中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 328-337.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00227
• • 上一篇
杨述睿1( ), 杨甜2, 张璐2, 张定海2(
), 杨甜2, 张璐2, 张定海2( ), 戚海迪2
), 戚海迪2
收稿日期:2025-05-23
修回日期:2025-07-23
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-27
通讯作者:
张定海
作者简介:杨述睿(1981—),男,甘肃民勤人,高级工程师,主要从事自然保护工作。E-mail: 13629356991@163.com
基金资助:
Shurui Yang1( ), Tian Yang2, Lu Zhang2, Dinghai Zhang2(
), Tian Yang2, Lu Zhang2, Dinghai Zhang2( ), Haidi Qi2
), Haidi Qi2
Received:2025-05-23
Revised:2025-07-23
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-27
Contact:
Dinghai Zhang
摘要:
土壤水分是干旱沙区固沙植被格局和过程的驱动力,在沙区不同微地貌上呈现出较大的差异。以腾格里沙漠东南缘半固定沙丘为研究对象,分析了土壤水分在迎风坡、背风坡、丘顶和丘底的分布特征,利用基于偏最小二乘法的结构方程模型(PLS-SEM)确定了地形、灌木和草本因子对土壤水分的影响路径。同时,采用基于可解释机器学习算法(SHAP)模型筛选了地形和植被影响土壤水分的重要因子并阐明了其影响机制。结果表明:丘底的表层土壤含水量最高,为1.21%,而背风坡上中层和深层土壤含水量最高分别为2.25%和2.43%。随着草本盖度的增加和坡向的变化,不同深度土壤含水量呈现先降低后升高的趋势。表层土壤水分以3 m的高差为阈值界限随着高差的变化呈现先降低后升高的趋势;中深层土壤水分随生物量和灌木盖度的增加也呈现先增加后减少趋势,二者分别以30 g和40%为阈值界限。
中图分类号:
杨述睿, 杨甜, 张璐, 张定海, 戚海迪. 腾格里沙漠东南缘半固定沙丘土壤水分影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 328-337.
Shurui Yang, Tian Yang, Lu Zhang, Dinghai Zhang, Haidi Qi. Moisture influencing factors on semi-fixed sand dunes in southeast edge of Tengger Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 328-337.
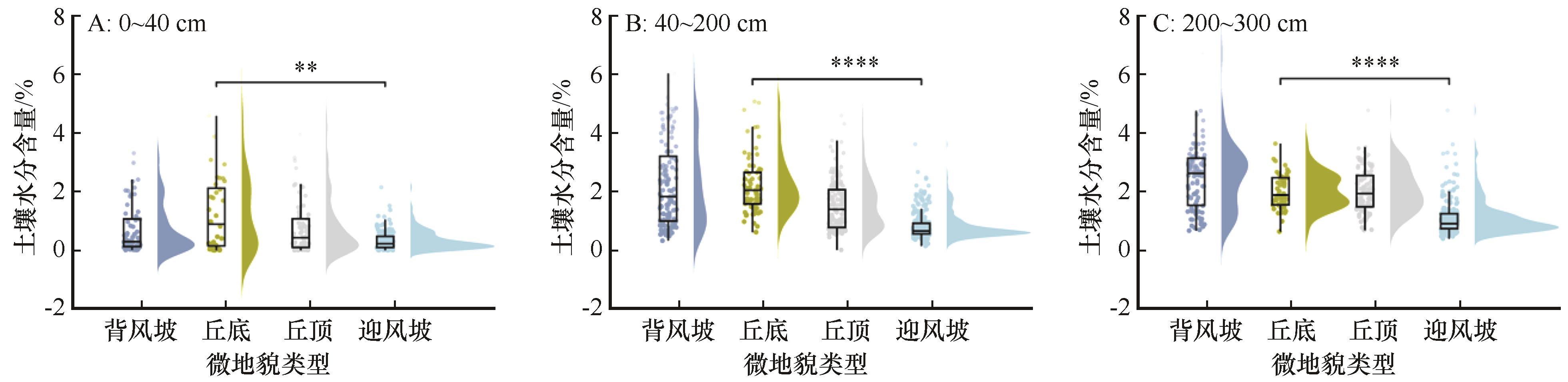
图2 4种微地貌上表层、中层和深层土壤水分的分布注:**表示P<0.01,极显著,****表示P<0.001,极其显著
Fig.2 Distribution of soil moisture in surface, middle and deep layers on four microtopography types
| 微地貌 | 0~40 cm | 40~200 cm | 200~300 cm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均土壤水分/% | 变异系数 | 平均土壤水分/% | 变异系数 | 平均土壤水分/% | 变异系数 | |
| 背风坡 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 2.25 | 0.52 | 2.43 | 0.36 |
| 丘底 | 1.21 | 0.41 | 2.23 | 0.25 | 1.98 | 0.23 |
| 丘顶 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 1.57 | 0.46 | 2.01 | 0.27 |
| 迎风坡 | 0.33 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.41 | 1.09 | 0.51 |
表1 4种微地貌上表层、中层和深层土壤平均水分含量及变异系数
Table 1 Average soil moisture content and coefficient of variation in surface, middle and deep layers of four microtopography types
| 微地貌 | 0~40 cm | 40~200 cm | 200~300 cm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均土壤水分/% | 变异系数 | 平均土壤水分/% | 变异系数 | 平均土壤水分/% | 变异系数 | |
| 背风坡 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 2.25 | 0.52 | 2.43 | 0.36 |
| 丘底 | 1.21 | 0.41 | 2.23 | 0.25 | 1.98 | 0.23 |
| 丘顶 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 1.57 | 0.46 | 2.01 | 0.27 |
| 迎风坡 | 0.33 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.41 | 1.09 | 0.51 |
| 潜变量 | 克伦巴赫α系数 | DG. rho系数 | 第一特征根 | 第二特征根 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地形 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 2.58 | 0.53 |
| 灌木植被 | 0.61 | 0.84 | 1.43 | 0.56 |
| 草本植被 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 2.09 | 0.99 |
| 土壤水分 | 0.79 | 0.88 | 2.14 | 0.70 |
表2 外部模型有效性检验
Table 2 External model validity test
| 潜变量 | 克伦巴赫α系数 | DG. rho系数 | 第一特征根 | 第二特征根 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地形 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 2.58 | 0.53 |
| 灌木植被 | 0.61 | 0.84 | 1.43 | 0.56 |
| 草本植被 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 2.09 | 0.99 |
| 土壤水分 | 0.79 | 0.88 | 2.14 | 0.70 |
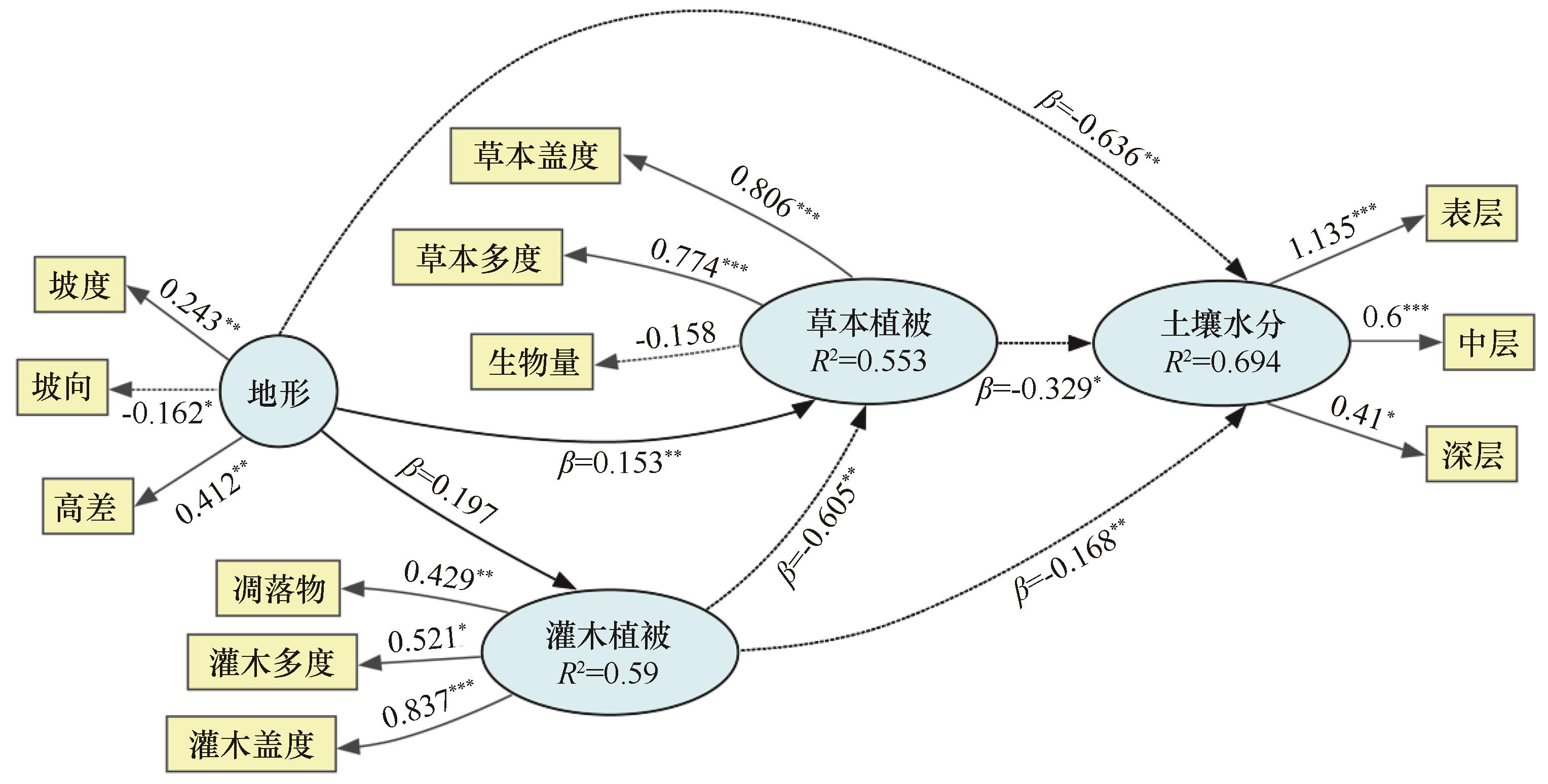
图3 基于PLS-SEM模型的地形和植被因子对土壤水分的影响路径注:*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01,***表示P<0.001
Fig.3 Effects of topography and vegetation factors on soil moisture based on PLS-SEM Model
| 评价指标 | 算法 | 表层 | 中层 | 深层 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.83 | |
| XGBoost | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.59 | |
| MSE | RF | 0.19 | 0.52 | 0.30 |
| XGBoost | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.36 | |
| MAE | RF | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.35 |
| XGBoost | 0.28 | 0.58 | 0.41 | |
| MAPE/% | RF | 5.25 | 13.5 | 5.47 |
| XGBoost | 7.11 | 13.7 | 11.59 |
表3 两种机器学习模型对表层、中层和深层土壤水分的模型评价结果
Table 3 Model evaluation results of two machine learning models for surface, middle and deep soil moisture
| 评价指标 | 算法 | 表层 | 中层 | 深层 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.83 | |
| XGBoost | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.59 | |
| MSE | RF | 0.19 | 0.52 | 0.30 |
| XGBoost | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.36 | |
| MAE | RF | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.35 |
| XGBoost | 0.28 | 0.58 | 0.41 | |
| MAPE/% | RF | 5.25 | 13.5 | 5.47 |
| XGBoost | 7.11 | 13.7 | 11.59 |
| [1] | Wang C, Fu B, Zhang L,et al.Soil moisture-plant interactions:an ecohydrological review[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments,2019,19(1):1-9. |
| [2] | Asbjornsen H, Goldsmith G R, Alvarado-Barrientos M S,et al. Ecohydrological advances and applications in plant-water relations research:a review[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology,2011,4(1):3-22. |
| [3] | D'Odorico P, Laio F, Porporato A,et al.Ecohydrology of terrestrial ecosystems[J].BioScience,2010,60(11):898-907. |
| [4] | Western A W, Zhou S L, Grayson R B,et al.Spatial correlation of soil moisture in small catchments and its relationship to dominant spatial hydrological processes[J].Journal of Hydrology,2004,286(1):113-134. |
| [5] | Liu Y, Cui Z, Huang Z,et al.Influence of soil moisture and plant roots on the soil infiltration capacity at different stages in arid grasslands of China[J].Catena,2019,182:104147. |
| [6] | Anderson C M, Kustas P W, Norman M J.Upscaling and Downscaling:a regional view of the soil-plant-atmosphere continuum[J].Agronomy Journal,2003,95(6):1408-1423. |
| [7] | 凤紫棋,孙文义,穆兴民,等.黄土高塬沟壑区植被恢复方式对小流域土壤水分的影响[J].中国水土保持科学,2023,21(4):1-10. |
| [8] | 郭艳菊,马晓静,许爱云,等.宁夏东部风沙区沙化草地土壤水分和植被的空间特征[J].生态学报,2022,42(4):1571-1581. |
| [9] | Asbjornsen H, Ashton M S, Vogt D J,et al.Effects of habitat fragmentation on the buffering capacity of edge environments in a seasonally dry tropical oak forest ecosystem in Oaxaca,Mexico[J].Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,2004,103(3):481-495. |
| [10] | Potts D L, Scott R L, Bayram S,et al.Woody plants modulate the temporal dynamics of soil moisture in a semi‐arid mesquite savanna [J].Ecohydrology,2010,3(1):20-27. |
| [11] | Li X Y, Yang Z P, Li Y T,et al.Connecting ecohydrology and hydropedology in desert shrubs:stemflow as a source of preferential flow in soils [J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2009,13(7):1133-1144. |
| [12] | Moeslund J E, Arge L, Bøcher P K,et al.Topography as a driver of local terrestrial vascular plant diversity patterns[J].Nordic Journal of Botany,2013,31(2):129-144. |
| [13] | Qiu Y, Fu B, Wang J,et al.Soil moisture variation in relation to topography and land use in a hillslope catchment of the Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2001,240(3):243-263. |
| [14] | Perring F.Topographical gradients of chalk grassland[J].The Journal of Ecology,1959,88:447-481. |
| [15] | Biederman L A, Whisenant S G.Using mounds to create microtopography alters plant community development early in restoration[J].Restoration Ecology,2011,19(101):53-61. |
| [16] | 张世才,王慧娟,张定海,等.腾格里沙漠东南缘3种沙丘4种微地貌上土壤水分与地形-植被因子之间的关系[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2023,58(3):160-168. |
| [17] | 孙琰蕙,张定海,张志山.腾格里沙漠不同类型沙丘土壤水分含量与地形-植被因子关系研究[J].干旱区地理,2022,45(5):1570-1578. |
| [18] | 李新荣,张志山,谭会娟,等.我国北方风沙危害区生态重建与恢复:腾格里沙漠土壤水分与植被承载力的探讨[J].中国科学生命科学,2014,44(3):1-10. |
| [19] | Hair J F, Matthews L M, Matthews R L,et al.PLS-SEM or CB-SEM:updated guidelines on which method to use[J].International Journal of Multivariate Data Analysis,2017,1(2):107-123. |
| [20] | Edeh E, Lo W J, Khojasteh J.Review of partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using R:a workbook[J].Structural Equation Modeling:A Multidisciplinary Journal,2023,30(1):165-167. |
| [21] | Tavakol M, Dennick R.Making sense of Cronbach's alpha[J].International Journal of Medical Education,2011,2:53-55. |
| [22] | Mehmetoglu Mehmet.Partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling for tourism research[M]//Chen J S.Advances in Hospitality and Leisure.Leeds,UK:Emerald Group Publishing Limited,2012:43-61. |
| [23] | Dijkstra T K, Henseler J R.Linear indices in nonlinear structural equation models:best fitting proper indices and other composites[J].Quality & Quantity,2011,45(6):1505-1518. |
| [24] | Wetzels M, Odekerken-Schröder G, Van Oppen C.Using PLS path modeling for assessing hierarchical construct models:guidelines and empirical illustration[J].MIS Quarterly,2009:177-195. |
| [25] | Zipper S C, Soylu M E, Booth E G,et al.Untangling the effects of shallow groundwater and soil texture as drivers of subfield-scale yield variability[J].Water Resources Research,2015,51(8):6338-6358. |
| [26] | 李新荣,张志山,黄磊,等.我国沙区人工植被系统生态-水文过程和互馈机理研究评述[J].科学通报,2013,58(5):387-410. |
| [27] | Song G, Li X R, Hui R.Biological soil crusts increase stability and invasion resistance of desert revegetation communities in northern China[J].Ecosphere,2020,11(2):1 |
| [28] | Chamizo S, Cantón Y, Lázaro R,et al.The role of biological soil crusts in soil moisture dynamics in two semiarid ecosystems with contrasting soil textures[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,489(6):74-84. |
| [29] | Zhong J M, Xiao H D, Yong G,et al.Interactive effects of wind speed,vegetation coverage and soil moisture in controlling wind erosion in a temperate desert steppe,Inner Mongolia of China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2018,10(2):534-547. |
| [30] | Srivastava A, Saco P M, Rodriguez J F,et al.The role of landscape morphology on soil moisture variability in semi‐arid ecosystems[J].Hydrological Processes,2021,35(1):e13990. |
| [31] | John A, Olden J D, Oldfather M F,et al.Topography influences diurnal and seasonal microclimate fluctuations in hilly terrain environments of coastal California[J].PLoS ONE,2024,19(3):1-19. |
| [32] | Singh S.Understanding the role of slope aspect in shaping the vegetation attributes and soil properties in Montane ecosystems[J].Tropical Ecology,2018,59(3):417-430. |
| [33] | Wunsch M, Betzler C, Eberli G P,et al.Sedimentary dynamics and high-frequency sequence stratigraphy of the southwestern slope of Great Bahama Bank[J].Sedimentary Geology,2018,363:96-117. |
| [34] | Gong X, Zhang H, Ren C,et al.Optimization allocation of irrigation water resources based on crop water requirement under considering effective precipitation and uncertainty[J].Agricultural Water Management,2020,239:106-264. |
| [35] | Zheng L, Wang X, Li D,et al.Spatial heterogeneity of vegetation extent and the response to water level fluctuations and micro-topography in Poyang Lake,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2021,124:107420. |
| [36] | Liu Y, Du J, Xu X,et al.Microtopography-induced ecohydrological effects alter plant community structure[J].Geoderma,2020,362:114-119. |
| [37] | Mata-González R, Averett J P, Abdallah M A,et al.Variations in groundwater level and microtopography influence desert plant communities in shallow aquifer areas[J].Environmental Management,2022,69(1):45-60. |
| [38] | Rita A, Bonanomi G, Allevato E,et al.Topography modulates near-ground microclimate in the Mediterranean Fagus sylvatica treeline[J].Scientific reports,2021,11(1):8122. |
| [39] | Zhao L, Fang Q, Yang Y,et al.Stemflow contributions to soil erosion around the stem base under simulated maize-planted and rainfall conditions[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2020,281:107814. |
| [40] | Li B B, Li P P, Zhang W T,et al.Deep soil moisture limits the sustainable vegetation restoration in arid and semi-arid Loess Plateau[J].Geoderma,2021,399:115122. |
| [41] | Yang L, Wei W, Chen L,et al.Spatial variations of shallow and deep soil moisture in the semi-arid Loess Plateau,China[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2012,16(9):3199-3217. |
| [42] | Thomas A, Yadav B K, Šimůnek J.Root water uptake under heterogeneous soil moisture conditions:an experimental study for unraveling compensatory root water uptake and hydraulic redistribution[J].Plant and Soil,2020,457:421-435. |
| [43] | D'Odorico P, Caylor K, Okin G S,et al.On soil moisture-vegetation feedbacks and their possible effects on the dynamics of dryland ecosystems[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences,2007,112(G4):1-11. |
| [1] | 姚淑霞, 张铜会, 赵传成. 科尔沁沙地沙质草地土壤水分时间序列分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 67-74. |
| [2] | 马亚丽, 马莉, 杨丽萍, 王思晴, 赵长明, 陈宁. 生态水文视角下的旱区生物土壤结皮-维管植物共存模式[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 121-130. |
| [3] | 钟诗瑶, 李传华, 乔鹏飞. 2000—2020年干旱梯度下西北干旱半干旱区植被突变及归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 275-283. |
| [4] | 饶玉良, 曹春, 张晓雪, 鲁畅, 岳平. 内蒙古荒漠草原土壤氨挥发对外源氮输入的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 178-186. |
| [5] | 贺郝钰, 刘蔚, 常宗强, 侯春梅, 孙力炜, 迟秀丽. 腾格里沙漠南缘植被恢复对土壤有机碳组成及稳定性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 307-317. |
| [6] | 陈强, 迟洪明, 丁伟, 杨昊天, 吴吉军, 杨奕颖, 吴旭东, 张亚峰, 季波, 李云飞, 张志山, 刘立超. 腾格里沙漠南缘大型光伏基地植被保护和生态修复的理论与对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 123-132. |
| [7] | 宁婷, 张定海, 赵有益, 江晶. 腾格里沙漠土壤水分含量与地形、植被的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 133-142. |
| [8] | 楼科尔, 曲文杰, 王磊, 王兴, 郜永贵, 杨新国. 腾格里沙漠东南缘猪毛菜( Salsola collina )根系构型特征比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 193-201. |
| [9] | 孔维远, 崔桂鹏, 高攀, 周尚哲, 熊伟, 卢琦. 阿拉善沙漠物源和输沙带研究进展及其对“三北”工程风沙口治理的启示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 236-243. |
| [10] | 陈链璇, 曹生奎, 曹广超, 雷义珍, 赵浩然, 李文斌. 青海湖流域蒸散发对土壤水分的时空响应特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 202-212. |
| [11] | 雍天, 张金霞, 陈丽娟, 席海洋, 张斌武, 甘开元. 乌兰布和沙漠沿黄河段土壤水盐空间分异特征及其成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 247-258. |
| [12] | 陈阳, 吕萍, 曹敏, 夏子书, 马芳, 余军林. 腾格里沙漠湖泊群小气候特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 231-238. |
| [13] | 刘丹一, 冯伟, 王涛, 杨文斌, 朱斌, 邹慧, 周密. 低覆盖治沙理论下人工与自然耦合的植被修复机理综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 170-177. |
| [14] | 潘颜霞, 赵洋, 张志山. 生态垫铺设对流沙固定及土壤温湿度的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 186-193. |
| [15] | 卫雨西, 陈丽娟, 席海洋, 张成琦, 甘开元, 雍天, 张金霞. 石羊河流域土壤水分和电导率的空间分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 264-273. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
