中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 313-325.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00046
收稿日期:2025-03-31
修回日期:2025-05-11
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-06-30
作者简介:杨岩岩(1987—),女,甘肃礼县人,助理研究员,主要从事水土保持与荒漠化防治研究。E-mail: yyyang@caf.ac.cn
基金资助:
Yanyan Yang1( ), Lianyou Liu2, Bo Wu1, Yingjun Pang1
), Lianyou Liu2, Bo Wu1, Yingjun Pang1
Received:2025-03-31
Revised:2025-05-11
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-06-30
摘要:
荒漠植物是沙漠生态系统的核心。沙丘沿风向移动造成荒漠植物死亡,目前对植物死亡后枯落物在沙丘埋压状况下分解研究较少。本文通过遥感测算、样品采集和实验分析等方法,研究沙丘对典型荒漠植物白刺(Nitraria tangutorum)和小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)埋压时长与沙丘形态关系以及沙丘埋压状况下荒漠植物枯落物分解特征。结果表明:(1)沙丘对荒漠植物埋压时长与沙丘形态参数呈显著幂函数正相关,与沙丘移动速度呈显著幂函数负相关,沙丘规模越大对植物埋压时间越长。(2)被埋压植物枝条枯落物质量损失率与埋压时长呈显著对数函数正相关。被沙丘埋压的前25年枝条枯落物的分解速率较大,年平均质量损失率达2.6%,之后分解速率趋于平缓。被沙丘埋压期间小叶锦鸡儿枝条枯落物分解速率大于白刺。荒漠植物枝条枯落物分解速率与其直径呈显著正相关。(3)沙丘埋压可导致植物枝条枯落物C和N元素富集,且富集程度随埋压时长的增加而增加。N元素富集程度明显高于C元素,但随埋压时长的增加呈减小趋势。研究结果将为准确预测干旱区荒漠植物碳周转速率提供科学依据。
中图分类号:
杨岩岩, 刘连友, 吴波, 庞营军. 沙丘埋压对典型荒漠植物枝条枯落物分解的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 313-325.
Yanyan Yang, Lianyou Liu, Bo Wu, Yingjun Pang. Effects of sand dune burial on the litter decomposition of desert plant branches[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(3): 313-325.

图1 巴丹吉林-乌兰布和沙漠输沙带位置注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号GS(2016)2884号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.1 The position of sand transport belt between Badain Jaran and Ulan Buh Desert
| 沙丘编号 | 沙丘迎风坡和背风 坡在地面投影的 最大长度/m | 沙丘 高度 /m | 移动速度 /(m·a-1) | 采集的 植物 种类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 150.2 | 6.3 | 10.2 | 白刺 |
| D2 | 174.0 | 6.2 | 10.3 | 白刺 |
| D3 | 123.5 | 7.3 | 9.1 | 白刺 |
| D4 | 77.3 | 4.2 | 13.6 | 白刺 |
| D5 | 124.7 | 4.6 | 12.8 | 白刺 |
| D6 | 98.6 | 4.8 | 12.4 | 白刺 |
| D7 | 203.8 | 8.8 | 7.5 | 白刺 |
| D8 | 74.5 | 4.0 | 13.8 | 白刺 |
| D9 | 97.7 | 3.3 | 15.5 | 白刺 |
| D10 | 242.7 | 11.2 | 5.6 | 白刺 |
| D11 | 110.6 | 5.6 | 11.2 | 白刺 |
| D12 | 223.8 | 10.8 | 5.9 | 白刺 |
| D13 | 347.0 | 23.0 | 3.7 | 白刺和小叶锦鸡儿 |
表1 沙丘概况及被埋压植物种类
Table 1 Dune characteristics and buried plant species
| 沙丘编号 | 沙丘迎风坡和背风 坡在地面投影的 最大长度/m | 沙丘 高度 /m | 移动速度 /(m·a-1) | 采集的 植物 种类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 150.2 | 6.3 | 10.2 | 白刺 |
| D2 | 174.0 | 6.2 | 10.3 | 白刺 |
| D3 | 123.5 | 7.3 | 9.1 | 白刺 |
| D4 | 77.3 | 4.2 | 13.6 | 白刺 |
| D5 | 124.7 | 4.6 | 12.8 | 白刺 |
| D6 | 98.6 | 4.8 | 12.4 | 白刺 |
| D7 | 203.8 | 8.8 | 7.5 | 白刺 |
| D8 | 74.5 | 4.0 | 13.8 | 白刺 |
| D9 | 97.7 | 3.3 | 15.5 | 白刺 |
| D10 | 242.7 | 11.2 | 5.6 | 白刺 |
| D11 | 110.6 | 5.6 | 11.2 | 白刺 |
| D12 | 223.8 | 10.8 | 5.9 | 白刺 |
| D13 | 347.0 | 23.0 | 3.7 | 白刺和小叶锦鸡儿 |

图3 沙丘丘间地的荒漠植物、枝条枯落物及采样示意图注:A、C和E为被沙丘埋压前后的白刺植株及其枯落物;B、D和F为被沙丘埋压前后的小叶锦鸡儿植株及其枯落物;G为沙丘D13被埋压植物枯落物的采样示意图,红色线条所示为采样区域,虚线箭头所指为沿沙丘迎风坡坡脚采样的先后顺序及方向
Fig.3 Distribution and sampling schematic of sand-buried plants in interdune areas of a barchan dune
| 采样编号 | 距上一采样位置的距离/m | 植物种类 | 采样编号 | 距上一采样位置的距离/m | 植物种类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L15 | 8.7(紧邻沙丘中轴线) | 白刺 |
| L2 | 18.5 | 白刺 | L16 | 19.4 | 白刺 |
| L3 | 25.2 | 白刺 | L17 | 20.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L4 | 16.2 | 白刺 | L18 | 24.4 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L5 | 49.8 | 白刺 | L19 | 14.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L6 | 18.5 | 白刺 | L20 | 15.8 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L7 | 11.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L21 | 8.7 | 白刺 |
| L8 | 35.5 | 白刺 | L22 | 28.2 | 白刺 |
| L9 | 22.3 | 白刺 | L23 | 4.8 | 白刺 |
| L10 | 16.3 | 白刺 | L24 | 7.0 | 白刺 |
| L11 | 14.2 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L25 | 11.0 | 白刺 |
| L12 | 8.3 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L26 | 20.2 | 白刺 |
| L13 | 4.3(紧邻沙丘中轴线) | 白刺 | L27 | 15.4 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L14 | 9.0(紧邻丘中轴线) | 白刺 | L28 | 58.0 | 白刺 |
表2 沙丘D13迎风坡坡脚被埋压植物枝条枯落物采集概况
Table 2 Sampling details of buried plants at the windward toe of sand dune
| 采样编号 | 距上一采样位置的距离/m | 植物种类 | 采样编号 | 距上一采样位置的距离/m | 植物种类 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 0.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L15 | 8.7(紧邻沙丘中轴线) | 白刺 |
| L2 | 18.5 | 白刺 | L16 | 19.4 | 白刺 |
| L3 | 25.2 | 白刺 | L17 | 20.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L4 | 16.2 | 白刺 | L18 | 24.4 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L5 | 49.8 | 白刺 | L19 | 14.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L6 | 18.5 | 白刺 | L20 | 15.8 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L7 | 11.0 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L21 | 8.7 | 白刺 |
| L8 | 35.5 | 白刺 | L22 | 28.2 | 白刺 |
| L9 | 22.3 | 白刺 | L23 | 4.8 | 白刺 |
| L10 | 16.3 | 白刺 | L24 | 7.0 | 白刺 |
| L11 | 14.2 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L25 | 11.0 | 白刺 |
| L12 | 8.3 | 小叶锦鸡儿 | L26 | 20.2 | 白刺 |
| L13 | 4.3(紧邻沙丘中轴线) | 白刺 | L27 | 15.4 | 小叶锦鸡儿 |
| L14 | 9.0(紧邻丘中轴线) | 白刺 | L28 | 58.0 | 白刺 |
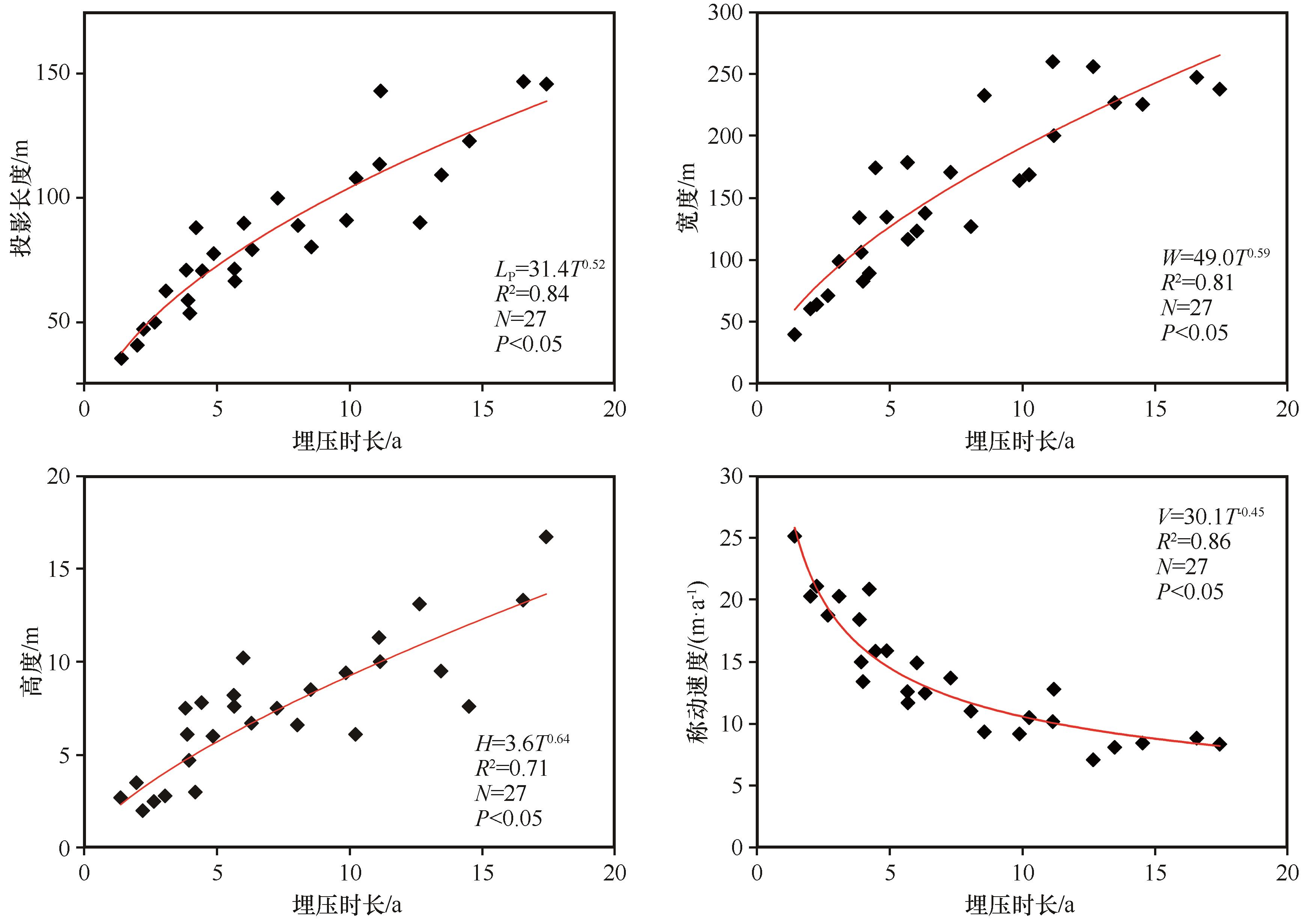
图5 沙丘对植物的埋压时长与沙丘形态参数及移动速度间的关系注:T为沙丘对植物的埋压时长(a);Lp为迎风坡长度和背风坡长度在水平面投影的最大长度(m);W、H和V分别为沙丘的宽度(m)、高度(m)和移动速度(m·a-1)
Fig.5 Relationships between burial duration of plants by dunes and morphological parameters/movement speed of sand dunes
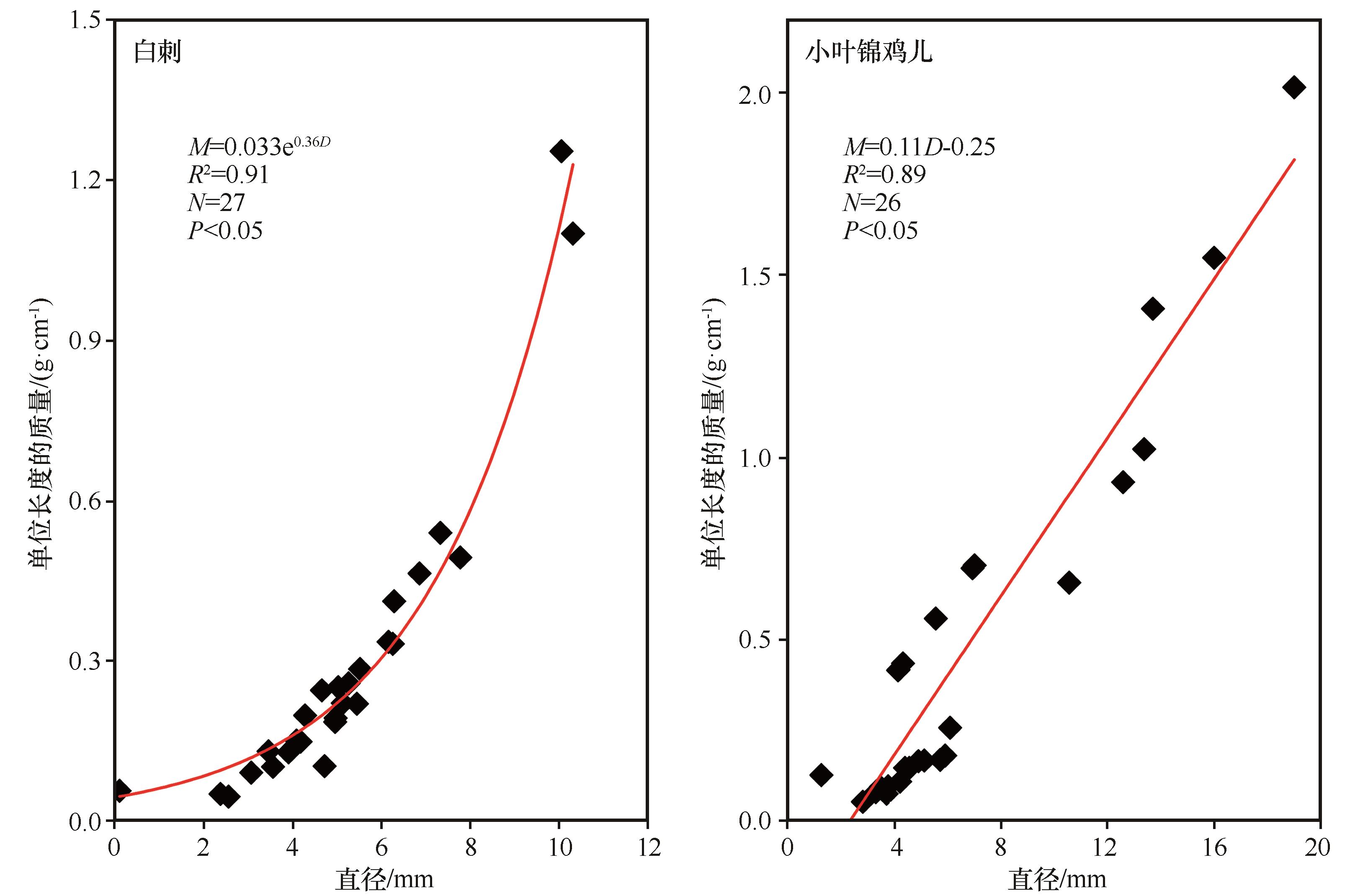
图7 新鲜白刺和小叶锦鸡儿枝条的直径与其单位长度质量间的关系注:M为单位长度植物枝条的质量(g·cm-1);D为植物枝条的直径(mm)
Fig.7 Relationship between branch diameter and mass per unit length in fresh branches of Nitraria tangutorum and Caragana microphylla

图11 沙丘D1~D12迎风坡坡脚白刺枝条枯落物C、N和H元素含量
Fig.11 The content of C,N,and H elements in the buried Nitraria tangutorum branches at the toe of the windward slope of sand dunes D1-D12

图12 植物枝条枯落物C、N和H元素含量与沙丘埋压时长的关系
Fig.12 The relationship between C,N,and H element content of buried plant branches and the duration of sand dune burial

图13 沙丘迎风坡坡脚不同位置植物枝条枯落物C、N和H元素的含量
Fig.13 Content of C,N,and H elements in buried plant branches at different positions on the windward slope toe of the sand dune
| 1 | 刘铮瑶,董治宝,罗万银,等.巴丹吉林沙漠边缘地带植物区系及其资源利用[J].水土保持通报,2016,36(5):255-260. |
| 2 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980. |
| 3 | Nickling W G, Wolfe S A.The morphology and origin of Nabkhas,region of Mopti,Mali,West Africa[J].Journal of Arid Environments,1994,28(1):13-30. |
| 4 | Lancaster N, Baas A.Influence of vegetation cover on sand transport by wind: field studies at Owens Lake,California[J].Earth Surface Processes & Landforms,2015,23(1):69-82. |
| 5 | Leenders J K, Boxel J H V, Sterk G.The effect of single vegetation elements on wind speed and sediment transport in the Sahelian zone of Burkina Faso[J].Earth Surface Processes & Landforms,2007,32(10):1454-1474. |
| 6 | Zou X Y, Li J F, Liu B,et al.The protective effects of nebkhas on an oasis[J].Aeolian Research,2016,20:71-79. |
| 7 | Meigs P.World distribution of arid and semi-arid homoclimates[J].Arid Zone Program,1953,1:203-209. |
| 8 | Danin A.Plants of Desert Dunes[M].Berlin,Germany Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1996. |
| 9 | 曾加芹.森林凋落物研究开展[J].防护林科技,2017():80-83. |
| 10 | 董学德,高鹏,李腾,等.土壤微生物群落对麻栎-刺槐混交林凋落物分解的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(6):2315-2325. |
| 11 | 池静姚,潘磊磊, SeMyung Kwon,等.呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松天然林结构多样性和竞争对树木生长的影响[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(5):29-40. |
| 12 | Kwabiah A B, Voroney R P, Palm C A,et al.Inorganic fertilizer enrichment of soil: effect on decomposition of plant litter under subhumid tropical conditions[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,1999,30:224-231. |
| 13 | 谌贤,刘洋,唐实玉,等.川西亚高山森林凋落物不同分解阶段基质质量特征[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(3):586-594. |
| 14 | 李学斌,马林,陈林,等.草地枯落物分解研究进展及展望[J].生态环境学报,2010,19(9):2260-2264. |
| 15 | 苟小林,周青平,陈有军,等.青藏高原不同气候区高寒沙地两种优势植物及其根际土壤的养分特征[J].植物生态学报,2018,42(1):133-142. |
| 16 | Liu P, Huang J H, Sun O J,et al.Litter decomposition and nutrient release as affected by soil nitrogen availability and litter quality in a semiarid grassland ecosystem[J].Oecologia,2010,162(3):771-780. |
| 17 | 赵娟.宁夏荒漠草原单种与混合植物枯落物分解过程及土壤动物的贡献[D].银川:宁夏大学,2019. |
| 18 | 魏晓凤.松嫩草地不同放牧强度下植物物种枯落物分解的变化规律研究[D].长春:东北师范大学,2013. |
| 19 | 王小平,杨雪,杨楠,等.凋落物多样性及组成对凋落物分解和土壤微生物群落的影响[J].生态学报,2019,39(17):6264-6272. |
| 20 | 王新源,赵学勇,李玉霖,等.环境因素对干旱半干旱区凋落物分解的影响研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(11):3300-3310. |
| 21 | 罗永清,岳祥飞,李玉强,等.降水格局对科尔沁沙地三种草本植物凋落物分解的影响[J].草业学报,2018,27(2):206-212. |
| 22 | Throop H L, Archer S R.Resolving the dryland decomposition conundrum:some new perspectives on potential drivers[J].Progress in Botany,2009,70:171-194. |
| 23 | 贾丙瑞.凋落物分解及其影响机制[J].植物生态学报,2019,43(8):648-657. |
| 24 | Hansen R A, Coleman D C.Litter complexity and composition are determinants of the diversity and species composition of oribatid mites in litter bags[J].Applied Soil Ecology,1998,9(1/3):17-23. |
| 25 | 王嘉年,李向义,李成道,等.自然光照和荫蔽条件下两种荒漠植物叶片凋落物分解特征研究[J].干旱区地理,2023,46(6):949-957. |
| 26 | 范琳杰,李向义,李成道,等.极端干旱区花花柴(Karelinia caspia)和胡杨(Populus euphratica)叶凋落物分解和养分释放特征[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(2):479-486. |
| 27 | 朱金峰,王乃昂,陈红宝,等.基于遥感的巴丹吉林沙漠范围与面积分析[J].地理科学进展,2010,29(9):1087-1094. |
| 28 | 杨岩岩.阿拉善高原风沙地貌过程研究[D].北京:北京师范大学,2015. |
| 29 | 乌友罕,殷婕,武子丰,等.巴丹吉林-乌兰布和沙漠输沙带新月形沙丘动态[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(2):78-89. |
| 30 | Sun W Q, Gao X, Lei J Q.Shaping effects of sand flow channels on aeolian geomorphology:a case study of the Badain Jaran,Tengger,and Ulan Buh Deserts,northern China[J].Catena,2022,214:106255. |
| 31 | 张稼乐,裴浩,苗百岭,等.巴丹吉林沙漠与亚玛雷克沙漠之间连接带的动态研究[J].内蒙古气象,2021,4:22-29. |
| 32 | 刘红梅,吕世杰,刘青泉,等.巴丹吉林沙漠东缘主要植物种群空间分布关系[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(4):959-967. |
| 33 | 刘苹.克氏针茅草原植物凋落物分解特性及其对环境变化的响应[D].北京:中国科学院植物研究所,2006. |
| 34 | 曲浩,赵学勇,赵哈林,等.陆地生态系统凋落物分解研究进展[J].草业科学,2010,27(8):44-51. |
| 35 | 赵镇贤,陈银萍,王立龙,等.河西走廊荒漠区不同功能类群植物叶片建成成本的比较[J].植物生态学报,2023,47(11):1551-1560. |
| 36 | 郭剑芬,杨玉盛,陈光水,等.森林凋落物分解研究进展[J].林业科学,2006,42(4):93-100. |
| 37 | Song P, Zhang N L, Ma K P,et al.Impacts of global warming on litter decomposition[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2014,34(6):1327-1339. |
| 38 | Bohlen P J, Parmelee R W, Mccartney D A,et al.Earthworm effects on carbon and nitrogen dynamics of surface litter in corn agroecosystems[J].Ecological Applications,1997,7(4):1341-1349. |
| 39 | Moore T R, Trofymow J A, Taylor B,et al.Litter decomposition rates in Canadian forests[J].Global Change Biology,1999,5(1):75-82. |
| 40 | Bray S R, Kitajima K, Mack M C.Temporal dynamics of microbial communities on decomposing leaf litter of 10 plant species in relation to decomposition rate[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2012,49:30-37. |
| 41 | 章志琴,林开敏,邹双全,等.不同调控措施对杉木枯落物分解的影响[J].浙江林学院学报,2006,23(1):65-69. |
| 42 | Coq S, Weigel J, Butenschoen O,et al.Litter composition rather than plant presence affects decomposition of tropical litter mixtures[J].Plant and Soil,2011,343(1/2):273-286. |
| 43 | Koukoura Z, Mamolos A P, Kalburtji K L.Decomposition of dominant plant species litter in a semi-arid grassland[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2003,23(1):13-23. |
| 44 | 耿元波,史晶晶.草原凋落物的分解及影响元素的分解与累积[J].地理科学进展,2012,31(5):655-663. |
| 45 | Ngao J, Epron D, Brechet C,et al.Estimating the contribution of leaf litter decomposition to soil CO2 efflux in a beech forest using 13C-depleted litter[J].Global Change Biology,2005,11:1768-1776. |
| 46 | Raich J W, Schlesinger W H.The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate[J].Tellus,1992,44(2):81-99. |
| 47 | Berg B, Staaf H.Leaching,accumulation and release of nitrogen in decomposing forest litter[J].Ecological Bulletins,1981,33:163-173. |
| 48 | 孙本华,高明霞,吕家珑,等.荒漠生态条件下植物残体分解和养分释放的研究[J].中国农学通报,2005,21(5):390-392. |
| [1] | 周尚哲, 席磊, 崔梦淳, 崔桂鹏, 孔维远, 高攀, 卢琦. 乌兰布和沙漠北部典型植被的叶蜡正构烷烃特征及指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 45-54. |
| [2] | 丁甲, 唐逸云, 李蕾, 杨宏玉, 张泽琦, 王君, 余舒畅, 冯金朝, 石莎, 杨昊天. 土壤水分与氮含量对宁夏荒漠草原甘肃蒿( Artemisia gansuensis )、胡枝子( Lespedeza bicolor )、针茅( Stipa capillata )生理的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 271-282. |
| [3] | 张红霞, 贾荣亮, 赵鹏善, 赵昕, 崔晓云. 荒漠植物逆境生理生态学研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 72-79. |
| [4] | 满多清, 唐进年, 杨雪梅, 李得禄, 郭树江, 陈芳, 丁峰. 1960—2021年民勤沙区10种典型荒漠植物种群变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 20-28. |
| [5] | 赵春彦, 秦洁, 贺晓慧, 周冬蒙. 轻度沙埋对典型荒漠植物的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 63-72. |
| [6] | 杨利贞, 冯丽, 杨贵森, 黄磊. 柠条(Caragana korshinskii)、油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)、花棒(Hedysarum scoparium)叶片吸水潜力及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 214-221. |
| [7] | 张瑞, 周晓兵, 张元明. 生物土壤结皮对温带荒漠植物凋落物分解的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 151-158. |
| [8] | 靳正忠, 王永东, 雷加强, 李生宇, 徐新文. 塔里木沙漠公路防护林土壤环境因子的根际效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(4): 808-814. |
| [9] | 王玉阳, 陈亚鹏, 李卫红, 王日照, 周莹莹, 张建鹏. 塔里木河下游典型荒漠河岸植物水分来源[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(6): 1150-1157. |
| [10] | 石勇, 刘源, 殷恒霞, 燕霞, 马小飞. 红砂(Reaumuria soongarica)种子萌发特性及其局部适应性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(3): 644-650. |
| [11] | 任运涛, 韩炳宏, 张宝林, 赵慧, 傅华, 牛得草. 阿拉善荒漠植物叶片矿质元素含量的季节变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(2): 383-391. |
| [12] | 李双, 肖洪浪, 王芳, 周茂先. 热平衡茎流仪测量精度及误差来源分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(6): 1544-1551. |
| [13] | 李国栋, 张元明. 生物土壤结皮与种子附属物对4种荒漠植物种子萌发的交互影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(3): 725-731. |
| [14] | 霍 红, 冯 起, 苏永红, 司建华, 席海洋, 鱼腾飞. 额济纳绿洲植物群落种间关系和生态位研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(4): 1027-1033. |
| [15] | 鲁 艳1, 李新荣2, 何明珠2, 冯 丽2, 曾凡江1. 镍、铜对矿业废弃地先锋植物盐生草和骆驼蓬抗氧化物质和渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(6): 1681-1690. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
