中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 205-216.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00118
段瑞兵1,2( ), 张瑞2, 王乐乐2, 张亚鑫2, 杨战1, 董雪1, 马迎宾1(
), 张瑞2, 王乐乐2, 张亚鑫2, 杨战1, 董雪1, 马迎宾1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-08
修回日期:2024-09-04
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-10-15
通讯作者:
马迎宾
作者简介:马迎宾(E-mail: mayingbin1988@126.com)基金资助:
Ruibing Duan1,2( ), Rui Zhang2, Lele Wang2, Yaxin Zhang2, Zhan Yang1, Xue Dong1, Yingbin Ma1(
), Rui Zhang2, Lele Wang2, Yaxin Zhang2, Zhan Yang1, Xue Dong1, Yingbin Ma1( )
)
Received:2024-06-08
Revised:2024-09-04
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-15
Contact:
Yingbin Ma
摘要:
灌木在荒漠化防治和植被恢复中发挥着重要作用,特别是在应对气候变化引发的干旱方面。然而,沙漠灌木通过形态和解剖结构特征适应干旱环境的机制仍不清楚。对乌兰布和沙漠10种常见植物在干旱胁迫环境下的叶片压力-容积(PV)曲线水分参数、叶片解剖和结构等特征及其适应机制进行研究。结果显示:(1)10种植物在PV曲线水分参数(PV性状)和解剖特征差异显著。(2)C3植物和C4植物在PV性状、叶片厚度、角质层厚度、比叶面积(SLA)和叶干物质含量(LDMC)等方面存在显著差异。C3植物的失膨点水势(Ψtlp)和饱和含水时的渗透势(Ψ0)值较高,但叶片水容(Cleaf)较低。C3植物的叶片厚度和角质层厚度显著低于C4植物,而SLA和LDMC显著高于C4植物。(3)叶片厚度、栅栏组织和海绵组织与Ψtlp、Cleaf和弹性模量(ε)等PV性状之间存在显著相关关系,并且不同光合作用途径植物叶片解剖特征与PV性状之间的关系表现出差异。
中图分类号:
段瑞兵, 张瑞, 王乐乐, 张亚鑫, 杨战, 董雪, 马迎宾. 乌兰布和沙漠10种植物叶片PV曲线水分参数与解剖特征关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 205-216.
Ruibing Duan, Rui Zhang, Lele Wang, Yaxin Zhang, Zhan Yang, Xue Dong, Yingbin Ma. Relationship between leaf PV curve water parameters and anatomical characteristics of ten plants spieces in the Ulan Buh Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 205-216.
| 树种 | 光合途径 | Ψtlp/MPa | Ψ0/MPa | Cleaf/(mol·m-2·MPa-1) | ε/MPa | RWCtlp/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白刺 | C3 | -2.45±0.11 | -1.33±0.12 | 1.28 ±0.23 | 7.51±1.36 | 85.91±1.39 |
| 沙棘 | C3 | -1.97±0.07 | -1.64±0.09 | 1.36±0. 11 | 8.65±1.46 | 86.53±1.43 |
| 霸王 | C4 | -3.39±0.16 | -2.50±0.17 | 1.43±0. 08 | 10.52±0.69 | 83.45±0.74 |
| 柽柳 | C3 | -1.98±0.03 | -1.85±0.08 | 0.61±0.11 | 27.79±5.88 | 96.93±.0.68 |
| 黑沙蒿 | C4 | -1.52±0.07 | -1.40±0.06 | 1.85±0.23 | 7.25±0.88 | 93.05±0.99 |
| 花棒 | C3 | -1.68±0.06 | -1.57±0.06 | 2.74±0.07 | 6.61±0.40 | 93.39±0.56 |
| 沙拐枣 | C4 | -1.82±0.13 | -1.57±0.07 | 3.04±0.35 | 7.99±1.27 | 88.64±1.84 |
| 梭梭 | C4 | -3.44±0.11 | -2.66±0.09 | 1.98±0.19 | 14.20±1.11 | 86.35±1.15 |
| 柠条 | C3 | -2.07±0.04 | -1.75±0.09 | 1.03±0.13 | 6.39±1.25 | 77.07±3.09 |
| 沙冬青 | C3 | -2.56±0.09 | -2.14±0.06 | 1.06±0.08 | 12.24±0.63 | 87.09±1.86 |
| 变异系数CV/% | 29.16 | 25.30 | 49.32 | 66.24 | 6.89 |
表1 乌兰布和沙漠10种植物叶片/同化枝PV性状
Table 1 PV traits of leaves/assimilating branches in ten woody plant species from the Ulan Buh Desert
| 树种 | 光合途径 | Ψtlp/MPa | Ψ0/MPa | Cleaf/(mol·m-2·MPa-1) | ε/MPa | RWCtlp/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白刺 | C3 | -2.45±0.11 | -1.33±0.12 | 1.28 ±0.23 | 7.51±1.36 | 85.91±1.39 |
| 沙棘 | C3 | -1.97±0.07 | -1.64±0.09 | 1.36±0. 11 | 8.65±1.46 | 86.53±1.43 |
| 霸王 | C4 | -3.39±0.16 | -2.50±0.17 | 1.43±0. 08 | 10.52±0.69 | 83.45±0.74 |
| 柽柳 | C3 | -1.98±0.03 | -1.85±0.08 | 0.61±0.11 | 27.79±5.88 | 96.93±.0.68 |
| 黑沙蒿 | C4 | -1.52±0.07 | -1.40±0.06 | 1.85±0.23 | 7.25±0.88 | 93.05±0.99 |
| 花棒 | C3 | -1.68±0.06 | -1.57±0.06 | 2.74±0.07 | 6.61±0.40 | 93.39±0.56 |
| 沙拐枣 | C4 | -1.82±0.13 | -1.57±0.07 | 3.04±0.35 | 7.99±1.27 | 88.64±1.84 |
| 梭梭 | C4 | -3.44±0.11 | -2.66±0.09 | 1.98±0.19 | 14.20±1.11 | 86.35±1.15 |
| 柠条 | C3 | -2.07±0.04 | -1.75±0.09 | 1.03±0.13 | 6.39±1.25 | 77.07±3.09 |
| 沙冬青 | C3 | -2.56±0.09 | -2.14±0.06 | 1.06±0.08 | 12.24±0.63 | 87.09±1.86 |
| 变异系数CV/% | 29.16 | 25.30 | 49.32 | 66.24 | 6.89 |
| 树种 | 叶片厚度LT/μm | 栅栏组织 厚度PT/μm | 海绵组织 厚度ST/μm | 栅栏/海绵 组织厚度 比值PT/ST | 角质层厚度ET/μm | 叶肉组织占叶肉细胞百分比MES/% | 维管束占叶肉细胞百分比VB/% | 贮水组织占叶肉细胞百分比STO/% | 比叶面积SLA/(cm2·g-1) | 叶干物质含量LDMC/(g·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白刺 | 455.58±27.72 | 98.67±2.12 | 80.12±4.76 | 1.24±0.50 | 4.95±0.10 | 43.30±1.06 | 3.29±0.30 | 53.41±0.81 | 69.33± 3.80 | 0.29±0.12 |
| 沙棘 | 275.70±45.98 | 94.19±3.33 | 34.14±11.80 | 3.51±0.75 | 4.16±0.40 | 46.00±0.72 | 3.18±0.48 | 50.82±0.63 | 114.72±5.72 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 霸王 | 1006.97±26.05 | 145.50±7.69 | — | — | 5.34±0.19 | 34.30±0.39 | 4.03±1.15 | 61.68±1.52 | 45.83±1.27 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 柽柳 | 610.76±26.78 | 75.70±4.43 | 28.71±1.19 | 2.65±0.18 | 6.34±0.37 | 32.03±0.96 | 16.08±1.51 | 51.89±1.79 | 46.69±1.81 | 0.42±0.01 |
| 黑沙蒿 | 442.61±20.31 | 104.71±4.02 | 43.90±2.18 | 2.39±0.08 | 6.93±0.55 | 54.44±0.06 | 3.42±0.34 | 42.14±0.33 | 69.21±2.39 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 花棒 | 776.09±20.72 | 94.15±3.30 | — | — | 4.09±0.30 | 35.68±1.26 | 13.20±0.64 | 51.11±1.17 | 47.13±0.84 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 沙拐枣 | 1108.54±30.84 | 51.28±5.76 | — | — | 6.64±0.33 | 22.05±1.31 | 7.35±0.65 | 70.60±1.42 | 29.95±2.61 | 0.30±0.03 |
| 梭梭 | 1035.64±37.78 | 32.24±0.52 | — | — | 5.16±0.25 | 16.82±1.18 | 4.71±0.87 | 78.47±0.60 | 30.64±0.91 | 0.31±0.02 |
| 柠条 | 200.23±1.54 | 51.68±1.59 | 14.91±0.67 | 3.48±0.15 | 1.86±0.04 | 59.22±0.59 | 10.85±0.66 | 29.93±1.06 | 115.78±3.04 | 0.38±0.02 |
| 沙冬青 | 414.14±14.16 | 111.98±4.74 | 65.11±1.00 | 1.72±0.09 | 2.50±0.32 | 57.85±2.18 | 3.61±0.49 | 38.54±2.11 | 52.57±0.99 | 0.39±0.01 |
| 变异系数CV/% | 50.68 | 38.66 | 51.28 | 49.09 | 35.49 | 35.24 | 68.39 | 26.76 | 48.37 | 14.04 |
表2 乌兰布和沙漠10种植物叶片/同化枝解剖与结构特征
Table 2 Anatomical and structural characteristics of leaves/assimilating branches in ten woody plant species from the Ulan Buh Desert
| 树种 | 叶片厚度LT/μm | 栅栏组织 厚度PT/μm | 海绵组织 厚度ST/μm | 栅栏/海绵 组织厚度 比值PT/ST | 角质层厚度ET/μm | 叶肉组织占叶肉细胞百分比MES/% | 维管束占叶肉细胞百分比VB/% | 贮水组织占叶肉细胞百分比STO/% | 比叶面积SLA/(cm2·g-1) | 叶干物质含量LDMC/(g·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白刺 | 455.58±27.72 | 98.67±2.12 | 80.12±4.76 | 1.24±0.50 | 4.95±0.10 | 43.30±1.06 | 3.29±0.30 | 53.41±0.81 | 69.33± 3.80 | 0.29±0.12 |
| 沙棘 | 275.70±45.98 | 94.19±3.33 | 34.14±11.80 | 3.51±0.75 | 4.16±0.40 | 46.00±0.72 | 3.18±0.48 | 50.82±0.63 | 114.72±5.72 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 霸王 | 1006.97±26.05 | 145.50±7.69 | — | — | 5.34±0.19 | 34.30±0.39 | 4.03±1.15 | 61.68±1.52 | 45.83±1.27 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 柽柳 | 610.76±26.78 | 75.70±4.43 | 28.71±1.19 | 2.65±0.18 | 6.34±0.37 | 32.03±0.96 | 16.08±1.51 | 51.89±1.79 | 46.69±1.81 | 0.42±0.01 |
| 黑沙蒿 | 442.61±20.31 | 104.71±4.02 | 43.90±2.18 | 2.39±0.08 | 6.93±0.55 | 54.44±0.06 | 3.42±0.34 | 42.14±0.33 | 69.21±2.39 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 花棒 | 776.09±20.72 | 94.15±3.30 | — | — | 4.09±0.30 | 35.68±1.26 | 13.20±0.64 | 51.11±1.17 | 47.13±0.84 | 0.33±0.01 |
| 沙拐枣 | 1108.54±30.84 | 51.28±5.76 | — | — | 6.64±0.33 | 22.05±1.31 | 7.35±0.65 | 70.60±1.42 | 29.95±2.61 | 0.30±0.03 |
| 梭梭 | 1035.64±37.78 | 32.24±0.52 | — | — | 5.16±0.25 | 16.82±1.18 | 4.71±0.87 | 78.47±0.60 | 30.64±0.91 | 0.31±0.02 |
| 柠条 | 200.23±1.54 | 51.68±1.59 | 14.91±0.67 | 3.48±0.15 | 1.86±0.04 | 59.22±0.59 | 10.85±0.66 | 29.93±1.06 | 115.78±3.04 | 0.38±0.02 |
| 沙冬青 | 414.14±14.16 | 111.98±4.74 | 65.11±1.00 | 1.72±0.09 | 2.50±0.32 | 57.85±2.18 | 3.61±0.49 | 38.54±2.11 | 52.57±0.99 | 0.39±0.01 |
| 变异系数CV/% | 50.68 | 38.66 | 51.28 | 49.09 | 35.49 | 35.24 | 68.39 | 26.76 | 48.37 | 14.04 |
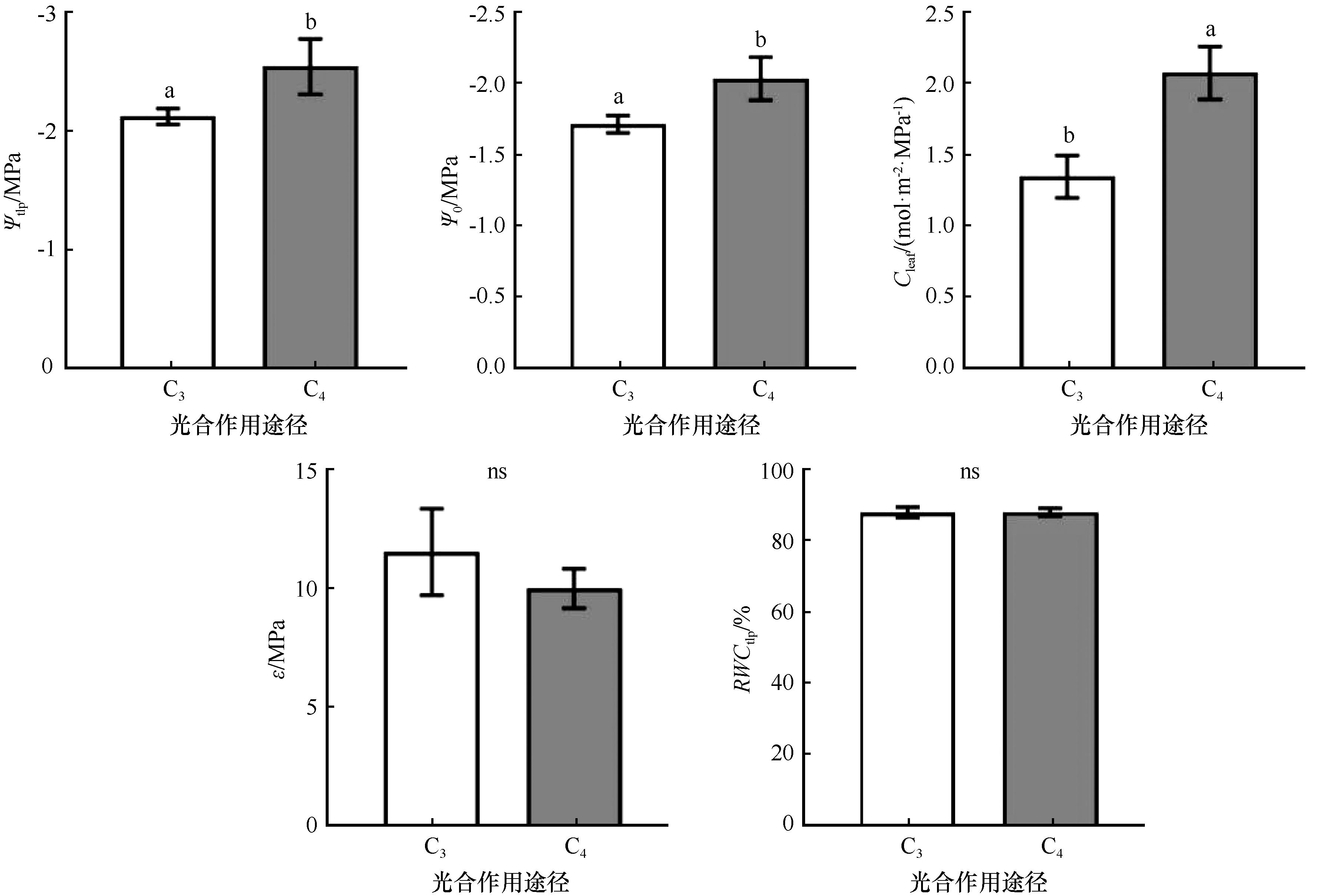
图1 乌兰布和沙漠不同光合作用途径植物PV性状特征比较(平均值±标准误)注:不同小写字母代表不同植物间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.1 Comparison of PV traits in plants with different photosynthetic pathways from the Ulan Buh Desert (mean ± SE)Note: different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among plant species (P< 0.05) , ns, not significant
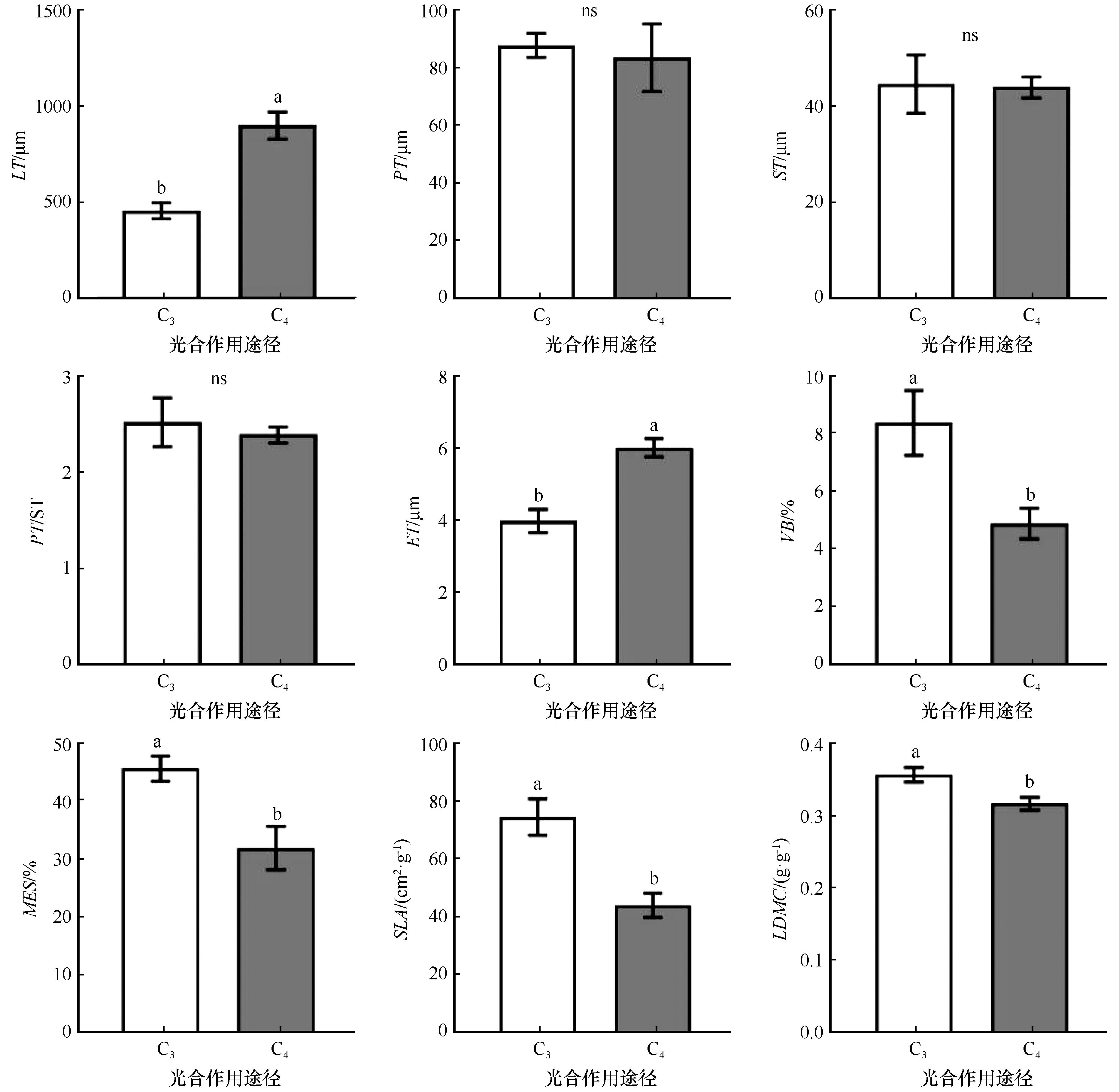
图2 乌兰布和沙漠不同光合作用途径植物叶片结构和解剖特征比较注:不同小写字母代表不同植物间差异显著(P<0.05)
Fig.2 Comparison of leaf structure and anatomical characteristics in plants with different photosynthetic pathways from the Ulan Buh Desert. Note: different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among plant species (P< 0.05) ,ns, not significant
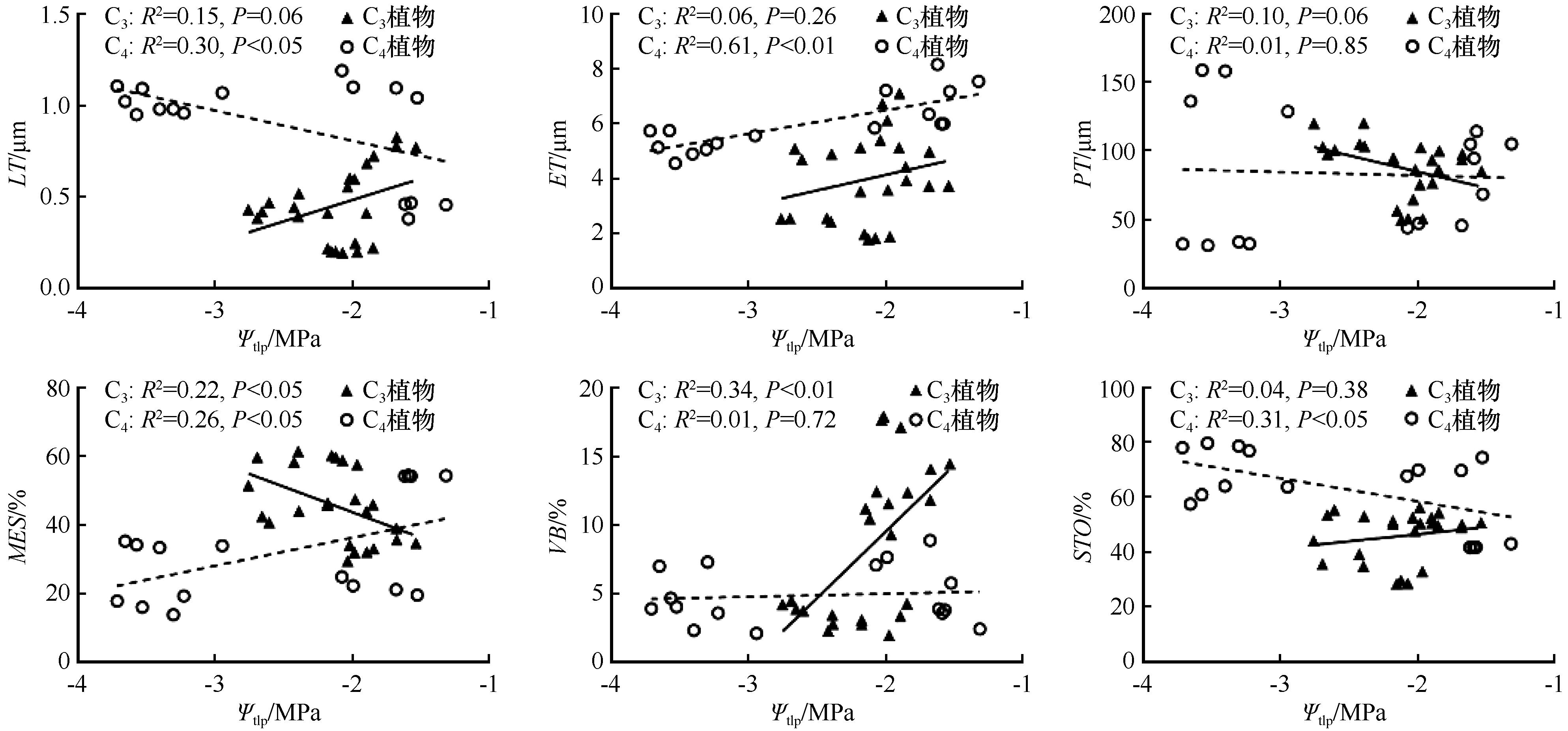
图3 乌兰布和沙漠不同光合作用途径植物叶片解剖特征与Ψtlp的关系
Fig.3 Relationship between leaf anatomical characteristics and Ψtlp in plants with different photosynthetic pathways from the Ulan Buh Desert
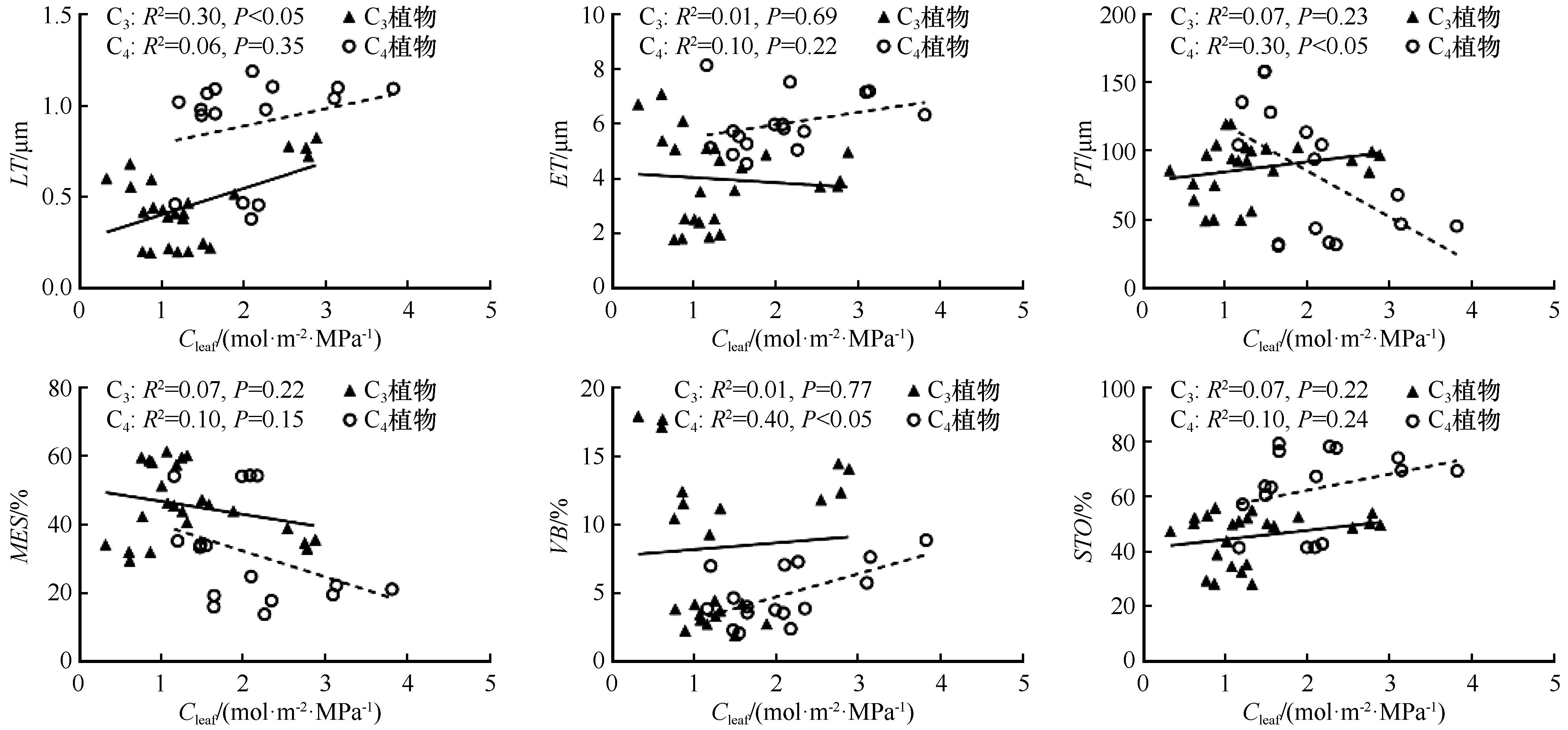
图4 乌兰布和沙漠不同光合作用途径植物叶片解剖特征与Cleaf的关系
Fig.4 Relationship between leaf anatomical characteristics and Cleaf in plants with different photosynthetic pathways from the Ulan Buh Desert
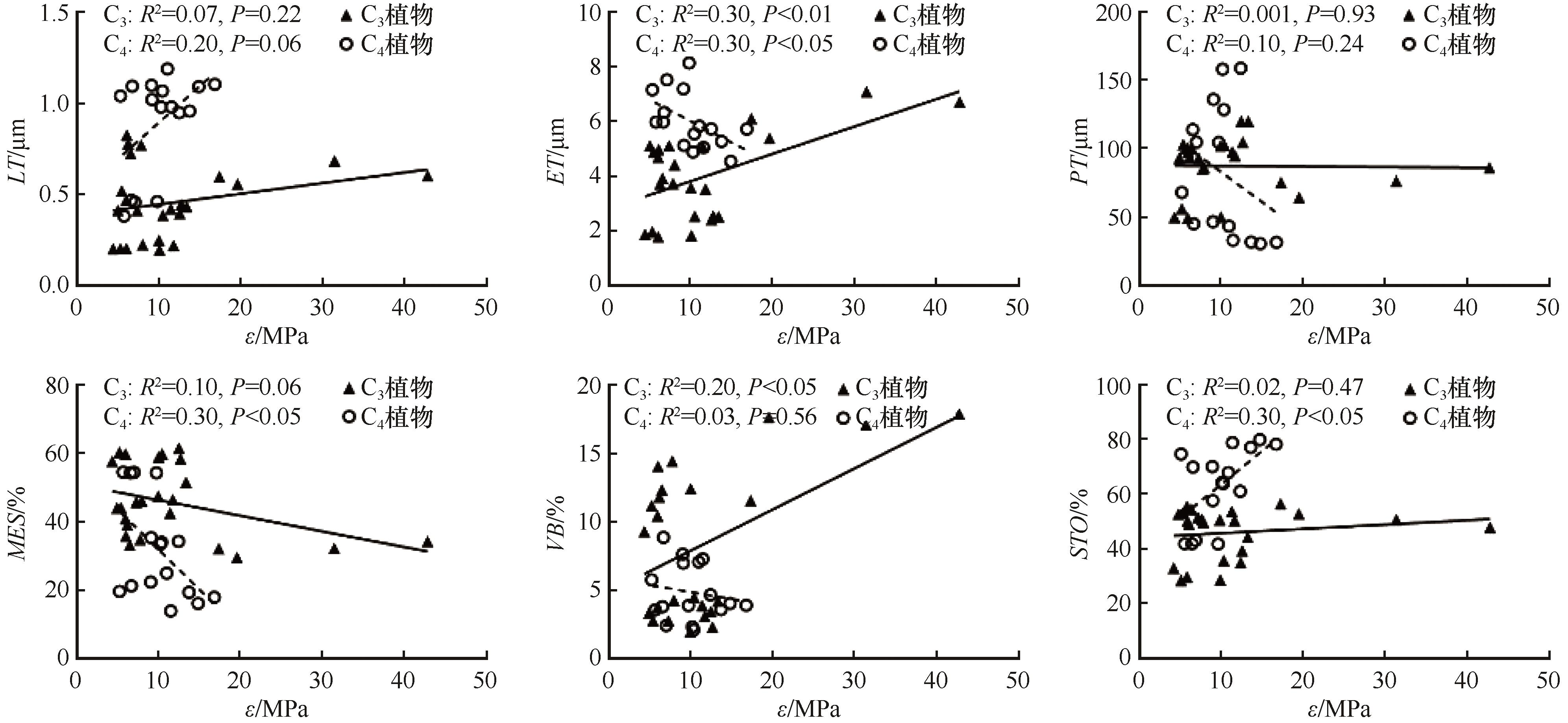
图5 乌兰布和沙漠不同光合作用途径植物叶片解剖特征与ε的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between leaf anatomical characteristics and ε in plants with different photosynthetic pathways from the Ulan Buh Desert
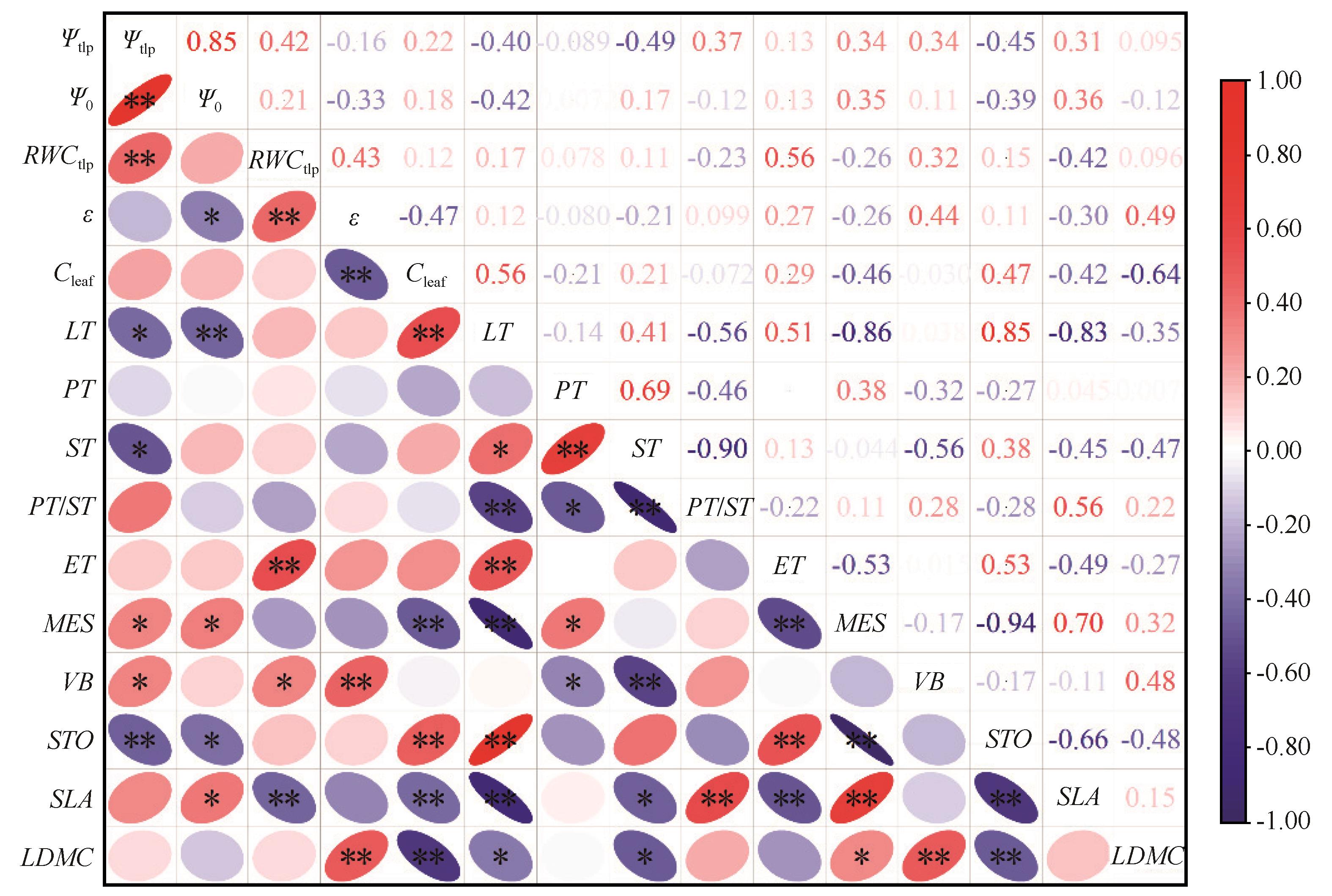
图6 乌兰布和沙漠10种植物叶片/同化枝PV性状与解剖、结构特征的相关性分析注:*:P<0.05;**:P<0.01
Fig.6 Correlation analysis of PV traits and anatomical and structural characteristics of leaves/assimilating branches in ten woody plant species from the Ulan Buh Desert. Note: *, P<0.05;**, P<0.01
| 1 | Li X R, Xiao H L, Zhang J G,et al.Long‐term ecosystem effects of sand‐binding vegetation in the Tengger Desert,northern China[J].Restoration Ecology,2004,12(3):376-390. |
| 2 | Chu X, Zhan J, Li Z,et al.Assessment on forest carbon sequestration in the Three-North Shelterbelt Program region,China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,215:382-389. |
| 3 | Zhang D, Zuo X, Zang C.Assessment of future potential carbon sequestration and water consumption in the construction area of the Three-North Shelterbelt Programme in China[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2021,303:108377. |
| 4 | Bai Y, Zhang Y, Michalet R,et al.Responses of different herb life-history groups to a dominant shrub species along a dune stabilization gradient[J].Basic and Applied Ecology,2019,38:1-12. |
| 5 | McDowell N G, Allen C D.Darcy's law predicts widespread forest mortality under climate warming[J].Nature Climate Change,2015,5(7):669-672. |
| 6 | Yu T, Liu P, Zhang Q,et al.Detecting forest degradation in the three-north forest shelterbelt in China from multi-scale satellite images[J].Remote Sensing,2021,13(6):1131. |
| 7 | 杨柳,孙慧珍.植物水分生理研究中的压力-容积测定技术几个关键问题[J].生态学杂志,2014,33(1):229-234. |
| 8 | 吴建慧,郭瑶,赵倩竹,等.干旱胁迫对绢毛委陵菜叶片解剖结构和生理指标的影响[J].草业科学,2012,29(8):1229-1234. |
| 9 | 李瑞强,王玉祥,孙玉兰,等.盐胁迫对无芒雀麦幼苗叶片形态及解剖结构的影响[J].草地学报,2022,30(6):1450-1459. |
| 10 | Ehleringer J R, Cerling T E.C3 and C4 photosynthesis[J].Encyclopedia of Global Environmental Change,2002,2(4):186-190. |
| 11 | Brodribb T, Holbrook N M, Gutierrez M.Hydraulic and photosynthetic co-ordination in seasonally dry tropical forest trees[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2002,25(11):1435-1444. |
| 12 | Kocacinar F, Mckown A D, Sage T L,et al.Photosynthetic pathway influences xylem structure and function in Flaveria (Asteraceae)[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2008,31(10):1363-1376. |
| 13 | Liu H, Taylor S H, Xu Q,et al.Life history is a key factor explaining functional trait diversity among subtropical grasses,and its influence differs between C3 and C4 species[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2019,70(5):1567-1580. |
| 14 | 种培芳,李航逸,李毅.荒漠植物红砂根系对干旱胁迫的生理响应[J].草业学报,2015,24(1):72-80. |
| 15 | 徐梦琦,高艳菊,张志浩,等.干旱胁迫对疏叶骆驼刺幼苗生长和生理的影响[J].干旱区研究,2023,40(2):257-267. |
| 16 | Hinckley T, Duhme F, Hinckley A,et al.Water relations of drought hardy shrubs:osmotic potential and stomatal reactivity[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,1980,3(2):131-140. |
| 17 | Turner N C.Measurement of plant water status by the pressure chamber technique[J].Irrigation Science,1988,9(4):289-308. |
| 18 | Meinzer F C, Woodruff D R, Marias D E,et al.Dynamics of leaf water relations components in co-occurring iso-and anisohydric conifer species[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2014,37(11):2577-2586. |
| 19 | Tyree M T, Hammel H T.The measurement of the turgor pressure and the water relations of plants by the pressure-bomb technique[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,1972,23(1):267-282. |
| 20 | Bartlett M K, Scoffoni C, Sack L.The determinants of leaf turgor loss point and prediction of drought tolerance of species and biomes:a global meta‐analysis[J].Ecology Letters,2012,15(5):393-405. |
| 21 | 王万里.压力室 (PRESSURE CHAMBER) 在植物水分状况研究中的应用[J].植物生理学通讯,1984,3:52-57. |
| 22 | 李吉跃.PV技术在油松侧柏苗木抗旱特性研究中的应用[J].北京林业大学学报,1989,11(1):3-11. |
| 23 | 李向义,张希明,何兴元,等.沙漠-绿洲过渡带四种多年生植物水分关系特征[J].生态学报,2004,24(6):1164-1171. |
| 24 | Bartlett M K, Zhang Y, Kreidler N,et al.Global analysis of plasticity in turgor loss point,a key drought tolerance trait[J].Ecology Letters,2014,17(12):1580-1590. |
| 25 | Zhu S D, Chen Y J, Ye Q,et al.Leaf turgor loss point is correlated with drought tolerance and leaf carbon economics traits[J].Tree Physiology,2018,38(5):658-663. |
| 26 | Blackman C J.Leaf turgor loss as a predictor of plant drought response strategies[J].Tree Physiology,2018,38(5):655-657. |
| 27 | 斯琴巴特尔,秀敏.荒漠植物蒙古扁桃水分生理特征[J].植物生态学报,2007,31(3):484-489. |
| 28 | 王乐乐,周正虎,金鹰,等.东北温带森林20 种乔木树种叶片干旱容忍性特征[J].应用生态学报,2022,33(1):1-8. |
| 29 | Rosas T, Mencuccini M, Barba J,et al.Adjustments and coordination of hydraulic,leaf and stem traits along a water availability gradient[J].New Phytologist,2019,223(2):632-646. |
| 30 | Xu H, Li Y, Xu G,et al.Ecophysiological response and morphological adjustment of two Central Asian desert shrubs towards variation in summer precipitation[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2007,30(4):399-409. |
| 31 | 石松利,王迎春,周红兵,等.濒危种四合木与其近缘种霸王水分关系参数和光合特性的比较[J].生态学报,32(4):1163-1173. |
| 32 | 李芳兰,包维楷.植物叶片形态解剖结构对环境变化的响应与适应[J].植物学报,2005,22():118-127. |
| 33 | 庞杰,张凤兰,郝丽珍,等.沙芥幼苗叶片解剖结构和光合作用对干旱胁迫的响应[J].生态环境学报,2013,22(4):575-581. |
| 34 | 黄振英,吴鸿,胡正海.30种新疆沙生植物的结构及其对沙漠环境的适应[J].植物生态学报,1997,21(6):521-530. |
| 35 | 刘玉冰,李新荣,李蒙蒙,等.中国干旱半干旱区荒漠植物叶片 (或同化枝) 表皮微形态特征[J].植物生态学报,2016,40(11):1189. |
| 36 | Feng X, Liu R, Li C,et al.Multi-level physiological and morphological adjustment of haloxylon ammodendron related to groundwater drawdown in a desert ecosystem[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2022,324:109096. |
| 37 | Zhang K Y, Yang D, Zhang Y B,et al.Differentiation in stem and leaf traits among sympatric lianas,scandent shrubs and trees in a subalpine cold temperate forest[J].Tree Physiology,2021,41(11):1992-2003. |
| 38 | 张海娜,苏培玺,李善家,等.荒漠区植物光合器官解剖结构对水分利用效率的指示作用[J].生态学报,2013,33(16):4909-4918. |
| 39 | Ivanova L A, Yudina P K, Ronzhina D A,et al.Quantitative mesophyll parameters rather than whole-leaf traits predict response of C3 steppe plants to aridity[J].New Phytologist,2018,217(2):558-570. |
| 40 | 李爱平,王晓江,杨小玉,等.库布齐沙漠几种沙生灌木叶解剖结构耐旱特征研究[J].中国沙漠,2010,30(6):1405-1410. |
| 41 | 杨树德,陈国仓,张承烈,等.胡杨披针形叶与宽卵形叶的渗透调节能力的差异[J].西北植物学报,2004(9):1583-1588. |
| 42 | 杨戈,王常贵.罗布泊地区几种旱生植物茎、叶结构的初步研究[J].干旱区研究,1984,57(1):57-63. |
| 43 | 昝丹丹,庄丽,黄刚,等.不同梭梭种群同化枝的解剖结构特征及其与生态因子的关系分析[J].西北植物学报,2016,36(2):309-315. |
| 44 | 刘莉,任昱.几种沙生植物水分代谢问题探讨[J].内蒙古林业科技,2011,37(3):8-12. |
| 45 | 龚春梅,宁蓬勃,王根轩,等.C3和C4植物光合途径的适应性变化和进化[J].植物生态学报,2009,33(1):206-221. |
| 46 | Jacob V, Choat B, Churchill A C,et al.High safety margins to drought‐induced hydraulic failure found in five pasture grasses[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2022,45(6):1631-1646. |
| 47 | Ogburn R M, Edwards E J.Quantifying succulence:a rapid,physiologically meaningful metric of plant water storage[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2012,35(9):1533-1542. |
| 48 | 闫海龙,张希明,许浩,等.塔里木沙漠公路防护林植物沙拐枣气体交换特性对干旱胁迫的响应[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(3):460-465. |
| 49 | Niinemets Ü.Global‐scale climatic controls of leaf dry mass per area,density,and thickness in trees and shrubs[J].Ecology,2001,82(2):453-469. |
| 50 | Liu C, Li Y, Xu L,et al.Variation in leaf morphological,stomatal,and anatomical traits and their relationships in temperate and subtropical forests[J].Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):5803. |
| 51 | Moore P D.High hopes for C4 plants[J].Nature,1994,367(6461):322-323. |
| 52 | Akram M A, Zhang Y, Wang X,et al.Phylogenetic independence in the variations in leaf functional traits among different plant life forms in an arid environment[J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2022,272:153671. |
| 53 | Sack L, Scoffoni C, John G P,et al.How do leaf veins influence the worldwide leaf economic spectrum?Review and synthesis[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2013,64(13):4053-4080. |
| 54 | Wright I J, Reich P B, Cornelissen J H,et al.Assessing the generality of global leaf trait relationships[J].New Phytologist,2005,166(2):485-496. |
| 55 | Nguyen H T, Meir P, Sack L,et al.Leaf water storage increases with salinity and aridity in the mangrove Avicennia marina:integration of leaf structure,osmotic adjustment and access to multiple water sources[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2017,40(8):1576-1591. |
| 56 | Nguyen H T, Meir P, Wolfe J,et al.Plumbing the depths:extracellular water storage in specialized leaf structures and its functional expression in a three‐domain pressure-volume relationship[J].Plant,Cell and Environment,2017,40(7):1021-1038. |
| [1] | 方进, 刘任涛, 赵璇, 杨敏. 绿洲农田中小型土壤动物多样性与功能群结构对土壤质地的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 155-166. |
| [2] | 卢建男, 李玉强, 赵学勇, 李宝成, 王旭洋, 张蕊. 半干旱区典型沙地生态环境演变特征及沙漠化防治建议[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 284-292. |
| [3] | 张腾, 苗运法, 邹亚国, 张孜越, 冯国平. 极端干旱区苏干湖湿地植被分类与变化分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 81-90. |
| [4] | 卫雨西, 陈丽娟, 冯起, 席海洋, 郭瑞, 张成琦. 干旱区盐碱土微生物特征及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 18-30. |
| [5] | 万雨晨, 刘彦平, 吴永胜, 贾鸿飞, 张甜, 高艳红, 杨昊天, 尤万学, 杜军, 贾荣亮. 腾格里沙漠人工固沙植被区藓类植物形态演变特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 298-307. |
| [6] | 邵梅, 罗万银, 顿耀权, 逯军峰, 王芳, 李得禄, 满多清, 雷丰丰, 张彩霞. 干旱区退化湖盆表土及降尘的微观形貌特征和化学元素组成差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 187-196. |
| [7] | 潘昌祥, 欧阳茜如, 廖梦榆, 范裕, 郭群, 张志山, 吴戈男, 赵洋, 刘立超, 潘颜霞, 李新荣, 屈建军, 穆松林, 李胜功. 西北干旱区沙漠化土地生态修复技术及沙产业的适用范围[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 155-165. |
| [8] | 刘俊壕, 周海盛, 郭群. 中国北方干旱半干旱区沙漠化治理对植被格局的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 204-213. |
| [9] | 尤其, 许宝荣, 邹松兵, 秦艺豪, 王铎, 于冬. 中国北方干旱半干旱区植被-气候响应关系特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 274-287. |
| [10] | 程姗岭, 于海鹏, 任钰, 周洁, 罗红羽, 刘晨汐, 龚咏琪. 中国干旱半干旱区气候异常影响机理研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 21-35. |
| [11] | 李琳, 刘鹄, 孙程鹏, 赵文智. 基于地下水位与土壤含水量的地下水蒸散发估算[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 277-287. |
| [12] | 赵康, 张磊, 李凯凯, 王斐, 张丙昌. 干旱区土壤自养微生物研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 177-186. |
| [13] | 吴倩倩, 张晓, 徐书兴, 杨晓晖, 刘艳书, 李瀚之, 时忠杰. 亚洲内陆干旱区NDVI与树木生长的气候响应及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 1-10. |
| [14] | 唐红林, 陈佳, 石若晗, 杨新军, 张小文, 马江浩. 乡村类型视角下干旱区社区恢复力评估及优化策略[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 199-208. |
| [15] | 张越, 陈思宇, 毕鸿儒, 曹佳慧, 罗源, 龚咏琪, 陈渔. 干旱半干旱区农田土壤风蚀特征及参数化研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 105-117. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
