中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 221-231.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00041
收稿日期:2022-01-23
修回日期:2022-03-17
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-09-22
通讯作者:
王旭洋,周立业
作者简介:王旭洋(E-mail: xuyangwang@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Meng Yan1( ), Xuyang Wang2(
), Xuyang Wang2( ), Liye Zhou1(
), Liye Zhou1( ), Yuqiang Li2
), Yuqiang Li2
Received:2022-01-23
Revised:2022-03-17
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-09-22
Contact:
Xuyang Wang,Liye Zhou
摘要:
科尔沁沙地是中国半干旱地区沙漠化发展的典型地区和沙漠化防治的重点区域。本研究以科尔沁沙地为研究区域,以沙漠化逆转不同阶段的沙地为研究对象,通过野外调查和室内分析,采用空间代替时间的方法,在区域尺度上探讨了土壤有机碳对沙漠化过程的响应规律,并结合气候、植被和地形因子阐释了该区域土壤有机碳空间变异的主导因素。结果表明:(1)土壤有机碳含量随沙漠化程度的加剧表现出疏林草地(未沙漠化)>固定沙地(轻度沙漠化)>半固定沙地(中度沙漠化)>半流动沙地(重度沙漠化)>流动沙地(极重度沙漠化)。(2)固定沙地、半固定沙地、半流动沙地和流动沙地土壤有机碳密度分别比疏林草地降低了29.1%、49.3%、62.9%和84.1%。(3)随着沙漠化的发展,土壤质地发生粗化现象,即中、细砂粒含量明显增加,而土壤细颗粒(极细砂和黏粉粒)含量明显下降。(4)科尔沁沙地沙漠化过程中,土壤黏粉粒的损失是土壤粗化、有机碳含量下降的主要原因,而pH的变化受沙漠化影响较小。(5)气候因子是导致SOC含量受经纬度影响的主要因素,而地形因子的影响次之。
中图分类号:
闫蒙, 王旭洋, 周立业, 李玉强. 科尔沁沙地沙漠化过程中土壤有机碳含量变化特征及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 221-231.
Meng Yan, Xuyang Wang, Liye Zhou, Yuqiang Li. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in the process of desertification in Horqin Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 221-231.
| 沙漠化程度 | 裸沙面积占比/% | 植被盖度/% |
|---|---|---|
| 轻度沙漠化 | <5 | >60 |
| 中度沙漠化 | 5—25 | 30—60 |
| 重度沙漠化 | 25—50 | 10—30 |
| 极重度沙漠化 | >50 | <10 |
表1 科尔沁沙地沙漠化程度划分标准[16]
Table 1 Division standard of desertification degree in Horqin Sandy Land[16]
| 沙漠化程度 | 裸沙面积占比/% | 植被盖度/% |
|---|---|---|
| 轻度沙漠化 | <5 | >60 |
| 中度沙漠化 | 5—25 | 30—60 |
| 重度沙漠化 | 25—50 | 10—30 |
| 极重度沙漠化 | >50 | <10 |
| 粒径/mm | 分类 |
|---|---|
| 2.00—0.50 | 粗砂 |
| 0.50—0.25 | 中砂 |
| 0.25—0.10 | 细砂 |
| 0.10—0.05 | 极细砂 |
| <0.05 | 黏粉粒 |
表2 土壤粒级
Table 2 Soil particle size
| 粒径/mm | 分类 |
|---|---|
| 2.00—0.50 | 粗砂 |
| 0.50—0.25 | 中砂 |
| 0.25—0.10 | 细砂 |
| 0.10—0.05 | 极细砂 |
| <0.05 | 黏粉粒 |
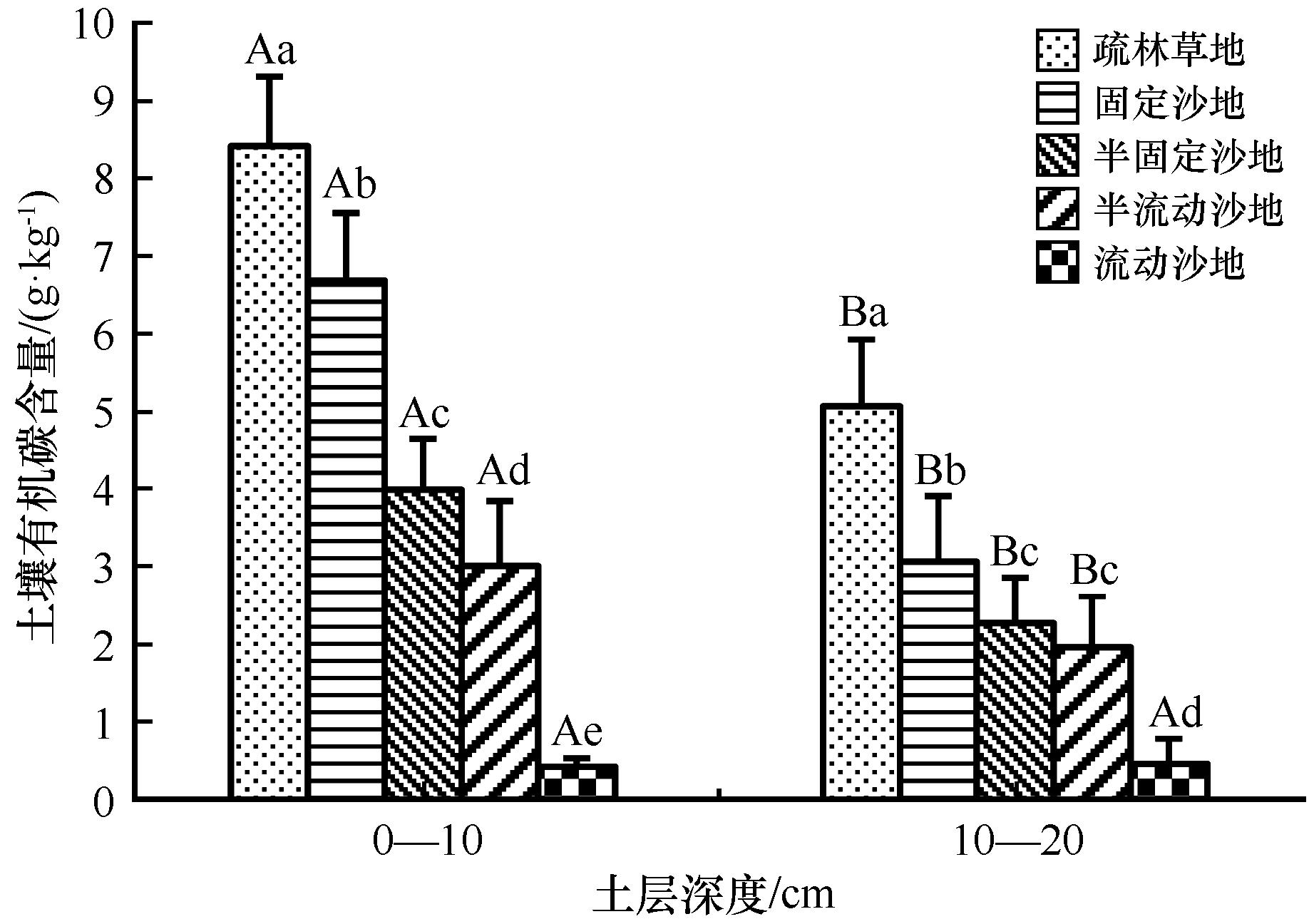
图2 同一土层深度土壤有机碳含量沿沙漠化程度分布特征不同大写字母表示同一沙漠化阶段不同土层间差异显著(P<0.05),不同小写字母表示同一土层不同沙漠化阶段间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.2 Distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon content along desertification degree at the same soil layer depth
| 土壤因子 | 土层深度 /cm | 沙漠化阶段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疏林草地 | 固定沙地 | 半固定沙地 | 半流动沙地 | 流动沙地 | ||
| 土壤全氮含量/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 0.91±0.11a | 0.60±0.04b | 0.33±0.14c | 0.15±0.06d | 0.07±0.01d |
| 10—20 | 0.37±0.05a | 0.27±0.01b | 0.17±0.07c | 0.12±0.07d | 0.06±0.01d | |
| 土壤全磷含量/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 0.20±0.01a | 0.15±0.04b | 0.11±0.03c | 0.09±0.02d | 0.06±0.02d |
| 10—20 | 0.15±0.01a | 0.10±0.03b | 0.08±0.02bc | 0.07±0.02c | 0.06±0.01c | |
| 土壤容重/(g·cm-3) | 0—10 | 1.61±0.06a | 1.63±0.06a | 1.64±0.07a | 1.63±0.06a | 1.64±0.04a |
| 10—20 | 1.64±0.06a | 1.66±0.04a | 1.66±0.07a | 1.67±0.06a | 1.67±0.03a | |
| pH值 | 0—10 | 7.02±0.69ab | 7.21±0.69ab | 6.80±0.61ab | 6.72±0.54b | 6.90±0.66ab |
| 10—20 | 7.07±0.47b | 7.59±0.84a | 7.09±0.67b | 6.88±0.61b | 6.90±0.71b | |
| 电导率/(μS·cm-1) | 0—10 | 42.38±4.71a | 39.17±3.87a | 27.18±4.20b | 19.55±3.88c | 13.82±1.32d |
| 10—20 | 36.20±2.50a | 37.41±5.44a | 25.19±5.53b | 21.70±3.79bc | 17.20±5.03c | |
| 粗砂/% | 0—10 | 1.29±0.33b | 1.39±0.40b | 2.10±0.40a | 1.90±0.42a | 0.58±0.36c |
| 10—20 | 1.27±0.46ab | 1.18±0.44ab | 2.01±0.31a | 2.18±0.93a | 0.75±0.12b | |
| 中砂/% | 0—10 | 14.36±3.57b | 18.02±3.23a | 20.74±2.86a | 19.62±2.85a | 9.54±2.08c |
| 10—20 | 16.23±3.87b | 17.48±1.33b | 23.82±5.31a | 19.26±4.27b | 9.25±1.13c | |
| 细砂/% | 0—10 | 45.43±7.38e | 51.70±7.83d | 57.40±8.07c | 64.60±7.99b | 72.61±8.87a |
| 10—20 | 54.02±2.54b | 56.07±5.55b | 59.02±6.44b | 60.40±6.01b | 74.70±7.22a | |
| 极细砂/% | 0—10 | 16.97±3.01a | 13.47±3.01b | 9.52±2.81c | 6.62±2.18d | 7.28±2.26d |
| 10—20 | 14.49±3.72a | 11.27±2.51b | 9.54±1.38b | 7.64±1.36b | 7.31±1.90b | |
| 黏粉粒/% | 0—10 | 21.20±3.52a | 17.11±4.01b | 11.69±3.45c | 6.79±2.53d | 9.43±2.44c |
| 10—20 | 14.89±3.90a | 12.04±3.34b | 8.20±2.61c | 5.97±2.20c | 6.02±2.14c | |
表3 不同沙漠化阶段不同土层土壤因子相关指标
Table 3 Relevant indicators of environmental factors of different soil layers in different desertification stages
| 土壤因子 | 土层深度 /cm | 沙漠化阶段 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 疏林草地 | 固定沙地 | 半固定沙地 | 半流动沙地 | 流动沙地 | ||
| 土壤全氮含量/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 0.91±0.11a | 0.60±0.04b | 0.33±0.14c | 0.15±0.06d | 0.07±0.01d |
| 10—20 | 0.37±0.05a | 0.27±0.01b | 0.17±0.07c | 0.12±0.07d | 0.06±0.01d | |
| 土壤全磷含量/(g·kg-1) | 0—10 | 0.20±0.01a | 0.15±0.04b | 0.11±0.03c | 0.09±0.02d | 0.06±0.02d |
| 10—20 | 0.15±0.01a | 0.10±0.03b | 0.08±0.02bc | 0.07±0.02c | 0.06±0.01c | |
| 土壤容重/(g·cm-3) | 0—10 | 1.61±0.06a | 1.63±0.06a | 1.64±0.07a | 1.63±0.06a | 1.64±0.04a |
| 10—20 | 1.64±0.06a | 1.66±0.04a | 1.66±0.07a | 1.67±0.06a | 1.67±0.03a | |
| pH值 | 0—10 | 7.02±0.69ab | 7.21±0.69ab | 6.80±0.61ab | 6.72±0.54b | 6.90±0.66ab |
| 10—20 | 7.07±0.47b | 7.59±0.84a | 7.09±0.67b | 6.88±0.61b | 6.90±0.71b | |
| 电导率/(μS·cm-1) | 0—10 | 42.38±4.71a | 39.17±3.87a | 27.18±4.20b | 19.55±3.88c | 13.82±1.32d |
| 10—20 | 36.20±2.50a | 37.41±5.44a | 25.19±5.53b | 21.70±3.79bc | 17.20±5.03c | |
| 粗砂/% | 0—10 | 1.29±0.33b | 1.39±0.40b | 2.10±0.40a | 1.90±0.42a | 0.58±0.36c |
| 10—20 | 1.27±0.46ab | 1.18±0.44ab | 2.01±0.31a | 2.18±0.93a | 0.75±0.12b | |
| 中砂/% | 0—10 | 14.36±3.57b | 18.02±3.23a | 20.74±2.86a | 19.62±2.85a | 9.54±2.08c |
| 10—20 | 16.23±3.87b | 17.48±1.33b | 23.82±5.31a | 19.26±4.27b | 9.25±1.13c | |
| 细砂/% | 0—10 | 45.43±7.38e | 51.70±7.83d | 57.40±8.07c | 64.60±7.99b | 72.61±8.87a |
| 10—20 | 54.02±2.54b | 56.07±5.55b | 59.02±6.44b | 60.40±6.01b | 74.70±7.22a | |
| 极细砂/% | 0—10 | 16.97±3.01a | 13.47±3.01b | 9.52±2.81c | 6.62±2.18d | 7.28±2.26d |
| 10—20 | 14.49±3.72a | 11.27±2.51b | 9.54±1.38b | 7.64±1.36b | 7.31±1.90b | |
| 黏粉粒/% | 0—10 | 21.20±3.52a | 17.11±4.01b | 11.69±3.45c | 6.79±2.53d | 9.43±2.44c |
| 10—20 | 14.89±3.90a | 12.04±3.34b | 8.20±2.61c | 5.97±2.20c | 6.02±2.14c | |
| 土层深度/cm | 土壤全氮含量 | 土壤全磷含量 | 土壤容重 | pH值 | 电导率 | 粗砂 | 中砂 | 细砂 | 极细砂 | 黏粉粒 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 0.883** | 0.784** | -0.046 | 0.02 | 0.511** | -0.020 | -0.089 | -0.389** | 0.320** | 0.586** |
| 10—20 | 0.503** | 0.411** | -0.097** | -0.08 | 0.051 | -0.053 | -0.102 | -0.045 | 0.102 | 0.147 |
表4 不同土层土壤有机碳与土壤因子相关性
Table 4 Correlation between soil organic carbon and environmental factors in different soil layers
| 土层深度/cm | 土壤全氮含量 | 土壤全磷含量 | 土壤容重 | pH值 | 电导率 | 粗砂 | 中砂 | 细砂 | 极细砂 | 黏粉粒 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 0.883** | 0.784** | -0.046 | 0.02 | 0.511** | -0.020 | -0.089 | -0.389** | 0.320** | 0.586** |
| 10—20 | 0.503** | 0.411** | -0.097** | -0.08 | 0.051 | -0.053 | -0.102 | -0.045 | 0.102 | 0.147 |
| 变量 | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 | |
| 土壤全氮含量 | 0.853 | -0.166 | -0.299 | 0.807 | -0.254 | -0.142 |
| 土壤全磷含量 | 0.897 | -0.110 | -0.261 | 0.801 | -0.105 | -0.226 |
| 土壤容重 | -0.107 | 0.431 | 0.032 | -0.059 | 0.287 | 0.547 |
| pH值 | 0.510 | 0.089 | 0.816 | 0.607 | 0.004 | 0.577 |
| 电导率 | 0.791 | -0.035 | 0.340 | 0.632 | -0.211 | 0.535 |
| 粗砂 | 0.136 | 0.814 | -0.125 | 0.150 | 0.754 | 0.113 |
| 中砂 | 0.013 | 0.865 | -0.052 | -0.100 | 0.840 | -0.040 |
| 细砂 | -0.777 | -0.533 | 0.117 | -0.628 | -0.705 | 0.237 |
| 极细砂 | 0.732 | -0.072 | 0.158 | 0.755 | -0.025 | 0.074 |
| 黏粉粒 | 0.793 | -0.271 | -0.251 | 0.642 | -0.027 | -0.450 |
| 特征值 | 4.215 | 2.008 | 1.061 | 3.475 | 1.976 | 1.268 |
| 解释变量/% | 42.148 | 20.075 | 10.612 | 34.755 | 19.761 | 12.678 |
| 累计解释变量/% | 42.148 | 62.223 | 72.835 | 34.755 | 54.515 | 67.193 |
表5 不同土层土壤有机碳与土壤因子主成分( F )分析
Table 5 Principal component analysis of soil organic carbon and environmental factors in different soil layers
| 变量 | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F3 | |
| 土壤全氮含量 | 0.853 | -0.166 | -0.299 | 0.807 | -0.254 | -0.142 |
| 土壤全磷含量 | 0.897 | -0.110 | -0.261 | 0.801 | -0.105 | -0.226 |
| 土壤容重 | -0.107 | 0.431 | 0.032 | -0.059 | 0.287 | 0.547 |
| pH值 | 0.510 | 0.089 | 0.816 | 0.607 | 0.004 | 0.577 |
| 电导率 | 0.791 | -0.035 | 0.340 | 0.632 | -0.211 | 0.535 |
| 粗砂 | 0.136 | 0.814 | -0.125 | 0.150 | 0.754 | 0.113 |
| 中砂 | 0.013 | 0.865 | -0.052 | -0.100 | 0.840 | -0.040 |
| 细砂 | -0.777 | -0.533 | 0.117 | -0.628 | -0.705 | 0.237 |
| 极细砂 | 0.732 | -0.072 | 0.158 | 0.755 | -0.025 | 0.074 |
| 黏粉粒 | 0.793 | -0.271 | -0.251 | 0.642 | -0.027 | -0.450 |
| 特征值 | 4.215 | 2.008 | 1.061 | 3.475 | 1.976 | 1.268 |
| 解释变量/% | 42.148 | 20.075 | 10.612 | 34.755 | 19.761 | 12.678 |
| 累计解释变量/% | 42.148 | 62.223 | 72.835 | 34.755 | 54.515 | 67.193 |
| 土层深度/cm | 回归方程 | R2 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | y=8.595STNC+0.118 | 0.778 | 484.174 | <0.01 |
| y=45.435STPC-0.074 | 0.612 | 218.398 | ||
| y=0.011EC+0.126 | 0.995 | 48.399 | ||
| y=-0.088Fsa+0.954 | 0.145 | 24.465 | ||
| y=0.162Vfs+0.273 | 0.096 | 15.647 | ||
| y=0.255Scl+0.130 | 0.339 | 71.625 | ||
| 10—20 | y=15.193STNC+0.154 | 0.363 | 79.598 | |
| y=37.905STPC+0.121 | 0.239 | 44.452 | ||
| y=-0.147SBD+0.692 | -0.002 | 0.659 |
表6 不同土层土壤有机碳含量与土壤因子的一元线性回归方程
Table 6 Univariate linear regression equation between soil organic carbon content and soil factors in different soil layers
| 土层深度/cm | 回归方程 | R2 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | y=8.595STNC+0.118 | 0.778 | 484.174 | <0.01 |
| y=45.435STPC-0.074 | 0.612 | 218.398 | ||
| y=0.011EC+0.126 | 0.995 | 48.399 | ||
| y=-0.088Fsa+0.954 | 0.145 | 24.465 | ||
| y=0.162Vfs+0.273 | 0.096 | 15.647 | ||
| y=0.255Scl+0.130 | 0.339 | 71.625 | ||
| 10—20 | y=15.193STNC+0.154 | 0.363 | 79.598 | |
| y=37.905STPC+0.121 | 0.239 | 44.452 | ||
| y=-0.147SBD+0.692 | -0.002 | 0.659 |
| 变量 | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
| 纬度 | 0.448 | -0.048 | -0.791 | 0.314 | 0.442 | -0.053 | -0.823 | 0.188 |
| 经度 | 0.921 | 0.024 | 0.080 | 0.123 | 0.920 | 0.049 | 0.060 | 0.108 |
| 年降水量 | 0.645 | 0.236 | 0.269 | -0.168 | 0.637 | 0.257 | 0.277 | -0.106 |
| 年积温 | 0.480 | 0.156 | 0.367 | 0.469 | 0.496 | 0.172 | 0.309 | 0.453 |
| 高程 | -0.926 | 0.017 | 0.003 | -0.280 | -0.933 | -0.005 | 0.041 | -0.238 |
| 地面剖面曲率 | -0.073 | 0.802 | -0.102 | 0.029 | -0.091 | 0.798 | -0.128 | 0.009 |
| 地面粗糙度 | -0.310 | 0.883 | 0.059 | 0.206 | -0.323 | 0.872 | 0.026 | 0.255 |
| 坡度 | -0.398 | 0.831 | 0.029 | 0.162 | -0.413 | 0.817 | 0.007 | 0.223 |
| 生长季平均气温 | 0.720 | -0.053 | 0.130 | 0.427 | 0.739 | -0.037 | 0.075 | 0.380 |
| 生长季降水量 | 0.192 | -0.111 | 0.917 | -0.115 | 0.204 | -0.084 | 0.928 | -0.030 |
| 生长季EVI均值 | 0.674 | 0.391 | -0.040 | -0.482 | 0.649 | 0.414 | -0.024 | -0.554 |
| 生长季NDVI均值 | 0.737 | 0.367 | -0.118 | -0.454 | 0.712 | 0.389 | -0.101 | -0.520 |
| 特征值 | 4.695 | 2.500 | 1.851 | 1.191 | 4.729 | 2.515 | 1.804 | 1.171 |
| 解释变量/% | 36.112 | 19.232 | 14.236 | 9.163 | 36.374 | 19.347 | 13.876 | 9.006 |
| 累计解释变量/% | 36.112 | 55.343 | 69.579 | 78.743 | 36.374 | 55.721 | 69.597 | 78.603 |
表7 不同土层土壤有机碳与环境因子主成分( F )分析
Table 7 Principal component analysis of soil organic carbon and environmental factors in different soil layers
| 变量 | 0—10 cm | 10—20 cm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
| 纬度 | 0.448 | -0.048 | -0.791 | 0.314 | 0.442 | -0.053 | -0.823 | 0.188 |
| 经度 | 0.921 | 0.024 | 0.080 | 0.123 | 0.920 | 0.049 | 0.060 | 0.108 |
| 年降水量 | 0.645 | 0.236 | 0.269 | -0.168 | 0.637 | 0.257 | 0.277 | -0.106 |
| 年积温 | 0.480 | 0.156 | 0.367 | 0.469 | 0.496 | 0.172 | 0.309 | 0.453 |
| 高程 | -0.926 | 0.017 | 0.003 | -0.280 | -0.933 | -0.005 | 0.041 | -0.238 |
| 地面剖面曲率 | -0.073 | 0.802 | -0.102 | 0.029 | -0.091 | 0.798 | -0.128 | 0.009 |
| 地面粗糙度 | -0.310 | 0.883 | 0.059 | 0.206 | -0.323 | 0.872 | 0.026 | 0.255 |
| 坡度 | -0.398 | 0.831 | 0.029 | 0.162 | -0.413 | 0.817 | 0.007 | 0.223 |
| 生长季平均气温 | 0.720 | -0.053 | 0.130 | 0.427 | 0.739 | -0.037 | 0.075 | 0.380 |
| 生长季降水量 | 0.192 | -0.111 | 0.917 | -0.115 | 0.204 | -0.084 | 0.928 | -0.030 |
| 生长季EVI均值 | 0.674 | 0.391 | -0.040 | -0.482 | 0.649 | 0.414 | -0.024 | -0.554 |
| 生长季NDVI均值 | 0.737 | 0.367 | -0.118 | -0.454 | 0.712 | 0.389 | -0.101 | -0.520 |
| 特征值 | 4.695 | 2.500 | 1.851 | 1.191 | 4.729 | 2.515 | 1.804 | 1.171 |
| 解释变量/% | 36.112 | 19.232 | 14.236 | 9.163 | 36.374 | 19.347 | 13.876 | 9.006 |
| 累计解释变量/% | 36.112 | 55.343 | 69.579 | 78.743 | 36.374 | 55.721 | 69.597 | 78.603 |
| 1 | 段翰晨,王涛,薛娴,等.基于RS与GIS的科尔沁沙地沙漠化时空演变[J].中国沙漠,2013, 33(2):470-477. |
| 2 | 胡光印,董治宝,逯军峰,等.黄河流域沙漠化空间格局与成因[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):213-224. |
| 3 | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Council.Ecosystems and human well-bein:desertification synthesis[R].Washington,D C,USA:World Resources Institute,2005. |
| 4 | Liang B C, Vanden Bygarrt A J, MacDonald J D,et al.Revisiting no-till's impact on soil organic carbon storage in Canada[J].Soil and Tillage Research,2020,198:104529. |
| 5 | Guenet B, Gabrielle B, Chenu C,et al.Can N2O emissions offset the benefits from soil organic carbon storage?[J].Global Change Biology,2021,27(2):237-256. |
| 6 | 李巧玲,阎欣,吴秀芝,等.荒漠草原沙漠化对土壤无机碳和有机碳的影响[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(1):98-103,110. |
| 7 | Schlesinger W H.Evidence from chronosequence studies for a low carbon-storage potential of soils[J].Nature,1990,348(6298):232-234. |
| 8 | Dixon R K, Solomon A M, Brown S,et al.Carbon pools and flux of global forest ecosystems[J].Science,1994,263(5144):185-190. |
| 9 | 刘树林,王涛,屈建军.浑善达克沙地土地沙漠化过程中土壤粒度与养分变化研究[J].中国沙漠,2008,28(4):611-616. |
| 10 | 马建业,佟小刚,李占斌,等.毛乌素沙地沙漠化逆转过程土壤颗粒固碳效应[J].应用生态学报,2016,27(11):3487-3494. |
| 11 | 赵哈林,周瑞莲,赵学勇,等.呼伦贝尔沙质草地土壤理化特性的沙漠化演变规律及机制[J].草业学报,2012,21(2):1-7. |
| 12 | 连杰,赵学勇,王少昆,等.科尔沁沙地风蚀作用对土壤碳、氮分布的影响[J].生态学杂志,2013,32(3):529-535. |
| 13 | 李玉强,赵哈林,移小勇,等.沙漠化过程中科尔沁沙地植物-土壤系统碳氮储量动态[J].环境科学,2006(4):635-640. |
| 14 | 王少昆,赵学勇,曲浩,等.科尔沁沙地和浑善达克沙地流动沙丘中土壤微生物学特征比较[J].环境科学研究,2010,23(12):1516-1522. |
| 15 | 王建华.中国沙漠10万分布图集中国西部环境与生态科学数据中心[DB/OL].[2006-8].. |
| 16 | Duan H C, Wang T, Xue X,et al.Dynamics of aeolian desertification and its driving forces in the Horqin Sandy Land,Northern China[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2014,186:6083-6096. |
| 17 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:272-282. |
| 18 | 张彦军,郁耀闯,牛俊杰,等.秦岭太白山北坡土壤有机碳储量的海拔梯度格局[J].生态学报,2020,40(2):629-639. |
| 19 | Li Y Q, Zhang J P, Zhao X Y,et al.Comparison of soil physico-chemical properties under different land-use and cover types in northeastern China's Horqin Sandy Land[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2016,8(6):495-506. |
| 20 | Li X, Xiao J.A global,0.05-degree product of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence derived from OCO-2,MODIS,and reanalysis data[J].Remote Sensing,2019,11(5):517. |
| 21 | 赵青,刘爽,陈凯,等.武夷山自然保护区不同海拔甜槠天然林土壤有机碳变化特征及影响因素[J].生态学报,2021,41(13):5328-5339. |
| 22 | 常帅,于红博,曹聪明,等.锡林郭勒草原土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(5):1355-1366. |
| 23 | 丁越岿,杨劼,宋炳煜,等.不同植被类型对毛乌素沙地土壤有机碳的影响[J].草业学报,2012,21(2):18-25. |
| 24 | Fierer N, Schimel J P.Effects of drying-rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2002,34(6):777-787. |
| 25 | 曲浩,赵学勇,赵哈林,等.陆地生态系统凋落物分解研究进展[J].草业科学,2010,27(8):44-51. |
| 26 | 赵哈林,周瑞莲,赵学勇,等.科尔沁沙地沙漠化正、逆过程的地面判别方法[J].中国沙漠,2008(1):8-15. |
| 27 | Han F P, Hu W, Zheng J Y,et al.Estimating soil organic carbon storage and distribution in a catchment of Loess Plateau,China[J].Geoderma,2010,154(3/4):261-266. |
| 28 | Knapp A K, Briggs J M, Collins S L,et al.Shrub encroachment in North American grasslands: shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs[J].Global Change Biology,2008,14:615-623. |
| 29 | 张青青,伍海兵,梁晶.上海市绿地表层土壤有机碳储量的估算[J].土壤,2020,52(4):819-824. |
| 30 | 阎欣,安慧,刘任涛.荒漠草原沙漠化对土壤物理和化学特性的影响[J].土壤,2019,51(5):1006-1012. |
| 31 | 左小安,赵学勇,赵哈林,等.科尔沁沙地草地退化过程中的物种组成及功能多样性变化特征[J].水土保持学报,2006(1):181-185. |
| 32 | 唐庄生,安慧,上官周平.荒漠草原沙漠化对土壤养分与植被根冠比的影响[J].草地学报,2015,23(3):463-468. |
| 33 | 马志良,赵文强.植物群落向土壤有机碳输入及其对气候变暖的响应研究进展[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(1):270-281. |
| 34 | 舒向阳,胡玉福,蒋双龙,等.川西北沙化草地植被群落、土壤有机碳及微生物特征[J].草业学报,2016,25(4):45-54. |
| 35 | 于秀丽.莫莫格湿地土壤微生物量碳动态及与酶活性的关系[J].东北林业大学学报,2020,48(4):59-63. |
| 36 | 王霖娇,李瑞,盛茂银.典型喀斯特石漠化生态系统土壤有机碳时空分布格局及其与环境的相关性[J].生态学报,2017,37(5):1367-1378. |
| 37 | 田慎重,宁堂原,王瑜,等.不同耕作方式和秸秆还田对麦田土壤有机碳含量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2010,21(2):373-378. |
| 38 | 赵芳,欧阳勋志.飞播马尾松林土壤有机碳空间分布及其影响因子[J].生态学报,2016,36(9):2637-2645. |
| 39 | 曹小玉,李际平,闫文德.不同龄组杉木林土壤有机碳与氮磷钾分布特征及耦合关系[J].土壤通报,2014,45(5):1137-1143. |
| 40 | 席军强,杨自辉,郭树江,等.人工梭梭林对沙地土壤理化性质和微生物的影响[J].草业学报,2015,24(5):44-52. |
| 41 | 李强,周道玮,陈笑莹.地上枯落物的累积、分解及其在陆地生态系统中的作用[J].生态学报,2014,34(14):3807-3819. |
| 42 | Wang Y Q, Shao M A, Liu Z P,et al. Prediction of bulk density of soils in the Loess Plateau region of China[J].Surveys in Geophysics,2014,35(2):395-413. |
| 43 | Sequeira C H, Wills S A, Seybold C A,et al. Predicting soil bulk density for incomplete databases[J].Geoderma,2014,213(1):64-73. |
| 44 | 刘顺,盛可银,刘喜帅,等.赣南毛竹林土壤的渗透性特征[J].安徽农业大学学报,2018,45(2):252-257. |
| 45 | 夏汉平,蔡锡安.采矿地的生态恢复技术[J].应用生态学报,2002(11):1471-1477. |
| 46 | Six J, Conant R T, Paul E A,et al.Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils[J]. Plant and Soil,2002,241(2):155-176. |
| 47 | 孙忠祥,李勇,赵云泽,等.旱作区土壤有机碳密度空间分布特征与其驱动力分析[J].农业机械学报,2019,50(1):255-262. |
| 48 | 杨敏,杨飞,杨仁敏,等.祁连山中段土壤有机碳剖面垂直分布特征及其影响因素[J].土壤,2017,49(2):386-392. |
| 49 | 阎欣,安慧.沙化草地恢复过程中土壤有机碳物理组分和全氮含量的变化[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(6):1242-1251. |
| 50 | 赵兴敏,赵兰坡,郭欣欣,等.水体沉积物与岸边土壤颗粒组成及有机碳分布特征[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(6):304-308. |
| 51 | Baumann F, He J S, Schmidt K,et al.Pedogenesis,permafrost,and soil moisture as controlling factors for soil nitrogen and carbon contents across the Tibetan Plateau[J].Global Change Biology,2009,15(12):3001-3017. |
| 52 | 王春燕,何念鹏,吕瑜良.中国东部森林土壤有机碳组分的纬度格局及其影响因子[J].生态学报,2016,36(11):3176-3188. |
| 53 | Feng X M, Fu B J, Lu N,et al.How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: an analysis of carbon sequestration in China's Loess Plateau[J].Scientific Reports,2013,3:2846. |
| 54 | 李妙宇,上官周平,邓蕾.黄土高原地区生态系统碳储量空间分布及其影响因素[J].生态学报,2021,41(17):6786-6799. |
| 55 | Nie X Q, Yang L C, Li F,et al.Storage,patterns and controls of soil organic carbon in the alpine shrubland in the Three Rivers Source Region on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Catena,2019,178:154-162. |
| 56 | Yuan Z Q, Fang C, Zhang R,et al.Topographic influences on soil properties and aboveground biomass in lucerne-rich vegetation in a semi-arid environment[J].Geoderma,2019,344:137-143. |
| [1] | 张美兰, 崔增团, 顿志恒, 贾蕊鸿, 张玉霞, 郭世乾, 崔倩怡, 葛承暄, 蔡立群, 董博. 近40年甘肃省耕层土壤有机碳时空分异及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 295-303. |
| [2] | 李世龙. 青藏高原东缘玛曲沙化高寒草地土壤理化性质[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 44-52. |
| [3] | 冯净雪, 丁占良, 尤莉, 韩广. 科尔沁沙地西部横向沙丘间的风况和输沙势[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 110-119. |
| [4] | 贺超, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 王冠丽, 郝丽娜. 科尔沁沙地差巴嘎蒿( Artemisia halodendron )水分利用特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 190-198. |
| [5] | 胡菁菁, 胡光印, 董治宝. 黄河源区玛多盆地沙漠化土地粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 242-252. |
| [6] | 张亦然, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 贾天宇, 季亚新. 基于多源遥感和机器学习方法的科尔沁沙地植被覆盖度反演[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 187-195. |
| [7] | 胡延斌, 张强, 肖国举, 仇正跻, 李永平, 郭占强. 中国半干旱区农田土壤碳、氮、磷含量对玉米生产的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 261-273. |
| [8] | 赵啸龙, 谢玉鸿, 马旭君, 王少昆. 科尔沁沙质草地不同恢复年限草本层群落结构及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [9] | 詹瑾, 韩丹, 杨红玲, 李玉霖. 科尔沁沙地植被恢复过程中群落组成及多样性演变特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 194-206. |
| [10] | 于钊, 李奇铮, 王培源, 蒋齐. 退化和恢复过程驱动的荒漠草地生态系统有机碳密度变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 215-222. |
| [11] | 孙迎涛, 岳艳鹏, 成龙, 庞营军, 赵河聚, 费兵强, 修晓敏, 吴波, 赵雨兴, 石麟, 何金军, 贾晓红. 毛乌素沙地油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)生长及生物量分配对沙漠化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 123-133. |
| [12] | 刘志民, 余海滨. “山水林田湖草沙生命共同体”理念下的科尔沁沙地生态治理[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 34-40. |
| [13] | 马全林, 尚雯, 王新友, 马婧, 詹科杰, 王多泽. 风沙活动对人工梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)林土壤碳氮含量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 71-78. |
| [14] | 胡光印, 董治宝, 逯军峰, 杨林海, 南维鸽, 肖锋军. 黄河流域沙漠化空间格局与成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 213-224. |
| [15] | 韩丹, 李玉霖, 詹瑾, 杨红玲. 基于能值的科尔沁沙地不同农牧比例村落发展可持续性对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 235-244. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
