
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 110-121.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00064
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhenliang Yin1,2( ), Rui Zhu3, Chunshuang Fang3(
), Rui Zhu3, Chunshuang Fang3( ), Huaqing Yang3, Zexia Chen1
), Huaqing Yang3, Zexia Chen1
Received:2024-04-29
Revised:2024-05-22
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-06
Contact:
Chunshuang Fang
CLC Number:
Zhenliang Yin, Rui Zhu, Chunshuang Fang, Huaqing Yang, Zexia Chen. Attribution analysis of runoff variations in the Changma River Basin based on the Budyko hypothesis[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 110-121.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00064
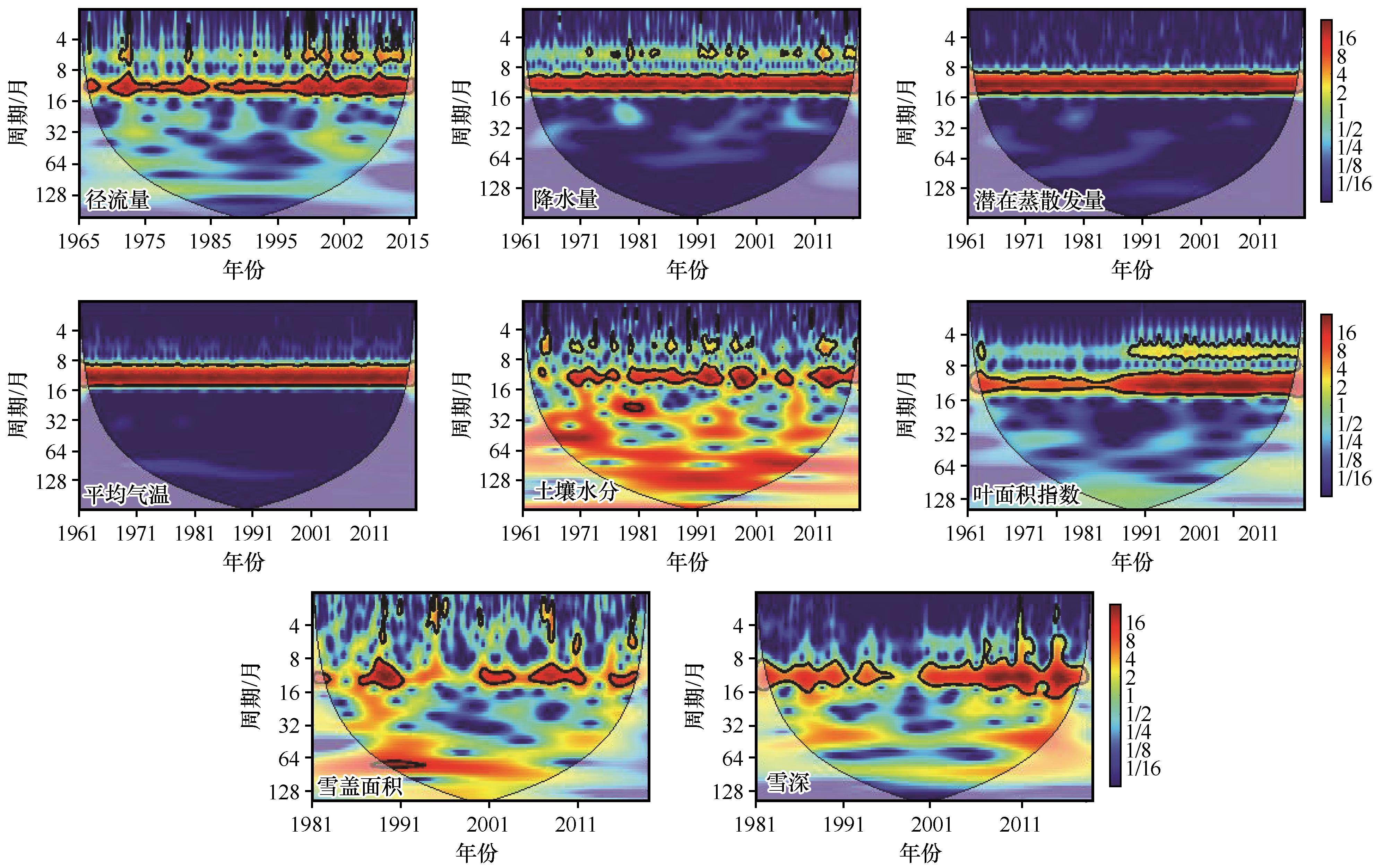
Fig.4 Continuous wavelet transforms of runoff and impact factors. Thick contours denote 5% significance levels against red noise; pale regions denote the cone of influence where edge effects might distort the results; the color denotes the strength of wavelet power
| 时期 | 弹性系数( | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基准期(1965—2000年) | 78.4 | 283.4 | 833.4 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 2.94 | 1.69 | -0.69 | -1.59 |
| 变化期(2001—2015年) | 113.5 | 309.6 | 858.0 | 0.80 | 0.367 | 2.78 | 1.53 | -0.53 | -1.33 |
| 差值 | 35.1 | 26.2 | 24.6 | -0.15 | 0.087 | -0.16 | -0.16 | 0.16 | 0.26 |
Table 1 Statistics in hydro-climatic variables and elasticity coefficient of streamflow to P, ET0, and ω in two periods
| 时期 | 弹性系数( | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基准期(1965—2000年) | 78.4 | 283.4 | 833.4 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 2.94 | 1.69 | -0.69 | -1.59 |
| 变化期(2001—2015年) | 113.5 | 309.6 | 858.0 | 0.80 | 0.367 | 2.78 | 1.53 | -0.53 | -1.33 |
| 差值 | 35.1 | 26.2 | 24.6 | -0.15 | 0.087 | -0.16 | -0.16 | 0.16 | 0.26 |
| 基准期 | 变化期 | ΔRo/mm | ΔRP /mm | Δ | ΔRω /mm | ΔRc/mm | 贡献率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONp | CONw | ||||||||
| 1965—2000年 | 2000—2015年 | 35.10 | 14.68 | -1.72 | 27.66 | 40.62 | 33.31% | -3.90% | 62.79% |
Table 2 Contribution of P, ET0, and ω to runoff change
| 基准期 | 变化期 | ΔRo/mm | ΔRP /mm | Δ | ΔRω /mm | ΔRc/mm | 贡献率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONp | CONw | ||||||||
| 1965—2000年 | 2000—2015年 | 35.10 | 14.68 | -1.72 | 27.66 | 40.62 | 33.31% | -3.90% | 62.79% |
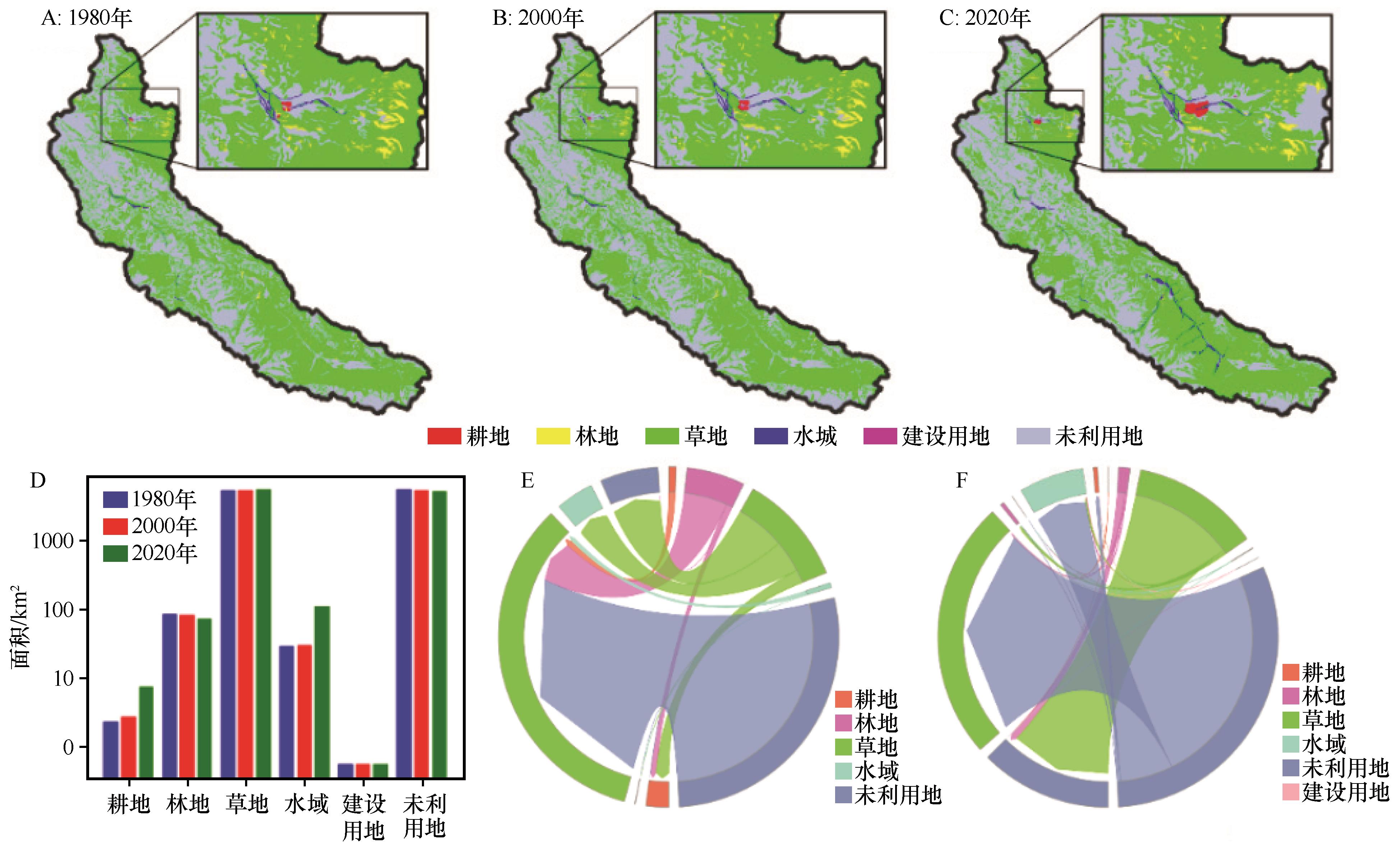
Fig.5 Land cover classification maps over the study area in 1980 (A), 2000 (B) and 2020 (C); Land cover classification proportions (D); Land use change over the study area between 1980 and 2000 (E) and between 2000 and 2020 (F)
| 时期 | 冰川面积 /km2 | 冰川数量 | 冰储量/km3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCGI(1960s—1970s) | 494.46[ | 505[ | 30.58[ |
| 1990年 | 481.07 | 503 | 28.07 |
| 1995年 | 456.28 | 506 | 26.64 |
| 2000年 | 437.39 | 505 | 25.51 |
| 2005年 | 421.24 | 505 | 24.57 |
| SCGI(2005—2010年) | 415.29[ | 501[ | 24.81[ |
| 2010年 | 414.12 | 506 | 24.13 |
| 2015年 | 401.14 | 520 | 23.31 |
| 2020年 | 384.05 | 519 | 22.80 |
Table 3 Glacier change over the study area between 1970s and 2020
| 时期 | 冰川面积 /km2 | 冰川数量 | 冰储量/km3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCGI(1960s—1970s) | 494.46[ | 505[ | 30.58[ |
| 1990年 | 481.07 | 503 | 28.07 |
| 1995年 | 456.28 | 506 | 26.64 |
| 2000年 | 437.39 | 505 | 25.51 |
| 2005年 | 421.24 | 505 | 24.57 |
| SCGI(2005—2010年) | 415.29[ | 501[ | 24.81[ |
| 2010年 | 414.12 | 506 | 24.13 |
| 2015年 | 401.14 | 520 | 23.31 |
| 2020年 | 384.05 | 519 | 22.80 |
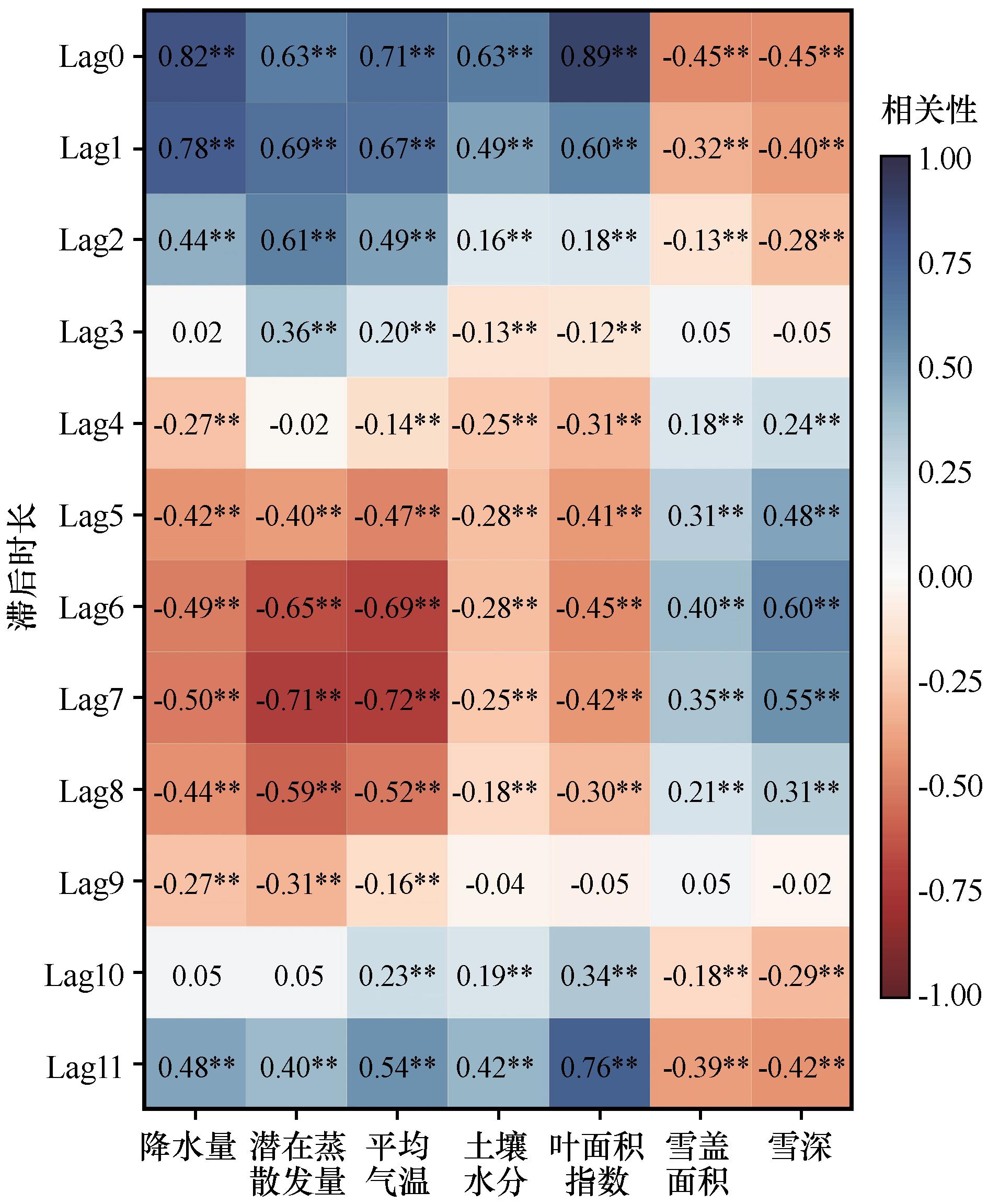
Fig.6 The interrelation between runoff and influencing factors.Lag0-Lag 11 denotes the impact of runoff lagging behind influencing factors by 0 to 11 months. Significance P0.05, marked as **; significance P0.1, marked as *
| PCP | ET0 | TMP | SW | LAI | SCE | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTC | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.85 |
| PASC | 46.67% | 29.99% | 25.04% | 41.82% | 54.48% | 15.85 | 18.05 |
Table 4 Coherence between runoff and individual influencing factor
| PCP | ET0 | TMP | SW | LAI | SCE | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTC | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.85 |
| PASC | 46.67% | 29.99% | 25.04% | 41.82% | 54.48% | 15.85 | 18.05 |
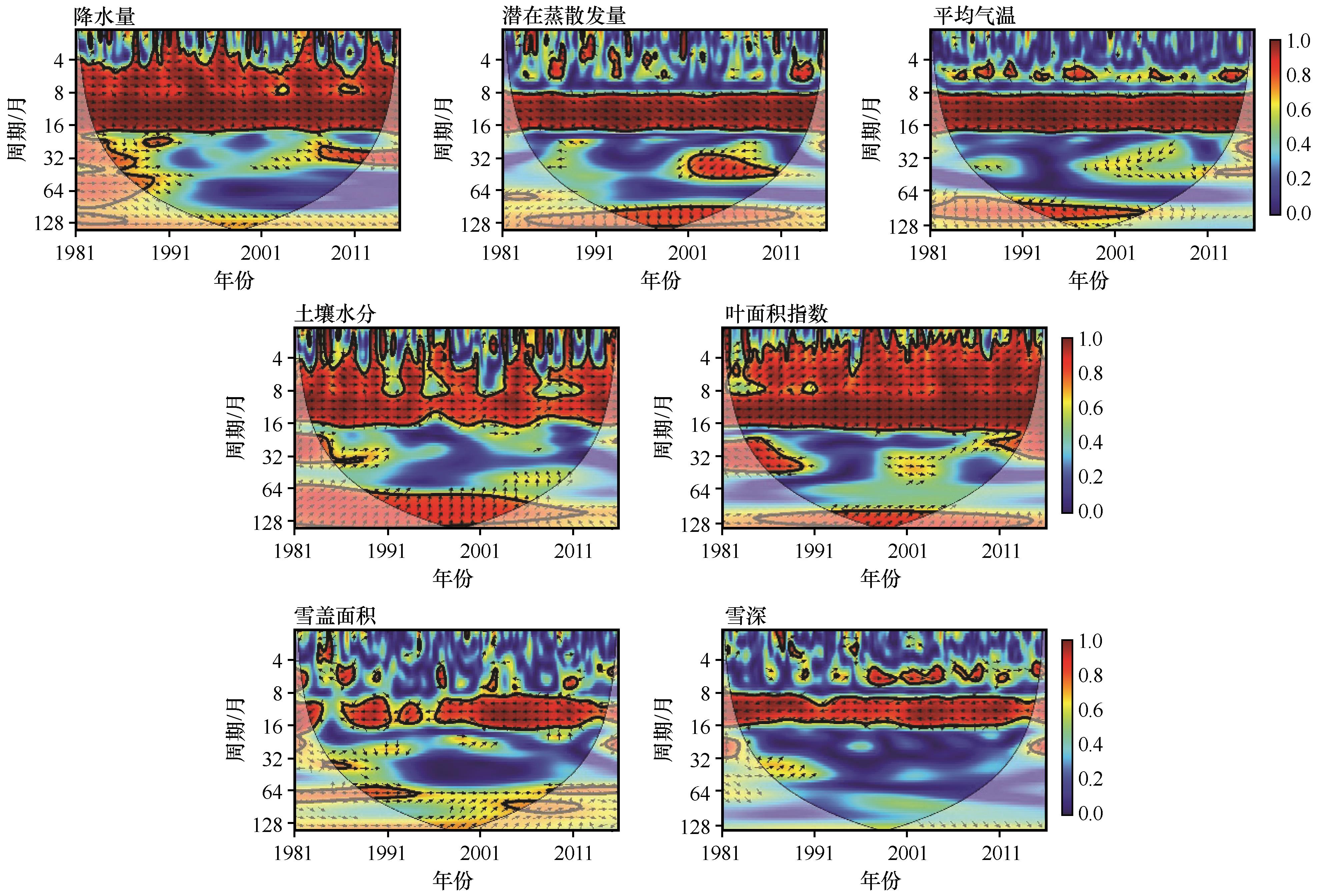
Fig.7 Wavelet coherence between runoff and individual influencing factor. Thick contours denote 5% significance levels against red noise; pale regions denote the cone of influence where edge effects might distort the results; the color denotes the strength of coherence
| 双变量 | MWC2 | PASC/% | 三变量 | MWC3 | PASC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI-SW | 0.95 | 60.65 | LAI-SW-SCE | 0.98 | 58.87 |
| LAI-SCE | 0.94 | 55.23 | LAI-SW-PCP | 0.98 | 58.03 |
| LAI-PCP | 0.95 | 53.40 | LAI-SW-ET0 | 0.98 | 55.55 |
| LAI-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.75 | LAI-SCE-PCP | 0.98 | 54.60 |
| PCP-SW | 0.95 | 51.24 | LAI-SCE-ET0 | 0.97 | 54.31 |
| PCP-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.19 | LAI-SW-SD | 0.97 | 54.29 |
| LAI-SD | 0.94 | 50.03 | LAI-PCP-ET0 | 0.98 | 53.11 |
| LAI-TMP | 0.95 | 47.23 | LAI-SCE-TMP | 0.97 | 51.84 |
| PCP-SCE | 0.96 | 44.40 | LAI-PCP-SD | 0.98 | 51.78 |
| PCP-SD | 0.95 | 40.47 | LAI-SW-TMP | 0.98 | 51.38 |
| PCP-TMP | 0.95 | 39.30 | LAI-SCE-SD | 0.97 | 49.20 |
Table 5 Coherence between runoff and multiple influencing factor
| 双变量 | MWC2 | PASC/% | 三变量 | MWC3 | PASC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI-SW | 0.95 | 60.65 | LAI-SW-SCE | 0.98 | 58.87 |
| LAI-SCE | 0.94 | 55.23 | LAI-SW-PCP | 0.98 | 58.03 |
| LAI-PCP | 0.95 | 53.40 | LAI-SW-ET0 | 0.98 | 55.55 |
| LAI-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.75 | LAI-SCE-PCP | 0.98 | 54.60 |
| PCP-SW | 0.95 | 51.24 | LAI-SCE-ET0 | 0.97 | 54.31 |
| PCP-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.19 | LAI-SW-SD | 0.97 | 54.29 |
| LAI-SD | 0.94 | 50.03 | LAI-PCP-ET0 | 0.98 | 53.11 |
| LAI-TMP | 0.95 | 47.23 | LAI-SCE-TMP | 0.97 | 51.84 |
| PCP-SCE | 0.96 | 44.40 | LAI-PCP-SD | 0.98 | 51.78 |
| PCP-SD | 0.95 | 40.47 | LAI-SW-TMP | 0.98 | 51.38 |
| PCP-TMP | 0.95 | 39.30 | LAI-SCE-SD | 0.97 | 49.20 |
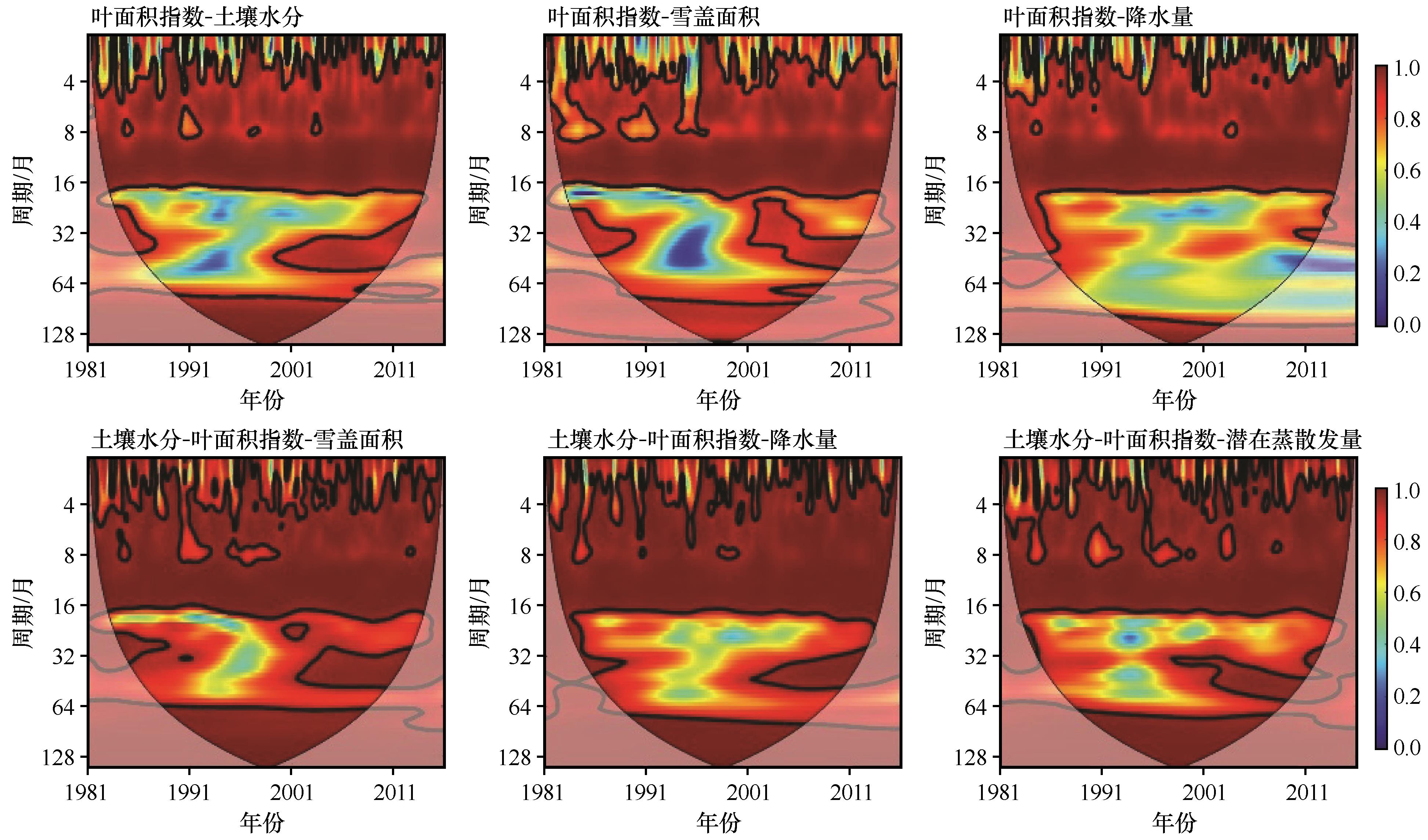
Fig.8 Wavelet coherence between runoff and multiple influencing factors. Thick contours denote 5% significance levels against red noise; pale regions denote the cone of influence where edge effects might distort the results; the color denotes the strength of coherence
| 1 | 冯起,龙爱华,王宁练,等.西北内陆区水资源安全保障技术集成与应用[J].人民黄河,2019,41(10):103-108. |
| 2 | 丁永建,赵求东,吴锦奎,等.中国冰冻圈水文未来变化及其对干旱区水安全的影响[J].冰川冻土,2020,42(1):23-32. |
| 3 | Chen Y N, Li B F, Li Z,et al.Water resource formation and conversion and water security in arid region of Northwest China[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2016,26(7):939-952. |
| 4 | 汤秋鸿,兰措,苏凤阁,等.青藏高原河川径流变化及其影响研究进展[J].科学通报,2019,64(27):2807-2821. |
| 5 | 常启昕,孙自永,潘钊,等.高寒山区河道径流的形成与水文调节机制研究进展[J].地球科学,2022,47(11):4196-4209. |
| 6 | 王磊,刘虎,雍斌,等.陆地冰冻圈水文过程的研究现状及展望[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2023,59(3):489-496. |
| 7 | 余国安,岳蓬胜,张晨笛,等.藏东南地区的河流水文研究:进展与挑战[J].科学通报,2024,69(3):394-413. |
| 8 | Dey P, Mishra A.Separating the impacts of climate change and human activities on streamflow:a review of methodologies and critical assumptions[J].Journal of Hydrology,2017,548:278-290. |
| 9 | 宋晓猛,张建云,占车生,等.气候变化和人类活动对水文循环影响研究进展[J].水利学报,2013,44(7):779-790. |
| 10 | 董磊华,熊立华,于坤霞,等.气候变化与人类活动对水文影响的研究进展[J].水科学进展,2012,23(2):278-285. |
| 11 | 尹振良,冯起,刘时银,等.水文模型在估算冰川径流研究中的应用现状[J].冰川冻土,2016,38(1):248-258. |
| 12 | Choudhury B J.Evaluation of an empirical equation for annual evaporation using field observations and results from a biophysical model[J].Journal of Hydrology,1999,216(1/2):99-110. |
| 13 | Yang H B, Yang D W, Lei Z,et al.New analytical derivation of the mean annual water‐energy balance equation[J].Water Resources Research,2008,44(3):2007WR006135. |
| 14 | Konapala G, Mishra A K.Three-parameter-based streamflow elasticity model:application to MOPEX basins in the USA at annual and seasonal scales[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2016,20(6):2545-2556. |
| 15 | 孙莉茹,毕华兴,马志瑾,等.1951-2020年黄河上中游径流变化特征及归因分析[J].北京林业大学学报,2024,46(1):82-92. |
| 16 | Xin J L, Sun X Y, Liu L,et al.Quantifying the contribution of climate and underlying surface changes to alpine runoff alterations associated with glacier melting[J].Hydrological Processes,2021,35(3):e14069. |
| 17 | 梁鹏飞,辛惠娟,李宗省,等.基于Budyko假设的党河径流变化归因[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):210-219. |
| 18 | 张晓晓,张钰,徐浩杰.疏勒河上游径流年内分配变化规律分析[J].人民黄河,2014,36(6):58-60. |
| 19 | 贾玲,张百祖,牛最荣,等.疏勒河上游径流变化与预测分析[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(5):1588-1597. |
| 20 | 王学良,陈仁升,刘俊峰,等.1956-2021年疏勒河流域主要河流出山径流变化及成因分析[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(6):1782-1792. |
| 21 | 孙美平,张磊,姚晓军,等.1954-2016年疏勒河上游径流变化特征及影响因素[J].冰川冻土,2022,44(2):657-666. |
| 22 | 李洪源,赵求东,吴锦奎,等.疏勒河上游径流组分及其变化特征定量模拟[J].冰川冻土,2019,41(4):907-917. |
| 23 | Zhang Z H, Deng S F, Zhao Q D,et al.Projected glacier meltwater and river run-off changes in the upper reach of the Shule River Basin,north-eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Hydrological Processes,2019,33(7):1059-1074. |
| 24 | Wu J K, Li H Y, Zhou J X,et al.Variation of runoff and runoff components of the upper Shule River in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under climate change[J].Water,2021,13(23):3357. |
| 25 | Zhou J X, Ding Y J, Wu J K,et al.Streamflow generation in semi-arid,glacier-coverd,montane catchments in the upper Shule River,Qilian Mountains,northeastern Tibetan plateau[J].Hydrological Processes,2021,35(8):e14276. |
| 26 | Guo W Q, Liu S Y, Xu J L,et al.The second Chinese glacier inventory:data,methods and results[J].Journal of Glaciology,2015,61(226):357-372. |
| 27 | 吴佳,高学杰.一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J].地球物理学报,2013,56(4):1102-1111. |
| 28 | Allen Richard G, Pereira Luis S, Raes Dirk,et al.Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements[M].Rome,Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations,1998. |
| 29 | Muñoz-Sabater J, Dutra E, Agustí-Panareda A,et al.ERA5-Land:a state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications[J].Earth System Science Data,2021,13(9):4349-4383. |
| 30 | Che T, Li X, Jin R,et al.Snow depth derived from passive microwave remote-sensing data in China[J].Annals of Glaciology,2008,49:145-154. |
| 31 | Hao X H, Huang G H, Che T,et al.The NIEER AVHRR snow cover extent product over China:a long-term daily snow record for regional climate research[J].Earth System Science Data,2021,13(10):4711-4726. |
| 32 | Hamed K H.Trend detection in hydrologic data:the Mann-Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis[J].Journal of Hydrology,2008,349(3/4):350-363. |
| 33 | Li C Y, Hao J S, Zhang G T,et al.Runoff variations affected by climate change and human activities in Yarlung Zangbo River,southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Catena,2023,230:107184. |
| 34 | Zhang Q, Xu C Y, Jiang T,et al.Possible influence of ENSO on annual maximum streamflow of the Yangtze River,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2007,333(2/4):265-274. |
| 35 | Su L, Miao C Y, Duan Q Y,et al.Multiple‐wavelet coherence of world's large rivers with meteorological factors and ocean signals[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2019,124(9):4932-4954. |
| 36 | Ukasha M, Ramirez J A, Niemann J D.Temporal variations of NDVI and LAI and interactions with hydroclimatic variables in a large and agro‐ecologically diverse region[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences,2022,127(4):e2021JG006395. |
| 37 | Chen T, de Jeu R A M, Liu Y Y,et al.Using satellite based soil moisture to quantify the water driven variability in NDVI:a case study over mainland Australia[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2014,140:330-338. |
| 38 | 陈亚宁,李忠勤,徐建华,等.中国西北干旱区水资源与生态环境变化及保护建议[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(3):385-393. |
| 39 | 张强,杨金虎,王朋岭,等.西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望[J].科学通报,2023,68(14):1814-1828. |
| 40 | Liu S Y, Sun W X, Shen Y P,et al.Glacier changes since the Little Ice Age maximum in the western Qilian Shan,Northwest China,and consequences of glacier runoff for water supply[J].Journal of Glaciology,2003,49(164):117-124. |
| 41 | Hu W, Si B C.Technical note:multiple wavelet coherence for untangling scale-specific and localized multivariate relationships in geosciences[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2016,20(8):3183-3191. |
| 42 | Ng E K, Chan J.Geophysical applications of partial wavelet coherence and multiple wavelet coherence[J].Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology,2012,29(12):1845-1853. |
| 43 | 包文,段安民,游庆龙,等.青藏高原气候变化及其对水资源影响的研究进展[J].气候变化研究进展,2024,20(2):158-169. |
| 44 | Gu C J, Mu X M, Gao P,et al.Distinguishing the effects of vegetation restoration on runoff and sediment generation on simulated rainfall on the hillslopes of the loess plateau of China[J].Plant and Soil,2020,447(1/2):393-412. |
| 45 | Guo X X, Du M, Gao P,et al.Response of runoff-sediment processes to vegetation restoration patterns under different rainfall regimes on the Loess Plateau[J].Catena,2024,234:107647. |
| 46 | Tan X Y, Jia Y W, Yang D W,et al.Impact ways and their contributions to vegetation-induced runoff changes in the Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Hydrology:Regional Studies,2024,51:101630. |
| 47 | Shi P, Li P, Li Z B,et al.Effects of grass vegetation coverage and position on runoff and sediment yields on the slope of Loess Plateau,China[J].Agricultural Water Management,2022,259:107231. |
| [1] | Sen Li, Zongying Yang, Hongyan Zhao, Narentuya, Guixiang An, Jiali Xie, Xiaopeng Jia, Changzhen Yan. Spatio-temporal changes of aeolian desertification in the Jiziwan of the Yellow River from 1975 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 13-22. |
| [2] | Zhenzi He, Bingxin Xu, Wenjing Liu, Yigang Hu. Carbon exchange of desert soil crust in response to simulated warming and changes of precipitation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 269-278. |
| [3] | Jianhui Ge, Bing Liu, Yujie Xu, Aijun Sun, Keqi Wang, Dongxue Li, hui Zhao. Interrelationships between climate change and surface processes in the First Meander of the Yellow River since the Last Deglaciation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 121-132. |
| [4] | Yang Chen, Ping Lv, Min Cao, Zishu Xia, Fang Ma, Junlin Yu. Microclimate characteristics of Tengger Desert lakes and its response to climate change [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 231-238. |
| [5] | Qing Li, Na Zhou, Sheng Wang, Tongzhou Li, Rende Wang, Jinfeng Wang. Quantitative assessment the impacts of climate change and human actives on wind erosion: a case study of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 178-188. |
| [6] | Xiao Feng, Jianjun Qu, Xinhui Ding, Qin Tian, Qingbin Fan. Temporal and spatial pattern of NPP in Yulin and its influencing factors during the desertification reversal [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 22-32. |
| [7] | Yanzhuo Zhao, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Yunping Chi, Lei Sun, Peng Wu, Zhenyu Wei. Holocene climate change recorded by paleosoil profile in Hulun Buir Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 85-96. |
| [8] | Jianbing Lu, Ke Ju, Weibin Liao. Variation in NDVI and its response to climate change and human activities in Gansu Province during 2000-2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 118-127. |
| [9] | Qi You, Baorong Xu, Songbing Zou, Yihao Qin, Duo Wang, Dong Yu. The vegetation-climate quantitative relationship and characteristics in arid and semi-arid region of northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 274-287. |
| [10] | Yaozong Wang, Xinbin Yue, Jiali Xie, Zhipeng Liu, Yuan Ma, Yahui Wang, Yan Gong. Desertification evolution in the sandy region to the east of the Yellow River in Ningxia from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 31-40. |
| [11] | Pengfei Liang, Huijuan Xin, Zongxing Li, Fusen Nan, Biao Tang, Wenbao Zhang. Study on the attribution of runoff variation in the Danghe River based on the Budyko hypothesis [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 210-219. |
| [12] | Ran Duan, Zongjie Li, Yu Wang, Xiaoying Liu, Juan Gui, Pengfei Liang, Yuchen Li, Jian Xue, Mengqing Liu, Bin Xu. Characteristics of runoff change in the Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 57-68. |
| [13] | Ziyan Han, Jijun Meng, Yi Zou, Likai Zhu. Vegetation dynamics and their response to climate change and ecological protection projects in the Heihe River Basin from 1982 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 96-106. |
| [14] | Chunming Xin, Mingzhu He, Chengyi Li, Libin Zhang, Xinrong Li. A review of research progress on nitrous oxide emissions from desert soil and its driving factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 184-194. |
| [15] | Hong Sun, Jiyun Duan, Yujie Liu, Ruilan Ran, Xiaofeng Li, Pengshan Zhao. Potential distribution of the genus Agriophyllum under climate change [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 255-263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech