
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 243-251.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00025
Gaoling Han1,2( ), Jianqiang Huo1,2, Yanqiao Zhao1,2, Rui Hu1, Zhishan Zhang1(
), Jianqiang Huo1,2, Yanqiao Zhao1,2, Rui Hu1, Zhishan Zhang1( ), Rihui Huang3, Shuwen Xue3
), Rihui Huang3, Shuwen Xue3
Received:2023-02-12
Revised:2023-03-21
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
Zhishan Zhang
CLC Number:
Gaoling Han, Jianqiang Huo, Yanqiao Zhao, Rui Hu, Zhishan Zhang, Rihui Huang, Shuwen Xue. Analysis of herbaceous species composition and diversity in the Ordos Arsenic Sandstone Areas[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 243-251.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00025
| 科 | 属 | 中文名 | 拉丁学名 | 重要值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盖土区 | 盖沙区 | 裸露区 | ||||
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 针茅属(Stipa) | 针茅 | Stipa capillata | 0.152 | 0.268 | 0.051 |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 猪毛菜属(Salsola) | 刺蓬 | Salsola tragus | 0.142 | 0.059 | 0.046 |
| 豆科(Fabaceae) | 胡枝子属(Lespedeza) | 胡枝子 | Lespedeza bicolor | 0.112 | 0.093 | 0.030 |
| 蒺藜科(Zygophyllaceae) | 蒺藜属(Tribulus) | 蒺藜 | Tribulus terrestris | 0.109 | 0.005 | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 艾蒿 | Artemisia argyi | 0.077 | 0.127 | — |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 虫实属(Corispermum) | 虫实 | Corispermum hyssopifolium | 0.061 | 0.014 | 0.011 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 画眉草属(Eragrostis) | 小画眉草 | Eragrostis minor | 0.051 | 0.060 | 0.055 |
| 唇形科(Lamiaceae Martinov) | 黄芩属(Scutellaria) | 黄苓 | Scutellaria baicalensis | 0.042 | — | — |
| 大戟科(Euphorbiaceae) | 大戟属(Euphorbia) | 地锦草 | Euphorbia humifusa | 0.032 | — | 0.025 |
| 石竹科(Caryophyllaceae) | 石头花属(Gypsophila) | 长蕊石头花 | Gypsophila oldhamiana | 0.029 | — | 0.034 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 狗尾草属(Setaria) | 狗尾草 | Setaria viridis | 0.025 | 0.133 | 0.031 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 冰草属(Agropyron) | 冰草 | Agropyron cristatum | 0.023 | 0.010 | — |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 隐子草属(Cleistogenes) | 无芒隐子草 | Cleistogenes squarrosa | 0.023 | 0.019 | — |
| 百合科(Liliaceae) | 葱属(Allium) | 多根葱 | Allium polyrhizum | 0.023 | 0.003 | — |
| 蔷薇科(Rosaceae) | 委陵菜属(Potentilla) | 委陵菜 | Potentilla chinensis | 0.021 | — | — |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 藜属(Chenopodium) | 灰条菜 | Chenopodium album | 0.021 | — | — |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 藜属(Chenopodium) | 刺藜 | Chenopodium aristatum | 0.018 | 0.062 | 0.399 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 飞廉属(Carduus) | 飞廉 | Carduus nutans | 0.016 | 0.001 | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 漏芦属(Stemmacantha) | 漏芦 | Rhaponticum uniflorum | 0.010 | — | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 青蒿 | Artemisia carvifolia | 0.006 | — | — |
| 瑞香科(Thymelaeaceae) | 狼毒属(Stellera) | 狼毒 | Stellera chamaejasme | 0.004 | 0.008 | — |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 棒头草属(Polypogon) | 棒头草 | Polypogon fugax | 0.003 | — | — |
| 小檗科(Berberidaceae) | 淫羊藿属(Epimedium) | 三枝九叶草 | Epimedium sagittatum | 0.002 | — | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 猪毛蒿 | Artemisia scoparia | — | 0.052 | 0.061 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 稗属(Echinochloa) | 稗草 | Echinochloa crusgalli | — | 0.041 | 0.003 |
| 豆科(Fabaceae) | 黄耆属(Astragalus) | 黄耆 | Astragalus membranaceus | — | 0.023 | 0.006 |
| 伞形科(Apiaceae) | 阿魏属(Ferula) | 阿魏 | Ferula sinkiangensis | — | 0.003 | — |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 虎尾草属(Chloris) | 虎尾草 | Chloris virgata | — | 0.012 | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 白莲蒿 | Artemisia stechmanniana | — | 0.005 | — |
| 天南星科(Araceae) | 菖蒲属(Acorus) | 菖蒲 | Acorus calamus | — | 0.001 | 0.004 |
| 百合科(Liliaceae) | 葱属(Allium) | 沙葱 | Allium mongolicum | — | — | 0.074 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 冷蒿 | Artemisia frigida | — | — | 0.046 |
| 唇形科(Lamiaceae Martinov) | 百里香属(Thymus) | 百里香 | Thymus mongolicus | — | — | 0.045 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 雀麦属(Bromus) | 雀麦 | Bromus japonicus | — | — | 0.025 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 狗娃花属(Heteropappus) | 阿尔泰狗娃花 | Heteropappus altaicus | — | — | 0.016 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 亚菊属(Ajania) | 蓍状亚菊 | Ajania achilleoides | — | — | 0.015 |
| 萝藦科(Asclepiadaceae) | 鹅绒藤属(Cynanchum) | 牛心朴子 | Cynanchum mongolicum | — | — | 0.009 |
| 豆科(Fabaceae) | 黄芪属(Astragalus) | 沙打旺 | Astragalus laxmannii | — | — | 0.006 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 早熟禾属(Poa) | 早熟禾 | Poa annua | — | — | 0.005 |
| 旋花科(Convolvulaceae) | 旋花属(Convolvulus) | 田旋花 | Convolvulus arvensis | — | — | 0.003 |
Table 1 Composition and importance of herbaceous species in different types of arsenic sandstone areas
| 科 | 属 | 中文名 | 拉丁学名 | 重要值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 盖土区 | 盖沙区 | 裸露区 | ||||
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 针茅属(Stipa) | 针茅 | Stipa capillata | 0.152 | 0.268 | 0.051 |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 猪毛菜属(Salsola) | 刺蓬 | Salsola tragus | 0.142 | 0.059 | 0.046 |
| 豆科(Fabaceae) | 胡枝子属(Lespedeza) | 胡枝子 | Lespedeza bicolor | 0.112 | 0.093 | 0.030 |
| 蒺藜科(Zygophyllaceae) | 蒺藜属(Tribulus) | 蒺藜 | Tribulus terrestris | 0.109 | 0.005 | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 艾蒿 | Artemisia argyi | 0.077 | 0.127 | — |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 虫实属(Corispermum) | 虫实 | Corispermum hyssopifolium | 0.061 | 0.014 | 0.011 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 画眉草属(Eragrostis) | 小画眉草 | Eragrostis minor | 0.051 | 0.060 | 0.055 |
| 唇形科(Lamiaceae Martinov) | 黄芩属(Scutellaria) | 黄苓 | Scutellaria baicalensis | 0.042 | — | — |
| 大戟科(Euphorbiaceae) | 大戟属(Euphorbia) | 地锦草 | Euphorbia humifusa | 0.032 | — | 0.025 |
| 石竹科(Caryophyllaceae) | 石头花属(Gypsophila) | 长蕊石头花 | Gypsophila oldhamiana | 0.029 | — | 0.034 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 狗尾草属(Setaria) | 狗尾草 | Setaria viridis | 0.025 | 0.133 | 0.031 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 冰草属(Agropyron) | 冰草 | Agropyron cristatum | 0.023 | 0.010 | — |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 隐子草属(Cleistogenes) | 无芒隐子草 | Cleistogenes squarrosa | 0.023 | 0.019 | — |
| 百合科(Liliaceae) | 葱属(Allium) | 多根葱 | Allium polyrhizum | 0.023 | 0.003 | — |
| 蔷薇科(Rosaceae) | 委陵菜属(Potentilla) | 委陵菜 | Potentilla chinensis | 0.021 | — | — |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 藜属(Chenopodium) | 灰条菜 | Chenopodium album | 0.021 | — | — |
| 藜科(Chenopodiaceae) | 藜属(Chenopodium) | 刺藜 | Chenopodium aristatum | 0.018 | 0.062 | 0.399 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 飞廉属(Carduus) | 飞廉 | Carduus nutans | 0.016 | 0.001 | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 漏芦属(Stemmacantha) | 漏芦 | Rhaponticum uniflorum | 0.010 | — | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 青蒿 | Artemisia carvifolia | 0.006 | — | — |
| 瑞香科(Thymelaeaceae) | 狼毒属(Stellera) | 狼毒 | Stellera chamaejasme | 0.004 | 0.008 | — |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 棒头草属(Polypogon) | 棒头草 | Polypogon fugax | 0.003 | — | — |
| 小檗科(Berberidaceae) | 淫羊藿属(Epimedium) | 三枝九叶草 | Epimedium sagittatum | 0.002 | — | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 猪毛蒿 | Artemisia scoparia | — | 0.052 | 0.061 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 稗属(Echinochloa) | 稗草 | Echinochloa crusgalli | — | 0.041 | 0.003 |
| 豆科(Fabaceae) | 黄耆属(Astragalus) | 黄耆 | Astragalus membranaceus | — | 0.023 | 0.006 |
| 伞形科(Apiaceae) | 阿魏属(Ferula) | 阿魏 | Ferula sinkiangensis | — | 0.003 | — |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 虎尾草属(Chloris) | 虎尾草 | Chloris virgata | — | 0.012 | — |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 白莲蒿 | Artemisia stechmanniana | — | 0.005 | — |
| 天南星科(Araceae) | 菖蒲属(Acorus) | 菖蒲 | Acorus calamus | — | 0.001 | 0.004 |
| 百合科(Liliaceae) | 葱属(Allium) | 沙葱 | Allium mongolicum | — | — | 0.074 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 蒿属(Artemisia) | 冷蒿 | Artemisia frigida | — | — | 0.046 |
| 唇形科(Lamiaceae Martinov) | 百里香属(Thymus) | 百里香 | Thymus mongolicus | — | — | 0.045 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 雀麦属(Bromus) | 雀麦 | Bromus japonicus | — | — | 0.025 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 狗娃花属(Heteropappus) | 阿尔泰狗娃花 | Heteropappus altaicus | — | — | 0.016 |
| 菊科(Asteraceae) | 亚菊属(Ajania) | 蓍状亚菊 | Ajania achilleoides | — | — | 0.015 |
| 萝藦科(Asclepiadaceae) | 鹅绒藤属(Cynanchum) | 牛心朴子 | Cynanchum mongolicum | — | — | 0.009 |
| 豆科(Fabaceae) | 黄芪属(Astragalus) | 沙打旺 | Astragalus laxmannii | — | — | 0.006 |
| 禾本科(Poaceae Barnhart) | 早熟禾属(Poa) | 早熟禾 | Poa annua | — | — | 0.005 |
| 旋花科(Convolvulaceae) | 旋花属(Convolvulus) | 田旋花 | Convolvulus arvensis | — | — | 0.003 |
| 砒砂岩类型区 | 盖土区 | 盖沙区 | 裸露区 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盖土区 | 63.6 | 39.1 | |
| 盖沙区 | 14 | 50.0 | |
| 裸露区 | 9 | 11 |
Table 2 Species number and similarity index of herbaceous species in different types of arsenic sandstone areas
| 砒砂岩类型区 | 盖土区 | 盖沙区 | 裸露区 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盖土区 | 63.6 | 39.1 | |
| 盖沙区 | 14 | 50.0 | |
| 裸露区 | 9 | 11 |
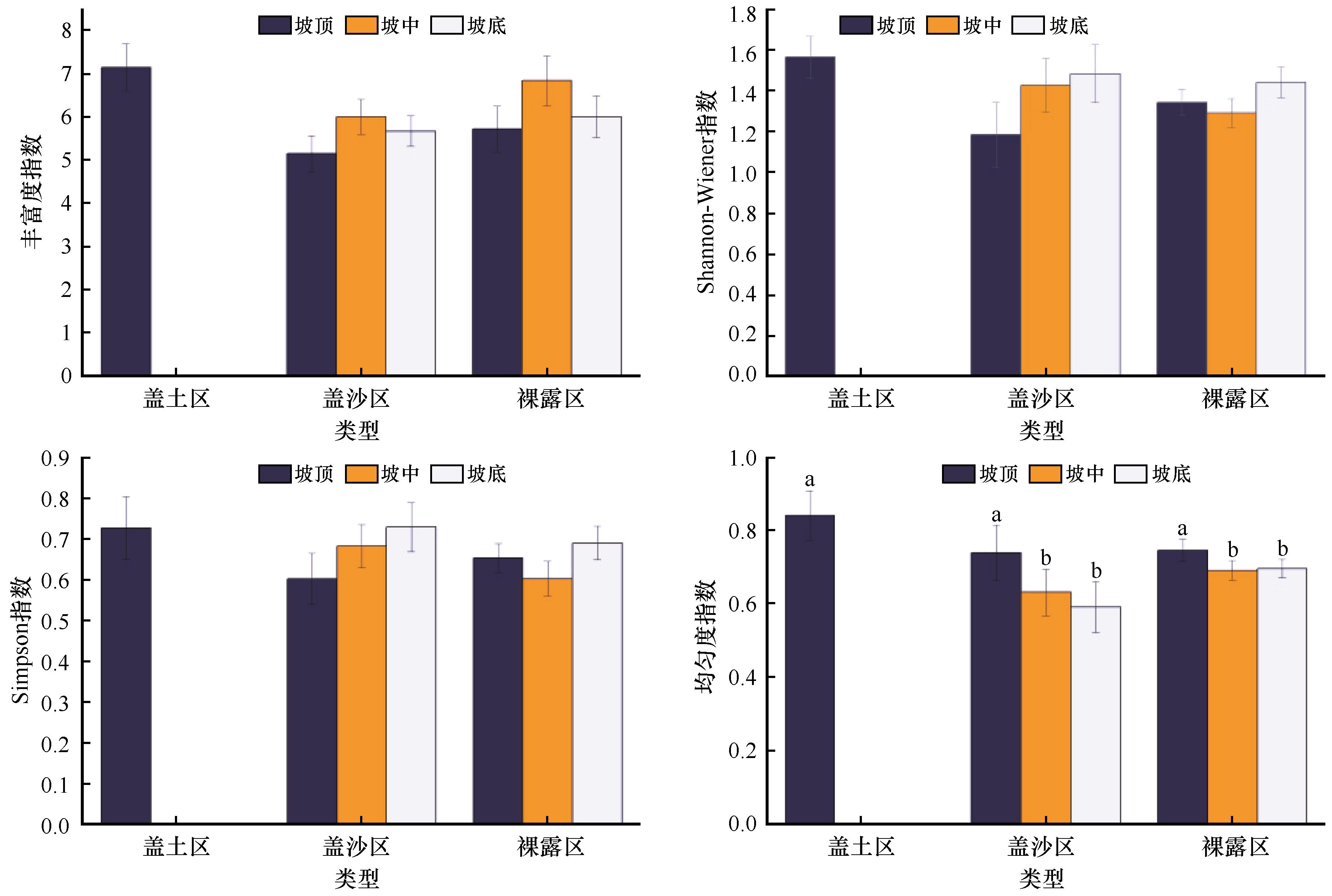
Fig.2 Species richness index, Shannon-wiener index, Simpson index and Evenness index of herbaceous species in different topographic locations of different arsenic sandstone areas
| 1 | 王立久,李长明,董晶亮.砒砂岩分布及岩性特征[J].人民黄河,2013,35(12):91-93. |
| 2 | 姚文艺,时明立,崔长江.黄河泥沙问题研究综述[J].黄河水利职业技术学院学报,2004(1):1-3. |
| 3 | 杨具瑞,方铎,毕慈芬,等.砒砂岩区小流域沟冻融风化侵蚀模型研究[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报,2003(2):89-95. |
| 4 | 王愿昌,吴永红,寇权,等.砒砂岩分布范围界定与类型区划分[J].中国水土保持科学,2007(1):14-18. |
| 5 | 范淑花.鄂尔多斯盆地准格尔旗砒砂岩成岩及风化作用机制研究[D].北京:中国地质大学(北京),2019. |
| 6 | 秦富仓,董晓宇,郭月峰,等.砒砂岩区不同植被类型土壤崩解特征及其影响因素研究[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),2022,43(5):61-70. |
| 7 | Spellerberg I F, Sawyer J W D.Standards for biodiversity: a proposal based on biodiversity standards for forest plantations[J].Biodiversity & Conservation,1996,5(4):447-459. |
| 8 | 袁勤,崔向新,蒙仲举.砒砂岩区不同人工林林下草本层植物的结构特征[J].绿色科技,2013(5):47-50. |
| 9 | 孟庆辉.朝阳地区草本植物区系组成及相似性分析[J].新农业,2021(24):7-8. |
| 10 | 马克平,刘玉明.生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅰα多样性的测度方法(下)[J].生物多样性,1994(4):231-239. |
| 11 | 马克平.生物群落多样性的测度方法Ⅰα多样性的测度方法(上)[J].生物多样性,1994(3):162-168. |
| 12 | 白永飞,李凌浩,王其兵,等.锡林河流域草原群落植物多样性和初级生产力沿水热梯度变化的样带研究[J].植物生态学报,2000(6):667-673. |
| 13 | Bai Y, Wu J, Clark C M,et al.Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from inner Mongolia Grasslands[J].Global Change Biology,2010,16(1):358-372. |
| 14 | 胡一鸣,梁健超,金崑,等.喜马拉雅山哺乳动物物种多样性垂直分布格局[J].生物多样性,2018,26(2):191-201. |
| 15 | 孙成,秦富仓,包雪源,等.砒砂岩区人工油松林下草本植物的生态位特征[J].水土保持通报,2021,41(3):81-86. |
| 16 | 孙成,秦富仓,李龙,等.砒砂岩区不同立地类型人工油松林下草本种群生态位特征及其环境解释[J].生态学报,2022,42(9):3613-3623. |
| 17 | 于顺利,陈灵芝,张承军.不同地点蒙古栎群落相似性的研究[J].植物学通报,2000(6):554-558. |
| 18 | 陈鹏,张铁钢,董智,等.不同灌草格局对砒砂岩区土壤剥蚀特征的影响[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(3):13-18. |
| 19 | Fan J, Xu Y, Ge H,et al.Vegetation growth variation in relation to topography in Horqin Sandy Land[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,113:106215. |
| 20 | 周国娜,袁胜亮,崔书文.不同林分林下植被的多样性特征及生物量研究[J].湖北农业科学,2012,51(18):4052-4056. |
| 21 | 谭许脉,张文,肖纳,等.杉木林改造成乡土阔叶林对林下植物物种组成和多样性的影响[J].生态学报,2022,42(7):2931-2942. |
| 22 | 程冬兵,蔡崇法,孙艳艳.退化生态系统植被恢复理论与技术探讨[J].世界林业研究,2006(5):7-14. |
| [1] | Qiwei Li, Zhijun Gong, Ming Luo, Huaming Peng, Han Wang, Wei Wang. Grain size analysis of two sand layers with parallel bedding in the sand hills around Poyang Lake and its implication for the sedimentary environment [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 152-159. |
| [2] | Enyue Zhang, Yingqing Su, Yunfeng Zhang, Yuzhen Li, Kexuan Li, Geng Liu. Coupling coordination pattern and driving factors of soil and water resources in Fenhe River Basin of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 169-177. |
| [3] | Xuying Bai, Yujie Wang, Yunqi Wang, Wenbin Yang, Tao Wang, Yiben Cheng. Changes and driving factors of water body area in Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 65-73. |
| [4] | Xiaohui He, Jianhua Si, Dongmeng Zhou, Chunlin Wang, Chunyan Zhao. Photosynthetic properties and leaf-scale water use efficiency of Haloxylon ammodendron in different stand ages [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 20-26. |
| [5] | Lijuan Wang, Ni Guo, Sha Sha, Die Hu. Influencing factors of surface energy conversion in Northwest China and applicability of characteristic space method [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 1-13. |
| [6] | Junyu Miao. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of industrial water resources efficiency and its influencing factors in nine provinces along the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 142-152. |
| [7] | Yaofang Hou, Shengkui Cao, Guangchao Cao, Zhigang Wang, Youcai Wang, Ligang Kang. Relationship between hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope compositions of soil water and soil water storage in Shaliuhe River Basin of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 153-164. |
| [8] | Shengtang Wang, Yingchun Ge, Shaokun Wang, Xiaolong Zhang, Ying Yang. Responses of plant species diversity to land use change: a case study in the Heihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 221-232. |
| [9] | Qi Zhang, Yonghong Su, Qi Feng, Tengfei Yu, Xiaohong Ma. Estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration of Populus euphratica forest ecosystem along desert river banks based on groundwater level dynamics [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 243-254. |
| [10] | Lin Li, Hu Liu, Chengpeng Sun, Wenzhi Zhao. Groundwater evapotranspiration estimation based on soil moisture and water table measurements [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 277-287. |
| [11] | Xinpeng Li, Chaoping Wang, Songbing Zou, Wei Yue, Shan Luo, Wenshu Wang, Yihao Qin, Jun Sang, Jikun Qian, Chunmiao Wang. Evaluation on ecological resilience in water conservation area in the upper Yellow River based on AHP: A case study of the Gannan and Linxia region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 85-93. |
| [12] | Jiawang Yin, Ala Musa, Yuhang Su. Effects of dune vegetation on water dynamics in interdune lowland in the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 194-203. |
| [13] | Qian Li, Long Ma, Tingxi Liu, Shuo Wang. Conversion of precipitation, surface water, groundwater and mine water affected by coal mining in the Hailiutu River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 146-157. |
| [14] | Yali Liu, Jianhua Bai, Wei Xiong, Yuqing Han, Honglin Lian, Hao Guo, Zhiming Xin, Xiangjie Liu, Huaiyuan Liu. The characteristics of branch nocturnal sap flow and its environmental driving mechanism of Haloxylon ammodendron artificial shrub in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 195-203. |
| [15] | Wenwen Xu, Yanqiao Zhao, Nan Wang, Yang Zhao. Effects of artificial biological soil crusts on the composition and diversity of herbaceous plant communities [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 204-211. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech