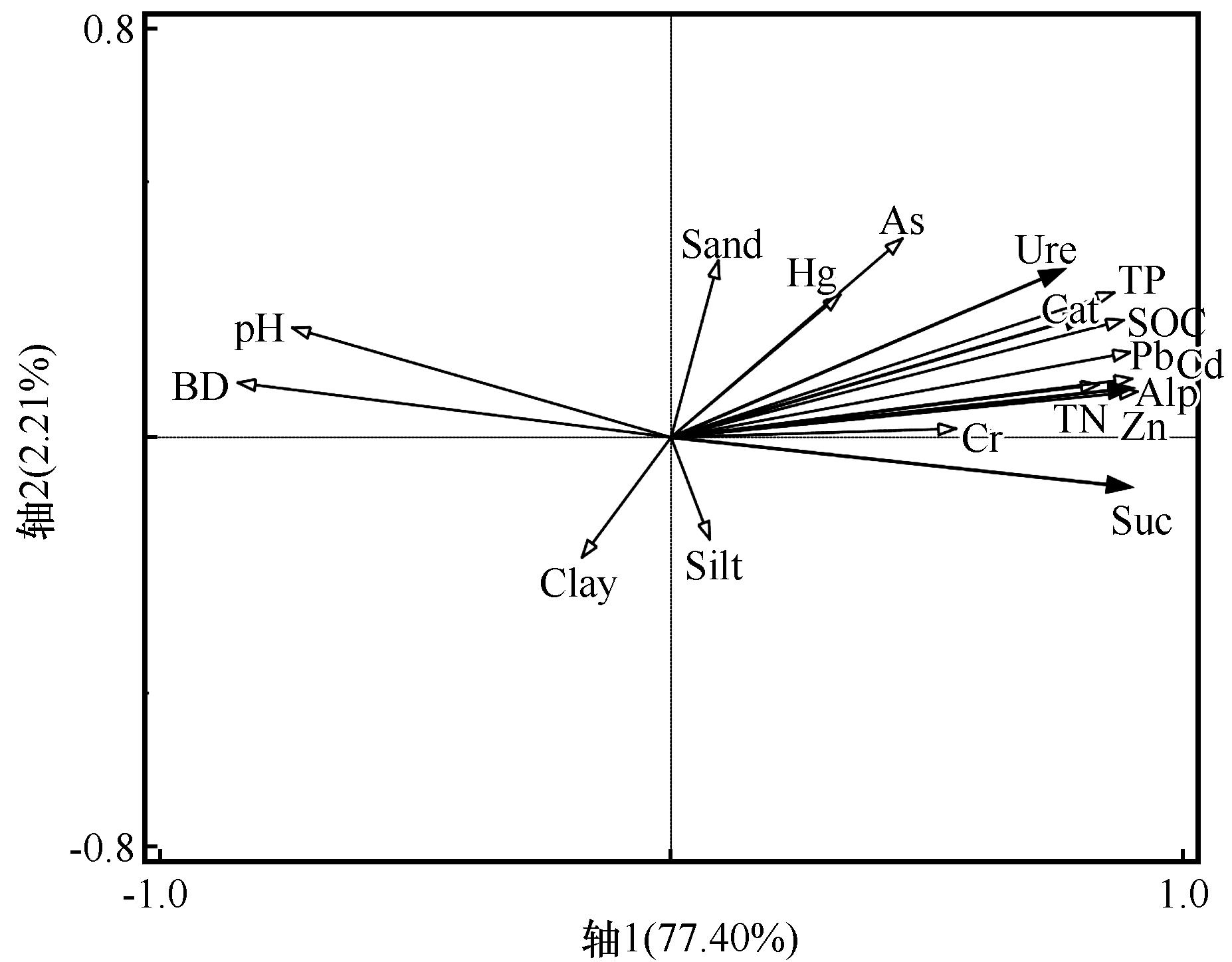
图2 环境因子与生物结皮酶活性的冗余分析排序图Clay: 黏粒; Silt: 粉粒; Sand: 砂粒; BD: 容重; SOC: 土壤有机碳; TP:全磷; TN: 全氮. Cat: 过氧化氢酶; Alp: 碱性磷酸酶; Ure: 脲酶; Suc: 蔗糖酶S
Fig.2 Redundancy analysis (RDA) ordination diagram of environmental factors and enzyme activities of biocrusts
| 项目 | Zn | Pb | Cd | 土壤有机碳 | 全磷 | 容重 | 全氮 | pH | Cr | As | Hg | 黏粒 | 砂粒 | 粉粒 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解释度/% | 64.4 | 62.9 | 62.5 | 60.7 | 58.2 | 55.4 | 54.1 | 42.5 | 24.1 | 16.2 | 8.8 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
| F | 61.4 | 57.6 | 56.6 | 52.5 | 47.3 | 42.3 | 40.1 | 25.2 | 10.8 | 6.6 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| P | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.076 | 0.356 | 0.634 | 0.746 |
表8 生物结皮酶活性与环境因子冗余分析(RDA)中的显著性检验
Table 8 Significance test of redundancy analysis (RDA) of biocrusts enzyme activities and environmental factors
| 项目 | Zn | Pb | Cd | 土壤有机碳 | 全磷 | 容重 | 全氮 | pH | Cr | As | Hg | 黏粒 | 砂粒 | 粉粒 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 解释度/% | 64.4 | 62.9 | 62.5 | 60.7 | 58.2 | 55.4 | 54.1 | 42.5 | 24.1 | 16.2 | 8.8 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
| F | 61.4 | 57.6 | 56.6 | 52.5 | 47.3 | 42.3 | 40.1 | 25.2 | 10.8 | 6.6 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| P | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.076 | 0.356 | 0.634 | 0.746 |
| 1 | 熊秋林,肖红伟,程朋根,等.北京表层土壤重金属污染分布及大气沉降贡献[J].生态环境学报,2021,30(4):816-824. |
| 2 | Chen J, Tan M, Li Y,et al.Characteritics of trace elements and lead isotope ratios in PM2.5 from four sites in Shanghai[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2008,156:36-43. |
| 3 | Duzgorcn-Aydin N S.Sources and characteristics of lead pollution in the urban environment of Guangzhou[J].Science of the Total Environment,2007,385:182-195. |
| 4 | 吴龙华,张长波,章海波,等.铅稳定同位素在土壤污染物来源识别中的应用[J].环境科学,2009,30(1):227-230. |
| 5 | Tian H Z, Cheng K, Wang Y.Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of atmospheric emissions of Cd,Cr and Pb from coal in China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2012,50:157-163. |
| 6 | Wu Y, Streets D G, Wang S X,et al.Uncertainties in estimating mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants in China[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2010,9(6):2937-2946. |
| 7 | Gupta A K, Dwivedi S, Sinha S,et al.Metal accumulation and growth performance of Phaseolus vulgaris grown in fly ash amended soil[J].Bioresource Technology,2007,98(3):3404-3407. |
| 8 | Manta D S, Angelone M, Bellanca A,et al.Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily),Italy[J].Science of the Total Environment,2002,300:229-243. |
| 9 | Kizilkaya R, Askin T, Bayrakli B,et al.Microbiological characteristics of soils contaminated with heavy metals[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2004,40:95-102. |
| 10 | Chen J L, Zheng C, Ruan J Z,et al.Cadmium bioavailability and accumulation in rice grain are controlled by pH and Ca in paddy soils with high geological background of transportation and deposition[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2021,106:92-98. |
| 11 | 张元明,王雪芹.荒漠地表生物土壤结皮形成与演替特征概述[J].生态学报,2010,30(16):4484-4492. |
| 12 | Rodriguez-Caballero E, Belnap J, Büdel B,et al.Dryland photoautotrophic soil surface communities endangered by global change[J].Nature Geoscience,2018,11(3):185-189. |
| 13 | Belnap J, Weber B, Büdel B.Biological soil crusts as an organizing principle in drylands[M]//Cham.Biological Soil Crusts:An Organizing Principle in Drylands.Switzerland:Springer International Publishing,2016:3-13. |
| 14 | Li X R, Zhou H Y, Wang P,et al.The effects of sand stabilization and revegetation on cryptogam species diversity and soil fertility in the Tengger Desert,Northern China[J].Plant and Soil,2003,251(2):237-245. |
| 15 | Su Y G, Li X R, Zheng J G,et al.The effect of biological soil crusts of different successional stages and conditions on the germination of seeds of three desert plants[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2009,73:931-936. |
| 16 | 徐杰,敖艳青,张璟霞,等.沙地不同发育阶段的人工生物结皮对重金属的富集作用[J].生态学报,2012,32(23):7402-7410. |
| 17 | 赵芷玉,律泽,魏炜,等.佳乐麝香与镉污染对土壤微生物和酶活性的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2021,40(8):1738-1745. |
| 18 | Hsu M J, Selvaraj K, Agoramoorthy G.Taiwan's industrial heavy metal pollution threatens terrestrial biota[J].Environmental Pollution,2006,143(2):327-334. |
| 19 | 腾应,黄昌勇,龙健,等.铜尾矿污染区土壤酶活性研究[J].应用生态学报,2003,14(11):1976-1980. |
| 20 | 周正虎,王传宽.微生物对分解底物碳氮磷化学计量的响应和调节机制[J].植物生态学报,2016,40(6):620-630. |
| 21 | Li X R, Zhang Y M, Zhao Y G.A study of biological soil crusts: recent development,trend and prospect[J].Advances in Earth Science,2009,24(1):11-24. |
| 22 | 邓杰文,石杨,李斌,等.微生物在沙化土壤修复中的应用研究进展[J].应用与环境生物学报,2022,28(5):1367-1374. |
| 23 | Zimmerman A R, Ahn M Y.Organovmineral-enzyme interaction and soil enzyme activity[M]//Shukla G,Varma A.Soil Enzymology.Berlin,Germany:Springer,2011:271-292. |
| 24 | Wang Z Q, Tian H X, Lu G N,et al.Catalytic efficiency is a better predictor of arsenic toxicity to soil alkaline phosphatase[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2018,148:721-148728. |
| 25 | Tian H X, Zhao Y M, Megharaj M,et al.Arsenate inhibition on kinetic characteristics of alkaline phosphatase as influenced by pH[J].Ecological Indicators,2018,85:1101-1106. |
| 26 | 智静,傅泽强,陈燕.宁东能源(煤)化工基地物质流分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2012,26(9):137-142. |
| 27 | 樊瑾,李诗瑶,杜雅仙,等.火电厂周边不同生物结皮细菌群落特征差异及其影响因素[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(11):4107-4118. |
| 28 | 关松荫.土壤酶及其研究方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,1986:101-122. |
| 29 | 李倩,秦飞,季宏兵,等.北京市密云水库上游金矿区土壤重金属含量、来源及污染评价[J].农业环境科学学报,2013,32(12):2384-2394. |
| 30 | 邓霞,崔东,王兴磊,等.伊犁煤矿土壤重金属累积对土壤酶活性的影响[J].环境化学,2018,37(7):1554-1564. |
| 31 | 中国环境监测总站.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社,1990. |
| 32 | 徐杰,敖艳青,张璟霞.生物结皮对沙地生态系统大气沉降重金属污染的指示[M].呼和浩特:内蒙古大学出版社,2012. |
| 33 | 姚宏佳,王宝荣,安韶山,等.黄土高原生物结皮形成过程中土壤胞外酶活性及其化学计量变化特征[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(2):456-468. |
| 34 | 张胜男,高海燕,闫德仁,等.沙漠生物土壤结皮演替对微生物群落结构和土壤酶活力的影响[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):178-187. |
| 35 | 柯善文,席亚丽,牟佳美,等.地衣生态功能研究进展[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(9):3138-3146. |
| 36 | 杨永胜,卜崇峰,高国雄.毛乌素沙地生物结皮对土壤温度的影响[J].干旱区研究,2012,29(2):352-359. |
| 37 | 孙福海,肖波,李胜龙,等.黄土高原不同发育阶段生物结皮的导水和持水特征[J].草业学报,2021,30(6):54-63. |
| 38 | 刘翔,周宏飞,刘昊,等.不同类型生物土壤结皮覆盖下风沙土的入渗特征及模拟[J].生态学报,2016,36(18):5820-5826. |
| 39 | 罗成科,张佳瑜,肖国举,等.宁东基地不同燃煤电厂周边土壤5种重金属元素污染特征及生态风险[J].生态环境学报,2018,27(7):1285-1291. |
| 40 | 赵彦敏.陕北黄土生物结皮种群特征及对土壤生物活性的影响[D].北京:北京林业大学,2014. |
| 41 | Zhao Y G, Xu M X, Belnap J.Potential nitrogen fixation activity of different aged biological soil crusts from rehabilitated grasslands of the Hilly Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2010,74(10):1186-1191. |
| 42 | Elbert W, Weber B, Burrows S,et al.Contribution of cryptogamic covers to the global cycles of carbon and nitrogen[J].Nature Geoscience,2012,5(7):459-462. |
| 43 | 张国秀,赵允格,许明祥,等.黄土丘陵区生物结皮对土壤磷素有效性及碱性磷酸酶活性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2012,18(3):621-628. |
| 44 | Ghiloufi W, Seo J, Kim J,et al.Effects of biological soil crusts on enzyme activities and microbial community in soils of an arid ecosystem[J].Microbial Ecology,2019,77(1):201-216. |
| 45 | 安韶山,黄懿梅,郑粉莉.黄土丘陵草地土壤脲酶活性特征及其与土壤性质的关系[J].草地学报,2005,13(3):233-237. |
| 46 | Yang H Y, Liu C Z, Liu Y M,et al.Impact of human trampling on biological soil crusts determined by soil microbial biomass,enzyme activities and nematode communities in a desert ecosystem[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2018,87:61-71. |
| 47 | Zhang B C, Zhou X B, Zhang Y M.Responses of microbial activities and soil physical-chemical properties to the successional process of biological soil crusts in the Gurbantunggut Desert,Xinjiang[J].Journal of Arid Land,2015(1):101-109. |
| 48 | Belnap J.Nitrogen fixation in biological soil crusts from southeast Utah,USA[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2002,35:128-135. |
| 49 | 王攀,朱湾湾,樊瑾,等.宁夏燃煤电厂周围降水降尘中硫氮沉降特征研究[J].生态环境学报,2020,29(6):1189-1197. |
| 50 | Khan S, Cao Q, Hesham A E,et al.Soil enzymatic activities and microbial community structure with different application rates of Cd and Pb[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2007,19(7):834-840. |
| 51 | Ciarkowska K, Sołek-Podwika K, Wieczorek J.Enzyme activity as an indicator of soil-rehabilitation processes at a zinc and lead ore mining and processing area[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2014,132:250-256. |
| 52 | 王广昊,孔星杰,孙彩丽,等.铅锌废渣场周边土地利用方式转变对土壤胞外酶活性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2022,41(6):1166-1172. |
| 53 | 牛玉斌,樊瑾,李诗瑶,等.宁东能源工业基地表层土壤粒径分布、养分、重金属含量与大气降尘的关联性[J].水土保持通报,2020,40(4):91-99. |
| [1] | 焦冰洁, 张丙昌, 赵康, 闫丽霞, 武志芳. 生物结皮演替对黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错区土壤氮素转化及微生物活性的促进效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 191-199. |
| [2] | 李静芸, 傅天阳, 申玉龙, 王立辉, 伍永秋. 毛乌素沙地新月形和抛物线形沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 226-232. |
| [3] | 贾鸿飞, 贾荣亮, 吴秀丽, 赵芸, 刘立超, 高艳红, 杨昊天, 张甜. 干旱沙区生物结皮对土壤膨胀的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 28-36. |
| [4] | 洪光宇, 王晓江, 苏庆溥, 海龙, 王少昆, 高孝威, 徐艳艳, 周景山, 李卓凡, 李梓豪, 胡尔查. 毛乌素沙地流动沙丘土壤水分模拟及渗漏特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 288-298. |
| [5] | 白旭赢, 王玉杰, 王云琦, 杨文斌, 王涛, 程一本. 毛乌素沙地水体面积变化及驱动因子[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 65-73. |
| [6] | 杨宇哲, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 刘怡婷, 李嘉宁, 杨天宇. 毛乌素沙地东南缘L3 、S3 黄土-古土壤色度特征及古气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 176-186. |
| [7] | 刘红梅, 王海兵, 李宽, 刘茜雅, 任余艳, 张彦东. 毛乌素沙地库伦生态经济圈结构、效益及农牧民行为[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 48-57. |
| [8] | 陈晓涵, 吴永胜, 海春兴. 毛乌素沙地南缘固沙灌丛下地表凝结水特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 83-95. |
| [9] | 洪光宇, 王晓江, 刘铁山, 海龙, 吴振廷, 胡尔查, 高孝威, 杨海峰, 李卓凡, 李梓豪, 斯琴, 王乐军. 基于Hydrus-1D模型的毛乌素沙地杨柴( Hedysarum laeve )灌木林土壤含水量模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 233-242. |
| [10] | 陶玲, 任汉儒, 周怡蕾, 任珺. 水分和养分供应对凹凸棒石复配苔藓结皮生长的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 288-294. |
| [11] | 南富森, 李宗省, 张小平, 崔乔, 李玉辰, 杨安乐, 熊雪婷. 黄河北岸兰州段丘陵区土壤生态化学计量与空间变异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 167-176. |
| [12] | 王蒙, 逯军峰, 付鹏, 董治宝. 巴丹吉林沙漠周边地区土壤养分和粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 232-244. |
| [13] | 顾立霞, 吕萍, 马芳, 陈国祥, 梁准, 许明静, 杨迎. 不同数据源下毛乌素沙地风况及输沙势特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 54-62. |
| [14] | 柳欣滢, 金明, 杨帆, 马亚鹏, 刘慧, 孙小云, 夏敦胜. 毛乌素沙地东缘中全新世以来环境变化及其对文明演化的影响初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 92-100. |
| [15] | 李昌盛, 张志山, 张金林, 张秀风, 徐冰鑫, 石亚飞, 霍建强. 荒漠-绿洲区土壤性质过渡特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 209-218. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
