中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 165-175.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00049
• • 上一篇
罗维成1( ), 赵文智1(
), 赵文智1( ), 刘继亮1, 杨竟艺1,2, 白雪莲1,3, 魏乐民1,3, 冯怡琳4
), 刘继亮1, 杨竟艺1,2, 白雪莲1,3, 魏乐民1,3, 冯怡琳4
收稿日期:2021-11-11
修回日期:2022-03-23
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2023-01-09
通讯作者:
赵文智
作者简介:赵文智(E-mail: zhaowzh@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Weicheng Luo1( ), Wenzhi Zhao1(
), Wenzhi Zhao1( ), Jiliang Liu1, Jingyi Yang1,2, Xuelian Bai1,3, Lemin Wei1,3, Yilin Feng4
), Jiliang Liu1, Jingyi Yang1,2, Xuelian Bai1,3, Lemin Wei1,3, Yilin Feng4
Received:2021-11-11
Revised:2022-03-23
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
Wenzhi Zhao
摘要:
恢复人工植被是祁连山自然保护区矿区废弃地修复的主要手段,经过近5年的修复,矿区废弃地修复区地上植被盖度明显提高,但关于作为评价土壤修复效果重要指标的土壤动物群落变化的认识还很有限。以祁连山自然保护区典型煤矿废弃地为研究对象,采用野外调查的方法对比研究了煤矿修复区和毗邻区(原始地貌)大型土壤动物分布特征及其影响因素。结果表明:(1)修复区植物丰富度、生物量、盖度及土壤粗砂、有机质、全氮含量均显著低于毗邻区(P<0.05),而土壤水分、细砂、黏粉粒、全钾和全磷含量差异不显著(P>0.05)。(2)修复区土壤动物活动密度和多样性均显著高于毗邻区,修复区和毗邻区土壤动物均以蝗科(12.7%和55.7%)和蚁科(14.4%和49.6%)为主;进房沟、水磨沟和柳树沟煤矿修复区及毗邻区土壤动物群落相似性分别为39.9%、52.9%和43.4%。(3)土壤有机质含量是影响煤矿修复区和对照区捕食性土壤动物群落变化的主要因子,而草本物种数和土壤粗砂含量是影响植食性土壤动物群落变化的主要因子。总之,人工修复后煤矿废弃地修复区土壤动物个体数均高于对照区,部分矿区修复生境类群丰富度及多样性已经超过了毗邻区,这表明蚂蚁、步甲和蝗虫等地表节肢动物对煤矿矿区覆土恢复植被和封禁等措施驱动的植被和土壤环境变化响应敏感。因此,还需要优化植被及土壤修复模式,提高土壤动物多样性及多功能性,使矿区废弃地生态环境能够得到快速修复。
中图分类号:
罗维成, 赵文智, 刘继亮, 杨竟艺, 白雪莲, 魏乐民, 冯怡琳. 祁连山自然保护区煤矿修复区地表节肢动物分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 165-175.
Weicheng Luo, Wenzhi Zhao, Jiliang Liu, Jingyi Yang, Xuelian Bai, Lemin Wei, Yilin Feng. Distribution pattern and influencing factors of ground arthropods in coalmines restoration area of Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 165-175.
| 环境变量 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 |
|---|---|---|
| 植物丰富度 | 1.67±0.33 | 4.67±0.88* |
| 植物盖度/% | 33.67±1.86 | 66.67±4.41** |
| 植物生物量/g | 57.34±7.31 | 149.27±12.94** |
| 土壤粗砂含量/% | 26.83±5.57 | 43.16±8.29* |
| 土壤细砂含量/% | 12.71±3.85 | 12.55±0.79ns |
| 土壤黏粉粒含量/% | 0.42±0.10 | 0.32±0.14ns |
| 土壤含水量/% | 10.70±0.003 | 10.32±0.01ns |
| 土壤pH | 8.70±0.29 | 8.20±0.19* |
| 土壤有机碳含量/(g·kg-1) | 17.00±7.24 | 121.60±21.01** |
| 土壤全氮含量/(g·kg-1) | 0.70±0.37 | 3.40±1.06* |
| 土壤全钾含量/(g·kg-1) | 41.60±13.18 | 46.80±1.64ns |
| 土壤全磷含量/(g·kg-1) | 0.50±0.19 | 0.60±0.06ns |
表1 祁连山自然保护区典型煤矿修复区和毗邻区植被和土壤环境特征对比
Table 1 Comparison of vegetation and soil environmental characteristics between typical coal mine restoration area and adjacent area in Qilian Mountain Nature Reserve
| 环境变量 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 |
|---|---|---|
| 植物丰富度 | 1.67±0.33 | 4.67±0.88* |
| 植物盖度/% | 33.67±1.86 | 66.67±4.41** |
| 植物生物量/g | 57.34±7.31 | 149.27±12.94** |
| 土壤粗砂含量/% | 26.83±5.57 | 43.16±8.29* |
| 土壤细砂含量/% | 12.71±3.85 | 12.55±0.79ns |
| 土壤黏粉粒含量/% | 0.42±0.10 | 0.32±0.14ns |
| 土壤含水量/% | 10.70±0.003 | 10.32±0.01ns |
| 土壤pH | 8.70±0.29 | 8.20±0.19* |
| 土壤有机碳含量/(g·kg-1) | 17.00±7.24 | 121.60±21.01** |
| 土壤全氮含量/(g·kg-1) | 0.70±0.37 | 3.40±1.06* |
| 土壤全钾含量/(g·kg-1) | 41.60±13.18 | 46.80±1.64ns |
| 土壤全磷含量/(g·kg-1) | 0.50±0.19 | 0.60±0.06ns |
| 科名 | 进房沟 | 水磨沟 | 柳树沟 | 合计 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 修复区 | 毗邻区 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 | |
| 石蜈蚣科(Lithobiidae) | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) |
| 蚰蜒科(Scutigeridae) | — | 1(0.4) | 1(0.2) | — | — | 1(0.3) | 1(0.1) | 2(0.2) |
| 硬体盲蛛科(Sclerosomatidae) | — | 29(12.3) | 15(3.3) | 2(0.6) | 6(1.7) | 51(15.6) | 21(1.8) | 82(9.3) |
| 管巢蛛科(Clubionidae) | — | 1(0.4) | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | 1(0.1) |
| 平腹蛛科(Gnaphosidae) | 16(4.6) | 6(2.6) | 15(3.3) | 5(1.5) | 16(4.5) | 6(1.8) | 47(4.1) | 17(1.9) |
| 狼蛛科(Lycosidae) | 21(6.1) | 4(1.7) | 12(2.6) | 23(7.1) | 10(2.8) | 8(2.5) | 43(3.7) | 35(4.0) |
| 球蛛科(Theridiidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | 2(0.6) | 1(0.3) | 3(0.3) | 1(0.1) |
| 蟹蛛科(Thomisidae) | 1(0.3) | 2(0.9) | 1(0.2) | 8(2.5) | 3(0.8) | 10(3.1) | 5(0.4) | 20(2.3) |
| 跳蛛科(Salticidae) | — | — | 3(0.7) | — | — | — | 3(0.3) | — |
| 微蛛亚科(Erigoninae) | 4(1.2) | 2(0.9) | 17(3.7) | 3(0.9) | 12(3.4) | 1(0.3) | 33(2.8) | 6(0.7) |
| 绒螨科(Trombidiidae) | — | 14(6.0) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 18(2.0) |
| 潮虫科(Oniscidae) | — | 5(2.1) | — | 1(0.3) | 2(0.6) | 3(0.9) | 2(0.2) | 9(1.0) |
| 蝗科(Acrididae) | 83(24.0) | 48(20.4) | 10(2.2) | 22(6.8) | 54(15.2) | 57(17.5) | 147(12.7) | 127(14.4) |
| 石蚋科(Machilidae) | — | — | — | — | — | 3(0.9) | — | 3(0.3) |
| 蚁狮科(Myrmeleontidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 长蝽科(Lygaeidae) | — | 1(0.4) | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | 1(0.1) |
| 蝽科( Pentatomidae) | — | — | 5(1.1) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 7(0.6) | — |
| 猎蝽科(Reduviidae) | 3(0.9) | — | 2(0.4) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 7(0.6) | — |
| 叶蝉科(Cicadellidae) | 3(0.9) | 4(1.7) | 8(1.8) | 5(1.5) | 2(0.6) | 3(0.9) | 13(1.1) | 12(1.4) |
| 蚜科(Aphididae) | — | — | — | — | 16(4.5) | 1(0.3) | 16(1.4) | 1(0.1) |
| 虎甲科(Cicindelidae) | — | 1(0.4) | 2(0.4) | — | — | — | 2(0.2) | 1(0.1) |
| 步甲科(Carabidae) | 14(4.0) | 14(6.0) | 38(8.3) | 33(10.2) | 40(11.2) | 14(4.3) | 92(7.9) | 61(6.9) |
| 瓢甲科(Coccinellidae) | — | 1(0.4) | — | 1(0.3) | 3(0.8) | — | 3(0.3) | 2(0.2) |
| 阎甲科(Histeridae) | 1(0.3) | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | 3(0.9) | 2(0.2) | 3(0.3) |
| 隐翅虫科(Staphylinidae) | 13(3.8) | 3(1.3) | 21(4.6) | 4(1.2) | 10(2.8) | 6(1.8) | 44(3.8) | 13(1.5) |
| 象甲科(Curculionidae) | — | 7(3.0) | — | 9(2.8) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.1) | 17(1.9) |
| 叶甲科(Chrysomelidae) | — | 4(1.7) | — | 1(0.3) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.1) | 6(0.7) |
| 谷盗科(Trogossitidae) | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 花金龟科(Cetoniidae) | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 天牛科(Cerambycidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 芫青科(Meloidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | 1(0.3) | — | 2(0.2) | — |
| 拟步甲科(Tenebrionidae) | 2(0.6) | 1(0.4) | 2(0.4) | 2(0.6) | 6(1.7) | 1(0.3) | 10(0.9) | 4(0.5) |
| 丸甲科(Byrrhidae) | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) |
| 球蕈甲科(Leiodidae) | — | 1(0.4) | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | 1(0.1) |
| 食蚜蝇科(Syrphidae) | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 夜蛾科(Noctuidae) | — | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) |
| 蚁科(Formicidae) | 185(53.5) | 86(36.6) | 298(65.4) | 200(61.9) | 162(45.5) | 152(46.6) | 645(55.7) | 438(49.5) |
表2 3个煤矿修复区和毗邻区地表节肢动物个体数量及所占比例
Table 2 Number of individuals and relative abundance of ground arthropods in different coal mine restoration areas and adjacent area
| 科名 | 进房沟 | 水磨沟 | 柳树沟 | 合计 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 修复区 | 毗邻区 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 | 修复区 | 毗邻区 | |
| 石蜈蚣科(Lithobiidae) | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) |
| 蚰蜒科(Scutigeridae) | — | 1(0.4) | 1(0.2) | — | — | 1(0.3) | 1(0.1) | 2(0.2) |
| 硬体盲蛛科(Sclerosomatidae) | — | 29(12.3) | 15(3.3) | 2(0.6) | 6(1.7) | 51(15.6) | 21(1.8) | 82(9.3) |
| 管巢蛛科(Clubionidae) | — | 1(0.4) | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | 1(0.1) |
| 平腹蛛科(Gnaphosidae) | 16(4.6) | 6(2.6) | 15(3.3) | 5(1.5) | 16(4.5) | 6(1.8) | 47(4.1) | 17(1.9) |
| 狼蛛科(Lycosidae) | 21(6.1) | 4(1.7) | 12(2.6) | 23(7.1) | 10(2.8) | 8(2.5) | 43(3.7) | 35(4.0) |
| 球蛛科(Theridiidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | 2(0.6) | 1(0.3) | 3(0.3) | 1(0.1) |
| 蟹蛛科(Thomisidae) | 1(0.3) | 2(0.9) | 1(0.2) | 8(2.5) | 3(0.8) | 10(3.1) | 5(0.4) | 20(2.3) |
| 跳蛛科(Salticidae) | — | — | 3(0.7) | — | — | — | 3(0.3) | — |
| 微蛛亚科(Erigoninae) | 4(1.2) | 2(0.9) | 17(3.7) | 3(0.9) | 12(3.4) | 1(0.3) | 33(2.8) | 6(0.7) |
| 绒螨科(Trombidiidae) | — | 14(6.0) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 18(2.0) |
| 潮虫科(Oniscidae) | — | 5(2.1) | — | 1(0.3) | 2(0.6) | 3(0.9) | 2(0.2) | 9(1.0) |
| 蝗科(Acrididae) | 83(24.0) | 48(20.4) | 10(2.2) | 22(6.8) | 54(15.2) | 57(17.5) | 147(12.7) | 127(14.4) |
| 石蚋科(Machilidae) | — | — | — | — | — | 3(0.9) | — | 3(0.3) |
| 蚁狮科(Myrmeleontidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 长蝽科(Lygaeidae) | — | 1(0.4) | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | 1(0.1) |
| 蝽科( Pentatomidae) | — | — | 5(1.1) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 7(0.6) | — |
| 猎蝽科(Reduviidae) | 3(0.9) | — | 2(0.4) | — | 2(0.6) | — | 7(0.6) | — |
| 叶蝉科(Cicadellidae) | 3(0.9) | 4(1.7) | 8(1.8) | 5(1.5) | 2(0.6) | 3(0.9) | 13(1.1) | 12(1.4) |
| 蚜科(Aphididae) | — | — | — | — | 16(4.5) | 1(0.3) | 16(1.4) | 1(0.1) |
| 虎甲科(Cicindelidae) | — | 1(0.4) | 2(0.4) | — | — | — | 2(0.2) | 1(0.1) |
| 步甲科(Carabidae) | 14(4.0) | 14(6.0) | 38(8.3) | 33(10.2) | 40(11.2) | 14(4.3) | 92(7.9) | 61(6.9) |
| 瓢甲科(Coccinellidae) | — | 1(0.4) | — | 1(0.3) | 3(0.8) | — | 3(0.3) | 2(0.2) |
| 阎甲科(Histeridae) | 1(0.3) | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | 3(0.9) | 2(0.2) | 3(0.3) |
| 隐翅虫科(Staphylinidae) | 13(3.8) | 3(1.3) | 21(4.6) | 4(1.2) | 10(2.8) | 6(1.8) | 44(3.8) | 13(1.5) |
| 象甲科(Curculionidae) | — | 7(3.0) | — | 9(2.8) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.1) | 17(1.9) |
| 叶甲科(Chrysomelidae) | — | 4(1.7) | — | 1(0.3) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.3) | 1(0.1) | 6(0.7) |
| 谷盗科(Trogossitidae) | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 花金龟科(Cetoniidae) | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 天牛科(Cerambycidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 芫青科(Meloidae) | — | — | 1(0.2) | — | 1(0.3) | — | 2(0.2) | — |
| 拟步甲科(Tenebrionidae) | 2(0.6) | 1(0.4) | 2(0.4) | 2(0.6) | 6(1.7) | 1(0.3) | 10(0.9) | 4(0.5) |
| 丸甲科(Byrrhidae) | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) |
| 球蕈甲科(Leiodidae) | — | 1(0.4) | 1(0.2) | — | — | — | 1(0.1) | 1(0.1) |
| 食蚜蝇科(Syrphidae) | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) | — |
| 夜蛾科(Noctuidae) | — | — | — | — | — | 1(0.3) | — | 1(0.1) |
| 蚁科(Formicidae) | 185(53.5) | 86(36.6) | 298(65.4) | 200(61.9) | 162(45.5) | 152(46.6) | 645(55.7) | 438(49.5) |
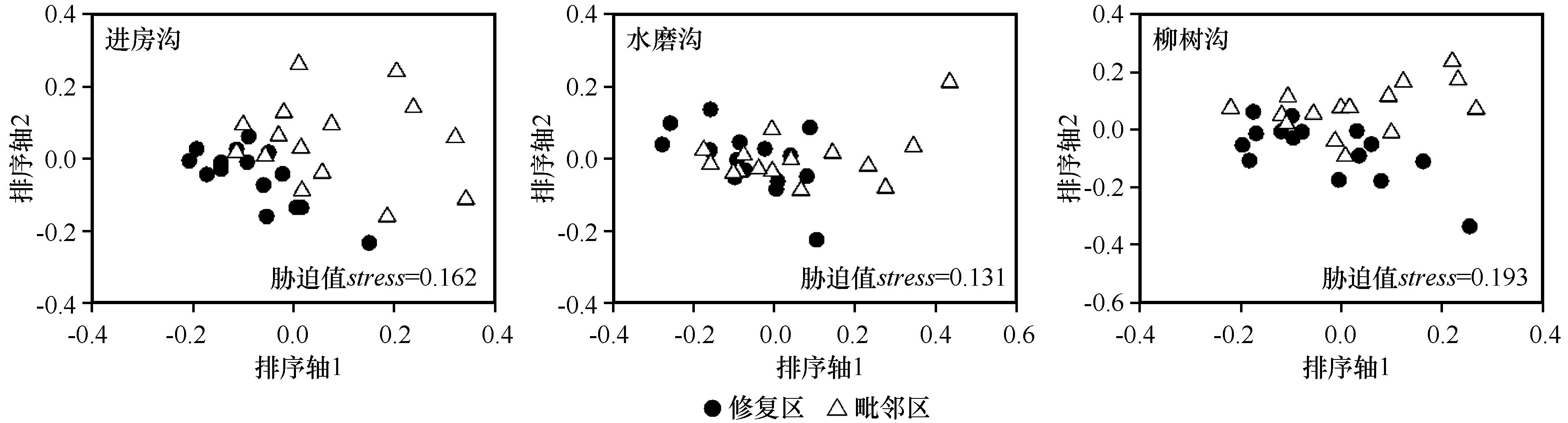
图1 不同煤矿修复区与毗邻区地表节肢动物非度量多维尺度排序图
Fig.1 Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots indicating 2-dimensional distances of ground arthropods assemblage in different coal mine restoration areas and adjacent area
| 因素 | 活动密度 | 类群丰富度 | 多样性指数 | 均匀度指数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 生境 | 3.10 | 0.050 | 0.87 | 0.425 | 4.30 | 0.017 | 9.46 | <0.001 |
| 微生境 | 7.05 | 0.009 | 2.51 | 0.117 | 0.12 | 0.735 | 8.49 | 0.005 |
| 生境×微生境 | 0.85 | 0.433 | 2.23 | 0.111 | 2.54 | 0.085 | 1.56 | 0.216 |
表3 煤矿矿区位置(生境)和修复(微生境)对地表节肢动物群落影响的二因素方差分析结果
Table 3 Results of two-factor ANOVA analysis of the effect of coal mine location and restoration on community characteristics of ground arthropods
| 因素 | 活动密度 | 类群丰富度 | 多样性指数 | 均匀度指数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 生境 | 3.10 | 0.050 | 0.87 | 0.425 | 4.30 | 0.017 | 9.46 | <0.001 |
| 微生境 | 7.05 | 0.009 | 2.51 | 0.117 | 0.12 | 0.735 | 8.49 | 0.005 |
| 生境×微生境 | 0.85 | 0.433 | 2.23 | 0.111 | 2.54 | 0.085 | 1.56 | 0.216 |
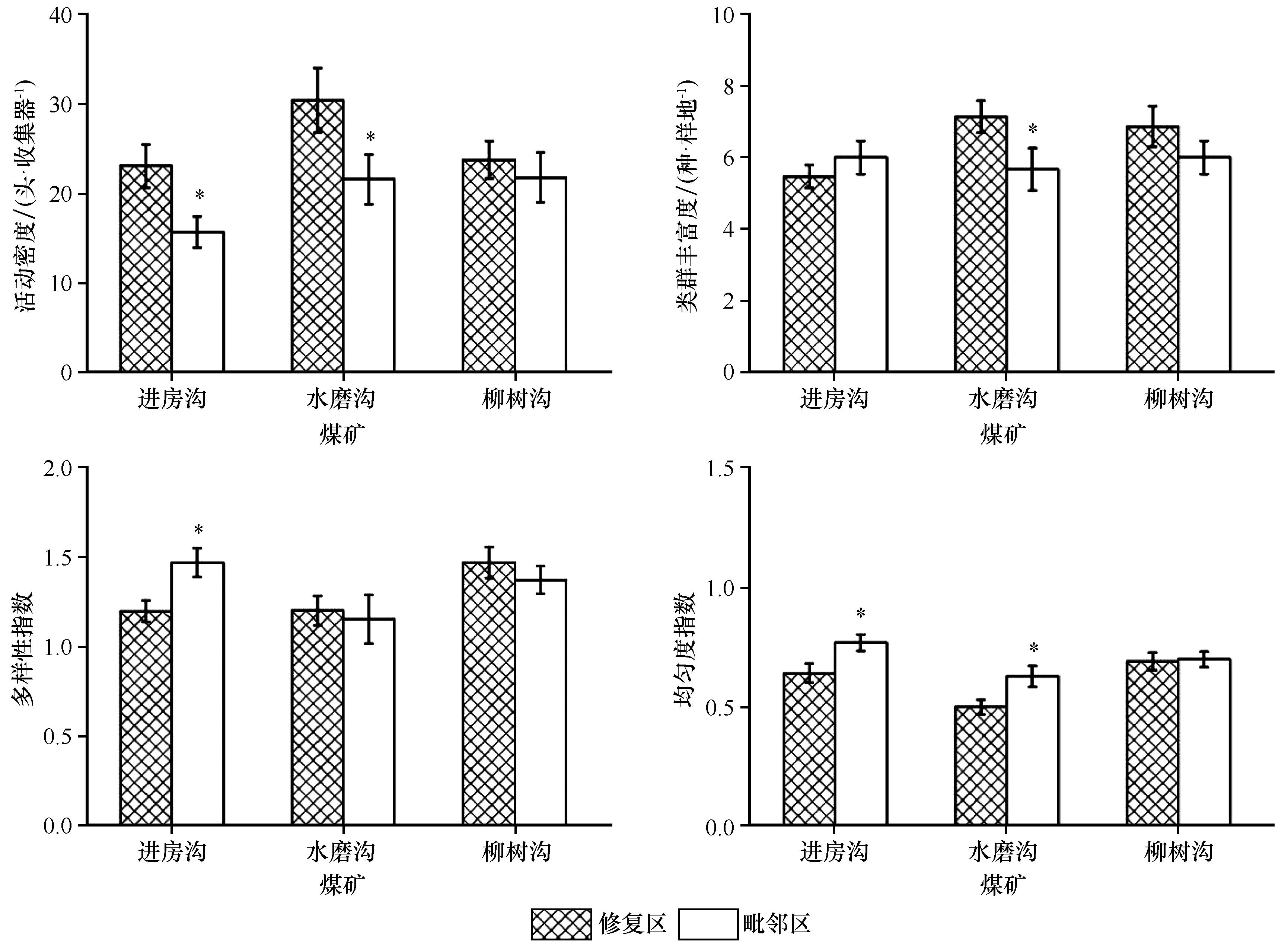
图2 不同煤矿修复区与毗邻区地表节肢动物活动密度、类群丰富度、多样性指数和均匀度指数比较*表示修复区与毗邻区差异显著,P<0.05
Fig.2 Comparison of activity density, groups richness, diversity index and evenness index of ground arthropods in different coal mine restoration areas and adjacent areas
| 因素 | 捕食性类群 | 植食性类群 | 其他类群 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 生境 | 3.10 | <0.001 | 7.30 | <0.001 | 3.15 | <0.007 |
| 微生境 | 7.61 | <0.001 | 2.24 | 0.05 | 4.04 | 0.010 |
| 生境×微生境 | 4.19 | <0.001 | 1.77 | 0.07 | 0.60 | 0.74 |
表4 煤矿矿区位置(生境)及修复(微生境)对煤矿捕食性、植食性和其他食性群落影响的多元方差分析结果
Table 4 Results of two-factor PERMANOVA of the effect of coal mine location and restoration on predators, herbivores, others of ground arthropods in coal mine
| 因素 | 捕食性类群 | 植食性类群 | 其他类群 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 生境 | 3.10 | <0.001 | 7.30 | <0.001 | 3.15 | <0.007 |
| 微生境 | 7.61 | <0.001 | 2.24 | 0.05 | 4.04 | 0.010 |
| 生境×微生境 | 4.19 | <0.001 | 1.77 | 0.07 | 0.60 | 0.74 |
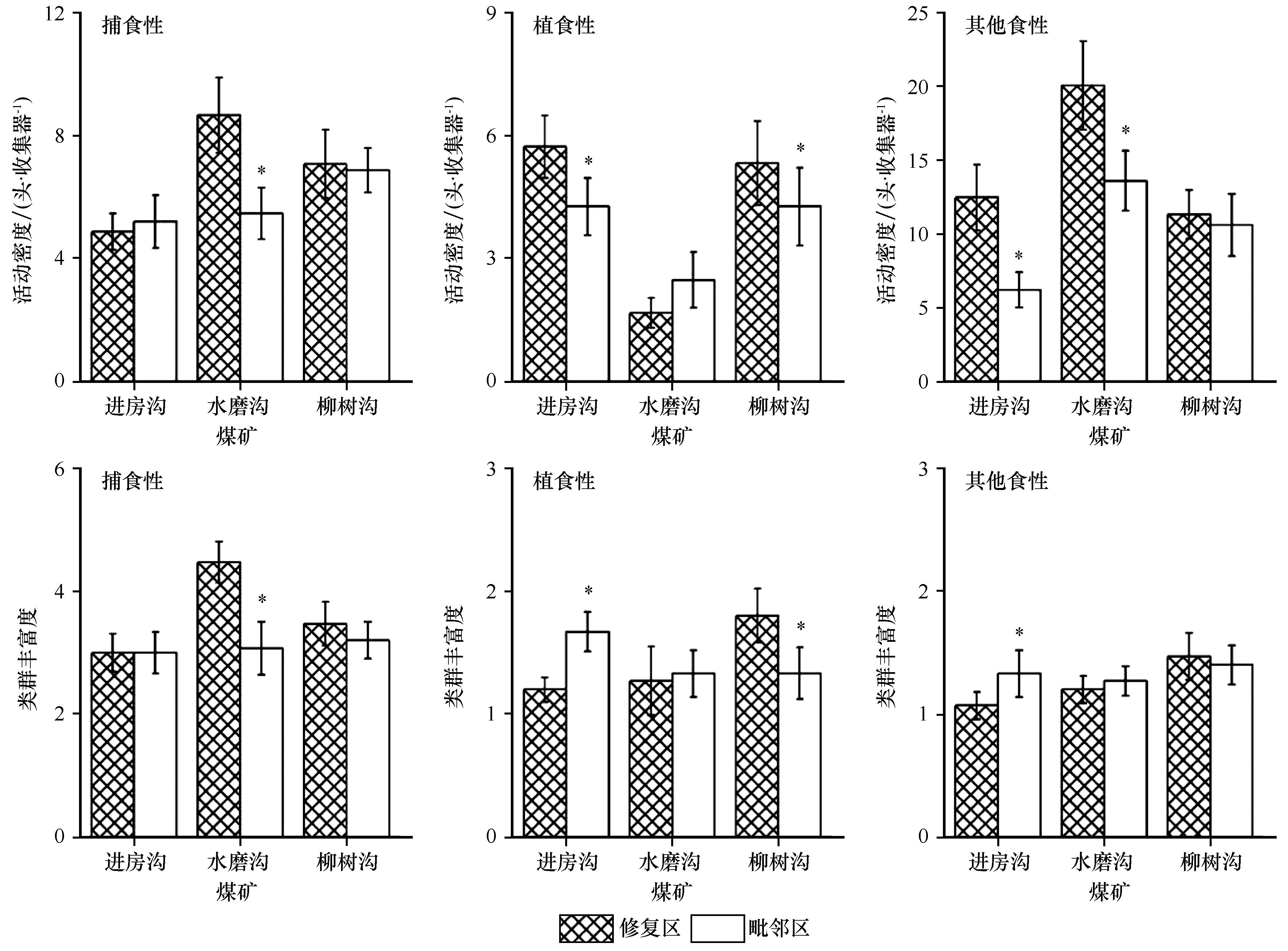
图3 不同煤矿修复区和毗邻区捕食性、植食性和其他食性地表节肢动物活动密度及类群丰富度比较*表示修复区与毗邻区差异显著,P<0.05
Fig.3 Comparison of activity density and groups richness of predators, herbivores and other groups on ground arthropods in different coal mine restoration areas and adjacent areas
| 解释变量 | 解释量/% | 贡献率/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 捕食性类群 | ||||
| 草本盖度 | 1.73 | 5.70 | 0.60 | 0.686 |
| 草本物种数 | 3.98 | 13.10 | 1.60 | 0.184 |
| 土壤粗砂含量 | 1.89 | 6.30 | 0.70 | 0.634 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 13.58 | 45.00 | 4.20 | 0.006 |
| 土壤全氮含量 | 4.76 | 15.70 | 1.70 | 0.126 |
| 土壤全钾含量 | 4.25 | 14.10 | 1.40 | 0.230 |
| 植食性类群 | ||||
| 草本盖度 | 0.67 | 4.00 | 0.30 | 0.813 |
| 草本物种数 | 6.25 | 37.70 | 3.00 | 0.037 |
| 土壤粗砂含量 | 5.33 | 32.20 | 3.30 | 0.022 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 0.99 | 6.00 | 0.60 | 0.622 |
| 土壤全氮含量 | 2.44 | 14.70 | 1.60 | 0.208 |
| 土壤全钾含量 | 0.92 | 5.50 | 0.50 | 0.787 |
表5 pRDA分析确定6个植被和土壤环境因子对捕食性和植食性地表节肢动物分布的相对贡献率
Table 5 pRDA analysis determined the relative contribution rates of six vegetation and soil environmental factors to the distribution of predatory and herbivorous ground arthropods
| 解释变量 | 解释量/% | 贡献率/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 捕食性类群 | ||||
| 草本盖度 | 1.73 | 5.70 | 0.60 | 0.686 |
| 草本物种数 | 3.98 | 13.10 | 1.60 | 0.184 |
| 土壤粗砂含量 | 1.89 | 6.30 | 0.70 | 0.634 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 13.58 | 45.00 | 4.20 | 0.006 |
| 土壤全氮含量 | 4.76 | 15.70 | 1.70 | 0.126 |
| 土壤全钾含量 | 4.25 | 14.10 | 1.40 | 0.230 |
| 植食性类群 | ||||
| 草本盖度 | 0.67 | 4.00 | 0.30 | 0.813 |
| 草本物种数 | 6.25 | 37.70 | 3.00 | 0.037 |
| 土壤粗砂含量 | 5.33 | 32.20 | 3.30 | 0.022 |
| 土壤有机质含量 | 0.99 | 6.00 | 0.60 | 0.622 |
| 土壤全氮含量 | 2.44 | 14.70 | 1.60 | 0.208 |
| 土壤全钾含量 | 0.92 | 5.50 | 0.50 | 0.787 |
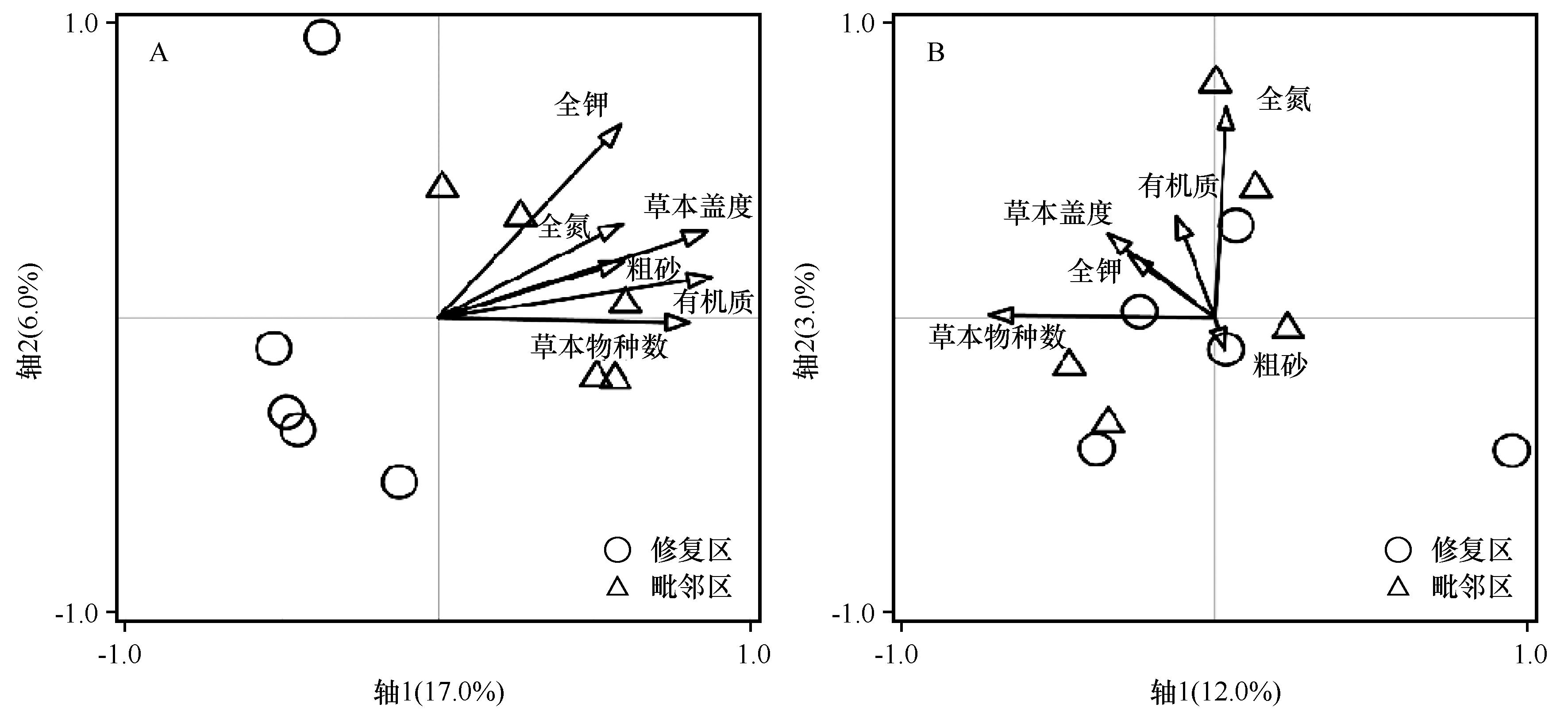
图4 典型煤矿修复区与毗邻区土壤捕食性(A)和植食性(B)地表节肢动物与主要环境因子的RDA排序图
Fig.4 The RDA two-dimensional ordination diagram of predators (A) and herbivores (B) and main environmental factors in typical coal mine restoration area and adjacent area. ○ represents the restoration area and △ represents the adjacent area
| 1 | 生态环境部. “美丽中国先锋榜(24)|甘肃整治祁连山国家级自然保护区生态环境破坏问题”[Z].2019-09-20. |
| 2 | 卫智军,李青丰,贾鲜艳,等.矿业废弃地的植被恢复与重建[J].水土保持学报,2003(4):172-175. |
| 3 | 郝蓉,白中科,赵景逵,等.黄土区大型露天煤矿废弃地植被恢复过程中的植被动态[J].生态学报,2003,33(8):1470-1476. |
| 4 | 郭逍宇,张金屯,宫辉力,等.安太堡矿区复垦地植被恢复过程多样性变化[J].生态学报,2005,25(4):763-770. |
| 5 | 姚虹,马建军,张树礼.煤矿复垦地不同恢复阶段植物群落功能群结构与生物多样性变化[J].西北植物学报,2012,32(5):1013-1020. |
| 6 | 朱琦,聂欣然,张勇,等.华北地区煤矸石山生态修复草本植物种优选[J].北京林业大学学报,2021,43(8):90-97. |
| 7 | 秦文展.露天铝土矿生态恢复过程中生物多样性研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2011. |
| 8 | 李琦峰.肃南县马苏河矿区生态环境调研评估与修复方案研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| 9 | 董玉锟.内蒙露天煤矿排土场边坡抗冲性及减水减沙效益研究[D].陕西杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2015. |
| 10 | 叶凌枫.不同修复措施对矿区土壤肥力质量的影响及评价[D].西安:长安大学,2016. |
| 11 | 魏光普.轻稀土尾矿库周边植被恢复模式及其土壤修复效应研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2019. |
| 12 | 刘莉莉,姚德利,文屹,等.鞍山铁矿废弃地生态恢复与重建中土壤动物群落研究[J].土壤通报,2009,40(2):248-251. |
| 13 | 李娜,张雪萍,张利敏.三种温带森林大型土壤动物群落结构的时空动态[J].生态学报,2013,33(19):6236-6245. |
| 14 | 辛未冬,刘华煜,杨轶萌,等.复垦对煤矸石山地表节肢动物群落特征的影响[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(7):2213-2222. |
| 15 | 殷秀琴,宋博,董炜华,等.我国土壤动物生态地理研究进展[J].地理学报,2010,65(1):91-102. |
| 16 | 李红涛.不同植被配置下矿区大型土壤动物群落结构研究[D].北京:中国地质大学,2016. |
| 17 | 郑乐怡,归鸿.昆虫分类[M].南京:南京师范大学出版社,1999. |
| 18 | Song D X, Zhu M S, Chen J.The Spiders of China[M].Shijiazhuang:Hebei Science and Technology Publishing House,1999. |
| 19 | 任国栋,于有志.中国荒漠半荒漠的拟步甲科昆虫[J].保定:河北大学出版社,1999. |
| 20 | 梁宏斌,虞佩玉.中国捕食粘虫的步甲种类检索[J].昆虫天敌,2000,22(4):160-167. |
| 21 | 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,2000. |
| 22 | Clarke K R, Gorley R N.PRIMER V6:User Manual/Tutorial(Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research)[M].Plymouth,UK:Primer-E Ltd,2006. |
| 23 | Ter Braak C J F, Smilauer P.Canoco reference manual and user's guide:software for ordination (version 5.0)[Z].Ithaca,USA:Microcomputer Power,2012. |
| 24 | Jitendra A, Kumar M S.Assessment of soil carbon pool,carbon sequestration and soil CO2 flux in unreclaimed and reclaimed coal mine spoils[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2018,77(1):1-13. |
| 25 | 王丽艳,韩有志,张成梁,等.不同植被恢复模式下煤矸石山复垦土壤性质及煤矸石风化物的变化特征[J].生态学报,2011,31(21):6429-6441. |
| 26 | 李晓莹,徐学华,郭江,等.不同造林树种对铁尾矿基质理化性质和土壤动物的影响[J].生态学报,2014,34(20):5746-5757. |
| 27 | 田佳榕,马伟波,戚旭东,等.内蒙古某铁矿尾矿库生态修复区的植被恢复效果[J].农业资源与环境学报,2020,37(4):601-608. |
| 28 | 陶贵鑫,周宏轩,孙婧,等.关闭/废弃煤矿的生态修复研究进展及展望[J].中国矿业,2021,30(5):10-19. |
| 29 | 杜华栋,曹祎晨,聂文杰,等.黄土沟壑区采煤塌陷地人工与自然植被恢复下土壤性质演变特征[J].煤炭学报,2021,46(5):1641-1649. |
| 30 | 王金满,杨睿璇,白中科.草原区露天煤矿排土场复垦土壤质量演替规律与模型[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(14):229-235. |
| 31 | 谢伟,钱晓彤,王东丽,等.鄂尔多斯矿区排土场苜蓿恢复地土壤种子库的演变特征[J].中国水土保持科学,2020,18(4):29-37. |
| 32 | 温明霞,邵明安,周蓓蓓.马家塔露天煤矿复垦区不同土地利用类型的土壤水分入渗过程研究[J].水土保持研究,2009,16(4):170-173. |
| 33 | 崔艳,白中科,李晋川,等.露天煤矿不同恢复阶段大型土壤动物群落结构[J].生态学杂志,2007,26(4):607-610. |
| 34 | 王金满,郭凌俐,白中科,等.黄土区露天煤矿排土场复垦后土壤与植被的演变规律[J].农业工程学报,2013,29(21):223-232. |
| 35 | Cristescu R H, Frère C, Banks P B.A review of fauna in mine rehabilitation in Australia:current state and future directions[J].Biological Conservation,2012,149(1):60-72. |
| 36 | Kędzior R, Szwalec A, Mundała P,et al.Ground beetle (Coleoptera,Carabidae) life history traits as indicators of habitat recovering processes in postindustrial areas[J].Ecological Engineering,2020,142:105615. |
| 37 | Wanner M, Dunger W.Primary immigration and succession of soil organisms on reclaimed opencast coal mining areas in eastern Germany[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2002,38(2):137-143. |
| 38 | 林英华,宋百敏,韩茜,等.北京门头沟废弃采石矿区地表土壤动物群落多样性[J].生态学报,2007,27(11):4832-4839. |
| 39 | 王军,李红涛,白中科,等.矿区不同复垦模式下大型土壤动物功能类群及其分布研究:以山西省平朔矿区为例[J].中国土地科学,2017,31(11):83-90. |
| 40 | Rufaut C G, Clearwater S, Craw D.Recolonization and recovery of soil invertebrate assemblages at an inactive coal mine in southern New Zealand[J].New Zealand Natural Sciences,2010,35:17-30. |
| 41 | Hendrychová M, Šálek M, Tajovský K,et al.Soil properties and species richness of invertebrates on afforested sites after brown coal mining[J].Restoration Ecology,2012,20(5):561-567. |
| 42 | Topp W, Simon M, Kautz G,et al.Soil fauna of a reclaimed lignite open-cast mine of the Rhineland:improvement of soil quality by surface pattern[J].Ecological Engineering,2001,17(2/3):307-322. |
| 43 | 路凯亮,腾悦,李俊兰.围封对内蒙古退化典型草原大型土壤动物群落多样性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(9):2680-2689. |
| 44 | 朱永恒,沈非,余健,等.铜尾矿废弃地土壤动物多样性特征[J].生态学报,2013,33(5):1495-1505. |
| 45 | 崔艳,张继栋,白中科,等.露天煤矿不同恢复植被大型土壤动物群落比较[J].生态环境,2008,17(3):1024-1027. |
| [1] | 赵啸龙, 谢玉鸿, 马旭君, 王少昆. 科尔沁沙质草地不同恢复年限草本层群落结构及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [2] | 王亚妮, 胡宜刚, 王增如, 李昌盛. 开垦对阿拉尔绿洲盐渍化荒漠土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 126-137. |
| [3] | 冯永宏, 刘任涛, 刘纪贤, 蒋嘉瑜, 白燕娇, 郭志霞, 王文帆, 张安宁. 荒漠区油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)灌丛冠层中节肢动物群落结构特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 94-102. |
| [4] | 滕泽宇, 肖生春, 陈小红, 韩超. 阿拉善荒漠5种灌丛下土壤细菌特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 34-44. |
| [5] | 董六文, 韩佳龙, 赵文智, 刘继亮, 巴义彬. 黑河流域湖泊湿地及毗邻沙丘地表节肢动物群落结构比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 250-258. |
| [6] | 刘任涛, 张安宁. 固沙灌丛林营造初期地面节肢动物群落结构特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 190-199. |
| [7] | 李得禄, 马全林, 张锦春, 陈芳, 李新荣, 袁宏波, 魏林源, 杨昊天, 张忠. 腾格里沙漠植被特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| [8] | 王昱, 刘娟娟, 冯起, 刘贤德, 王之君, 郭亚敏, 孔德星. 黑河底栖动物群落结构及生物多样性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 125-135. |
| [9] | 熊炳桥, 赵丽娅, 高丹丹. 围封对退化沙质草地植物群落的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 324-328. |
| [10] | 李婷, 张威, 刘光琇, 陈拓. 荒漠土壤微生物群落结构特征研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 329-338. |
| [11] | 刘任涛, 郗伟华, 刘佳楠, 赵娟, 常海涛. 沙地柠条(Caragana)灌丛微生境节肢动物群落特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 117-125. |
| [12] | 李效雄1, 刘贤德1,2, 赵维俊2. 祁连山青海云杉林动态监测样地群落特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(1): 94-100. |
| [13] | 刘任涛1,2, 赵哈林2, 赵学勇2. 流动沙地灌丛内外生境中土壤动物群落结构研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(1): 167-173. |
| [14] | 刘世增, 马全林, 严子柱, 贺访印. 甘肃沙葱的地理分布与群落结构特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2005, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [15] | 赵成章, 樊胜岳, 殷翠琴, 贺学斌. 毒杂草型退化草地植被群落特征的研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2004, 24(4): 507-512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
