
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 222-230.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00107
Jiayu Du( ), Xianfeng Liu(
), Xianfeng Liu( ), Gaopeng Sun, Shuangshuang Li
), Gaopeng Sun, Shuangshuang Li
Received:2023-09-04
Revised:2023-12-04
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-11
Contact:
Xianfeng Liu
CLC Number:
Jiayu Du, Xianfeng Liu, Gaopeng Sun, Shuangshuang Li. Spatiotemporal variation in vegetation optical depth and its influencing factors over the Loess Plateau during 2003-2018[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 222-230.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00107
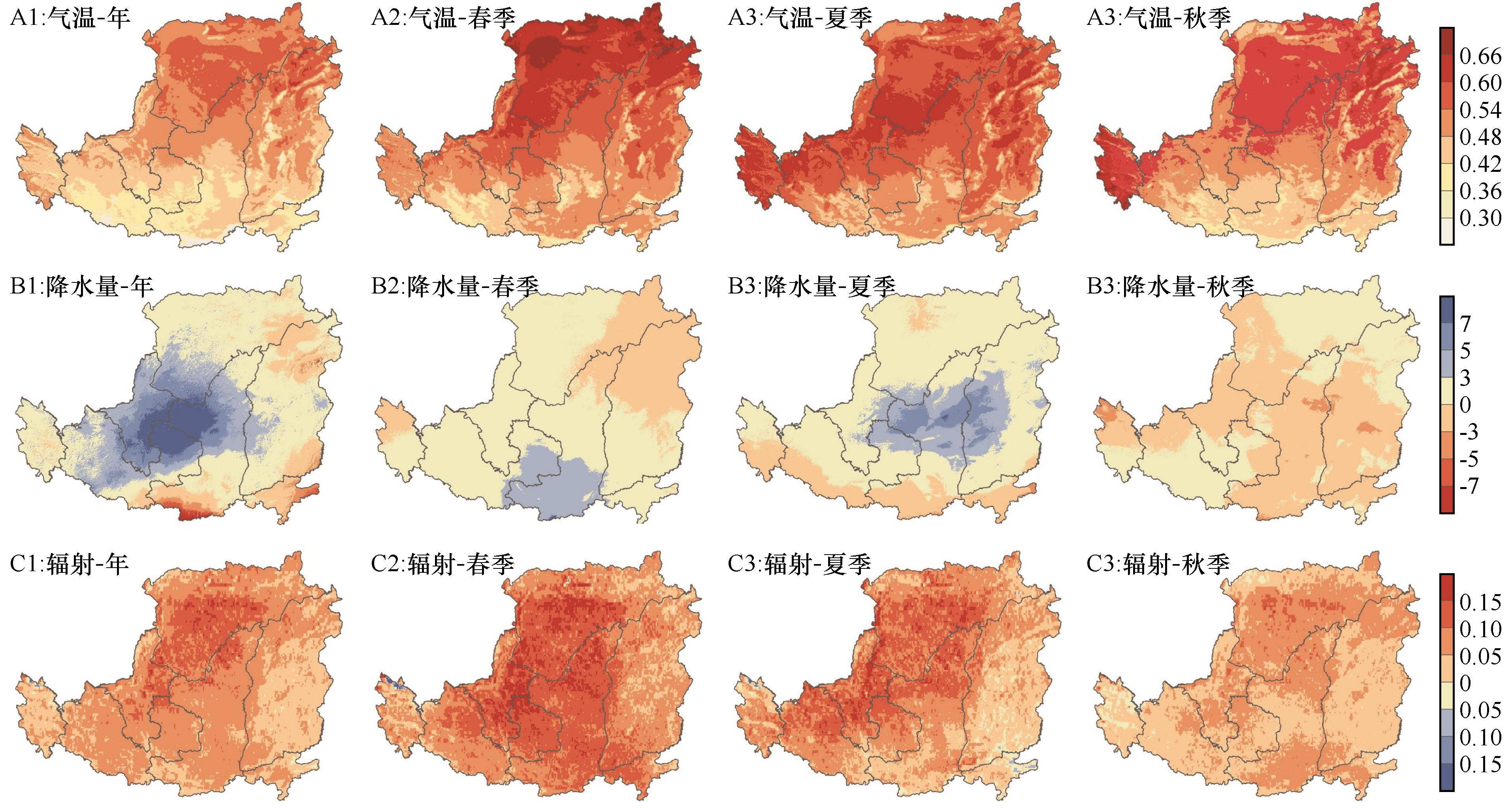
Fig.6 Temporal trends in temperature, precipitation, and radiation on the Loess Plateau for the years 2003-2018 and seasonal variations (spring, summer, and autumn)
| 1 | 韦红波,李锐,杨勤科.我国植被水土保持功能研究进展[J].植物生态学报,2002(4):489-496. |
| 2 | 孙高鹏,刘宪锋,王小红,等.2001-2020年黄河流域植被覆盖变化及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):205-212. |
| 3 | 姜彤,翟建青,罗勇,等.气候变化影响适应和脆弱性评估报告进展:IPCC AR5到AR6的新认知[J].大气科学学报,2022,45(4):502-511. |
| 4 | 刘宪锋,傅伯杰.干旱对作物产量影响研究进展与展望[J].地理学报,2021,76(11):2632-2646. |
| 5 | Liu X, Sun G, Fu Z,et al.Compound droughts slow down the greening of the Earth[J].Global Change Biology,2023,29(1):1-13. |
| 6 | 刘宪锋,潘耀忠,朱秀芳,等.2000-2014年秦巴山区植被覆盖时空变化特征及其归因[J].地理学报,2015,70(5):705-716. |
| 7 | Woodhouse I H.Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing[M].Florida,USA:CRC Press,2005. |
| 8 | Momen M, Wood J D, Novick K A,et al.Interacting effects of leaf water potential and biomass on vegetation optical depth[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences,2017,122(11):3031-3046. |
| 9 | Teubner I E, Forkel M, Jung M,et al.Assessing the relationship between microwave vegetation optical depth and gross primary production[J].International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2018,65:79-91. |
| 10 | Du J, Kimball J S, Jones L A,et al.A global satellite environmental data record derived from AMSR-E and AMSR2 microwave Earth observations[J].Earth System Science Data,2017,9(2):791-808. |
| 11 | Liu Y Y, Van Dijk A I J M, De Jeu R A M,et al.Recent reversal in loss of global terrestrial biomass[J].Nature Climate Change,2015,5(5):470-474. |
| 12 | Li X, Wigneron J P, Frappart F,et al.Global-scale assessment and inter-comparison of recently developed/reprocessed microwave satellite vegetation optical depth products[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2021,253:112208. |
| 13 | Liu Y Y, De Jeu R A M, McCabe M F,et al.Global long‐term passive microwave satellite‐based retrievals of vegetation optical depth[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2011,38(18):L18402. |
| 14 | Tian F, Brandt M, Liu Y Y, et al. Remote sensing of vegetation dynamics in drylands: evaluating vegetation optical depth (VOD) using AVHRR NDVI and in situ green biomass data over West African Sahel[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 177: 265-276. |
| 15 | Zhou X, Yamaguchi Y, Arjasakusuma S.Distinguishing the vegetation dynamics induced by anthropogenic factors using vegetation optical depth and AVHRR NDVI:a cross-border study on the Mongolian Plateau[J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,616:730-743. |
| 16 | Brandt M, Yue Y, Wigneron J P,et al.Satellite‐observed major greening and biomass increase in south China karst during recent decade[J].Earth's Future,2018,6(7):1017-1028. |
| 17 | 刘悦,刘欢欢,陈印,等.2000-2018年中国植被光学厚度时空动态特征及驱动因素[J].地理学报,2023,78(3):729-745. |
| 18 | 刘宪锋,杨勇,任志远,等.2000-2009年黄土高原地区植被覆盖度时空变化[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(4):1244-1249. |
| 19 | Moesinger L, Dorigo W, de Jeu R,et al.The global long-term microwave vegetation optical depth climate archive (VODCA)[J].Earth System Science Data,2020,12(1):177-196. |
| 20 | Liu Y Y, van Dijk A I J M, McCabe M F,et al.Global vegetation biomass change (1988-2008) and attribution to environmental and human drivers[J].Global Ecology and Biogeography,2013,22(6):692-705. |
| 21 | Schmidt L, Forkel M, Zotta R M,et al.Assessing the sensitivity of multi-frequency passive microwave vegetation optical depth to vegetation properties[J].Biogeosciences,2023,20(5):1027-1046. |
| 22 | 王军邦.2000-2018年全国1 km每8天陆地表面净辐射数据集[DB/OL].北京:国家生态科学数据中心,2021.DOI:10. 12199/nesdc.ecodb.rs.2021.017 . |
| 23 | Sen P K.Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's tau[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association,1968,63(324):1379-1389. |
| 24 | Moran P A P, Kendall M G.Rank correlation methods[J].International Statistical Review,1973,41(3):399. |
| 25 | Zomer R J, Xu J, Trabucco A.Version 3 of the global aridity index and potential evapotranspiration database[J].Scientific Data,2022,9(1):409. |
| 26 | Zhou J, Jiang T, Wang Y,et al.Spatiotemporal variations of aridity index over the Belt and Road region under the 1.5 ℃ and 2.0 ℃ warming scenarios[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2020,30:37-52. |
| 27 | Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wang Y,et al.Assessing the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on vegetation in southwest China[J].Journal of Mountain Science,2022,19(9):2678-2692. |
| 28 | Wessels K J, Van Den Bergh F, Scholes R J.Limits to detectability of land degradation by trend analysis of vegetation index data[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2012,125:10-22. |
| 29 | 余玉洋,宋丰艺,张世杰.2000-2020年河南省NDVI时空变化及其驱动因素定量分析[J].生态环境学报,2022,31(10):1939-1950. |
| 30 | 赵安周,田新乐.基于GEE平台的1986-2021年黄土高原植被覆盖度时空演变及影响因素[J].生态环境学报,2022,31(11):2124-2133. |
| 31 | Lai W, Wang M, Wei J,et al.Separating the impact of climate changes and human activities on vegetation growth based on the NDVI in China[J].Advances in Meteorology,2022:1-11. |
| 32 | Ge W, Deng L, Wang F,et al.Quantifying the contributions of human activities and climate change to vegetation net primary productivity dynamics in China from 2001 to 2016[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,773:145648. |
| 33 | 高江波,焦珂伟,吴绍洪.1982-2013年中国植被NDVI空间异质性的气候影响分析[J].地理学报,2019,74(3):534-543. |
| 34 | Piao S, Wang X, Ciais P,et al.Changes in satellite‐derived vegetation growth trend in temperate and boreal Eurasia from 1982 to 2006[J].Global Change Biology,2011,17(10):3228-3239. |
| 35 | 涂又,姜亮亮,刘睿,等.1982-2015年中国植被NDVI时空变化特征及其驱动分析[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(22):75-84. |
| [1] | Mingdou Zhang, Yuxin Yang. Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factors of urban ecological industrial structure in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 108-118. |
| [2] | Ziao Shen, Jing Wu, Chunbin Li. Temporal and spatial changes of vegetation cover and its driving forces in the Hexi inland river basin from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 119-127. |
| [3] | Changxiang Pan, Qianru Ouyang, Mengyu Liao, Yu Fan, Qun Guo, Zhishan Zhang, Genan Wu, Yang Zhao, Lichao Liu, Yanxia Pan, Xinrong Li, Jianjun Qu, Songlin Mu, Shenggong Li. The applicability of ecological restoration technologies and sand industries to the deserted land in northwest arid region of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 155-165. |
| [4] | Jing Yang, Qun Guo. Study on carbon emission estimation methods and emission reduction pathways at provincial level [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 176-185. |
| [5] | Yanqiao Zhao, Yuchao Lian, Wenwen Xu, Yixue Zhao, Gaoling Han, Yang Zhao. Research progress and prospect of artificial cyanobacteria crusts in China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 214-222. |
| [6] | Jinfeng Wang, Xiaoling Liu, Qing Li, Rende Wang, Sheng Wang. Spatio-temporal differentiation and driving factors of windbreak and sand fixation services in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 220-230. |
| [7] | Fangmiao Chen, Huiping Huang, Guang Yang, Xu Li. Research on the dynamic change of the ecological environment and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin based on Remote Sensing Ecological Index [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 252-262. |
| [8] | Yushuo Zhang, Xuerui Shen, Renjing Sui, Jie Bao, Zhonglei Yu, Lin Zhao, Xuebin Zhang. Multi-scale analysis of spatial pattern and the influencing factors of A-grade scenic spots in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 103-115. |
| [9] | Weicheng Luo, Wenzhi Zhao, Jiliang Liu, Jingyi Yang, Xuelian Bai, Lemin Wei, Yilin Feng. Distribution pattern and influencing factors of ground arthropods in coalmines restoration area of Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 165-175. |
| [10] | Yang Liu, Ya Wang, Lihua Zhou. Performance evaluation of ecological migration project based on process and outcome: a case study of Huanghuatan migration area in Gulang, Gansu, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 185-193. |
| [11] | Wen Zhang, Dingding Du, Zhiwen Li, Wangyang Wu, Xiangjie Li, Yonghui Bai. Grain size characteristics of sediments in sandy land around the Poyang Lake and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 122-132. |
| [12] | Guangzhao Han, Guangchao Cao, Shengkui Cao, Wenqian Ye. Soil particle organic carbon isotope decomposition characteristics of ecological restoration grassland and woodland in alpine region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 36-43. |
| [13] | Qianqian Wu, Xiao Zhang, Shuxing Xu, Xiaohui Yang, Yanshu Liu, Hanzhi Li, Zhongjie Shi. Climatic responses of NDVI and tree growth in the arid areas of inland Asia and their influencing factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 1-10. |
| [14] | Lei Kang, Zhaoping Yang, Fang Han. Analysis of structural characteristics and spatial distribution of the intangible cultural heritage in Xinjiang and its influencing factor [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 158-166. |
| [15] | Wei Mao, Yanghe Zhao, Bohao He, Biying Jia, Weidong Li. Review on degradation mechanism and restoration strategies of seagrass ecosystem [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 87-95. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech