
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 32-43.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00090
Previous Articles Next Articles
Di Hu1,2a( ), Ning Huang2a,2b, Binbin Pei2a,2b, Pakzad Rezaali2a,2b, Jie Zhang2a,2b(
), Ning Huang2a,2b, Binbin Pei2a,2b, Pakzad Rezaali2a,2b, Jie Zhang2a,2b( )
)
Received:2024-05-20
Revised:2024-07-10
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-13
Contact:
Jie Zhang
CLC Number:
Di Hu, Ning Huang, Binbin Pei, Pakzad Rezaali, Jie Zhang. Numerical simulation study on the wind pressure characteristics of low-rise buildings in sandstorm environment[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(1): 32-43.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00090
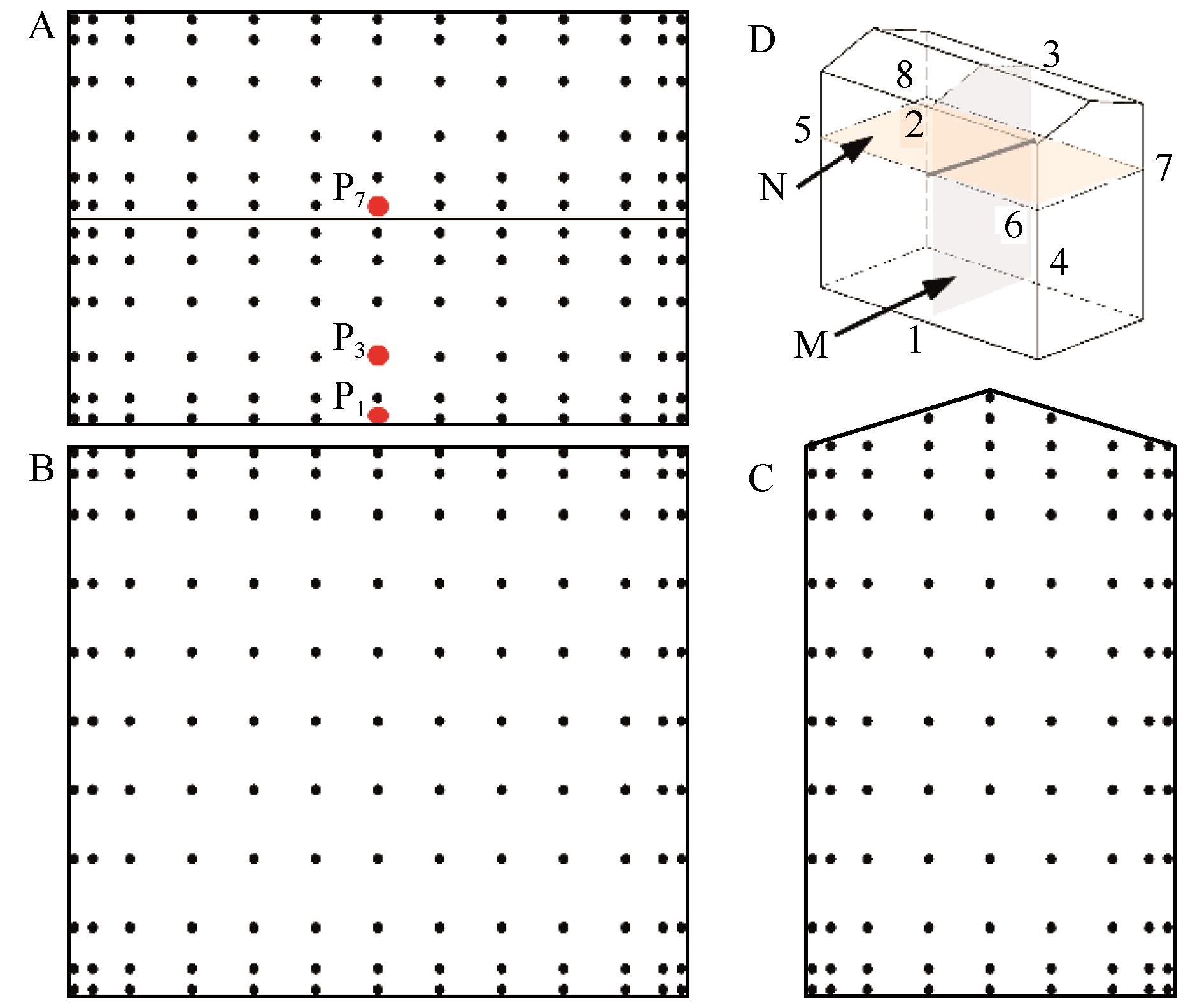
Fig.3 Survey point layout on the roof (A), windward side and leeward side (B), and two sides (C), and two sections are defined for the ensuing analyses (D): section M (1-2-3-4) and section N (5-6-7-8)
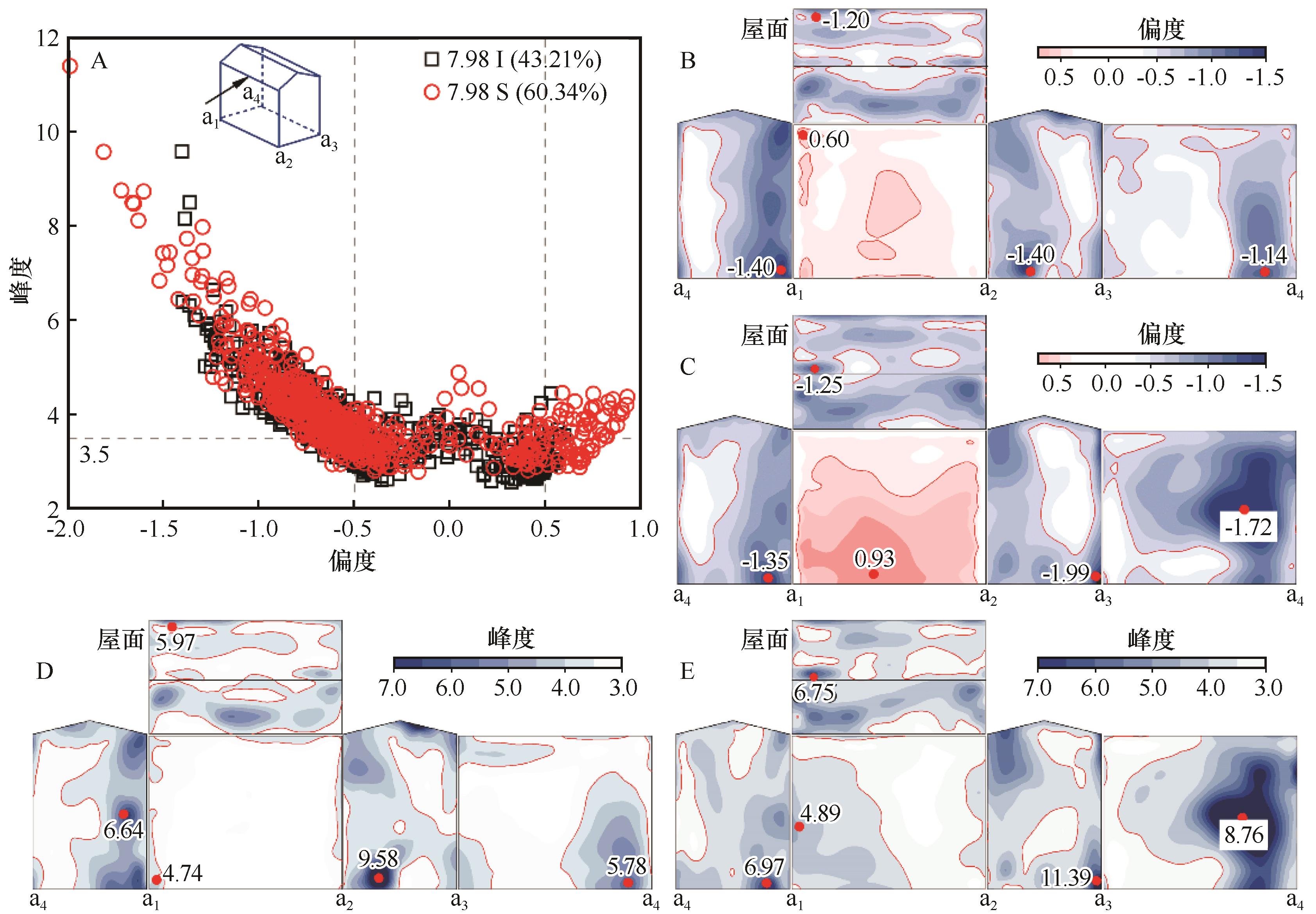
Fig.11 Statistical results of Skewness and Kurtosis (A), Skewness for 7.98 I (B), Skewness for 7.98 S (C), Kurtosis for 7.98 I (D), and Kurtosis for 7.98 S (E) at 0° wind angle
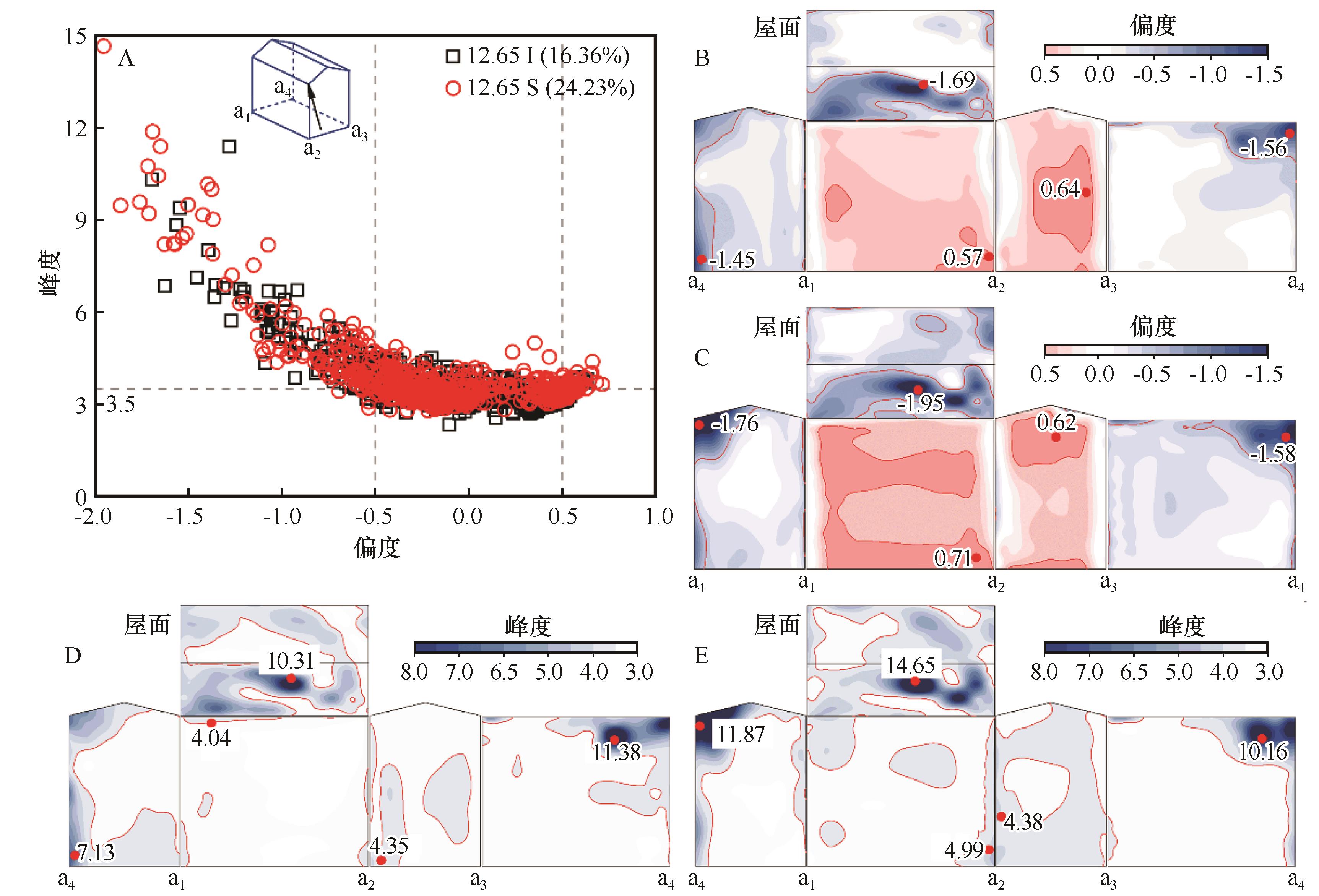
Fig.12 Statistical results of Skewness and Kurtosis (A), Skewness for 12.65 I (B), Skewness for 12.65 S (C), Kurtosis for 12.65 I (D), and Kurtosis for 12.65 S (E) at 45° wind angle
| 风向角 | 偏度 | 峰度 |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0.004 | 3.75×10-15 |
| 45° | 3.29×10-6 | 7.72×10-9 |
Table 1 P-values of significance test
| 风向角 | 偏度 | 峰度 |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0.004 | 3.75×10-15 |
| 45° | 3.29×10-6 | 7.72×10-9 |
| 1 | Saracoglu B O, Ohunakin O S, Adelekan D S,et al.A framework for selecting the location of very large photovoltaic solar power plants on a global/supergrid[J].Energy Reports,2018,4:586-602. |
| 2 | 国家发展改革委,国家能源局.以沙漠、戈壁、荒漠地区为重点的大型风电光伏基地规划布局方案[EB/OL].[2022-03-07].. |
| 3 | Cao S, Wang J.Statistical summary and case studies of strong wind damage in China[J].Journal of Disaster Research,2013,8(6):1096-1102. |
| 4 | 贺沅平,张云伟,顾兆林.特强沙尘暴灾害性天气的研究及展望[J].中国环境科学,2021,41(8):3511-3522. |
| 5 | Cao S.Typhoon and tornado induced damages in China[J].Wind Engineers,JAWE,2015,40(3):261-265. |
| 6 | Banks D, Meroney R N, Sarkar P P,et al.Flow visualization of conical vortices on flat roofs with simultaneous surface pressure measurement[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2000,84(1):65-85. |
| 7 | Huang P, Tao L, Gu M,et al.Wind effects of architectural details on gable-roofed low-rise buildings in southeastern coast of China[J].Advances in Structural Engineering,2014,17(11):1551-1565. |
| 8 | Razavi A, Sarkar P P.Tornado-induced wind loads on a low-rise building:influence of swirl ratio,translation speed and building parameters[J].Engineering Structures,2018,167:1-12. |
| 9 | Haines M, Taylor I.Numerical investigation of the flow field around low-rise buildings due to a downburst event using large eddy simulation[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,172:12-30. |
| 10 | Huang B, Li Z, Zhao Z,et al.Near-ground impurity-free wind and wind-driven sand of photovoltaic power stations in a desert area[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,179:483-502. |
| 11 | Huang B, Li Z, Zhang Z,et al.Study on flow field characteristics in sandstorm conditions using wind tunnel test[J].Atmosphere,2022,13(3):446. |
| 12 | Huang B, Li Z, Gong B,et al.Study on the sandstorm load of low-rise buildings via wind tunnel testing[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2023,65:105821. |
| 13 | Versteeg H K, Malalasekera W.An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics:The Finite Volume Method[M].London,UK:Pearson Education,2007. |
| 14 | 张默.基于FLUENT的建筑物风沙两相流场数值模拟[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2008. |
| 15 | 白江涛.风沙两相流绕圆柱工程结构的数值模拟[D].兰州:兰州大学,2020. |
| 16 | Valentine J R, Decker R A.A Lagrangian-Eulerian scheme for flow around an airfoil in rain[J].International Journal of Multiphase Flow,1995,21(4):639-648. |
| 17 | 陈峥,许晨豪,蒋崇文.建筑表面沙粒撞击压计算方法研究[C]//中国力学学会,北京理工大学.中国力学大会暨庆祝中国力学学会成立60周年大会论文集,2017:597-604. |
| 18 | Zhang Z, Chen Q.Comparison of the Eulerian and Lagrangian methods for predicting particle transport in enclosed spaces[J].Atmospheric Environment,2007,41(25):5236-5248. |
| 19 | Kaufmann A, Moreau M, Simonin O,et al.Comparison between Lagrangian and mesoscopic Eulerian modelling approaches for inertial particles suspended in decaying isotropic turbulence[J].Journal of Computational Physics,2008,227(13):6448-6472. |
| 20 | Zheng X, Feng S, Wang P.Modulation of turbulence by saltating particles on erodible bed surface[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2021,918:A16. |
| 21 | Xu B, Zhang J, Huang N,et al.Characteristics of turbulent aeolian sand movement over straw checkerboard barriers and formation mechanisms of their internal erosion form[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2018,123(13):6907-6919. |
| 22 | Yamamoto Y, Potthoff M, Tanaka T,et al.Large-eddy simulation of turbulent gas-particle flow in a vertical channel:effect of considering inter-particle collisions[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2001,442:303-334. |
| 23 | Kok J F, Renno N O.A comprehensive numerical model of steady state saltation (COMSALT)[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2009,114(D17):17204. |
| 24 | Elghobashi S.On predicting particle-laden turbulent flows[J].Applied Scientific Research,1994,52:309-329. |
| 25 | Clift R, Grace J R, Weber M E.Bubbles,drops,and particles[M].New York,USA:Academic Press,1978. |
| 26 | Liu H, He X, Zheng X.Amplitude modulation in particle-laden atmospheric surface layers[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2023,957:A14. |
| 27 | Blott S J, Pye K.Particle size distribution analysis of sand-sized particles by laser diffraction:an experimental investigation of instrument sensitivity and the effects of particle shape[J].Sedimentology,2006,53(3):671-685. |
| 28 | Tominaga Y, Mochida A, Yoshie R,et al.AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2008,96(10/11):1749-1761. |
| 29 | Melaku A F, Bitsuamlak G T.A divergence-free inflow turbulence generator using spectral representation method for large-eddy simulation of ABL flows[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2021,212:104580. |
| 30 | Cabot W, Moin P.Approximate wall boundary conditions in the large-eddy simulation of high Reynolds number flow[J].Flow,Turbulence and Combustion,2000,63:269-291. |
| 31 | 陶文铨.数值传热学[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社,2001. |
| 32 | Hu D, Zhang J, Pakzad R,et al.A numerical study on load effects of low-rise buildings in a wind-blown sand environment[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2024:108610. |
| 33 | Spalart P R, Deck S, Shur M L,et al.A new version of detached-eddy simulation,resistant to ambiguous grid densities[J].Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics,2006,20:181-195. |
| 34 | Levitan M L, Mehta K C, Vann W P,et al.Field measurements of pressures on the Texas Tech building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1991,38(2/3):227-234. |
| 35 | Ko N H, You K P, Kim Y M.The effect of non-Gaussian local wind pressures on a side face of a square building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2005,93(5):383-397. |
| 36 | Wang G, Gu H, Zheng X.Large scale structures of turbulent flows in the atmospheric surface layer with and without sand[J].Physics of Fluids,2020,32(10):106604. |
| 37 | Zhang W, Wang Y, Lee S J.Simultaneous PIV and PTV measurements of wind and sand particle velocities[J].Experiments in Fluids,2008,45(2):241-256. |
| 38 | Li B, McKenna Neuman C.Boundary-layer turbulence characteristics during aeolian saltation[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2012,39(11):L052234. |
| 39 | Balachandar S, Eaton J K.Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow[J].Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,2010,42:111-133. |
| 40 | Vasaturo R, Kalkman I, Blocken B,et al.Large eddy simulation of the neutral atmospheric boundary layer:performance evaluation of three inflow methods for terrains with different roughness[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,173:241-261. |
| 41 | Baskaran B A, Molleti S, Roodvoets D.Understanding low-sloped roofs under hurricane charley from field to practice[J].Journal of ASTM International,2007,4(10):1-13. |
| 42 | Mahmood M.Experiments to study turbulence and flow past a low-rise building at oblique incidence[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2011,99(5):560-572. |
| 43 | Kumar K S, Stathopoulos T.Power spectra of wind pressures on low building roofs[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1998,74:665-674. |
| 44 | Kumar K S, Stathopoulos T.Wind loads on low building roofs:a stochastic perspective[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2000,126(8):944-956. |
| [1] | Hanyong Ding, Hanqing Kang, Jingjing Lv. Impact of soil moisture products on the simulation results of super sandstorms during March of 2021 in North China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 172-184. |
| [2] | Yayun Li, Wei Cheng, Ning Wang, Xin Li, Rui Gao. Comparative study on the characteristic of spring sandstorms and the related meteorological factors of the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 1-9. |
| [3] | Jingping Chen, Ziying Yu, Fan Yang, Mi Wang, Han Hu, Guanzhong Ni, Xin Gao, Xin Wang. Particle size characteristics of sandstorm and surface sand at Tazhong area of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [4] | Jiapeng Pan, Kecun Zhang, Zhishan An, Hongxue Zhang, Chengjie Xue. Analysis of comprehensive benefits of wind-blown sand control projects: a case study of Heishanzui, Dunhuang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 233-242. |
| [5] | Haojun Qin, Xiaojun Yang, Li Ma, Yicheng Wang, Zhao Fu, Junxia Zhang, Zhengqi Lu. Characteristics and causes of regional sandstorms in Northwest of China from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 53-64. |
| [6] | Yanhui Lei, Guodong Ding, Zimeng Li, Wenfeng Chi, Guanglei Gao, Yuanyuan Zhao. Land use/cover change and its ecosystem service value response in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 29-40. |
| [7] | Lingping Li, Yanying Li, Xiaojing Li, Bo Wang, Lili Hu. Characteristics of circulation and dynamic of the different cold front sandstorm processes in Hexi Corridor [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 219-228. |
| [8] | Wang Juan, Li Xingcai. Exploration of the atmospheric electricity at 5-7 000 m height in sandstorm and its effect on the electrification of sands [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 23-28. |
| [9] | Yuan Guobo. Characteristics and Cause of the Sandstorm in Inner Mongolia in 2001—2015 [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(6): 1204-1209. |
| [10] | Yang Xiaoling, Ding Wenkui, Wang Heling, Zhang Aiping, Zhou Hua. Climatic Characteristics and Short-term Forecast of Sandstorm in East of Hexi Corridor [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(2): 449-457. |
| [11] | Qian Li, Yao Yubi, Yang Xin, Liu Juju. An Analysis of Sandstorm Weather Process in the Hexi Corridor in Summer [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(2): 458-466. |
| [12] | Meng Xuefeng, Sun Yonggang, Zhong Xia, Xun Xueyi. A Snow and Dust Weather Process in Inner Mongolia on February 21, 2015 [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(1): 239-246. |
| [13] | Luo Jingning, Xu Zhe, Qi Yonggang. Global Dust Remote Sensing with the FengYun-3 Satellite [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(3): 690-698. |
| [14] | Liu Shengyuan, Wang Jinyan, Wang Shigong, Shang Kezheng, Ni Jiangbo. Variation of the East Asian Subtropical Westerly Jet Stream in Spring and Its Relationship with Dust Weather in China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(2): 431-437. |
| [15] | Li Wanyuan, Lü Shihua, Dong Zhibao, Fan Guangzhou, Chen Leihua. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Precipitation over Areas Surrounding the Badan Jaran Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(1): 94-105. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech