
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 261-270.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00124
Shunyu Yao( ), Yanhong Guo, Huimin Bai, Dongwei Liu(
), Yanhong Guo, Huimin Bai, Dongwei Liu( )
)
Received:2024-05-05
Revised:2024-07-22
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-15
Contact:
Dongwei Liu
CLC Number:
Shunyu Yao, Yanhong Guo, Huimin Bai, Dongwei Liu. Large eddy simulation of saline dust entrainment from the dried lake bed of Qehan Lake, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 261-270.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00124
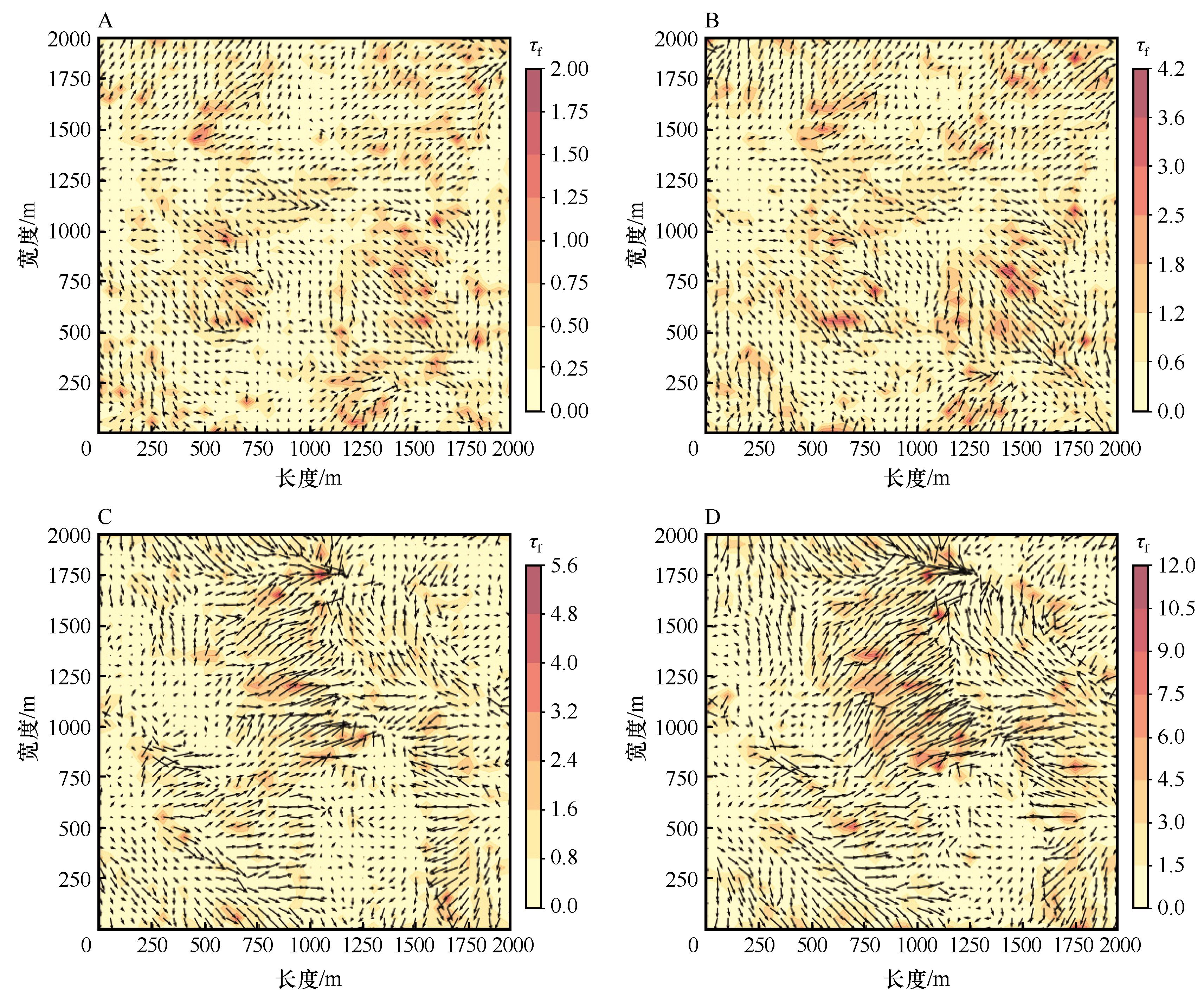
Fig.3 Instantaneous momentum flux τf at heights of 2 m (A,C) and 10 m (B,D) under u* =0.15 m·s-1, H=200 W·m-2 (A,B) and u* =0.15 m·s-1, H=600 W·m-2 (C,D)
| 1 | Shao Y.Physics and Modelling of Wind Erosion[M].Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,2009:303-360. |
| 2 | 张春来,宋长青,王振亭,等.土壤风蚀过程研究回顾与展望[J].地球科学进展,2018,33(1):27-41. |
| 3 | 康永德,何清,杨兴华,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠空气动力学粗糙度对粉尘释放的影响[J].应用基础与工程科学学报,2022,30(4):846-857. |
| 4 | Wang F, Zhao X, Gerlein-Safdi C,et al.Global sources,emissions,transport and deposition of dust and sand and their effects on the climate and environment:a review[J].Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering,2017,11(1):13. |
| 5 | Shao Y, Wyrwoll K H, Chappell A,et al.Dust cycle:an emerging core theme in Earth system science[J].Aeolian Research,2011,2(4):181-204. |
| 6 | Gherboudj I, Naseema Beegum S, Ghedira H.Identifying natural dust source regions over the Middle-East and North-Africa:estimation of dust emission potential[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2017,165:342-355. |
| 7 | 安晨宇,王仁德,周海涛,等.秋免耕对坝上地区农田风蚀及土壤理化性质的影响[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(2):95-103. |
| 8 | Csavina J, Field J, Félix O,et al.Effect of wind speed and relative humidity on atmospheric dust concentrations in semi-arid climates[J].Science of The Total Environment,2014,487:82-90. |
| 9 | 顾兆林,邱剑,鲁录义,等.尘卷风的研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(5):843-850. |
| 10 | Han Z, Zhang R, Wang Q,et al.Regional modeling of organic aerosols over China in summertime[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2008,113(D11):JD009436. |
| 11 | 刘东伟,吉力力·阿不都外力,雷加强,等.盐尘暴及其生态效应[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(1):168-173. |
| 12 | 吉力力·阿不都外力,刘东伟,徐俊荣.艾比湖干涸湖底不同地表类型风蚀强度及粉尘输移通量的风洞试验研究[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(1):63-67. |
| 13 | Ge Y, Abuduwaili J, Ma L,et al.Potential transport pathways of dust emanating from the playa of Ebinur Lake,Xinjiang,in arid northwest China[J].Atmospheric Research,2016,178/179:196-206. |
| 14 | Han L, Liu D, Cheng G,et al.Spatial distribution and genesis of salt on the saline playa at Qehan Lake,Inner Mongolia,China[J].Catena,2019,177:22-30. |
| 15 | Chun X, Yong M, Liu J,et al.Monitoring land cover change and its dynamic mechanism on the Qehan Lake Basin,Inner Mongolia,North China,during 1977-2013[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2018,190(4):205. |
| 16 | Klose M, Shao Y.Large-eddy simulation of turbulent dust emission[J].Aeolian Research,2013,8:49-58. |
| 17 | 梁国豪,毛睿, Shao Y,等.对流起沙的研究进展[J].干旱气象,2023,41(4):531-539. |
| 18 | 郑新倩,杨帆,李超凡,等.巴丹吉林沙漠北缘拐子湖流沙下垫面近地层湍流强度和陆面过程特征[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(4):103-112. |
| 19 | Liu D, Ishizuka M, Mikami M,et al.Turbulent characteristics of saltation and uncertainty of saltation model parameters[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2018,18(10):7595-7606. |
| 20 | Yamaguchi T, Feingold G.Technical note:large‐eddy simulation of cloudy boundary layer with the Advanced Research WRF model[J].Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems,2012,4(3):2012MS000164. |
| 21 | Yin X, Jiang C, Shao Y,et al.Large-eddy-simulation study on turbulent particle deposition and its dependence on atmospheric-boundary-layer stability[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2022,22(7):4509-4522. |
| 22 | Moeng C H, Dudhia J, Klemp J,et al.Examining two-way grid nesting for large eddy simulation of the PBL using the WRF Model[J].Monthly Weather Review,2007,135(6):2295-2311. |
| 23 | Klose M, Shao Y, Li X,et al.Further development of a parameterization for convective turbulent dust emission and evaluation based on field observations[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2014,119(17):10441-10457. |
| 24 | Spiga A, Barth E, Gu Z,et al.Large-eddy simulations of dust devils and convective vortices[J].Space Science Reviews,2016,203(1/4):245-275. |
| 25 | Cornwell G C, Xiao H, Berg L K,et al.Simulated dust transport in the convective boundary layer[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2021,126(5):JD033429. |
| 26 | Qi S, Ren X, Dang X,et al.Mechanisms of dust emissions from lakes during different drying stages in a semi-arid grassland in northern China[J].Frontiers in Environmental Science,2023,10:1110679. |
| 27 | Chun X, Su R, Liu J,et al.Climatic implications on variations of Qehan Lake in the arid regions of Inner Mongolia during the recent five decades[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2017,189(1):14. |
| [1] | Yue Wang, Nana Yi, Xuegong Jiang, Guicai Ning, Lian Su, Haiyun Xia. Diagnosis of severe dust weather process based on multi-source observational data [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 195-206. |
| [2] | Yaohua Su, Pengrui Zhao, Jiang Liu. Coupling and coordination of digital economy and high-quality development of manufacturing industry in the Yellow River Basin and its obstacle factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 268-276. |
| [3] | Congzhen Zhu, Jicheng Luo, Minzhong Wang, Lu Meng, Honglin Pan, Jiantao Zhang. Characteristics of the summer nighttime stable boundary layer in the hinterland of the Taklamakan Desert and its effect on dust aerosols concentration [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 1-12. |
| [4] | Zhigang Wang, Ruochen Jia, Fengmin Luo, Minghu Liu, Fang Liu, Chaoqun Ba, Zhimin Liu. Thermal dynamic mechanism of dust and dust suppression mechanism of farmland shelterbelts [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 116-122. |
| [5] | Cong Hua, Yun Cao, Jikang Wang, Ran Xu. Spring sand-dust weather distribution in Hunshandak Sandy Land in relation to vegetation and wind in 2000-2023 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 71-80. |
| [6] | Mingdou Zhang, Yuxin Yang. Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factors of urban ecological industrial structure in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 108-118. |
| [7] | Junyan Chen, Yawen Guan, Yue Zhang, Yu Chen, Hongru Bi, Gaotong Lou, Xinyang Guo, Yang Wang, Siyu Chen. Transport of dust from Gobi Desert to the Tibetan Plateau and its dynamic mechanism: a case study of a dust event in April of 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 158-171. |
| [8] | Yongtao Gou, Yongxiang Wu, Bo Peng, Yong Zhang, Huiping Kong, Xinghong Zhao, Pengju Ji, Yunhao Li, Mingzhu He, Mei Shao, Mingliang Tan, Junfeng Lu. Characteristics of aeolian sand activity in typical section of protection system of Wuhai-Maqen Highway (G1816) in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 279-289. |
| [9] | Yimeng Wang, Yaqiu Fan, Chuan Long, Benli Liu. Historical dust event sequence reconstruction in Dunhuang based on history records [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 162-171. |
| [10] | Jiahui Cao, Siyu Chen, Chao Zhang, Lulu Lian, Dan Zhao, Shikang Du. External contribution of the Tibetan Plateau dust [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 57-65. |
| [11] | Siyu Chen, Shikang Du, Hongru Bi, Dan Zhao, Yue Zhang, Yu Chen, Gaotong Lou, Junyan Chen. Review on identification and forecasting of dusty weather [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 11-21. |
| [12] | Ruirui Yuan, Jianying Wang, Weihong Zhang, Suzhao Zhang, Kun Wang, Jia Yong. Characteristics of heavy dust pollution weather coused by cold air with different routes in Ningxia, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 209-217. |
| [13] | Rende Wang, Hongjun Jiang, Qing Li, Gang Fu, Yuqiang Li, Yixiao Yuan, Chunping Chang, Zhongling Guo. Preliminary research on the relationship between soil dust emission ability and soil properties [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 43-49. |
| [14] | Lin Zhou, Xuhong Zhang, Cheng Zhou, Yiting Jing, Sisi Lv, Qiuyue Qin. A systematic evaluation of high-quality tourism development in provinces along the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 142-150. |
| [15] | Yaoquan Dun, Wanyin Luo, Mei Shao, Fang Wang, Junfeng Lu, Delu Li, Duoqing Man, Xuehua Che. Sand-dust horizontal flux and grain size of inland lake basin in arid region:a case of Qingtu Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 166-175. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech