中国沙漠 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 21-32.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00042
收稿日期:2021-01-25
修回日期:2021-04-13
出版日期:2021-09-20
发布日期:2021-09-23
通讯作者:
杨波
作者简介:杨波(E-mail: 0016220@zju.edu.cn)基金资助:
Boyu Gao( ), Bo Yang(
), Bo Yang( ), Deguo Zhang
), Deguo Zhang
Received:2021-01-25
Revised:2021-04-13
Online:2021-09-20
Published:2021-09-23
Contact:
Bo Yang
摘要:
沙丘形态演变过程记录着近地表风况与环境演化的历史,然而对其特征研究一直受限于大范围沙脊线提取效率低和成本高等问题。本文基于深度卷积神经网络搭建U-Net模型,实现批量、高精度沙脊线的提取。将数据增强技术、随机失活神经元、批标准化以及迁移学习技术应用于模型训练和参数更新,使得模型的精度更高。结果表明:U-Net模型以及各种策略能够高效、精确地识别遥感影像中的沙脊线;沙脊线走向的偏移与近地表风况变化有着很好的对应关系, U-Net模型可以有效地用于区域性的沙脊线走向分析。
中图分类号:
高博钰, 杨波, 张德国. U-Net深度卷积神经网络在沙脊线提取中的应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 21-32.
Boyu Gao, Bo Yang, Deguo Zhang. Extracting the sand dune crest lines from satellite images using U-Net deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 21-32.
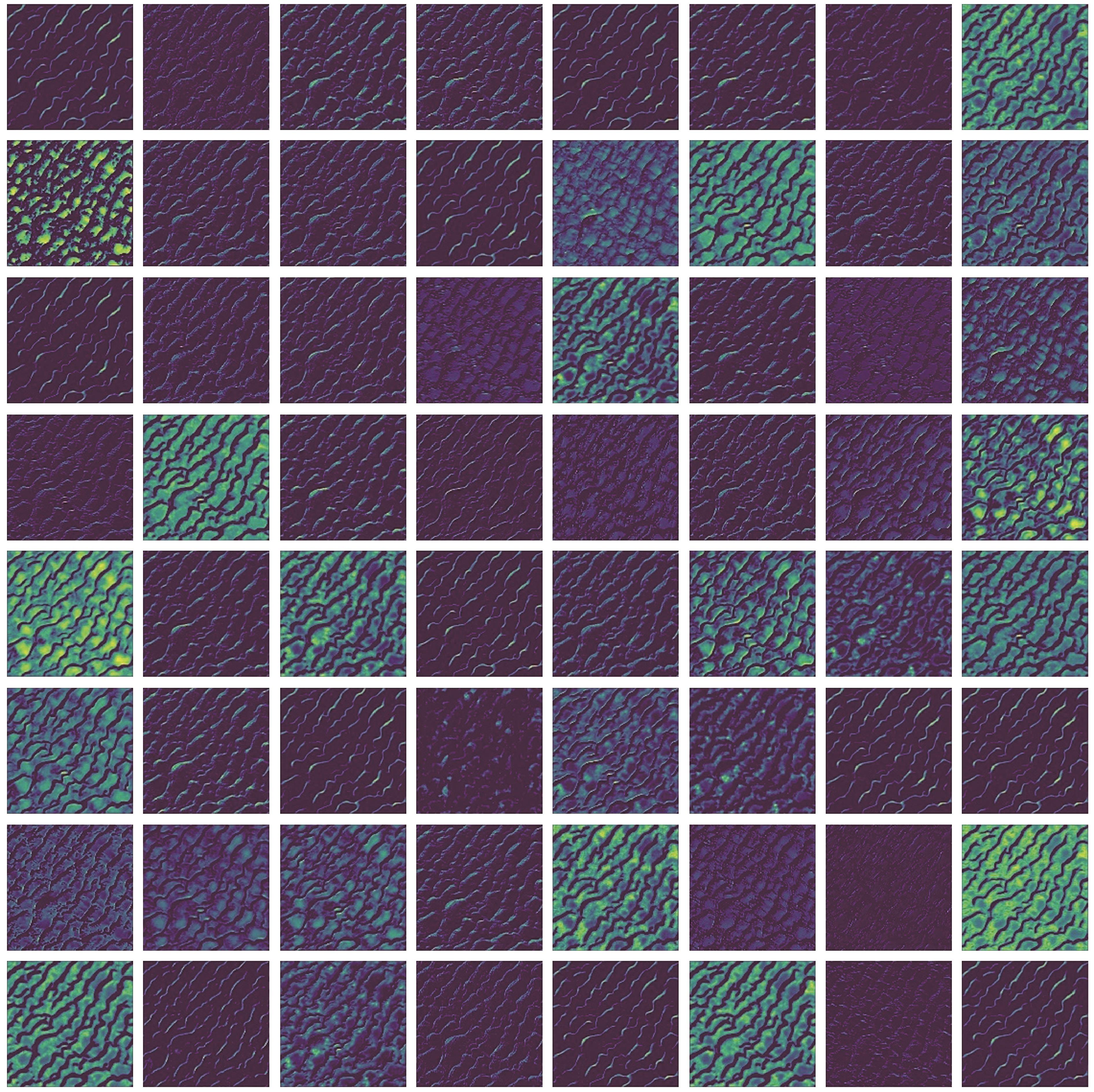
图4 训练好的U-Net模型中第一个卷积层中64个卷积核对一张输入图像的特征提取结果(提取到的不同的特征表现为图中不同的颜色)
Fig.4 An input image's feature extraction results of the 64 convolution kernels in the first layer of the trained U-net
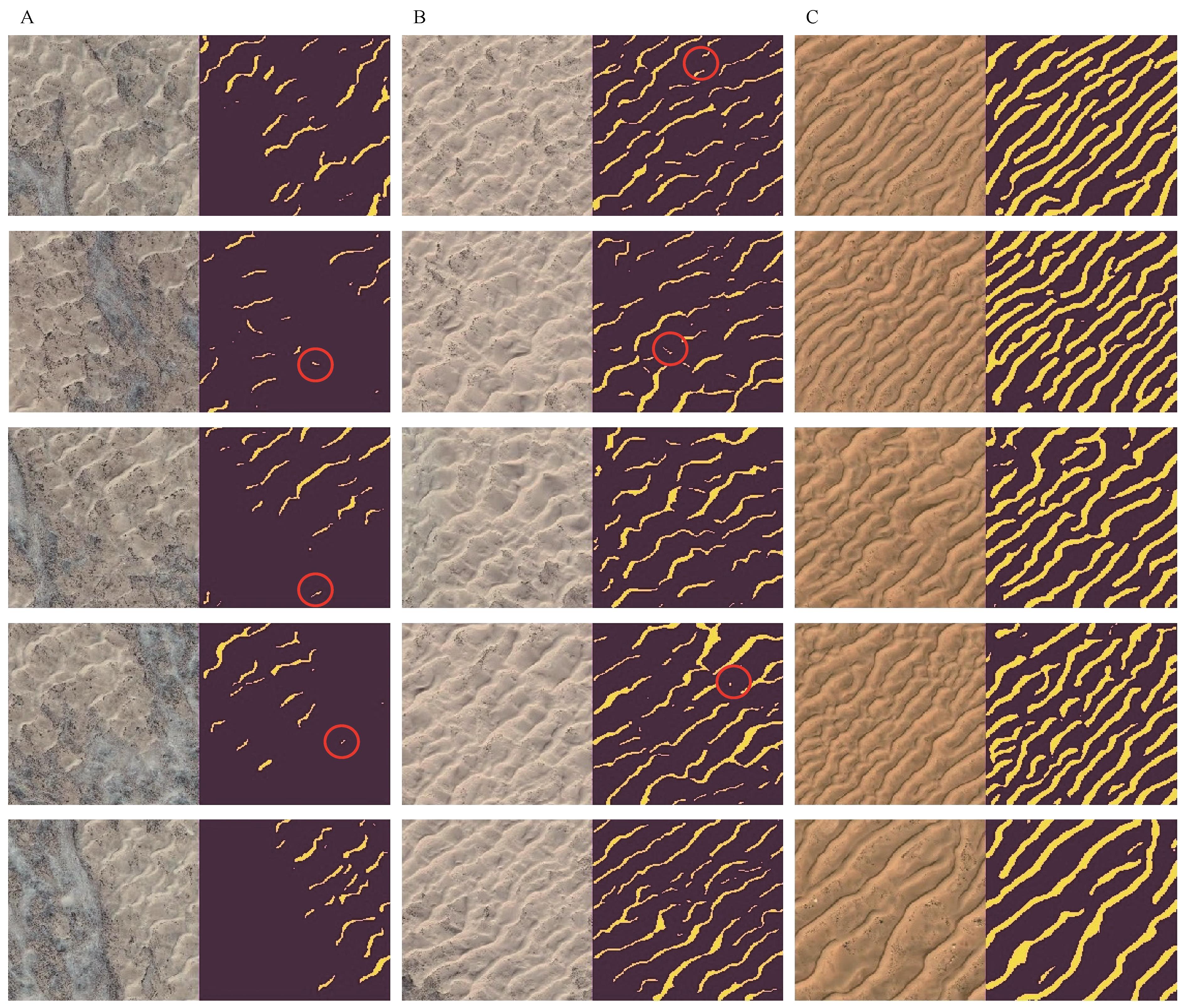
图7 模型对3种典型沙脊线区域提取结果(A列为后期受草场严重破坏的沙脊线类型;B列为后期受草场中等破坏的沙脊线类型;C列为后期未受草场破坏的沙脊线类型;红圈为提取不准确的模糊区域)
Fig.7 The extraction results of the trained model for 3 kinds of typical dune crest lines
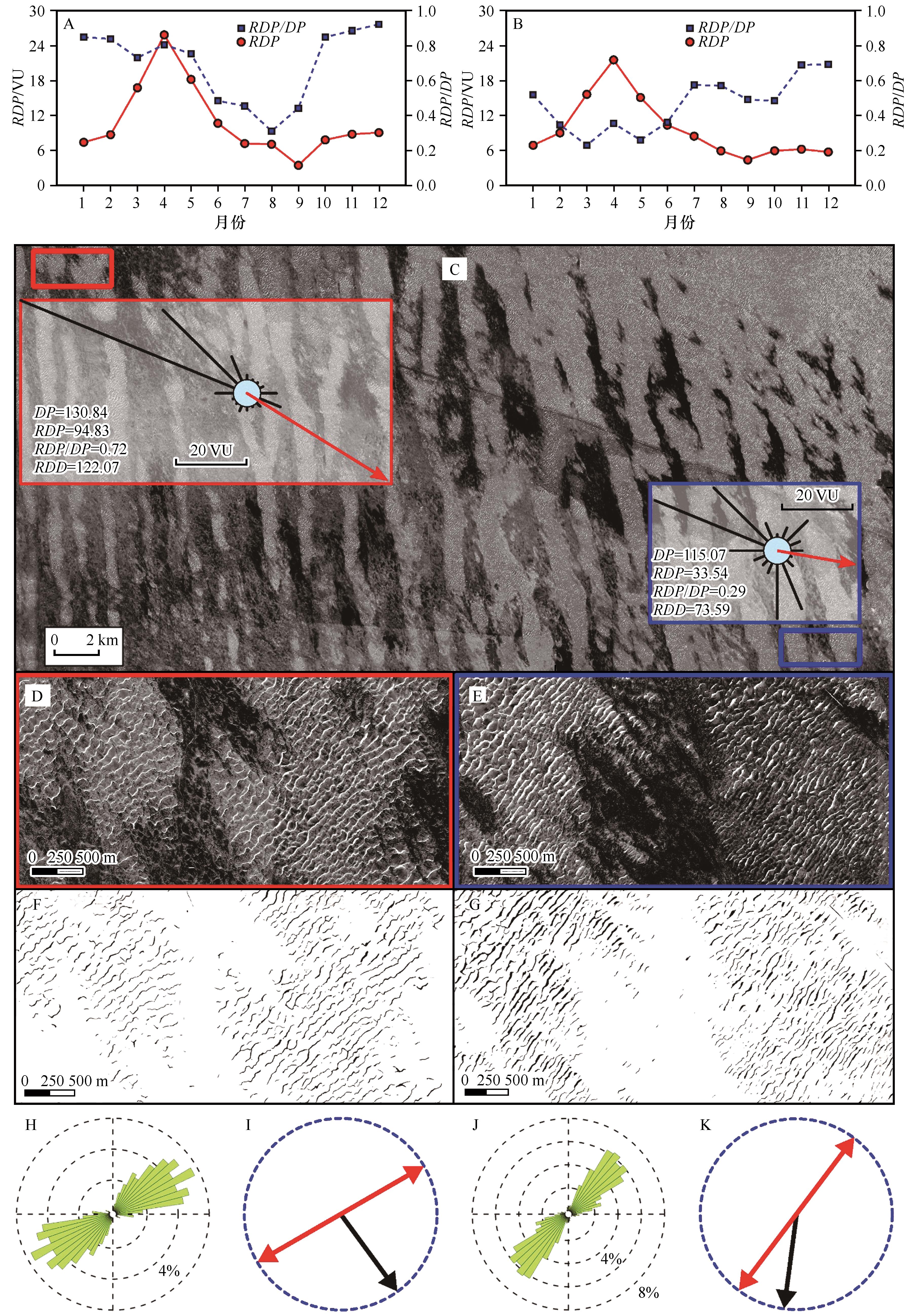
图8 腾格里沙漠内沙脊线走向分析(A—B为腾格里沙漠西南缘气象站点多年平均月输沙势与风向变率;C为腾格里沙漠西南缘沙脊线提取结果与气象站点多年平均年输沙势玫瑰图;D—G为东西部沙脊线提取结果;H和J为沙脊线走向玫瑰图;I和K为沙脊线提取走向图)
Fig.8 The results of dune crest lines orientation analysis in the Tengger Desert
| 1 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980:10-65. |
| 2 | 董治宝,吕萍.70年来中国风沙地貌学的发展[J].地理学报,2020,75(3):509-528. |
| 3 | Pye K,Tsoar H.Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer,2009:25-35. |
| 4 | Wasson R J,Hyde R.Factors determining desert dune type[J].Nature,1983,304:337-339. |
| 5 | Hunter R E,Richmond B M,Alpha T R.Storm-controlled oblique dunes of the Oregon Coast[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,1983,94(12):1450-1465. |
| 6 | Rubin D M,Hunter R E.Bedform alignment in directionally varying flows[J].Science,1987,237:276-278. |
| 7 | Werner B T,Kocurek G.Bed-form dynamics:does the tail wag the dog?[J].Geology,1997,25(9):771-774. |
| 8 | Fenton L K,Michaels T I,Beyer A R,et al.Inverse maximum gross bedform-normal transport 1:how to determine a dune-constructing wind regime using only imagery[J].Icarus,2014,230:5-14. |
| 9 | Telfer M W,Fyfe R M,Lewin S.Automated mapping of linear dunefield morphometric parameters from remotely-sensed data[J].Aeolian Research,2015,19:215-224. |
| 10 | Scuderi L.The fingerprint of linear dunes[J].Aeolian Research,2019,39:1-12. |
| 11 | 蒋缠文,董治宝,文青.基于MATLAB平台的遥感影像沙丘脊线提取与地貌格局表征参数计算[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(6):1636-1642. |
| 12 | LeCun Y,Bengio Y,Hinton G.Deep learning[J].Nature,2015,521:436-444. |
| 13 | 柳潜.基于深度学习的遥感图像场景分类研究[D].北京:北京邮电大学,2019. |
| 14 | Ma N,Wang C X,Sun L,et al.Cloud detection based on convolutional neural network using different bands information for Landsat 8 OLI[J].Journal of Remote Sening & GIS,2019,8(1):259. |
| 15 | 陈冠宇,安凯,李向.基于卷积神经网络的不良地质体识别与分类[J].地质科技情报,2016,35(1):205-211. |
| 16 | 张玉玺,刘洋,张浩然,等.基于深度学习的多属性盐丘自动识别方法[J].石油地球物理勘探,2020,55(3):475-483. |
| 17 | 段艳廷,郑晓东,胡莲莲,等.基于3D半密度卷积神经网络的断裂检测[J].地球物理学进展,2019,34(6):2256-2261. |
| 18 | Wu X M,Geng Z C,Shi Y Z,et al.Building realistic structure models to train convolutional neural networks for seismic structural interpretation[J].Geophysics,2019,85(4):1-48. |
| 19 | Wu X M,Shi Y Z,Fomel S,et al.FaultNet3D:predicting fault probabilities,strikes,and dips with a single convolutional neural network[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2019,57(11):1-18. |
| 20 | Zhang Y,Wang G,Li M C,et al.Automated classification analysis of geological structures based on images data and deep learning model[J].Applied Sciences,2018,8(12):2493. |
| 21 | Soroush M,Mehrtash A,Khazraee E,et al.Deep learning in archaeological remote sensing:automated qanat detection in the Kurdistan region of Iraq[J].Remote Sensing,2020,12(3):500. |
| 22 | Long J,Shelhamer E,Darrell T.Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[EB/OL].arXiv:1411.4038v2,2014. |
| 23 | Ronneberger O,Fischer P,Brox T.U-Net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[EB/OL].arXiv:,2015. |
| 24 | Dolz J,Ayed I B,Desrosiers C.Dense multi-path U-Net for Ischemic Stroke Lesion segmentation in multiple image modalities[EB/OL].arXiv:,2018. |
| 25 | Li X M,Chen H,Qi X J,et al.H-DenseU-Net:Hybrid densely connected U-Net for Liver and Tumor segmentation from CT volumes[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2017,37(12):2663-2674. |
| 26 | Inoue H.Data augmentation by pairing samples for images classification[EB/OL].arXiv:1801.02929v2,2018. |
| 27 | Ma J.Segmentation Loss Odyssey[EB/OL].arXiv:,2020. |
| 28 | Roder S.An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms[EB/OL].arXiv:1609.04747v2,2016. |
| 29 | Kingma D P,Ba J.Adam:a method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL].arXiv:1412.6980v9,2014. |
| 30 | Nwankpa C,Ljomah W,Gachagan A,et al.Activation functions:comparison of trends in practice and research for deep learning[EB/OL].arXiv:,2018. |
| 31 | Loffe S,Szegedy C.Batch normalization:accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[EB/OL].arXiv:1502.03167v3,2015. |
| 32 | Glorot X,Bengio Y.Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2010,9:249-256. |
| 33 | Srivastava N,Hinton G,Krizhevsky A,et al.Dropout:a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2014,15:1929-1958. |
| 34 | Tan C Q,Sun F C,Tao K,et al.A survey on deep transfer learning[EB/OL].arXiv:,2018. |
| 35 | Fryberger S G.Dune forms and wind regimes,a study of global sand seas[J].United States Geological Survey Professional Paper,1979,1052:137-140. |
| 36 | Gao X,Narteau C,Rozier O,et al.Phase diagrams of dune shape and orientation depending on sand availability[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5(1):14677. |
| 37 | Lucas A,Rodriguez S,Narteau C,et al.Growth mechanisms and dune orientation on Titan[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2015,41(17):6093-6100. |
| 38 | Courrech du Pont S,Narteau C,Gao X.Two modes for dune orientation[J].Geology,2014,42(9):743-746. |
| 39 | 许炯心,李炳元,杨小平,等.中国地貌与第四纪研究的近今进展与未来展望[J].地理学报,2009,64(11):1375-1393. |
| 40 | 杨小平,梁鹏,张德国,等.中国东部沙漠/沙地全新世地层序列及其古环境[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(8):129-143. |
| 41 | Lancaster N,Kocurek G,Singhvi A K,et al.Late Pleistocene and Holocene dune activity and wind regimes in the western Sahara Desert of Mauritania[J].Geology,2002,30(11):991-994. |
| [1] | 杨旭艳, 董治宝, 杨勤科, 李超. 基于DEM的地球与火星格状沙丘对比分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, (): 1-11. |
| [2] | 王萌, 郜学敏, 屈欣, 张思悦, 张姚姚, 陈冠春, 李继彦. 柴达木盆地西南缘山前沙丘区沙丘地貌形态特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 166-174. |
| [3] | 常菊, 肖锋军, 董治宝, 陈颢, 马慧榕. 基于激光垂直照射沙床面的风成沙波纹二维形态特征分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 33-42. |
| [4] | 于海云, 张正偲, 王志军. 阿拉善高原东南部干涸湖盆沉积物粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 177-184. |
| [5] | 胡光印, 董治宝, 逯军峰, 杨林海, 南维鸽, 肖锋军. 黄河流域沙漠化空间格局与成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 213-224. |
| [6] | 张焱, 马鹏飞, 曾林, 梁爱民, 张正偲. 基于沉积物理化性质的雅鲁藏布江中游粉尘物源研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 92-100. |
| [7] | 李军豪, 陈勇, 杨国靖, 周立华. 1975—2018年民勤绿洲沙漠化过程及其驱动机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 44-55. |
| [8] | 马鹏飞, 论珠群培, 张焱, 次仁尼玛, 逯军峰, 梁爱民, 张正偲. 雅鲁藏布江中游江心洲、河漫滩面积及其指示的沙源特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 25-33. |
| [9] | 郜学敏, 屈欣, 王萌, 张思悦, 张姚姚, 李继彦. 柴达木盆地西北部长垄状雅丹沉积物地球化学元素组成及指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 127-136. |
| [10] | 王兆云, 牛改红, 柳本立. 风沙活动强度3种估算指标对比及适用性分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 118-129. |
| [11] | 肖南, 董治宝, 刘铮瑶, 拓宇, 冯淼彦, 朱春鸣, 石寰宇. 等效沙厚度研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 1-6. |
| [12] | 潘凯佳, 张正偲, 梁爱民. 反向沙丘近地层气流变化及其对沙丘形态的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 1-8. |
| [13] | 杨迎, 吕萍, 马芳, 梁准, 许明静. 乌兰布和沙漠西南部风况对穹状沙丘形成的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 19-26. |
| [14] | 萨日娜, 董治宝, 南维鸽. 巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山地貌的线条美[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 221-230. |
| [15] | 朱春鸣, 董治宝, 刘铮瑶, 肖南, 杨军怀, 冯淼彦. 古尔班通古特沙漠树枝状沙丘沉积物粒度和微形态特征的空间分异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 9-18. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
