
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 83-95.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00079
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaohan Chen( ), Yongsheng Wu(
), Yongsheng Wu( ), Chunxing Hai
), Chunxing Hai
Received:2022-04-08
Revised:2022-05-11
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2023-01-17
Contact:
Yongsheng Wu
CLC Number:
Xiaohan Chen, Yongsheng Wu, Chunxing Hai. Effects of surface dew under different types of sand-fixing shrubs in the southern margin of Mu Us Sandy Land, Northern China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 83-95.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00079
| 指 标 | 灌丛类型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 沙柳 | 柠条 | 油蒿 | |
| 平均直径/cm | 333±9 | 299±16 | 98±4 |
| 平均高度/cm | 259±6 | 216±10 | 50±2 |
| 平均一级枝条数/枝 | 119±9 | 77±2 | 47±2 |
| 平均投影面积/m2 | 8.7±0.5 | 7.2±1.0 | 0.8±0.1 |
| 平均一级枝条直径/mm | 9.4±0.8 | 14.7±0.2 | 4.8±0.2 |
| 一级枝条与地面夹角/(°) | 55±2 | 55±1 | 33±1 |
Table 1 Basic characteristics of different types of sand-fix shrubs in the study area
| 指 标 | 灌丛类型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 沙柳 | 柠条 | 油蒿 | |
| 平均直径/cm | 333±9 | 299±16 | 98±4 |
| 平均高度/cm | 259±6 | 216±10 | 50±2 |
| 平均一级枝条数/枝 | 119±9 | 77±2 | 47±2 |
| 平均投影面积/m2 | 8.7±0.5 | 7.2±1.0 | 0.8±0.1 |
| 平均一级枝条直径/mm | 9.4±0.8 | 14.7±0.2 | 4.8±0.2 |
| 一级枝条与地面夹角/(°) | 55±2 | 55±1 | 33±1 |
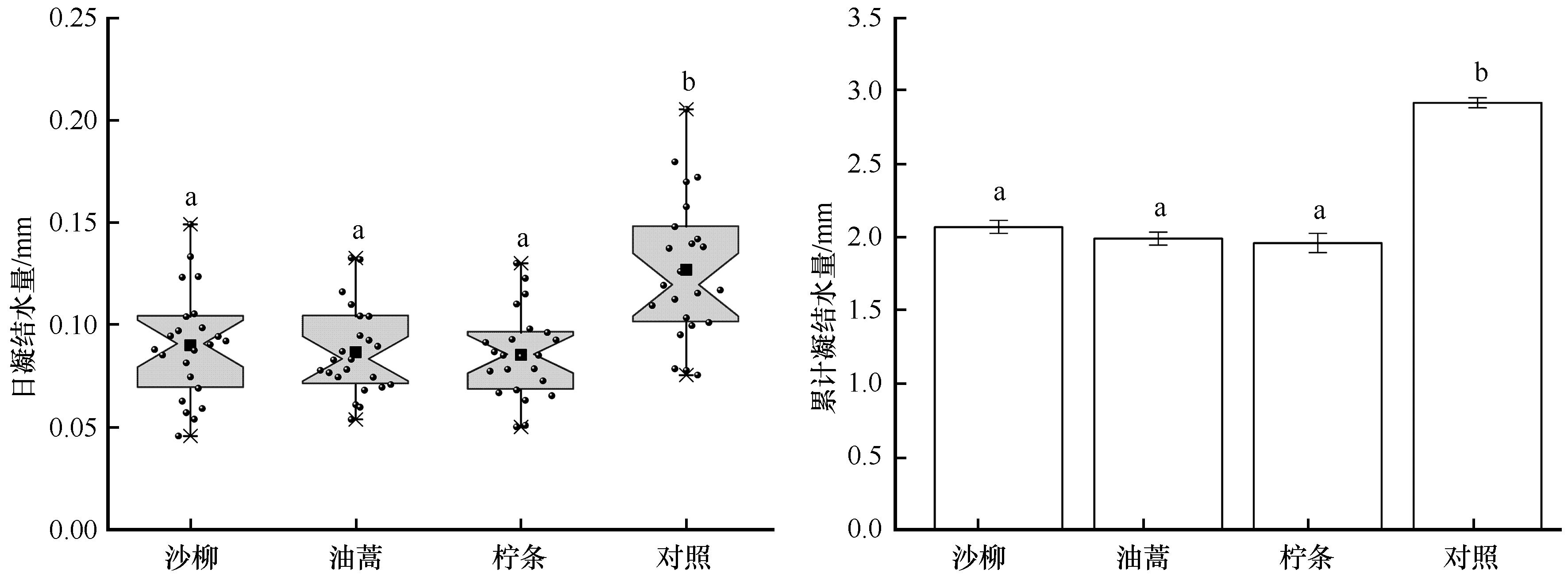
Fig.3 Variation of daily average dew amount and cumulative dew amount of different types of sand-fixing shrubs and control group during the experimental period
| 项目 | 自由度(df) | F | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灌丛类型 | 2 | 2.665 | 0.070 |
| 方向 | 3 | 1.137 | 0.333 |
| 位置 | 2 | 15.723 | 0.000 |
| 灌丛类型×方向 | 6 | 0.484 | 0.820 |
| 灌丛类型×位置 | 4 | 0.193 | 0.942 |
| 方向×位置 | 6 | 0.218 | 0.971 |
| 灌丛类型×方向×位置 | 12 | 0.133 | 1.000 |
Table 2 Results of multivariate analysis of variance on the effects of shrub types, directions, locations and their interactions on surface dew
| 项目 | 自由度(df) | F | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灌丛类型 | 2 | 2.665 | 0.070 |
| 方向 | 3 | 1.137 | 0.333 |
| 位置 | 2 | 15.723 | 0.000 |
| 灌丛类型×方向 | 6 | 0.484 | 0.820 |
| 灌丛类型×位置 | 4 | 0.193 | 0.942 |
| 方向×位置 | 6 | 0.218 | 0.971 |
| 灌丛类型×方向×位置 | 12 | 0.133 | 1.000 |
| 气象因子 | 对照凝结水量 | 沙柳凝结水量 | 柠条凝结水量 | 油蒿凝结水量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气温度 | -0.783** | -0.800** | -0.786** | -0.743** |
| 相对湿度 | 0.803** | 0.786** | 0.763** | 0.702** |
| 风速 | -0.143 | -0.131 | -0.095 | -0.019 |
| 对照地表温度 | -0.852** | -0.861** | -0.845** | -0.778** |
| 空气地表温度差 | 0.803** | 0.801** | 0.785** | 0.699** |
Table 3 Results of correlation analysis between dew amount and meteorological factors
| 气象因子 | 对照凝结水量 | 沙柳凝结水量 | 柠条凝结水量 | 油蒿凝结水量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气温度 | -0.783** | -0.800** | -0.786** | -0.743** |
| 相对湿度 | 0.803** | 0.786** | 0.763** | 0.702** |
| 风速 | -0.143 | -0.131 | -0.095 | -0.019 |
| 对照地表温度 | -0.852** | -0.861** | -0.845** | -0.778** |
| 空气地表温度差 | 0.803** | 0.801** | 0.785** | 0.699** |
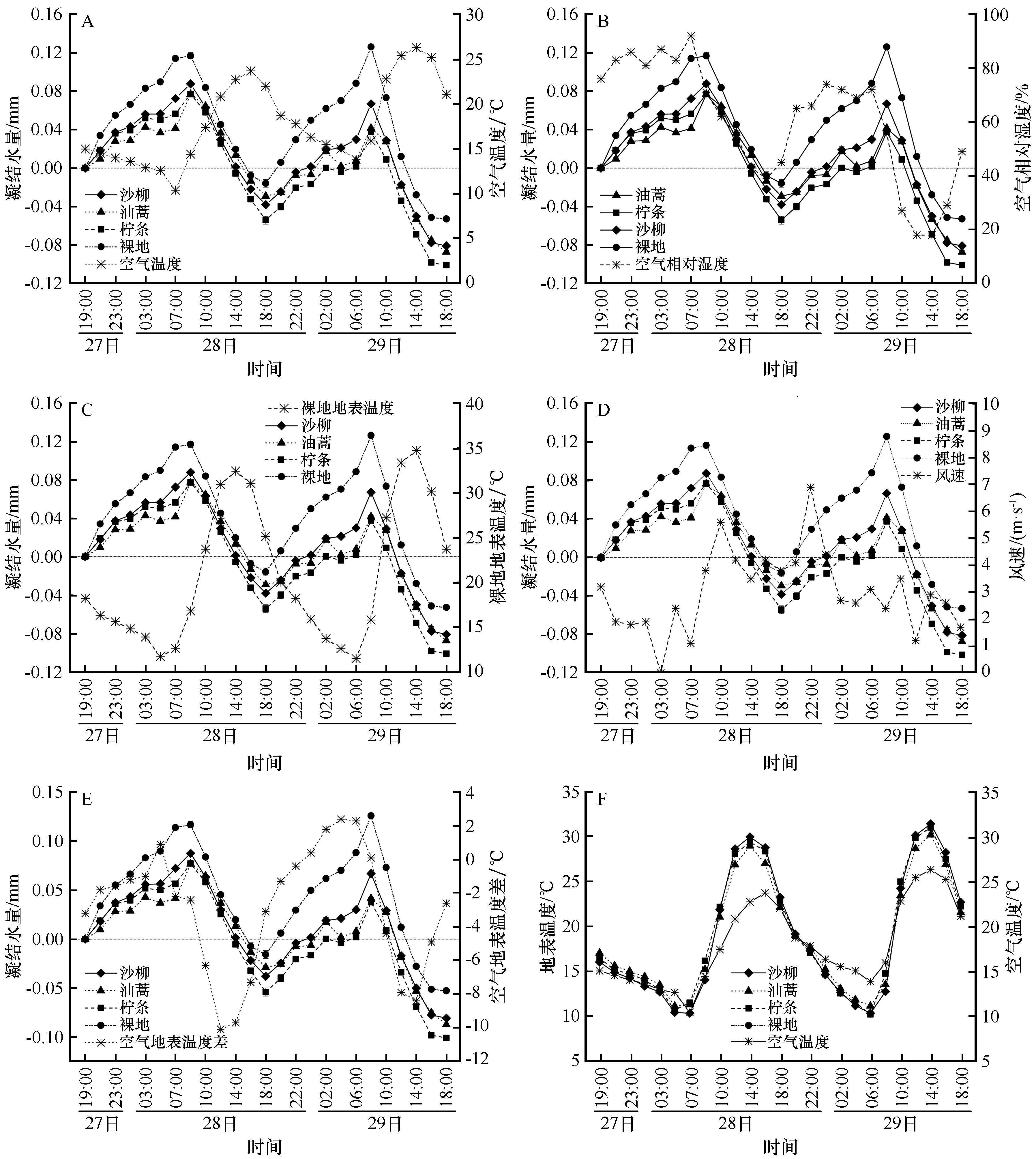
Fig.9 The relationship between the formation and evaporation process of dew and meteorological factors. A-E represent the relationship between dew deposition and evaporation process with air temperature, air relative humidity, control group surface temperature, wind speed and air surface temperature difference respectively; F represents the hange of air temperature and surface temperature. Observation on September 27-29,2021
| 1 | 郭占荣,刘建辉.中国干旱半干旱地区土壤凝结水研究综述[J].干旱区研究,2005,22(4):160-164. |
| 2 | Pan Y X, Wang X P, Zhang Y F.Dew formation characteristics in a revegetation-stabilized desert ecosystem in Shapotou area,Northern China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2010,387:265-272. |
| 3 | Kidron G J.Angle and aspect dependent dew and fog precipitation in the Negev desert[J].Journal of Hydrology,2005,301:66-74. |
| 4 | Kidron G J, Temina M.Non-rainfall water input determines lichen and cyanobacteria zonation on limestone bedrock in the Negev Highlands[J].Flora,2017,229:71-79. |
| 5 | Kidron G J, Starinsky A.Measurements and ecological implications of non‐rainfall water in desert ecosystems:a review[J].Ecohydrology,2019,12:1356-1366. |
| 6 | Comanns P, Withers P C, Esser F J,et al.Cutaneous water collection by a moisture-harvesting lizard,the thorny devil (Moloch horridus)[J].Journal of Experimental Biology,2016,219:3473-3479. |
| 7 | Pan Z, Pitt W G, Zhang Y M,et al.The upside-down water collection system of Syntrichia caninervis[J].Nature Plants,2016,2:16076. |
| 8 | 郭占荣,刘花台.西北地区凝结水及其生态环境意义[J].地球学报,1999,20(6):762-766. |
| 9 | Beysens D, Clus O, Mileta M,et al.Collecting dew as a water source on small islands: the dew equipment for water project in Bis˘evo (Croatia)[J].Energy,2007,32:1032-1037. |
| 10 | Kidron G J.The effect of substrate properties,size,position,sheltering and shading on dew:an experimental approach in the Negev Desert[J].Atmospheric Research,2010,98:378-386. |
| 11 | Agam N, Berliner P R.Dew formation and water vapor adsorption in semi-arid environments:review[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2006,65:572-590. |
| 12 | Li S L, Bowker M A, Xiao B.Biocrusts enhance non-rainfall water deposition and alter its distribution in dryland soils[J].Journal of Hydrology,2021,595:126050. |
| 13 | Pan Y X, Wang X P.Effects of shrub species and microhabitats on dew formation in a revegetation-stabilized desert ecosystem in Shapotou,northern China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2014,6:389-399. |
| 14 | Zhang J, Zhang Y M, Downing A,et al.The influence of biological soil crusts on dew deposition in Gurbantunggut Desert,Northwestern China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2009,379:220-228. |
| 15 | 成龙,贾晓红,吴波,等.高寒沙区生物土壤结皮对吸湿凝结水的影响[J].生态学报,2018,38(14):5037-5046. |
| 16 | 潘颜霞,张亚峰,虎瑞.吸湿凝结水对荒漠地区生物土壤结皮生态功能的影响综述[J].地球科学进展,2022,37(1):99-109. |
| 17 | 杨路明.毛乌素沙地地表凝结水形成过程及其环境影响因子[D].北京:北京林业大学,2016. |
| 18 | 尹瑞平,吴永胜,张欣,等.毛乌素沙地南缘沙丘生物结皮对凝结水形成和蒸发的影响[J].生态学报,2013,33(19):6173-6180. |
| 19 | Pan Y X, Wang X P, Zhang Y F,et al.Dew formation characteristics at annual and daily scale in xerophyte shrub plantations at Southeast margin of Tengger Desert,Northern China[J].Ecohydrology,2018,11:e1968. |
| 20 | 侯新伟,张发旺,崔晓梅,等.毛乌素沙地东南缘土壤凝结水的形成规律[J].干旱区资源与环境,2010,24(8):36-41. |
| 21 | Kidron G J.Altitude dependent dew and fog in the Negev Desert,Israel[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,1999,96:1-8. |
| 22 | 成龙,贾晓红,吴波,等.高寒沙区吸湿凝结水凝结过程与温湿度的关系[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(3):77-86. |
| 23 | 潘颜霞,王新平,张亚峰,等.沙坡头地区地形对凝结水形成特征的影响[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(1):118-124. |
| 24 | 王积强.关于“土壤凝结水”问题的探讨:与于庆和同志商榷[J].干旱区地理,1993,16(2):58-62. |
| 25 | 冯起,高前兆.半湿润沙地凝结水的初步研究[J].干旱区研究,1995,12(3):72-77. |
| 26 | 潘颜霞.沙坡头人工固沙过程中吸湿凝结水形成特征研究[D].北京:中国科学院大学,2010. |
| 27 | 张静,张元明,周晓兵,等.生物结皮影响下沙漠土壤表面凝结水的形成与变化特征[J].生态学报,2009,29(12):6600-6608. |
| 28 | 李胜龙,肖波,孙福海.黄土高原干旱半干旱区生物结皮覆盖土壤水汽吸附与凝结特征[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(15):111-119. |
| 29 | 李玉灵,朱帆,张国盛,等.毛乌素沙地凝结水动态变化及其影响因子的研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2008,22(8):61-66. |
| 30 | 刘新平,何玉惠,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地不同生境土壤凝结水的试验研究[J].应用生态学报,2009,20(8):1918-1924. |
| 31 | 钱连红,李洪波,张国盛,等.毛乌素沙地三种下垫面土壤吸湿凝结水量的比较[J].干旱区资源与环境,2009,23(3):122-125. |
| 32 | Xiao H, Meissner R, Seeger J,et al.Effect of vegetation type and growth stage on dewfall,determined with high precision weighing lysimeters at a site in northern Germany[J].Journal of Hydrology,2009,377:43-49. |
| 33 | 张新时.毛乌素沙地的生态背景及其草地建设的原则与优化模式[J].植物生态学报,1994,18(1):1-16. |
| 34 | 王博,丁国栋,顾小华,等.毛乌素沙地腹地植被恢复效果初步研究:以内蒙古乌审旗为例[J].水土保持研究,2007,14(3):237-238. |
| 35 | 李洪波,白爱宁,张国盛,等.毛乌素沙地土壤凝结水来源分析[J].中国沙漠,2010,30(2):241-246. |
| 36 | 张晓影,李小雁,王卫,等.毛乌素沙地南缘凝结水观测实验分析[J].干旱气象,2008,26(3):8-13. |
| 37 | Sun Y L, Li X Y, Xu H Y,et al.Effect of soil crust on evaporation and dew deposition in Mu Us Sandy Land,China[J].Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China,2008,2:480-486. |
| 38 | 李洪波.半干旱区凝结水形成机制及对植物水分特性的影响[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2010. |
| 39 | 桂子洋,秦树高,胡朝,等.毛乌素沙地两种典型灌木叶片凝结水吸收能力及吸水途径[J].植物生态学报,2021,45(6):583-593. |
| 40 | Kidron G J, Temina M.The Effect of dew and fog on lithic lichens along an altitudinal gradient in the Negev Desert[J].Geomicrobiology Journal,2013,30:281-290. |
| 41 | Temina M, Kidron G J.Lichens as biomarkers for dew amount and duration in the Negev Desert[J].Flora-Morphology,Distribution,Functional Ecology of Plants,2011,206:646-652. |
| 42 | Chávez-Sahagún E, Andrade J L, Zotz G,et al.Dew can prolong photosynthesis and water status during drought in some epiphytic bromeliads from a seasonally dry tropical forest[J].Tropical Conservation Science,2019,12(5):479-488. |
| 43 | 康跃虎,陈荷生.沙坡头地区凝结水及其在生态环境中的意义[J].干旱区资源与环境,1992,6(2):63-72. |
| 44 | 吴永胜,尹瑞平,田秀民,等.毛乌素沙地南缘人工植被区生物结皮发育特征[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(2):339-344. |
| 45 | 吴永胜,哈斯,屈志强.影响生物土壤结皮在沙丘不同地貌部位分布的风因子讨论[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(4):980-984. |
| 46 | 张义凡,陈林,刘学东,等.荒漠草原2种群落灌丛堆土壤水分的空间特征[J].西南农业学报,2017,30(4):836-841. |
| 47 | 李小军.地表径流对荒漠灌丛生境土壤水分空间特征的影响[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(6):1576-1582. |
| 48 | 徐丽萍,杨改河,姜艳,等.黄土高原人工植被小气候生态效应研究[J].水土保持学报,2008,22(1):163-167. |
| 49 | Kidron G J.Under-canopy microclimate within sand dunes in the Negev Desert[J].Journal of Hydrology,2010,392:201-210. |
| 50 | 陈荣毅.古尔班通古特沙漠表层土壤凝结水水汽来源特征分析[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(4):985-989. |
| 51 | 张亚峰,王新平,虎瑞,等.荒漠灌丛微生境土壤温度的时空变异特征:灌丛与降水的影响[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(2):536-542. |
| 52 | 方静,丁永建.干旱荒漠区沙土凝结水与微气象因子关系[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(5):1200-1205. |
| [1] | Yuzhe Yang, Dapeng Yue, Jingbo Zhao, Yiting Liu, Jianing Li, Tianyu Yang. Chroma characteristics and its paleoclimatic significance of L3 and S3 loess-paleosol in the southeast margin of Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 176-186. |
| [2] | Hongmei Liu, Haibing Wang, Kuan Li, Xiya Liu, Yuyan Ren, Yandong Zhang. Structure, benefits and behavior of farmers and herdsmen of the Kulun ecological economic circle in Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 48-57. |
| [3] | Guangyu Hong, Xiaojiang Wang, Tieshan Liu, Hailong, Zhenting Wu, Huercha, Xiaowei Gao, Haifeng Yang, Zhuofan Li, Zihao Li, Siqin, Lejun Wang. Applicability of Hydrus-1D Model in simulating the soil moisture in Hedysarum leave in Mu Us Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 233-242. |
| [4] | Lixia Gu, Ping Lv, Fang Ma, Guoxiang Chen, Zhun Liang, Mingjing Xu, Ying Yang. Drift potential characteristics of Mu Us Sandy Land calculated with different data sources [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 54-62. |
| [5] | Xinying Liu, Ming Jin, Fan Yang, Yapeng Ma, Hui Liu, Xiaoyun Sun, Dunsheng Xia. A preliminary study of environmental changes since middle Holocene and its impacts on the evolution of civilization in the eastern Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 92-100. |
| [6] | Yuyan Ren, Yufeng Zheng, Yandong Zhang, Haibing Wang, Shiqiang Wang, Jinjun He. Evaluation on development sustainability of kulun eco-economic circle in the Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 264-272. |
| [7] | Honglin Lian, Xueying Han, Yali Liu, Yuqing Han, Wenbin Yang, Wei Xiong. Study on spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric drought from 1981 to 2020 in the Mu Us Sandy Land of China based on SPEI index [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 71-80. |
| [8] | Shuo Qiao, Haibing Wang, Hejun Zuo, Xiya Liu, Yueru Wu. Evolution of ecological service value and network pattern of Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 118-126. |
| [9] | Ming Yan, Yinghua Zhang, Li He, Weiming Cheng, Suiji Wang, Jiongxin Xu. Blocking effect of upper reaches of Wuding River on desertification [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 62-68. |
| [10] | Hairong Liang, Tao Wang, Yu Yang, Wei Feng, Honglin Lian, Xuefeng Liu, Jiatao Li, Jia Liu. Comparison of deep soil recharge characteristics between Mu Us Sandy Land and Hunshandake Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 69-76. |
| [11] | Xiaoqin Yuan, Shengquan Liu, Feng Ai, Zheng Zhang, Qiang Li, Jinyu Jiang, Changchun Shi. Wind erosion resistance of litter of Salix psammophila community in the southeast edge of Mu Us Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 134-138. |
| [12] | Xiaopeng Jia, Qimin Ma, Yinping Long, Haibing Wang. Soil evaporation monitored with medium-lysimeter in an artificial forest in the Hobq Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 211-222. |
| [13] | Lin Shi, Yuxing Zhao, Eerdun Hasi, Ping Zhang, Yingjun Xu, Zhuoran Wang. Changes of vegetation and soil nutrient on windward slope of dune under sand barrier environment in Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 140-146. |
| [14] | Hong Zhou, Bo Wu, Ying Gao, Long Cheng, Xiaohong Jia, Yingjun Pang, Heju Zhao. Composition and influencing factors of the biological soil crust bacterial communities in the Sabina vulgaris community in Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 130-141. |
| [15] | Mingjing Xu, Lü Ping, Nan Xiao, Junhuai Yang, Zhengyao Liu, Miaoyan Feng, Zhun Liang. Effect of vegetation cover on dune migration in northwest Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 71-80. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech