中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 98-110.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00057
邹晓君1,2( ), 马运强1,2, 李志忠1,2,3(
), 马运强1,2, 李志忠1,2,3( ), 靳建辉1,2,3, 刘瑞1,2, 谭典佳1,2, 陶通炼1,2
), 靳建辉1,2,3, 刘瑞1,2, 谭典佳1,2, 陶通炼1,2
收稿日期:2023-03-10
修回日期:2023-05-10
出版日期:2023-11-20
发布日期:2023-11-30
通讯作者:
李志忠
作者简介:李志忠(E-mail: lizz@fjnu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Xiaojun Zou1,2( ), Yunqiang Ma1,2, Zhizhong Li1,2,3(
), Yunqiang Ma1,2, Zhizhong Li1,2,3( ), Jianhui Jin1,2,3, Rui Liu1,2, Dianjia Tan1,2, Tonglian Tao1,2
), Jianhui Jin1,2,3, Rui Liu1,2, Dianjia Tan1,2, Tonglian Tao1,2
Received:2023-03-10
Revised:2023-05-10
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-11-30
Contact:
Zhizhong Li
摘要:
古尔班通古特沙漠是中国受西风环流影响最明显、面积最大的固定半固定沙漠,但全新世以来沙漠风沙活动的时空变化特征及其成因尚存争议。选取沙漠南部边缘两处沙丘(沙垄)剖面加密采样,进行光释光测年和砂样粒度组分测试,基于光释光年龄概率密度分析和风积物粒度端元分析,综合提取风积序列光释光年代和粒度参数记录的风沙气候变化信息。结果表明:(1)从风积物粒度端元组分提取的敏感组分是区域风沙活动信息的重要气候代用指标,近源搬运的粗组分主要反映沙丘尺度的风沙活动信号,远源输送的细组分反映沙漠尺度的风沙活动信号;(2)上风边缘高输沙势地区的风积序列较多记录了沙丘尺度风沙活动信号,而下风低输沙势地区的风积序列较多记录了沙漠尺度的风沙活动信号;(3)全新世中晚期以来,研究区风沙活动强度变化可划分为5.0~3.5、3.5~1.8、1.8 ka BP至今3个阶段,风沙活动的区域性和阶段性特征是北半球西风环流变化、气候干湿变化以及局地尺度风动力、砂物质来源、植被覆盖等因素综合作用的结果。
中图分类号:
邹晓君, 马运强, 李志忠, 靳建辉, 刘瑞, 谭典佳, 陶通炼. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘风沙沉积记录的中晚全新世气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 98-110.
Xiaojun Zou, Yunqiang Ma, Zhizhong Li, Jianhui Jin, Rui Liu, Dianjia Tan, Tonglian Tao. Mid-Late Holocene climate change recorded by eolian sand deposition in the southern margin of Gurbantunggut Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 98-110.
| 前人研究 | 研究对象 | 测年方法 | 结论 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 陈惠中等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠西南部沙垄剖面 | 14C、TL | 剖面沉积序列反映了全新世以来气候变化特征与中国东部季风区沙区一致 |
| Li等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠南部线形沙丘和丘间地钻孔风积物 | OSL | 认为全新世以来研究区风沙活动主要受西风环流的影响 |
| Lu等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠风积序列 | OSL | 在全新世大暖期,古尔班通古特沙漠分布范围大幅缩小,与整个中国北方沙漠/沙地分布范围的变化趋势一致 |
| 东丽娜等[ | |||
| Ji等[ | 巴里坤盆地风成沉积序列 | OSL | 全新世以来新疆北部风沙活动总体反映了西风气流影响下的气候变化规律 |
| 徐宇杰等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠及周边多个风积、黄土古土壤序列 | OSL |
表1 前人对古尔班通古特沙漠全新世气候变化规律的研究
Table 1 Previous studies on the understanding of the Holocene climate change law in the Gurbantunggut Desert
| 前人研究 | 研究对象 | 测年方法 | 结论 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 陈惠中等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠西南部沙垄剖面 | 14C、TL | 剖面沉积序列反映了全新世以来气候变化特征与中国东部季风区沙区一致 |
| Li等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠南部线形沙丘和丘间地钻孔风积物 | OSL | 认为全新世以来研究区风沙活动主要受西风环流的影响 |
| Lu等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠风积序列 | OSL | 在全新世大暖期,古尔班通古特沙漠分布范围大幅缩小,与整个中国北方沙漠/沙地分布范围的变化趋势一致 |
| 东丽娜等[ | |||
| Ji等[ | 巴里坤盆地风成沉积序列 | OSL | 全新世以来新疆北部风沙活动总体反映了西风气流影响下的气候变化规律 |
| 徐宇杰等[ | 古尔班通古特沙漠及周边多个风积、黄土古土壤序列 | OSL |
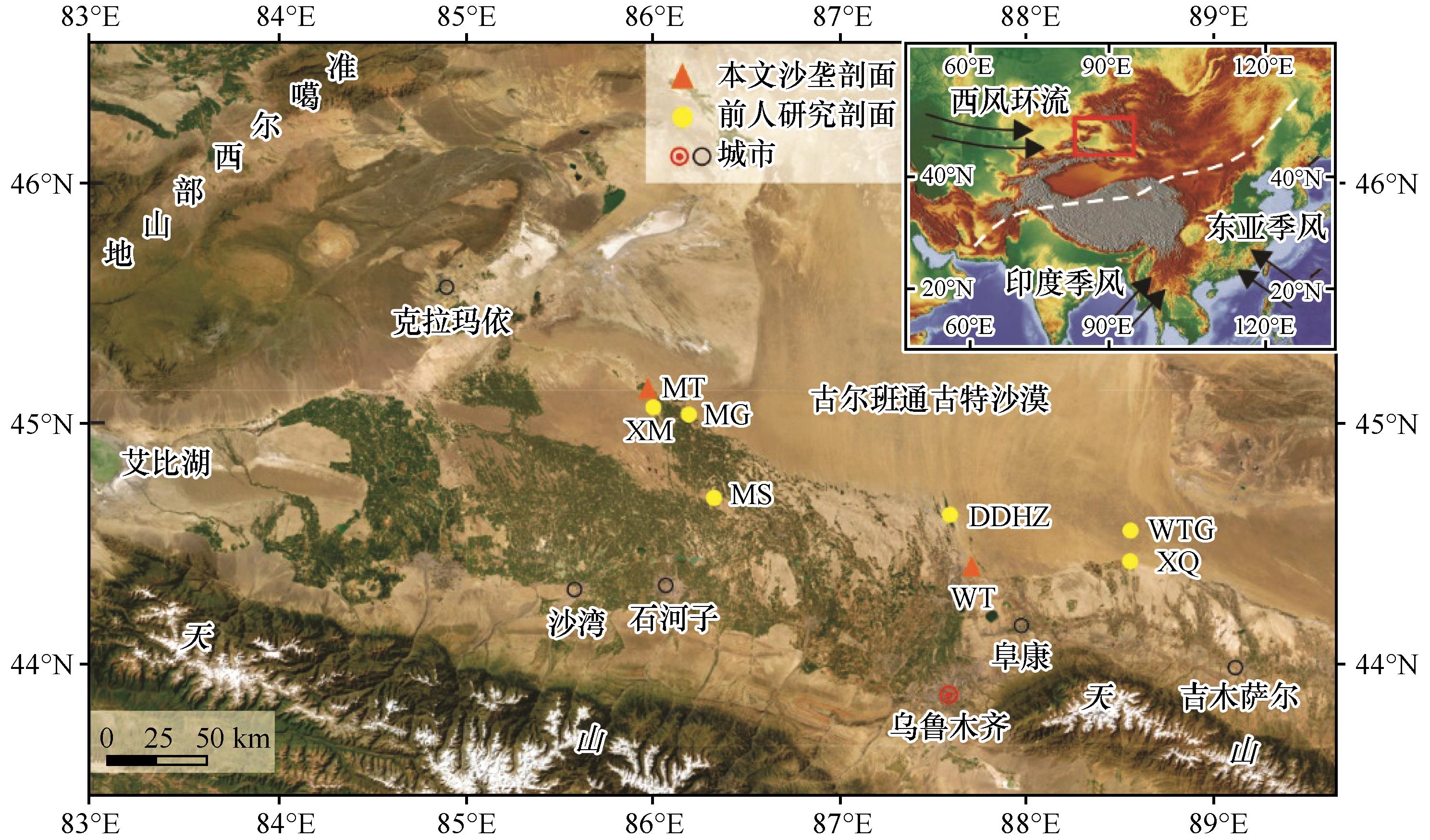
图1 研究区位置、沙丘(沙垄)剖面和对比剖面MS: [28];WTG: [29];DDHZ: [37];XM、MG、XQ: [38]
Fig.1 Location of sand dune ( sand ridge ) profiles and correlation profiles in the study area (MS profile[28]; WTG profile[29]; DDHZ profile [37]; XM、MG、XQ profile[38])
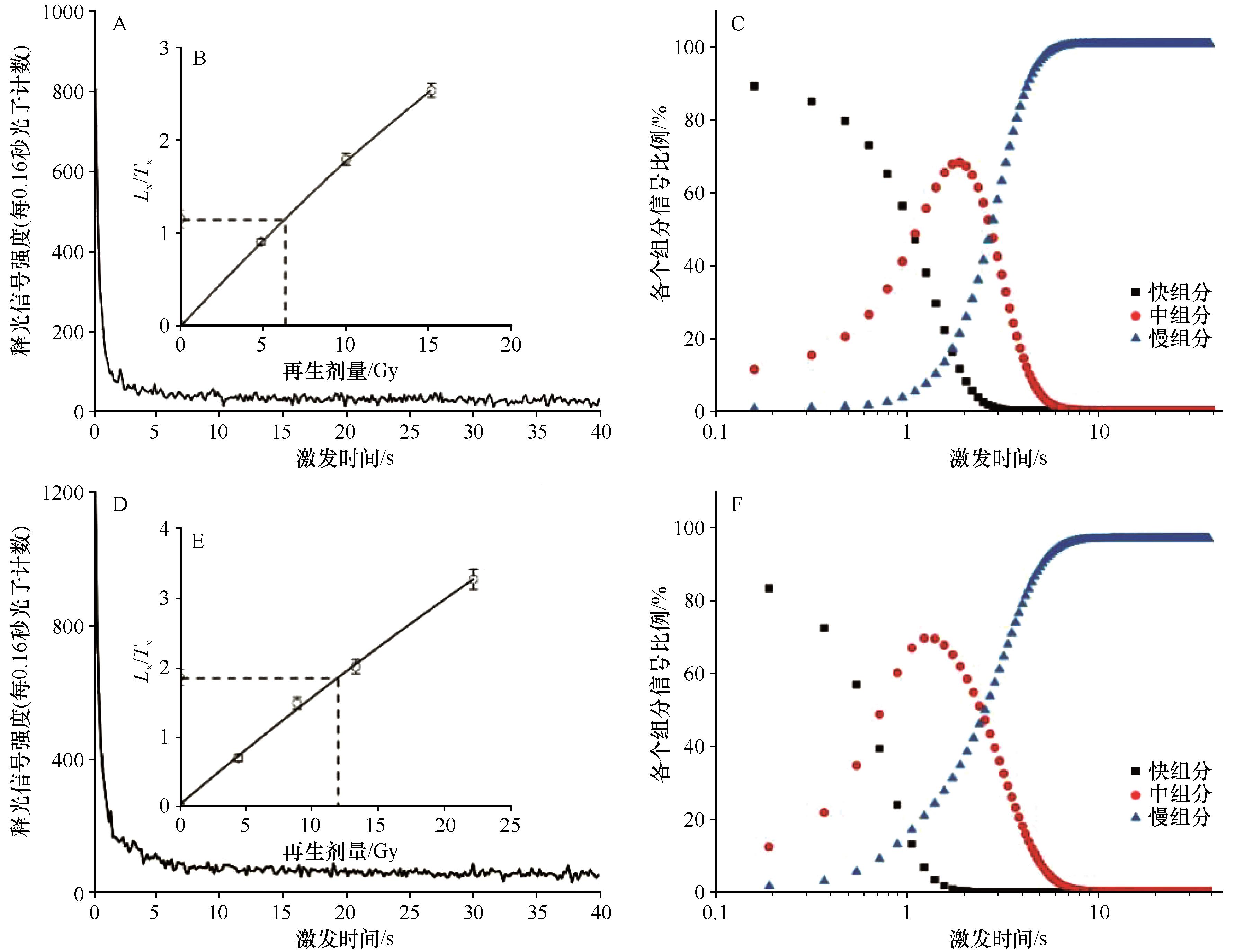
图3 样品ML-01天然OSL释光信号衰减曲线(A)和生长曲线(B)及各组分信号比例随时间变化(C);样品WT07天然OSL释光信号衰减曲线(D)和生长曲线(E)及各组分信号比例随时间变化(F)
Fig.3 (A) Decay curve; (B) growth curve; and (C) relative contributions to the OSL signal for sample ML-01; (D) Decay curve; (E) growth curve; and (F) relative contributions to the OSL signal for sample WT07
| 沙丘类型 | 野外 编号 | 埋深 /m | 测片数 | U /(mg·kg-1) | Th /(mg·kg-1) | K /% | D /(Gy·ka-1) | DeMAM /Gy | AgeMAM /ka | DeCAM /Gy | AgeCAM /ka | DeAVG /Gy | AgeAVG /ka | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
新 月 形 沙 丘 链 | 丘顶 | MT-01 | 0.6 | 38 | 1.43±0.02 | 5.17±0.07 | 2.04±0.02 | 2.78±0.12 | 0.26±0.02 | 0.09±0.01 | 0.41±0.03 | 0.15±0.01 | 0.44±0.03 | 0.16±0.01 |
| MT-02 | 1.5 | 28 | 1.57±0.02 | 4.64±0.03 | 2.01±0.02 | 2.72±0.12 | 4.97±0.3 | 1.82±0.13 | 5.75±0.17 | 2.11±0.11 | 5.79±0.17 | 2.13±0.11 | ||
| MT-03 | 3.6 | 26 | 1.33±0.01 | 4.71±0.02 | 1.92±0.02 | 2.55±0.11 | 5.40±0.3 | 2.11±0.15 | 5.95±0.17 | 2.33±0.12 | 5.98±0.18 | 2.34±0.12 | ||
| 背风坡 | ML-01 | 2.5 | 27 | 1.36±0.04 | 4.22±0.06 | 2.16±0.02 | 2.78±0.12 | 6.47±0.33 | 2.33±0.16 | 6.68±0.19 | 2.40±0.12 | 6.71±0.20 | 2.41±0.13 | |
| ML-02 | 2.5 | 24 | 1.45±0.05 | 4.88±0.12 | 2.17±0.02 | 2.85±0.12 | 5.89±0.16 | 2.07±0.11 | 5.99±0.28 | 2.10±0.13 | 5.99±0.15 | 2.10±0.10 | ||
| ML-03 | 2.5 | 29 | 1.37±0.04 | 4.49±0.07 | 2.19±0.02 | 2.83±0.12 | 5.83±0.13 | 2.06±0.10 | 5.93±0.12 | 2.10±0.10 | 5.78±0.12 | 2.04±0.10 | ||
| 线形沙丘(沙垄) | 丘顶 | WT01 | 1 | 27 | 1.78±0.04 | 5.98±0.06 | 1.95±0.02 | 2.83±0.12 | 6.6±0.26 | 2.33±0.13 | 6.63±0.13 | 2.34±0.11 | 6.62±0.13 | 2.34±0.11 |
| WT02 | 1.5 | 26 | 1.88±0.02 | 8.26±0.07 | 1.82±0.01 | 2.87±0.12 | 5.97±0.24 | 2.08±0.12 | 5.99±0.14 | 2.09±0.10 | 5.97±0.14 | 2.08±0.10 | ||
| WT03 | 2 | 28 | 1.58±0.02 | 5.78±0.04 | 1.96±0.01 | 2.76±0.12 | 6.40±0.38 | 2.32±0.17 | 7.13±0.23 | 2.59±0.14 | 7.19±0.24 | 2.61±0.14 | ||
| WT04 | 2.5 | 25 | 1.46±0.02 | 6.71±0.03 | 1.91±0.02 | 2.73±0.11 | 10.35±0.6 | 3.79±0.27 | 11.26±0.34 | 4.13±0.21 | 11.31±0.36 | 4.14±0.22 | ||
| WT05 | 3 | 29 | 1.23±0.02 | 5.19±0.03 | 1.9±0.01 | 2.56±0.11 | 9.93±0.56 | 3.88±0.27 | 10.68±0.27 | 4.18±0.21 | 10.71±0.28 | 4.19±0.21 | ||
| WT06 | 3.5 | 29 | 1.32±0.02 | 8.25±0.07 | 1.89±0.02 | 2.76±0.12 | 8.17±0.59 | 2.96±0.25 | 9.68±0.4 | 3.51±0.21 | 9.83±0.45 | 3.56±0.22 | ||
| WT07 | 4 | 24 | 1.30±0.01 | 5.59±0.04 | 2.03±0.02 | 2.7±0.12 | 11.7±0.71 | 4.33±0.32 | 12.74±0.44 | 4.71±0.26 | 12.84±0.47 | 4.75±0.27 | ||
表2 沙丘(沙垄)剖面样品光释光测年结果
Table 2 The OSL dating results of dune (sand ridge) profiles
| 沙丘类型 | 野外 编号 | 埋深 /m | 测片数 | U /(mg·kg-1) | Th /(mg·kg-1) | K /% | D /(Gy·ka-1) | DeMAM /Gy | AgeMAM /ka | DeCAM /Gy | AgeCAM /ka | DeAVG /Gy | AgeAVG /ka | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
新 月 形 沙 丘 链 | 丘顶 | MT-01 | 0.6 | 38 | 1.43±0.02 | 5.17±0.07 | 2.04±0.02 | 2.78±0.12 | 0.26±0.02 | 0.09±0.01 | 0.41±0.03 | 0.15±0.01 | 0.44±0.03 | 0.16±0.01 |
| MT-02 | 1.5 | 28 | 1.57±0.02 | 4.64±0.03 | 2.01±0.02 | 2.72±0.12 | 4.97±0.3 | 1.82±0.13 | 5.75±0.17 | 2.11±0.11 | 5.79±0.17 | 2.13±0.11 | ||
| MT-03 | 3.6 | 26 | 1.33±0.01 | 4.71±0.02 | 1.92±0.02 | 2.55±0.11 | 5.40±0.3 | 2.11±0.15 | 5.95±0.17 | 2.33±0.12 | 5.98±0.18 | 2.34±0.12 | ||
| 背风坡 | ML-01 | 2.5 | 27 | 1.36±0.04 | 4.22±0.06 | 2.16±0.02 | 2.78±0.12 | 6.47±0.33 | 2.33±0.16 | 6.68±0.19 | 2.40±0.12 | 6.71±0.20 | 2.41±0.13 | |
| ML-02 | 2.5 | 24 | 1.45±0.05 | 4.88±0.12 | 2.17±0.02 | 2.85±0.12 | 5.89±0.16 | 2.07±0.11 | 5.99±0.28 | 2.10±0.13 | 5.99±0.15 | 2.10±0.10 | ||
| ML-03 | 2.5 | 29 | 1.37±0.04 | 4.49±0.07 | 2.19±0.02 | 2.83±0.12 | 5.83±0.13 | 2.06±0.10 | 5.93±0.12 | 2.10±0.10 | 5.78±0.12 | 2.04±0.10 | ||
| 线形沙丘(沙垄) | 丘顶 | WT01 | 1 | 27 | 1.78±0.04 | 5.98±0.06 | 1.95±0.02 | 2.83±0.12 | 6.6±0.26 | 2.33±0.13 | 6.63±0.13 | 2.34±0.11 | 6.62±0.13 | 2.34±0.11 |
| WT02 | 1.5 | 26 | 1.88±0.02 | 8.26±0.07 | 1.82±0.01 | 2.87±0.12 | 5.97±0.24 | 2.08±0.12 | 5.99±0.14 | 2.09±0.10 | 5.97±0.14 | 2.08±0.10 | ||
| WT03 | 2 | 28 | 1.58±0.02 | 5.78±0.04 | 1.96±0.01 | 2.76±0.12 | 6.40±0.38 | 2.32±0.17 | 7.13±0.23 | 2.59±0.14 | 7.19±0.24 | 2.61±0.14 | ||
| WT04 | 2.5 | 25 | 1.46±0.02 | 6.71±0.03 | 1.91±0.02 | 2.73±0.11 | 10.35±0.6 | 3.79±0.27 | 11.26±0.34 | 4.13±0.21 | 11.31±0.36 | 4.14±0.22 | ||
| WT05 | 3 | 29 | 1.23±0.02 | 5.19±0.03 | 1.9±0.01 | 2.56±0.11 | 9.93±0.56 | 3.88±0.27 | 10.68±0.27 | 4.18±0.21 | 10.71±0.28 | 4.19±0.21 | ||
| WT06 | 3.5 | 29 | 1.32±0.02 | 8.25±0.07 | 1.89±0.02 | 2.76±0.12 | 8.17±0.59 | 2.96±0.25 | 9.68±0.4 | 3.51±0.21 | 9.83±0.45 | 3.56±0.22 | ||
| WT07 | 4 | 24 | 1.30±0.01 | 5.59±0.04 | 2.03±0.02 | 2.7±0.12 | 11.7±0.71 | 4.33±0.32 | 12.74±0.44 | 4.71±0.26 | 12.84±0.47 | 4.75±0.27 | ||
| 1 | Singhvi A K, Sharma Y P, Agrawal D P.Thermo-luminescence dating of sand dunes in Rajasthan,India[J].Nature,1982,295(5847):313-315. |
| 2 | Pye K, Tsoar H.Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer Science & Business Media,2009. |
| 3 | Thomas D S G, Hesse P P.Dune paleoenvironments[C]//Shroder J F.Treatise on Geomorphology.Amsterdam,Netherlands:Science Direct,2022:592-616. |
| 4 | Singhvi A K, Porat N.Impact of luminescence dating on geomorphological and palaeoclimate research in drylands[J].Boreas,2008,37(4):536-558. |
| 5 | Bristow C S, Armitage S J.Dune ages in the sand deserts of the southern Sahara and Sahel[J].Quaternary International,2016,410(Part B):46-57. |
| 6 | Lancaster N, Wolfe S, Thomas D S G,et al.The INQUA dunes atlas chronologic database[J].Quaternary International,2016,410(Part B):3-10. |
| 7 | Livingstone I, Thomas D S G.Modes of linear dune activity and their palaeoenvironmental significance:an evaluation with reference to southern African examples[J].Geological Society Special Publication,1993,72(1):91-101. |
| 8 | Munyikwa K.The role of dune morphogenetic history in the interpretation of linear dune luminescence chronologies:a review of linear dune dynamics[J].Progress in Physical Geography,2005,29(3):317-336. |
| 9 | Telfer M W, Bailey R M, Burrough S L,et al.Understanding linear dune chronologies:insights from a simple accumulation model[J].Geomorphology,2010,120(3):195-208. |
| 10 | Telfer M W, Hesse P P.Palaeoenvironmental reconstructions from linear dunefields:recent progress,current challenges and future directions[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2013,78(15):1-21. |
| 11 | Thomas D S G.Reconstructing paleoenvironments and palaeoclimates in drylands:What can landform analysis contribute?[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2013,38(1):3-16. |
| 12 | 中国科学院新疆综合考察队.新疆地貌[M].北京:科学出版社,1978. |
| 13 | 朱震达,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980. |
| 14 | 吴正,等.中国沙漠及其治理[M].北京:科学出版社,2009. |
| 15 | 刘峥瑶.古尔班通古特沙漠沙丘地貌及其发育环境[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2020. |
| 16 | 刘瑞,李志忠,靳建辉,等.古尔班通古特沙漠西南缘新月形沙丘内部沉积构造特征研究[J].干旱区地理,2022,45(3):802-813. |
| 17 | 解锡豪,李志忠,靳建辉,等.古尔班通古特沙漠东南部植被线形沙丘内部构造及发育模式[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):74-84. |
| 18 | 王雪芹,王涛,蒋进,等.古尔班通古特沙漠南部沙面稳定性研究[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学),2004,34(8):763-768. |
| 19 | 阎顺,穆桂金,孔昭宸,等.天山北麓晚全新世环境演变及其人类活动的影响[J].冰川冻土,2004,26(4):403-410. |
| 20 | Chen F H, Jia J, Chen J H,et al.A persistent Holocene wetting trend in arid Central Asia,with wettest conditions in the late Holocene,revealed by multi-proxy analyses of loess-paleosol sequences in Xinjiang,China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,146(15):134-146. |
| 21 | Jia J, Chen J H, Wang Z Y,et al.No evidence for an anti-phased Holocene moisture regim in mountains and basins in Central Asian:records from Ili loess,Xinjiang[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2021,572(15):110407. |
| 22 | 蒋庆丰,沈吉,刘兴起,等.西风区全新世以来湖泊沉积记录的高分辨率古气候演化[J].科学通报,2007,52(9):1042-1049. |
| 23 | Huang X Z, Peng W, Rudaya N,et al.Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics in the Altai Mountains and surrounding areas[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(13):6628-6636. |
| 24 | Wang W, Zhang D L.Holocene vegetation evolution and climatic dynamics inferred from an ombrotrophic peat sequence in the southern Altai Mountains within China[J].Global and Planetary Change,2019,179:10-22. |
| 25 | Feng Z D, Sun A Z, Abdusalih N,et al.Vegetation changes and associated climatic changes in the southern Altai Mountains within China during the Holocene[J].The Holocene,2016,27(5):683-693. |
| 26 | Zhang Y, Meyers P A, Liu X T,et al.Holocene climate changes in the Central Asia mountain region inferred from a peat sequence from the Altai Mountains,Xinjiang,northwestern China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,152(15):19-30. |
| 27 | Hong B, Gasse F, Uchida M,et al.Increasing summer rainfall in arid eastern Central Asia over the past 8500 years[J].Scientific Reports,2014,4:5279. |
| 28 | 陈惠中,金炯,董光荣.全新世古尔班通古特沙漠演化和气候变化[J].中国沙漠,2001,21(4):18-24. |
| 29 | Li S H, Fan A C.OSL chronology of sand deposits and climate change of last 18 ka in Gurbantunggut Desert,northwest China[J].Journal of Quaternary Science,2011,26(8):813-818. |
| 30 | Lu H Y, Yi S W, Xu Z W,et al.Chinese deserts and sand fields in Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene Optimum[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(23):2775-2783. |
| 31 | 东丽娜,鹿化煜,王晓勇,等.末次盛冰期和全新世大暖期新疆地区沙漠边界移动初探[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):398-400. |
| 32 | Ji J L, Wang G C, Yang L R,et al.Holocene climate in arid central Asia and timing of sand dunes accumulation in Balikun Basin,Northwest China[J].Geological Journal,2020,55(11):7346-7358. |
| 33 | 徐宇杰,刘冰,孙爱军,等.古尔班通古特沙漠及周边区域全新世环境演变研究进展[J].干旱区地理,2023,46(4):550-562. |
| 34 | 陈曦.中国干旱区自然地理[M].北京:科学出版社,2010. |
| 35 | 季方,叶玮,魏文寿.古尔班通古特沙漠固定与半固定沙丘成因初探[J].干旱区地理,2000,23(1):32-36. |
| 36 | 钱亦兵,吴兆宁.古尔班通古特沙漠环境研究[M].北京:科学出版社,2010. |
| 37 | 马妮娜,穆桂金,阎顺.中全新世以来乌鲁木齐东道海子B剖面沉积物源探讨与分析[J].干旱区地理,2005,28(2):188-193. |
| 38 | 马运强,刘瑞,李志忠,等.古尔班通古特沙漠南缘沉积记录的全新世环境演变[J].干旱区地理.. |
| 39 | 李红军,杨青,何清.艾比湖地区的输沙势分析[J].干旱区研究,2003,20(4):322-325. |
| 40 | 李红军,何清,杨青.近40 a新疆输沙势的分析[J].中国沙漠,2004,24(6):46-50. |
| 41 | Aitken M J.An Introduction to Optical Dating[M].Oxford,UK:Oxford University Press,1998:1-262. |
| 42 | Murray A S, Wintle A G.Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J].Radiation Measurements,2000,32(1):57-73. |
| 43 | Murray A S, Wintle A G.The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol:potential for improvements in reliability[J].Radiation Measurements,2003,37(4):377-381. |
| 44 | Blott S J, Pye K.Particle size scales and classification of sediment types based on particle size distributions:review and recommended procedures[J].Sedimentology,2012,59(7):2071-2096. |
| 45 | Folk R L, Ward W C.Brazos river bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1957,27(1):3-26. |
| 46 | Paterson G A, Heslop D.New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2015,16(12):4494-4506. |
| 47 | Vandenberghe J.Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:a powerful proxy for process identification[J].Earth Science Reviews,2013,121:18-30. |
| 48 | 梁爱民,屈建军,董治宝,等.库姆塔格沙漠沉积物粒度端元特征及其物源启示[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(2):33-42. |
| 49 | 白敏,鲁瑞洁,丁之勇,等.青海湖湖东沙地粒度端元分析及其指示意义[J].第四纪研究,2020,40(5):1203-1215. |
| 50 | Telfer M W, Thomas D S G.Late Quaternary linear dune accumulation and chronostratigraphy of the southwestern Kalahari:implications for aeolian palaeoclimatic reconstructions and predictions of future dynamics[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2007,26(19):2617-2630. |
| 51 | Hesse P P.How do longitudinal dunes respond to climate forcing?Insights from 25 years of luminescence dating of the Australian desert dunefields[J].Quaternary International,2016,410(Part B):11-29. |
| 52 | Li H W, Yang X P.Spatial and temporal patterns of aeolian activities in the desert belt of northern China revealed by dune chronologies[J].Quaternary International,2016,410(Part B):58-68. |
| 53 | Srivastava A, Thomas D S G, Durcan J A,et al.Holocene dune activity in the Thar Desert,India[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2019,44(7):1407-1418. |
| 54 | Xu Z W, Mason J A, Lu H Y,et al.Crescentic dune migration and stabilization:implications for interpreting paleo-dune deposits as paleoenvironmental records[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2017,27(11):1341-1358. |
| 55 | Bond G, Showers W, Cheseby M,et al.A pervasive millennial-scale cycle in north Atlantic Holocene and glacial climates[J].Science,1997,278(5341):1257-1266. |
| 56 | 陈吉阳.天山乌鲁木齐河源全新世冰川变化的地衣年代学等若干问题之初步研究[J].中国科学(B辑:化学 生物学 农学 医学 地学),1988,18(1):95-104. |
| 57 | Thomas D S G, Wiggs G F S.Aeolian system responses to global change:challenges of scale,process and temporal integration[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2008,33(9):1396-1418. |
| 58 | 范育新,张青松,蔡青松,等.光释光年代学对腾格里沙漠化机制及风沙物源的指示[J].第四纪研究,2022,42(2):350-367. |
| 59 | 刘英英.全新世北疆泥炭沉积记录的大气粉尘变化[D].兰州:兰州大学,2016. |
| 60 | Zhang Y, Yang P, Tong C,et al.Palynological record of Holocene vegetation and climate changes in a high-resolution peat profile from the Xinjiang Altai Mountains,northwestern China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2018,201(1):111-123. |
| 61 | Qiang M R, Lang W Z, He Z H,et al.A 1600-year record of eolian activity from Jili Lake in northern Xinjiang[J].Quaternary International,2022,631(10):93-104. |
| 62 | Kang S G, Wang X L, Roberts H M,et al.Increasing effective moisture during the Holocene in the semiarid regions of the Yili Basin,Central Asia:evidence from loess sections[J].Quaternary Science Review,2020,246(15):106553. |
| 63 | Gao F Y, Zheng X M,Jia,J,et al.Evolution of near-surface wind strength in northeastern arid Central Asia during the Holocene[J].Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology,2021,36(2):1-13 |
| 64 | Xie H C, Zhang H W, Ma J Y,et al.Trend of increasing Holocene summer precipitation in arid Central Asia:evidence from an organic carbon isotopic record from the LJW10 loess section in Xinjiang,NW China[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2018,509(15):24-32. |
| 65 | Gao F Y, Yang J H, Xia D S,et al.Linking moisture and near-surface wind with winter temperature to reveal the Holocene climate evolution in arid Xinjiang region of China[J].Geoscience Frontiers,2022,13(6):101433. |
| 66 | Han W X, Lü S, Appel E,et al.Dust storm outbreak in Central Asia after similar to 3.5 kyr BP[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2019,46(13):7624-7633. |
| 67 | Chen S Q, Liu J B, Wang X,et al.Holocene dust storm variations over northern China:transition from a natural forcing to an anthropogenic forcing[J].Science Bulletin,2021,66(24):2516-2527. |
| 68 | Xu B, Wang L, Gu Z Y,et al.Decoupling of climatic drying and Asian dust export during the Holocene[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2018,123(2):915-928. |
| [1] | 张世航, 岳平, 陈玉森, 郭浩, 陆永兴, 郭星, 刘朝红, 刘学军, 周晓兵, 张元明. 反硝化-分解模型在荒漠土壤CH4 和N2O通量估计中的应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 220-229. |
| [2] | 黄韵杰, 李永刚, 尹本丰, 张元明. 齿肋赤藓( Syntrichia caninervis )氮磷计量特征对降水量的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 1-10. |
| [3] | 解锡豪, 李志忠, 靳建辉, 刘瑞, 邹晓君, 马运强. 古尔班通古特沙漠东南部植被线形沙丘内部构造及发育模式[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 74-84. |
| [4] | 李志忠, 靳建辉, 刘瑞, 解锡豪, 邹晓君, 马运强, 谭典佳. 古尔班通古特沙漠风沙地貌研究进展评述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 41-47. |
| [5] | 陈东雪, 鲁瑞洁, 丁之勇, 刘小槺. 青海湖湖东沙地河湖-风成沉积记录的中晚全新世以来环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 99-110. |
| [6] | 李功麟, 张定海, 张志山, 胡宜刚, 黄磊, 路丽宁. 古尔班通古特沙漠沙丘主要灌木的种群数量动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 129-137. |
| [7] | 朱春鸣, 董治宝, 刘铮瑶, 肖南, 杨军怀, 冯淼彦. 古尔班通古特沙漠树枝状沙丘沉积物粒度和微形态特征的空间分异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 9-18. |
| [8] | 高佳程, 王豫, 阿吉古丽·沙依提null, 买买提艾力·买买提依明null, 刘永强, 赵雪赏, 杨兴华, 霍文, 杨帆, 周成龙. 古尔班通古特沙漠地表辐射收支特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 47-58. |
| [9] | 张瑞, 周晓兵, 张元明. 生物土壤结皮对温带荒漠植物凋落物分解的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 151-158. |
| [10] | 傅思华, 胡顺军, 李浩, 王泽锋. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)群落优势植物水分来源[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(5): 1024-1032. |
| [11] | 王银亚, 李晨华, 马健. 开垦对荒漠土壤微生物群落结构特征的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3): 514-522. |
| [12] | 陶冶, 吴甘霖, 刘耀斌, 张元明. 古尔班通古特沙漠典型灌木群落土壤化学计量特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2): 305-314. |
| [13] | 朱秉坚, 尹本丰, 张元明. 不同微生境下齿肋赤藓(Syntrichia caninervis)非结构性碳水化合物含量的季节动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2): 268-275. |
| [14] | 李军, 王新军, 贾宏涛, 赵成义. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘干季土壤水分含量空间异质性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(6): 1628-1636. |
| [15] | 韩彩霞, 张丙昌, 张元明, 邰凤姣, 张弛, 邵华. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘苔藓结皮中可培养真菌的多样性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(4): 1050-1055. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
