
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2020, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 10-17.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zisha Wang1,2( ), Yunfa Miao1,2(
), Yunfa Miao1,2( ), Yongtao Zhao1, Fang Li1, Yan Lei1,2, Mingxing Xiang1,2, Yaguo Zou1,2
), Yongtao Zhao1, Fang Li1, Yan Lei1,2, Mingxing Xiang1,2, Yaguo Zou1,2
Received:2019-10-30
Revised:2020-01-20
Online:2020-08-20
Published:2020-09-01
Contact:
Yunfa Miao
CLC Number:
Zisha Wang, Yunfa Miao, Yongtao Zhao, Fang Li, Yan Lei, Mingxing Xiang, Yaguo Zou. Characteristics of microcharcoal in the lake surface sediments in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin of China and its environmental significance[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 10-17.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00012
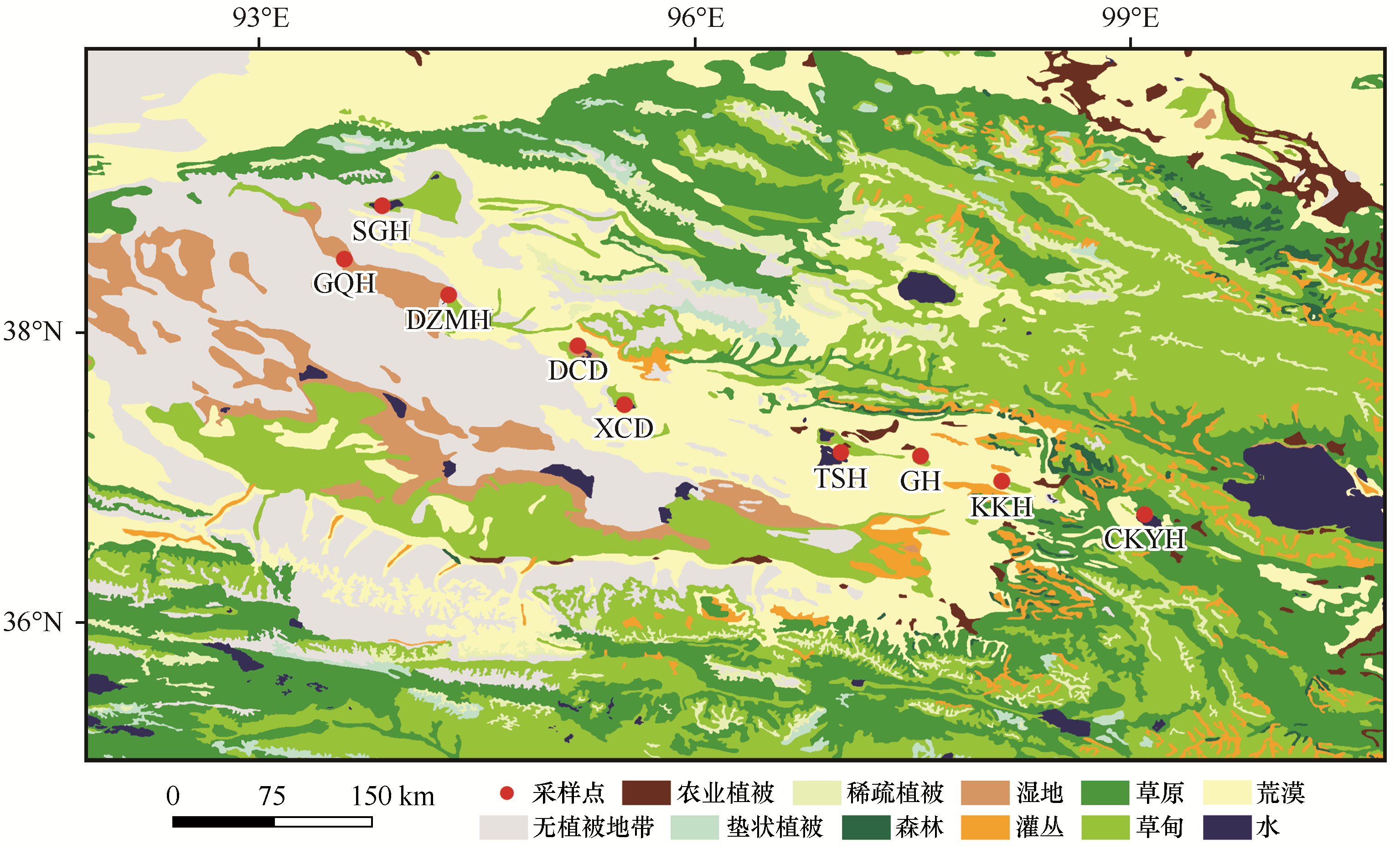
Fig.1 Location and vegetation type distribution of the research site (This data set is provided by “Environmental & Ecological Science Data Center for West China, National Natural Science Foundation of China”http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn)
| 采样点编码 | 采样点位置 | 所属植被区 | 主要植被 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGH | 苏干湖 | 北部中、低山山间盆地荒漠植被地区 | 优势种:超旱生的驼绒藜、中麻黄、木霸王、红沙、蒿叶猪毛菜、蒿子等;少量柽柳、芦苇 |
| GQH | 高泉湖 | ||
| DZMH | 德宗马海湖 | ||
| DCD | 大柴旦湖 | ||
| XCD | 小柴旦湖 | ||
| TSH | 托素湖 | ||
| GH | 尕海 | 东部荒漠草原植被地区 | 优势种:短花针茅、芨芨草、沙生针茅、密穗野青茅、冰草、普氏苔藓、红沙、西伯利亚白刺、唐古特白刺、早熟禾、紫花苜蓿、草木樨、赖草等;以及祁连圆柏、粗叶云杉、青杨等 |
| KKH | 柯柯湖 | ||
| CKYH | 茶卡盐湖 |
Table 1 Location and surrounding vegetations of samples[24]
| 采样点编码 | 采样点位置 | 所属植被区 | 主要植被 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGH | 苏干湖 | 北部中、低山山间盆地荒漠植被地区 | 优势种:超旱生的驼绒藜、中麻黄、木霸王、红沙、蒿叶猪毛菜、蒿子等;少量柽柳、芦苇 |
| GQH | 高泉湖 | ||
| DZMH | 德宗马海湖 | ||
| DCD | 大柴旦湖 | ||
| XCD | 小柴旦湖 | ||
| TSH | 托素湖 | ||
| GH | 尕海 | 东部荒漠草原植被地区 | 优势种:短花针茅、芨芨草、沙生针茅、密穗野青茅、冰草、普氏苔藓、红沙、西伯利亚白刺、唐古特白刺、早熟禾、紫花苜蓿、草木樨、赖草等;以及祁连圆柏、粗叶云杉、青杨等 |
| KKH | 柯柯湖 | ||
| CKYH | 茶卡盐湖 |
| 1 | Bowman D M J S,Balch J K,Paulo A,et al.Fire in the earth system[J]. Science,2009,324(5926):481-484. |
| 2 | Filion L.A relationship between dunes,fire and climate recorded in the Holocene deposits of Quebec[J].Nature,1984,309(5968):543-546. |
| 3 | Winkler M G.Charcoal analysis for paleoenvironmental interpretation:a chemical assay[J].Quaternary Research,1985,23(3):313-326. |
| 4 | 李宜垠,侯树芳,赵鹏飞.微炭屑的几种统计方法比较及其对人类活动的指示意义[J].第四纪研究,2010,30(2):356-363. |
| 5 | Patterson W A,Edwards K J,Maguire D J.Microscopic charcoal as a fossil indicator of fire[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1987,6(1):3-23. |
| 6 | Miao Y,Jin H,Cui J.Human activity accelerating the rapid desertification of the Mu Us Sandy Lands,North China[J].Scientific Reports,2016,6:23003. |
| 7 | 曹艳峰,黄春长,韩军青,等.黄土高原东西部全新世剖面炭屑记录的火环境变化[J].地理与地理信息科学,2007(1):92-96. |
| 8 | Rhodes A N.A method for the preparation and quantification of microscopic charcoal from terrestrial and lacustrine sedime nt cores[J].Holocene,1998,8(1):113-117. |
| 9 | 李小强,周新郢,尚雪,等.黄土炭屑分级统计方法及其在火演化研究中的意义[J].湖泊科学,2006(5):540-544. |
| 10 | Clark J S.Particle motion and the theory of charcoal analysis:source area,transport,deposition,and sampling[J].Quaternary Research,1988,30(1):67-80. |
| 11 | Thevenon F,Anselmetti F S.Charcoal and fly-ash particles from Lake Lucerne sediments (Central Switzerland) characterized by image analysis:anthropologic,stratigraphic and environmental implications[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2007,26(19/21):2631-2643. |
| 12 | Crawford A J,Belcher C M.Charcoal morphometry for paleoecological analysis:the effects of fuel type and transportation on morphological parameters[J].Applications in Plant Sciences,2014,2(8):1400004. |
| 13 | Daniau A L,Goni M F S,Martinez P,et al.Orbital-scale climate forcing of grassland burning in southern Africa[J].Proceedings Of the National Academy Of Sciences Of the United States Of America,2013,110(13):5069-5073. |
| 14 | Umbanhowar C E,Mcgrath M J.Experimental production and analysis of microscopic charcoal from wood,leaves and grasses[J].Holocene,1998,8(3):341-346. |
| 15 | Ma T,Zheng Z,Man M L,et al.Holocene fire and forest histories in relation to climate change and agriculture development in southeastern China[J].Quaternary International,2018,488:30-40. |
| 16 | Miao Y,Wu F,Warny S,et al.Miocene fire intensification linked to continuous aridification on the Tibetan Plateau [J].Geology,2019,47(4):303-307. |
| 17 | Miao Y F,Zhang D J,Cai X M,et al.Holocene fire on the northeast Tibetan Plateau in relation to climate change and human activity[J].Quaternary International,2017,443:124-131. |
| 18 | Tan Z H,Han Y M,Cao J J,et al.The linkages with fires,vegetation composition and human activity in response to climate changes in the Chinese Loess Plateau during the Holocene[J].Quaternary International,2018,488:18-29. |
| 19 | Miao Y F,Fang X,Song C,et al.Late Cenozoic fire enhancement response to aridification in mid-latitude Asia:evidence from microcharcoal records[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,139:53-66. |
| 20 | 李小强,赵宏丽,闫敏华,等.东北三江平原全新世火演化及其与植被和气候的关系[J].地理科学,2005(2):177-182. |
| 21 | 王彩红.青藏高原湖泊表层沉积物粒度和元素地球化学特征研究 [D].兰州:兰州大学,2015. |
| 22 | 尹斌.滇西北地区表层沉积物孢粉分析[D].昆明:云南师范大学,2017. |
| 23 | 秦鼎.滇东北、滇中地区现代花粉/炭屑组合与植被/火灾关系[D].昆明:云南师范大学,2018. |
| 24 | 杜庆,孙世洲.柴达木地区植被及其利用[M].北京:科学出版社,1990:65-75. |
| 25 | 魏振铎.青海省森林火灾发生规律的初步分析与防治对策[J].青海农林科技,1992(3):50-54. |
| 26 | 张景华,王希娟,钱有海,等.青海草原火灾环境因素分析[J].自然灾害学报,2007,16(1):71-75. |
| 27 | Zhao Y,Yu Z,Liu X,et al.Late Holocene vegetation and climate oscillations in the Qaidam Basin of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary Research,2010,73(1):59-69. |
| 28 | Zhao Y,Yu Z,Chen F,et al.Sensitive response of desert vegetation to moisture change based on a near-annual resolution pollen record from Gahai Lake in the Qaidam Basin,northwest China[J].Global and Planetary Change,2008,62(1/2):107-114. |
| 29 | Zhou A,Chen F,Qiang M,et al.The discovery of annually laminated sediments (varves) from shallow Sugan Lake in inland arid China and their paleoclimatic significance[J].Science in China:Series D,Earth sciences,2007,50(8):1218-1224. |
| 30 | 张健平,吕厚远.现代植物炭屑形态的初步分析及其古环境意义[J].第四纪研究,2006,26(5):857-863. |
| 31 | Highton P J C,Pearson A,Scott A C.Palynofacies and palynodebris and their use in Coal Measure palaeoecology and palaeoenvironmental analysis [J].Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie,Abh,1991,183:135-169. |
| 32 | 苗运法,吴福莉,方小敏,等.青藏高原北部柴达木盆地中新世菌孢子变化及其意义初探 [J].第四纪研究,2018,38(1):67-75. |
| 33 | Miao Y F,Warny S,Liu C,et al.Neogene fungal record from IODP Site U1433,South China Sea:implications for paleoenvironmental change and the onset of the Mekong River [J].Marine Geology,2017,390:23-35. |
| 34 | 罗甲渊,黄滚,熊阳涛,等.破碎后微小煤颗粒分布与破碎功关系实验研究[J].煤炭学报,2016,41(12):3054-3061. |
| 35 | 李万志.近54年柴达木盆地风速特征研究[J].青海气象,2017(1):40-44. |
| 36 | 曹唯,徐明生.煤堆和矸石山风蚀扬尘污染分析及防治简述[J].煤矿环境保护,1998(4):33-36. |
| 37 | 青海省统计局.青海统计年鉴[M].北京:中国统计出版社,2018. |
| [1] | Shuxing Xu, Qianqian Wu, Dianxue Qiao, Yinglin Mu, Xiao Zhang, Yanshu Liu, Xiaohui Yang, Zhongjie Shi. Spatiotemporal pattern and effecting factors of wildfire in eastern Mongolia [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 83-91. |
| [2] | Min Cao, Lupeng Yu, Ping An, Zhibao Dong, Junxiang Zhao, Zhongping Lai, Changsheng Wang. Luminescence chronology and environmental implications of palaeolacustrine sediments beneath linear dunes in northern Qarhan Salt Lake region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 101-110. |
| [3] | Yimei Sun, Qing Tian, Peng Lv, Aixia Guo, Pingping Li, Liqin Zhu, Xiaoan Zuo. Response of structure of plant community to extreme drought in fixed dunes and grassland in the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 129-136. |
| [4] | Xuyang Wang, Yulin Li, Jie Lian, Yulong Duan, Lilong Wang. Relationship between vegetation coverage and climate change in semi-arid sandy land and the significance to ecological construction [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 183-194. |
| [5] | Jun Lei, Xiaohu Yang, Hongmei Liu, Yuhong Zhao, Juping Fan, Caixia Guo. The characteristics of desert vegetation biomass and its influencing factors in the middle reaches of the Heihe River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 203-208. |
| [6] | Qingjie Han, Caiyuan Hao, Jianjun Qu, Hongjie Zhang, Fucheng Zhou. Characteristics of three-dimensional flow field and sand control efficiency at typical sand control engineering area along the Linhe-Hami Railway [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 1-12. |
| [7] | Lei Wu, Changbin Li, Liuming Wang, Xuhong Xie, Yuan Zhang, Jianmei Wei. Division and application of desert-oasis system in arid Northwest China based on ESA-LUC and MODIS-NDVI [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 139-150. |
| [8] | Mengyu Hao, Longjun Qin, Peng Mao, Jiechunyi Luo, Wenli Zhao, Guoyu Qiu. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) based methodology for spatial distribution pattern analysis of desert vegetation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 169-179. |
| [9] | Yongxiang Cao, Donglei Mao, Fuyan Cai, Xuemei Wang, Abulaiti Kaimaierguli, Songling Su. Spatial difference of microclimate over typical underlying surface in process of oasisization in Cele, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 180-189. |
| [10] | Yimei Sun, Qing Tian, Aixia Guo, Xiaoan Zuo, Peng Lv, Senxi Zhang. Effects of water and nitrogen changes on vegetation characteristics and leaf traits in Horqin Sandy land, Northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 223-232. |
| [11] | Zhun Liang, Lü Ping, Zhengyao Liu, Nan Xiao, Wei Liang, Mingjing Xu, Miaoyan Feng. The relationship between wind regime and yardang morphology in the Duck Lake Area of Qaidam Basin, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 42-48. |
| [12] | Caixia Zhang, Junpeng Lou, Diwen Cai. Major and minor elements content for fifteen-five vegetation samples in desert areas [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 18-23. |
| [13] | Fang Chen, Quanlin Ma, Linyuan Wei, Dekui Zhang, Hongbo Yuan, Feng Ding, Xiaoke Hu, Zhong Zhang. Soil seed bank characteristics of Agriophyllum squarrosum [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 190-196. |
| [14] | Delu Li, Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Xinrong Li, Hongbo Yuan, Linyuan Wei, Haotian Yang, Zhong Zhang. Vegetation characteristics of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| [15] | Mingjing Xu, Lü Ping, Nan Xiao, Junhuai Yang, Zhengyao Liu, Miaoyan Feng, Zhun Liang. Effect of vegetation cover on dune migration in northwest Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 71-80. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech