
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 304-317.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00188
Lingguang Zhang1( ), Caisheng Shen1,2, Yanli Huang3, Zaduo4, Lazhen5, Yan Zhang6, Zhengcai Zhang1(
), Caisheng Shen1,2, Yanli Huang3, Zaduo4, Lazhen5, Yan Zhang6, Zhengcai Zhang1( )
)
Received:2024-11-27
Revised:2024-12-30
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-13
Contact:
Zhengcai Zhang
CLC Number:
Lingguang Zhang, Caisheng Shen, Yanli Huang, Zaduo, Lazhen, Yan Zhang, Zhengcai Zhang. The spatial variations of sand drift potential in Yarlung Zangbo River Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(1): 304-317.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00188
| 流域划分 | 站点名称 | 纬度(N)/(°) | 经度(E)/(°) | 海拔/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上游 | 帕羊 | 30.04 | 83.47 | 4 583.6 |
| 拉让 | 29.76 | 84.03 | 4 583.0 | |
| 仲巴 | 29.68 | 84.03 | 4 558.8 | |
| 亚热 | 29.53 | 84.04 | 4 561.0 | |
| 中游 | 昌果 | 29.29 | 84.44 | 4 576.0 |
| 萨嘎 | 29.34 | 85.23 | 4 523.6 | |
| 折巴 | 29.22 | 85.36 | 4 511.0 | |
| 差那 | 29.18 | 85.88 | 4 442.0 | |
| 夏如 | 29.21 | 86.24 | 4 429.7 | |
| 多白 | 29.19 | 86.80 | 4 131.9 | |
| 定日 | 28.65 | 87.12 | 4 322.0 | |
| 定结 | 28.38 | 87.77 | 4 200.4 | |
| 拉孜 | 29.09 | 87.63 | 4 001.2 | |
| 曲玛 | 29.28 | 87.73 | 3 970.0 | |
| 彭措林 | 29.37 | 88.07 | 3 952.0 | |
| 谢通门 | 29.37 | 88.57 | 3 898.0 | |
| 江当 | 29.34 | 89.25 | 3 808.9 | |
| 联乡 | 29.30 | 89.56 | 3 934.0 | |
| 仁布 | 29.30 | 89.79 | 3 792.9 | |
| 尼木 | 29.34 | 90.06 | 3 757.2 | |
| 吞巴 | 29.34 | 90.29 | 3 695.0 | |
| 浪卡子 | 28.97 | 90.40 | 4 432.9 | |
| 茶巴拉 | 29.26 | 90.53 | 3 631.0 | |
| 曲水 | 29.36 | 90.74 | 3 589.2 | |
| 贡嘎 | 29.30 | 90.97 | 3 565.8 | |
| 杰德秀 | 29.28 | 91.13 | 3 566.0 | |
| 扎囊 | 29.26 | 91.33 | 3 567.6 | |
| 桑耶寺 | 29.33 | 91.50 | 3 569.8 | |
| 多颇章 | 29.32 | 91.68 | 3 710.2 | |
| 泽当 | 29.27 | 91.77 | 3 561.2 | |
| 桑日 | 29.23 | 92.00 | 3 584.5 | |
| 曲松 | 29.23 | 92.21 | 4 210.8 | |
| 加查 | 29.14 | 92.58 | 3 261.2 | |
| 仲达 | 29.06 | 92.83 | 3 143.0 | |
| 朗县 | 29.05 | 93.08 | 3 118.5 | |
| 下游 | 卧龙 | 29.13 | 93.73 | 2 984.2 |
| 扎西绕登 | 29.18 | 93.90 | 2 978.7 | |
| 羌纳 | 29.35 | 94.42 | 3 014.2 | |
| 丹娘 | 29.45 | 94.69 | 2 986.5 |
Table 1 Synopsis of stations in Yarlung Zangbo River Basin
| 流域划分 | 站点名称 | 纬度(N)/(°) | 经度(E)/(°) | 海拔/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上游 | 帕羊 | 30.04 | 83.47 | 4 583.6 |
| 拉让 | 29.76 | 84.03 | 4 583.0 | |
| 仲巴 | 29.68 | 84.03 | 4 558.8 | |
| 亚热 | 29.53 | 84.04 | 4 561.0 | |
| 中游 | 昌果 | 29.29 | 84.44 | 4 576.0 |
| 萨嘎 | 29.34 | 85.23 | 4 523.6 | |
| 折巴 | 29.22 | 85.36 | 4 511.0 | |
| 差那 | 29.18 | 85.88 | 4 442.0 | |
| 夏如 | 29.21 | 86.24 | 4 429.7 | |
| 多白 | 29.19 | 86.80 | 4 131.9 | |
| 定日 | 28.65 | 87.12 | 4 322.0 | |
| 定结 | 28.38 | 87.77 | 4 200.4 | |
| 拉孜 | 29.09 | 87.63 | 4 001.2 | |
| 曲玛 | 29.28 | 87.73 | 3 970.0 | |
| 彭措林 | 29.37 | 88.07 | 3 952.0 | |
| 谢通门 | 29.37 | 88.57 | 3 898.0 | |
| 江当 | 29.34 | 89.25 | 3 808.9 | |
| 联乡 | 29.30 | 89.56 | 3 934.0 | |
| 仁布 | 29.30 | 89.79 | 3 792.9 | |
| 尼木 | 29.34 | 90.06 | 3 757.2 | |
| 吞巴 | 29.34 | 90.29 | 3 695.0 | |
| 浪卡子 | 28.97 | 90.40 | 4 432.9 | |
| 茶巴拉 | 29.26 | 90.53 | 3 631.0 | |
| 曲水 | 29.36 | 90.74 | 3 589.2 | |
| 贡嘎 | 29.30 | 90.97 | 3 565.8 | |
| 杰德秀 | 29.28 | 91.13 | 3 566.0 | |
| 扎囊 | 29.26 | 91.33 | 3 567.6 | |
| 桑耶寺 | 29.33 | 91.50 | 3 569.8 | |
| 多颇章 | 29.32 | 91.68 | 3 710.2 | |
| 泽当 | 29.27 | 91.77 | 3 561.2 | |
| 桑日 | 29.23 | 92.00 | 3 584.5 | |
| 曲松 | 29.23 | 92.21 | 4 210.8 | |
| 加查 | 29.14 | 92.58 | 3 261.2 | |
| 仲达 | 29.06 | 92.83 | 3 143.0 | |
| 朗县 | 29.05 | 93.08 | 3 118.5 | |
| 下游 | 卧龙 | 29.13 | 93.73 | 2 984.2 |
| 扎西绕登 | 29.18 | 93.90 | 2 978.7 | |
| 羌纳 | 29.35 | 94.42 | 3 014.2 | |
| 丹娘 | 29.45 | 94.69 | 2 986.5 |
| 流域划分 | 站点名称 | DP/VU | RDP/VU | RDD/(°) | RDP/DP | 流域划分 | 站点名称 | DP/VU | RDP/VU | RDD/(°) | RDP/DP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上游 | 帕羊 | 169.0 | 143.6 | 90 | 0.85 | 中游 | 吞巴 | 251.2 | 133.1 | 40 | 0.53 |
| 拉让 | 252.6 | 190.6 | 67 | 0.75 | 浪卡子 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 117 | 0.68 | ||
| 仲巴 | 839.7 | 652.2 | 24 | 0.78 | 茶巴拉 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 114 | 0.48 | ||
| 亚热 | 411.7 | 385.5 | 29 | 0.94 | 曲水 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 97 | 0.88 | ||
| 中游 | 昌果 | 294.6 | 250.6 | 68 | 0.85 | 贡嘎 | 10.6 | 8.1 | 61 | 0.76 | |
| 萨嘎 | 9.5 | 0.3 | 135 | 0.04 | 杰德秀 | 5.1 | 2.7 | 316 | 0.53 | ||
| 折巴 | 269.8 | 210.9 | 61 | 0.78 | 扎囊 | 53.1 | 13.6 | 335 | 0.26 | ||
| 差那 | 267.0 | 254.0 | 28 | 0.95 | 桑耶寺 | 35.2 | 20.9 | 198 | 0.59 | ||
| 夏如 | 163.2 | 14.2 | 68 | 0.09 | 多颇章 | 20.6 | 13.1 | 194 | 0.63 | ||
| 多白 | 265.3 | 215.1 | 76 | 0.81 | 泽当 | 9.5 | 6.8 | 26 | 0.72 | ||
| 定日 | 52.0 | 49.6 | 88 | 0.95 | 桑日 | 45.0 | 20.8 | 3 | 0.46 | ||
| 定结 | 256.9 | 233.7 | 359 | 0.91 | 曲松 | 487.8 | 399.3 | 0 | 0.82 | ||
| 拉孜 | 11.6 | 8.1 | 71 | 0.70 | 加查 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 69 | 0.21 | ||
| 曲玛 | 15.3 | 2.9 | 110 | 0.19 | 仲达 | 100.8 | 86.7 | 247 | 0.86 | ||
| 彭措林 | 59.9 | 44.0 | 83 | 0.73 | 朗县 | 19.9 | 18.6 | 254 | 0.94 | ||
| 谢通门 | 62.2 | 30.1 | 112 | 0.48 | 下游 | 卧龙 | 194.3 | 141.2 | 213 | 0.73 | |
| 江当 | 12.5 | 10.1 | 75 | 0.80 | 扎西绕登 | 325.5 | 319.9 | 233 | 0.98 | ||
| 联乡 | 72.4 | 55.5 | 1 | 0.77 | 羌纳 | 264.0 | 237.6 | 358 | 0.90 | ||
| 仁布 | 19.8 | 9.7 | 72 | 0.49 | 丹娘 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 296 | 0.97 | ||
| 尼木 | 41.5 | 30.7 | 38 | 0.74 |
Table 2 Annual drift potential of stations in Yarlung Zangbo River Basin
| 流域划分 | 站点名称 | DP/VU | RDP/VU | RDD/(°) | RDP/DP | 流域划分 | 站点名称 | DP/VU | RDP/VU | RDD/(°) | RDP/DP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上游 | 帕羊 | 169.0 | 143.6 | 90 | 0.85 | 中游 | 吞巴 | 251.2 | 133.1 | 40 | 0.53 |
| 拉让 | 252.6 | 190.6 | 67 | 0.75 | 浪卡子 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 117 | 0.68 | ||
| 仲巴 | 839.7 | 652.2 | 24 | 0.78 | 茶巴拉 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 114 | 0.48 | ||
| 亚热 | 411.7 | 385.5 | 29 | 0.94 | 曲水 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 97 | 0.88 | ||
| 中游 | 昌果 | 294.6 | 250.6 | 68 | 0.85 | 贡嘎 | 10.6 | 8.1 | 61 | 0.76 | |
| 萨嘎 | 9.5 | 0.3 | 135 | 0.04 | 杰德秀 | 5.1 | 2.7 | 316 | 0.53 | ||
| 折巴 | 269.8 | 210.9 | 61 | 0.78 | 扎囊 | 53.1 | 13.6 | 335 | 0.26 | ||
| 差那 | 267.0 | 254.0 | 28 | 0.95 | 桑耶寺 | 35.2 | 20.9 | 198 | 0.59 | ||
| 夏如 | 163.2 | 14.2 | 68 | 0.09 | 多颇章 | 20.6 | 13.1 | 194 | 0.63 | ||
| 多白 | 265.3 | 215.1 | 76 | 0.81 | 泽当 | 9.5 | 6.8 | 26 | 0.72 | ||
| 定日 | 52.0 | 49.6 | 88 | 0.95 | 桑日 | 45.0 | 20.8 | 3 | 0.46 | ||
| 定结 | 256.9 | 233.7 | 359 | 0.91 | 曲松 | 487.8 | 399.3 | 0 | 0.82 | ||
| 拉孜 | 11.6 | 8.1 | 71 | 0.70 | 加查 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 69 | 0.21 | ||
| 曲玛 | 15.3 | 2.9 | 110 | 0.19 | 仲达 | 100.8 | 86.7 | 247 | 0.86 | ||
| 彭措林 | 59.9 | 44.0 | 83 | 0.73 | 朗县 | 19.9 | 18.6 | 254 | 0.94 | ||
| 谢通门 | 62.2 | 30.1 | 112 | 0.48 | 下游 | 卧龙 | 194.3 | 141.2 | 213 | 0.73 | |
| 江当 | 12.5 | 10.1 | 75 | 0.80 | 扎西绕登 | 325.5 | 319.9 | 233 | 0.98 | ||
| 联乡 | 72.4 | 55.5 | 1 | 0.77 | 羌纳 | 264.0 | 237.6 | 358 | 0.90 | ||
| 仁布 | 19.8 | 9.7 | 72 | 0.49 | 丹娘 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 296 | 0.97 | ||
| 尼木 | 41.5 | 30.7 | 38 | 0.74 |
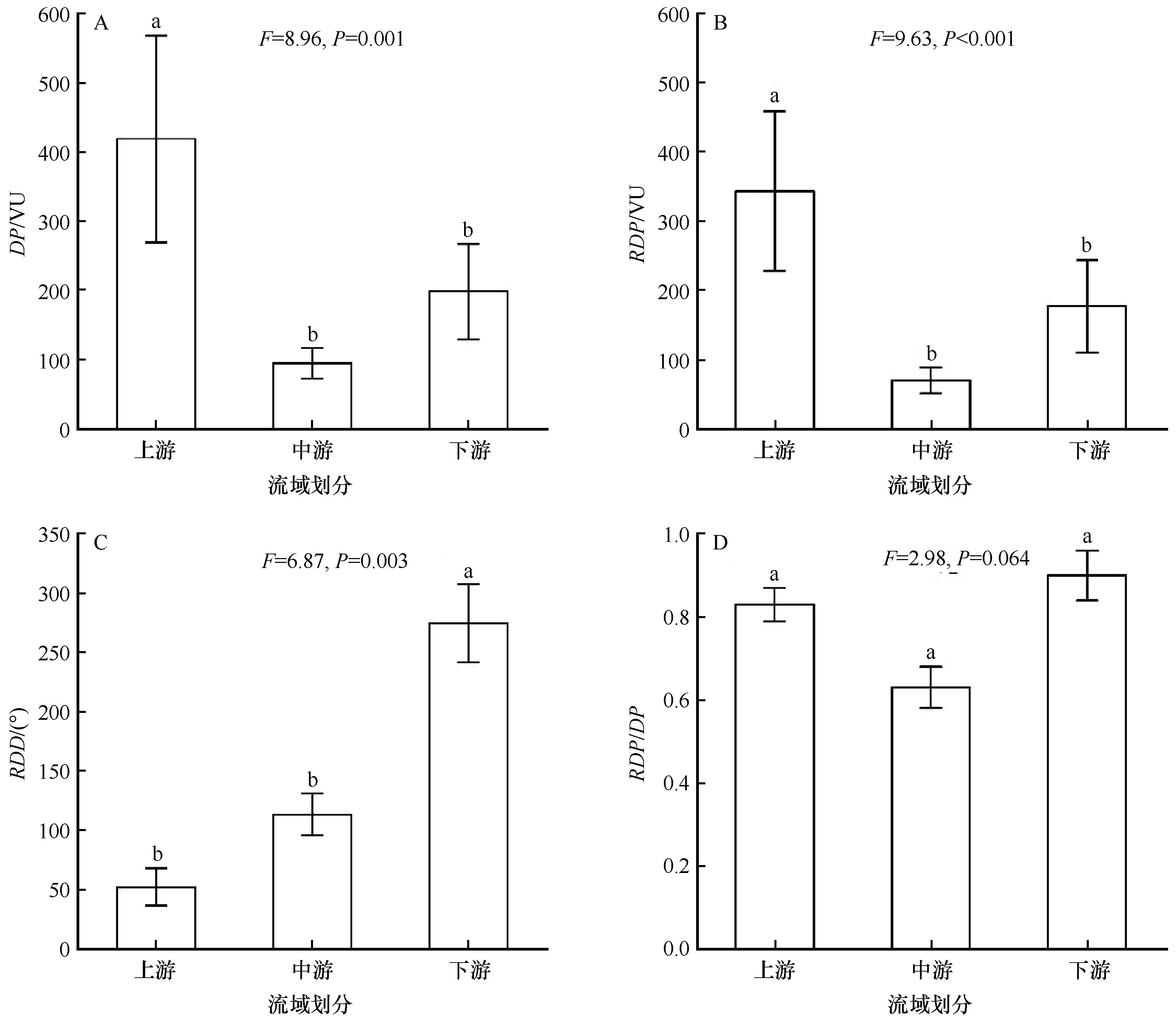
Fig.3 Drift potential of the whole year among upper, middle and downside reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. a, b and c indicate significant differences among different regions
| 站点 | DP/VU | RDP/VU | RDD/(°) | RDP/DP | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | ||
| 上游 | 帕羊 | 66.6 | 25.0 | 28.6 | 48.8 | 62.2 | 9.0 | 27.4 | 45.9 | 96 | 95 | 82 | 85 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| 拉让 | 81.6 | 48.3 | 39.5 | 83.1 | 61.0 | 39.7 | 34.8 | 69.6 | 84 | 23 | 64 | 75 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.84 | |
| 仲巴 | 242.4 | 331.2 | 142.7 | 123.4 | 164.6 | 319.0 | 118.8 | 92.9 | 31 | 7 | 26 | 70 | 0.68 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.75 | |
| 亚热 | 127.2 | 164.0 | 70.3 | 50.2 | 114.2 | 162.0 | 67.6 | 42.0 | 31 | 27 | 29 | 33 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.84 | |
| 中游 | 昌果 | 76.2 | 51.02 | 63.2 | 104.1 | 67.4 | 25.6 | 59.2 | 99.9 | 72 | 49 | 70 | 69 | 0.88 | 0.50 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 萨嘎 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 0.6 | 3.4 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 23 | 192 | 62 | 4 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 0.16 | 0.06 | |
| 折巴 | 115.6 | 76.6 | 32.5 | 45.1 | 97.2 | 60.2 | 27.1 | 37.0 | 60 | 43 | 58 | 98 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.82 | |
| 差那 | 101.9 | 61.9 | 44.0 | 59.3 | 98.4 | 54.2 | 43.0 | 58.5 | 27 | 26 | 29 | 30 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| 夏如 | 46.2 | 59.4 | 16.2 | 41.4 | 13.8 | 27.7 | 7.3 | 28.1 | 99 | 291 | 352 | 110 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.68 | |
| 多白 | 74.9 | 26.5 | 52.0 | 111.9 | 63.3 | 6.3 | 42.9 | 103.2 | 79 | 92 | 70 | 75 | 0.85 | 0.24 | 0.82 | 0.92 | |
| 定日 | 17.0 | 0.9 | 7.2 | 26.9 | 16.6 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 26.1 | 89 | 86 | 77 | 91 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| 定结 | 113.1 | 59.8 | 38.8 | 45.1 | 105.4 | 56.3 | 36.0 | 36.2 | 358 | 357 | 359 | 0 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.80 | |
| 拉孜 | 4.1 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 64 | 36 | 60 | 104 | 0.80 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.75 | |
| 曲玛 | 6.0 | 4.7 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 117 | 192 | 63 | 17 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.59 | |
| 彭措林 | 19.7 | 9.4 | 10.7 | 20.1 | 13.9 | 4.4 | 8.7 | 18.2 | 81 | 121 | 70 | 82 | 0.70 | 0.47 | 0.81 | 0.91 | |
| 谢通门 | 16.1 | 12.1 | 12.1 | 21.8 | 9.3 | 7.3 | 7.0 | 15.2 | 105 | 194 | 125 | 81 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.70 | |
| 江当 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 5.3 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 5.3 | 85 | 267 | 71 | 71 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.99 | |
| 联乡 | 28.7 | 19.0 | 12.0 | 12.6 | 24.7 | 12.7 | 8.0 | 11.1 | 10 | 347 | 345 | 10 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.88 | |
| 仁布 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 2.5 | 5.9 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 5.6 | 74 | 184 | 61 | 61 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 0.96 | |
| 尼木 | 17.1 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 11.7 | 13.8 | 1.7 | 5.7 | 10.2 | 42 | 347 | 41 | 39 | 0.81 | 0.28 | 0.88 | 0.87 | |
| 吞巴 | 94.5 | 41.4 | 45.2 | 70.1 | 47.1 | 6.4 | 35.0 | 56.6 | 43 | 251 | 38 | 42 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.77 | 0.81 | |
| 浪卡子 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 125 | 116 | 122 | 102 | 0.63 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.73 | |
| 茶巴拉 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 155 | 161 | 100 | 68 | 0.81 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.90 | |
| 曲水 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 110 | 135 | 85 | 92 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.89 | |
| 贡嘎 | 5.8 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 56 | 47 | 76 | 62 | 0.78 | 0.17 | 0.88 | 0.84 | |
| 杰德秀 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 339 | 257 | 338 | 313 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.72 | |
| 扎囊 | 19.8 | 16.5 | 7.6 | 9.3 | 6.3 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 328 | 290 | 47 | 10 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.35 | |
| 桑耶寺 | 13.1 | 10.5 | 3.4 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 1.4 | 2.9 | 201 | 196 | 183 | 201 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 0.35 | |
| 多颇章 | 10.4 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 3.8 | 199 | 191 | 202 | 186 | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.69 | |
| 泽当 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 18 | 77 | 31 | 22 | 0.82 | 0.53 | 0.67 | 0.77 | |
| 桑日 | 19.0 | 10.3 | 8.6 | 7.1 | 16.9 | 6.7 | 8.2 | 5.5 | 2 | 352 | 175 | 7 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 0.95 | 0.77 | |
| 曲松 | 176.0 | 65.6 | 118.7 | 127.5 | 132.6 | 56.4 | 110.3 | 100.6 | 356 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.79 | |
| 加查 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 107 | 321 | — | — | 0.56 | 0.60 | — | — | |
| 仲达 | 45.2 | 15.0 | 14.1 | 26.6 | 41.7 | 8.3 | 11.3 | 25.7 | 244 | 261 | 252 | 245 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.80 | 0.97 | |
| 朗县 | 7.1 | 3.4 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 6.5 | 3.2 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 257 | 249 | 252 | 254 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.98 | |
| 下游 | 卧龙 | 56.5 | 27.6 | 50.3 | 59.9 | 32.6 | 15.8 | 41.5 | 51.3 | 217 | 208 | 213 | 211 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.83 | 0.86 |
| 扎西绕登 | 118.3 | 55.8 | 57.7 | 93.7 | 116.6 | 54.8 | 56.8 | 92.0 | 234 | 235 | 230 | 231 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | |
| 羌纳 | 81.9 | 77.6 | 38.1 | 66.3 | 73.1 | 68.8 | 34.2 | 62.0 | 352 | 2 | 359 | 358 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.94 | |
| 丹娘 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 296 | 295 | 299 | 295 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
Table 3 Seasonal drift potential of stations in Yarlung Zangbo River Basin
| 站点 | DP/VU | RDP/VU | RDD/(°) | RDP/DP | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | ||
| 上游 | 帕羊 | 66.6 | 25.0 | 28.6 | 48.8 | 62.2 | 9.0 | 27.4 | 45.9 | 96 | 95 | 82 | 85 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| 拉让 | 81.6 | 48.3 | 39.5 | 83.1 | 61.0 | 39.7 | 34.8 | 69.6 | 84 | 23 | 64 | 75 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.84 | |
| 仲巴 | 242.4 | 331.2 | 142.7 | 123.4 | 164.6 | 319.0 | 118.8 | 92.9 | 31 | 7 | 26 | 70 | 0.68 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.75 | |
| 亚热 | 127.2 | 164.0 | 70.3 | 50.2 | 114.2 | 162.0 | 67.6 | 42.0 | 31 | 27 | 29 | 33 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.84 | |
| 中游 | 昌果 | 76.2 | 51.02 | 63.2 | 104.1 | 67.4 | 25.6 | 59.2 | 99.9 | 72 | 49 | 70 | 69 | 0.88 | 0.50 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 萨嘎 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 0.6 | 3.4 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 23 | 192 | 62 | 4 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 0.16 | 0.06 | |
| 折巴 | 115.6 | 76.6 | 32.5 | 45.1 | 97.2 | 60.2 | 27.1 | 37.0 | 60 | 43 | 58 | 98 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.82 | |
| 差那 | 101.9 | 61.9 | 44.0 | 59.3 | 98.4 | 54.2 | 43.0 | 58.5 | 27 | 26 | 29 | 30 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| 夏如 | 46.2 | 59.4 | 16.2 | 41.4 | 13.8 | 27.7 | 7.3 | 28.1 | 99 | 291 | 352 | 110 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.68 | |
| 多白 | 74.9 | 26.5 | 52.0 | 111.9 | 63.3 | 6.3 | 42.9 | 103.2 | 79 | 92 | 70 | 75 | 0.85 | 0.24 | 0.82 | 0.92 | |
| 定日 | 17.0 | 0.9 | 7.2 | 26.9 | 16.6 | 0.1 | 7.1 | 26.1 | 89 | 86 | 77 | 91 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| 定结 | 113.1 | 59.8 | 38.8 | 45.1 | 105.4 | 56.3 | 36.0 | 36.2 | 358 | 357 | 359 | 0 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.80 | |
| 拉孜 | 4.1 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 64 | 36 | 60 | 104 | 0.80 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.75 | |
| 曲玛 | 6.0 | 4.7 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 117 | 192 | 63 | 17 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.59 | |
| 彭措林 | 19.7 | 9.4 | 10.7 | 20.1 | 13.9 | 4.4 | 8.7 | 18.2 | 81 | 121 | 70 | 82 | 0.70 | 0.47 | 0.81 | 0.91 | |
| 谢通门 | 16.1 | 12.1 | 12.1 | 21.8 | 9.3 | 7.3 | 7.0 | 15.2 | 105 | 194 | 125 | 81 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.70 | |
| 江当 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 5.3 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 5.3 | 85 | 267 | 71 | 71 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 0.87 | 0.99 | |
| 联乡 | 28.7 | 19.0 | 12.0 | 12.6 | 24.7 | 12.7 | 8.0 | 11.1 | 10 | 347 | 345 | 10 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.88 | |
| 仁布 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 2.5 | 5.9 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 5.6 | 74 | 184 | 61 | 61 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 0.96 | |
| 尼木 | 17.1 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 11.7 | 13.8 | 1.7 | 5.7 | 10.2 | 42 | 347 | 41 | 39 | 0.81 | 0.28 | 0.88 | 0.87 | |
| 吞巴 | 94.5 | 41.4 | 45.2 | 70.1 | 47.1 | 6.4 | 35.0 | 56.6 | 43 | 251 | 38 | 42 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.77 | 0.81 | |
| 浪卡子 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 125 | 116 | 122 | 102 | 0.63 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.73 | |
| 茶巴拉 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 155 | 161 | 100 | 68 | 0.81 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.90 | |
| 曲水 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 110 | 135 | 85 | 92 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.89 | |
| 贡嘎 | 5.8 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 56 | 47 | 76 | 62 | 0.78 | 0.17 | 0.88 | 0.84 | |
| 杰德秀 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 339 | 257 | 338 | 313 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.72 | |
| 扎囊 | 19.8 | 16.5 | 7.6 | 9.3 | 6.3 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 328 | 290 | 47 | 10 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.35 | |
| 桑耶寺 | 13.1 | 10.5 | 3.4 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 8.9 | 1.4 | 2.9 | 201 | 196 | 183 | 201 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 0.35 | |
| 多颇章 | 10.4 | 3.1 | 1.6 | 5.5 | 6.5 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 3.8 | 199 | 191 | 202 | 186 | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.69 | |
| 泽当 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 18 | 77 | 31 | 22 | 0.82 | 0.53 | 0.67 | 0.77 | |
| 桑日 | 19.0 | 10.3 | 8.6 | 7.1 | 16.9 | 6.7 | 8.2 | 5.5 | 2 | 352 | 175 | 7 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 0.95 | 0.77 | |
| 曲松 | 176.0 | 65.6 | 118.7 | 127.5 | 132.6 | 56.4 | 110.3 | 100.6 | 356 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.79 | |
| 加查 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 107 | 321 | — | — | 0.56 | 0.60 | — | — | |
| 仲达 | 45.2 | 15.0 | 14.1 | 26.6 | 41.7 | 8.3 | 11.3 | 25.7 | 244 | 261 | 252 | 245 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.80 | 0.97 | |
| 朗县 | 7.1 | 3.4 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 6.5 | 3.2 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 257 | 249 | 252 | 254 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.98 | |
| 下游 | 卧龙 | 56.5 | 27.6 | 50.3 | 59.9 | 32.6 | 15.8 | 41.5 | 51.3 | 217 | 208 | 213 | 211 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.83 | 0.86 |
| 扎西绕登 | 118.3 | 55.8 | 57.7 | 93.7 | 116.6 | 54.8 | 56.8 | 92.0 | 234 | 235 | 230 | 231 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | |
| 羌纳 | 81.9 | 77.6 | 38.1 | 66.3 | 73.1 | 68.8 | 34.2 | 62.0 | 352 | 2 | 359 | 358 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.94 | |
| 丹娘 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 296 | 295 | 299 | 295 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
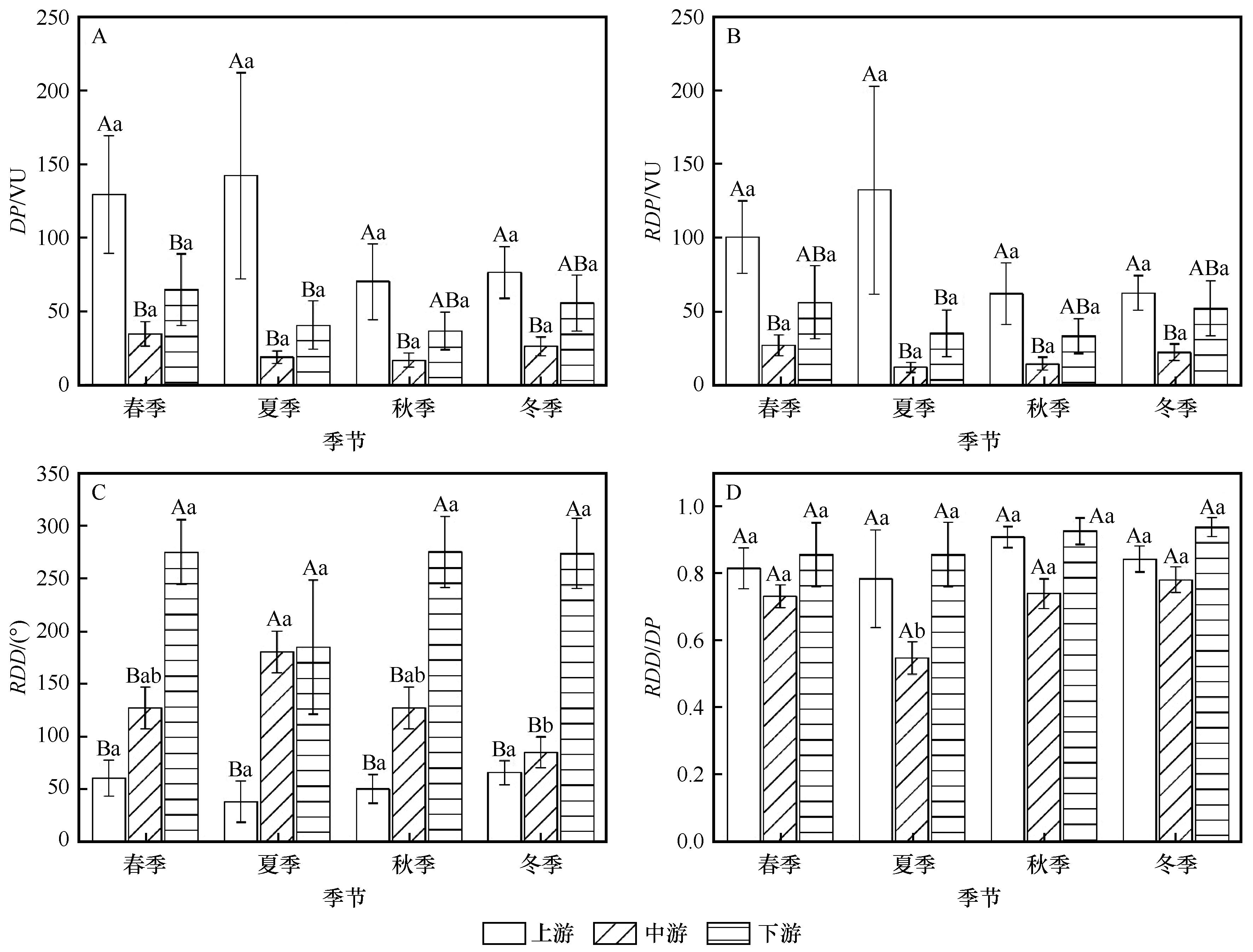
Fig.8 Seasonal drift potential statistics among upper, middle and downside reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Different capital letters indicate significant differences among different regions in the same season, and different lowercases indicate significant differences among different seasons in the same region (P<0.05)
| 1 | Dong Z B, Hu G Y, Qian G Q,et al.High-altitude aeolian research on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2017,55(4):864-901. |
| 2 | Dong Z B, Hu G Y, Yan C Z,et al.Aeolian desertification and its causes in the Zoige Plateau of China's Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2010,59(8):1731-1740. |
| 3 | Shen W S, Li H D, Sun M,et al.Dynamics of aeolian sandy land in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin of Tibet,China from 1975 to 2008[J].Global and Planetary Change,2012,86-87:37-44. |
| 4 | 孙小雲,房彦杰,赵景峰,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠输沙势时空分布特征[J].干旱区地理,2020,43(1):38-47. |
| 5 | 张正偲,董治宝,赵爱国,等.库姆塔格沙漠风沙活动特征[J].干旱区地理,2010,33(6):939-946. |
| 6 | 庞营军,吴波,贾晓红,等.毛乌素沙地风况及输沙势特征[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(1):62-67. |
| 7 | Shen Y P, Zhang C L, Zhang Y J.Assessment of wind erosivity based on wind speed conversion over different averaging times[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments,2023,23(5):2037-2047. |
| 8 | Zhang C L, Shen Y P, Li Q,et al.Sediment grain-size characteristics and relevant correlations to the aeolian environment in China's eastern desert region[J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,627:586-599. |
| 9 | 张正偲,董治宝,赵爱国,等.输沙量与输沙势的关系[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(4):824-827. |
| 10 | Abbasi H R, Opp C, Groll M,et al.Wind regime and aeolian sand transport in Khuzestan Sand Sea[J].Aeolian Research,2021,53:100746. |
| 11 | Louassa S.Sand drift potential in western Algerian Hautes Plaines[J].Aeolian Research,2018,34:27-34. |
| 12 | Meng N, Wang N A, Zhao L Q,et al.Wind regimes and associated sand dune types in the hinterland of the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2022,14(5):473-489. |
| 13 | Hu G Y, Dong Z B, Zhang Z C,et al.Wind regime and aeolian landforms on the eastern shore of Qinghai Lake,northeastern Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2021,188:104451. |
| 14 | 王永胜,杨文斌,李永华,等.库姆塔格沙漠东缘荒漠绿洲过渡带风况及输沙势[J].干旱区资源与环境,2015,29(1):140-144. |
| 15 | 张正偲,董治宝,赵爱国.输沙势计算中的“时距”问题[J].干旱区地理,2010,33(2):177-182. |
| 16 | Zhang Z C, Dong Z B, Zhao A G.The effect of the time interval used to calculate mean wind velocity on the calculated drift potential,relative drift potential,and resultant drift direction for sands from three deserts in northern China[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2016,123(1/2):151-160. |
| 17 | Zhou N, Li Q, Zhang C L,et al.Grain size characteristics of aeolian sands and their implications for the aeolian dynamics of dunefields within a river valley on the southern Tibet Plateau:a case study from the Yarlung Zangbo river valley[J].CATENA,2021,196:104794. |
| 18 | Zhang Z C, Ma P F, La Z,et al.Aeolian sediment provenance and transport in the upper and middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River,Tibet Plateau[J].Basin Research,2022,35(2):762-783. |
| 19 | Yang J H, Xia D S, Wang S Y,et al.Near-surface wind environment in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin,southern Tibetan Plateau[J].Journal of Arid Land,2020,12(6):917-936. |
| 20 | 张正偲,张焱,马鹏飞,等.雅鲁藏布江中游风沙区典型下垫面空气动力学参数研究[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(4):997-1005. |
| 21 | 李森,董光荣,申建友,等.雅鲁藏布江河谷风沙地貌形成机制与发育模式[J].中国科学:地球科学,1999,29(1):88-96. |
| 22 | Li T Y, Zhang J F, Wu Y Q,et al.Holocene aeolian activities linked to Indian summer monsoon in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2020,30(12):2002-2014. |
| 23 | Ma P F, Zhang Z C, Zhang Y,et al.Effect of meteorological conditions on PM10 concentrations in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River,Tibet Plateau[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2023,151(1/2):725-737. |
| 24 | Zhang Z C, Zhang Y, Ma P F,et al.Aeolian sediment transport rates in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River,Tibet Plateau[J].Science of the Total Environment,2022,826:154238. |
| 25 | 刘婷,贾晓鹏,陈定梅,等.雅鲁藏布江中游平坦流沙地表空气动力学特征[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(5):194-203. |
| 26 | 马鹏飞,高佳佳,扎多,等.雅鲁藏布江中游风沙灾害区地表沉积物养分特征[J].干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(6):96-101. |
| 27 | 张焱,马鹏飞,潘凯佳,等.雅鲁藏布江中游江心洲和河漫滩沉积物粒度特征[J].干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(8):161-168. |
| 28 | Zhang Y, Zhang Z C, Ma P F,et al.Wind regime features and their impacts on the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River on the Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2023,15(10):1174-1195. |
| 29 | 刘佳驹,李金城,郭怀成,等.基于人工神经网络的雅鲁藏布江水化学变化趋势研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2023,59(6):1043-1051. |
| 30 | 李世剑,康满春,刘流,等.雅鲁藏布江上游干、支流沉积物总有机碳分布特征初探[J].冰川冻土,2024,46(2):443-456. |
| 31 | Zhou N, Zhang C L, Wu X X,et al.The geomorphology and evolution of aeolian landforms within a river valley in a semi-humid environment:a case study from Mainling Valley,Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Geomorphology,2014,224:27-38. |
| 32 | Fryberger S G, Dean G.Dune forms and wind regime[M]//McKee E D.A Study of Global Sand Seas. Hawaii,USA:University Press of the Pacific,1979. |
| 33 | 赵宏胜,党晓宏,蒙仲举,等.黄河流域西柳沟中游输沙势及风沙入黄量估算[J].中国环境科学,2024,44(5):2606-2618. |
| 34 | 夏敦胜,杨军怀,王树源,等.雅鲁藏布江流域风成沉积空间格局、沉积模式及其环境效应[J].地学前缘,2023,30(4):229-244. |
| 35 | 田越,苗峻峰.中国地区山谷风研究进展[J].气象科技,2019,47(1):41-51. |
| 36 | 杨军怀,夏敦胜,高福元,等.雅鲁藏布江流域风成沉积研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2020,35(8):863-877. |
| 37 | 苟诗薇,伍永秋,夏冬冬,等.青藏高原冬、春季沙尘暴频次时空分布特征及其环流背景[J].自然灾害学报,2012,21(5):135-143. |
| 38 | Yang Z L, Qian G Q, Dong Z B,et al.Migration of barchan dunes and factors that influence migration in the Sanlongsha dune field of the northern Kumtagh Sand Sea,China[J].Geomorphology,2021,378:107615. |
| 39 | Zamani S, Mahmoodabadi M, Yazdanpanah N,et al.Meteorological application of wind speed and direction linked to remote sensing images for the modelling of sand drift potential and dune morphology[J].Meterological Applications,2020,27(1):e1851. |
| 40 | Liu Y, Wang Y S, Shen T.Spatial distribution and formation mechanism of aeolian sand in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River[J].Journal of Mountain Science,2019,16(9):1987-2000. |
| 41 | Du S S, Wu Y Q, Tan L H,et al.Geochemical characteristics of fine and coarse fractions of sediments in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin (southern Tibet,China)[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2018,77(9):337. |
| 42 | Wang B N, Gong J F, Zuza A V,et al.Aeolian sand dunes alongside the Yarlung River in southern Tibet:a provenance perspective[J].Geological Journal,2021,56(5):2625-2636. |
| [1] | Na Gao, Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong. Change characteristics of spatial distribution pattern of sandy land in Gonghe Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(1): 204-214. |
| [2] | Youyuan Guo, Guangqiang Qian, Zhuanling Yang, Xuegang Xing. Morphology, grain size and environmental wind regine of granule ripples in the Sanlongsha area of the Kumtagh Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 37-45. |
| [3] | Cong Hua, Yun Cao, Jikang Wang, Ran Xu. Spring sand-dust weather distribution in Hunshandak Sandy Land in relation to vegetation and wind in 2000-2023 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 71-80. |
| [4] | Tian Yong, Jinxia Zhang, Lijuan Chen, Haiyang Xi, Binwu Zhang, Kaiyuan Gan. Characteristics of soil water and salt spatial differentiation along the Yellow River section of Ulan Buh Desert and its causes [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 247-258. |
| [5] | Yongtao Gou, Yongxiang Wu, Bo Peng, Yong Zhang, Huiping Kong, Xinghong Zhao, Pengju Ji, Yunhao Li, Mingzhu He, Mei Shao, Mingliang Tan, Junfeng Lu. Characteristics of aeolian sand activity in typical section of protection system of Wuhai-Maqen Highway (G1816) in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 279-289. |
| [6] | Yongtao Gou, Yongxiang Wu, Bo Peng, Hao Yang, Jinku Ma, Chaohui Wang, Hailong Bai, Mingzhu He, Mingliang Tan, Mei Shao, Junfeng Lu. Evaluation of sand-fixation effect of different configuration measures of protection system in Wuhai-Maqen Highway in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 264-272. |
| [7] | Qiang Li. Characteristics of aeolian environment in typical sand-hazard sections along the Jiuquan-Dongfeng section of Jiuquan-Ejin Banner Railway [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 220-228. |
| [8] | Yuwei Li, Bo Wang, Yuhai Bao, Yanlong Han, Maolin Yan, Weifeng Wang. Effects of the development of grassland blowouts on soil ecological stoichiometry [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 166-175. |
| [9] | Jiyan Li, Dehua Xu, Yaoyao Zhang, Qianwen Xue, Ling Zhou. Characteristics of wind regime and sand drift potential in the Qaidam Basin, northwestern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 223-231. |
| [10] | Xiya Liu, Haibing Wang, Hejun Zuo, Wensuyalatu, Haiying Huo. Wind conditions and drift potential in Bayinwenduer Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 41-48. |
| [11] | Hongxue Zhang, Kecun Zhang, Zhishan An, Yanping Yu. Wind dynamic environment and sediment grain size characteristics of shrub desert along Dunhuang-Golmud Railway [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 49-58. |
| [12] | Haixuan Tao, Chunxiu Guo, Junmei Ma, Zhongwen Wang, Heran Zhao, Dacheng Song, Fanglan He. Influences of soil crust development on soil seed bank of herbaceous plants in arid desert area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 89-97. |
| [13] | Yadong Jiang, Shijie Lv, Hongmei Liu, Narenhua, Xinyu Liu. Analysis of quantitative characteristics and spatial distribution for main shrubs on the eastern edge of the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 295-304. |
| [14] | Jiapeng Pan, Kecun Zhang, Zhishan An, Hongxue Zhang, Chengjie Xue. Analysis of comprehensive benefits of wind-blown sand control projects: a case study of Heishanzui, Dunhuang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 233-242. |
| [15] | Xiangjie Li, Zhiwen Li, Dingding Du, Li Sun, Chu Hou, Shiqian Li, Wen Zhang. Sediments and spatial pattern characteristics of Vitex trifolia nebkhas in the Houtian sandy land of Nanchang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 211-220. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech