
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 196-210.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00210
Yulai Gong1,2( ), Shaoxiu Ma1(
), Shaoxiu Ma1( ), Weiqi Liu1,2
), Weiqi Liu1,2
Received:2021-11-15
Revised:2021-12-23
Online:2022-01-20
Published:2022-01-28
Contact:
Shaoxiu Ma
CLC Number:
Yulai Gong, Shaoxiu Ma, Weiqi Liu. A comparative study of machine learning and statistical models in climate downscaling in the Shiyang River Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 196-210.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00210
| 站点 | 主要土地类型 | 年平均气温/℃ | 年降水量/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 武威 | 耕地、草地 | 8.26 | 169.93 |
| 乌鞘岭 | 冰川、积雪、林地 | 0.13 | 401.27 |
| 民勤 | 沙地、戈壁 | 8.26 | 115.60 |
| 永昌 | 沙地、草地 | 5.21 | 204.88 |
Table 1 Information of stations in the Shiyang River Basin
| 站点 | 主要土地类型 | 年平均气温/℃ | 年降水量/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 武威 | 耕地、草地 | 8.26 | 169.93 |
| 乌鞘岭 | 冰川、积雪、林地 | 0.13 | 401.27 |
| 民勤 | 沙地、戈壁 | 8.26 | 115.60 |
| 永昌 | 沙地、草地 | 5.21 | 204.88 |
| 缩写 | 英文全名 | 中文全名 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tas | Near Surface Air Temperature | 近地面气温 | K |
| Ps | Surface Air Pressure | 地面气压 | Pa |
| Zg500 | 500hPa Geopotential Height | 500 hPa高度 | m |
| Huss | Near Surface Relative Humidity | 比湿 | |
| Hfls | Surface Upward LatentHeat Flux | 向上潜热通量 | W·m-2 |
| Hfss | Suface Upward SensibleHeat Flux | 向上感热通量 | W·m-2 |
| Rlds | Surface Downwelling Longwave Radiaion | 向下长波辐射 | W·m-2 |
| Rsds | Surface Downwelling Shortwave Radiation | 向下短波辐射 | W·m-2 |
Table 2 Variables of model dataset
| 缩写 | 英文全名 | 中文全名 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tas | Near Surface Air Temperature | 近地面气温 | K |
| Ps | Surface Air Pressure | 地面气压 | Pa |
| Zg500 | 500hPa Geopotential Height | 500 hPa高度 | m |
| Huss | Near Surface Relative Humidity | 比湿 | |
| Hfls | Surface Upward LatentHeat Flux | 向上潜热通量 | W·m-2 |
| Hfss | Suface Upward SensibleHeat Flux | 向上感热通量 | W·m-2 |
| Rlds | Surface Downwelling Longwave Radiaion | 向下长波辐射 | W·m-2 |
| Rsds | Surface Downwelling Shortwave Radiation | 向下短波辐射 | W·m-2 |
| 站点 名称 | 站点 编号 | 经度 /(°) | 纬度 /(°) | 气压传感器 海拔/m | 观测场 海拔/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武威 | 52679 | 102.4 | 37.55 | 1 532.7 | 1 531.5 |
| 乌鞘岭 | 52787 | 102.52 | 37.12 | 3 046.3 | 3 045.1 |
| 民勤 | 52681 | 103.05 | 38.38 | 1 368.7 | 1 367.5 |
| 永昌 | 52674 | 101.58 | 38.14 | 1 978.1 | 1 976.9 |
Table 3 Geographic information of sites in the Shiyang River Basin
| 站点 名称 | 站点 编号 | 经度 /(°) | 纬度 /(°) | 气压传感器 海拔/m | 观测场 海拔/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 武威 | 52679 | 102.4 | 37.55 | 1 532.7 | 1 531.5 |
| 乌鞘岭 | 52787 | 102.52 | 37.12 | 3 046.3 | 3 045.1 |
| 民勤 | 52681 | 103.05 | 38.38 | 1 368.7 | 1 367.5 |
| 永昌 | 52674 | 101.58 | 38.14 | 1 978.1 | 1 976.9 |
| 序号 | 模型名称 | 英文名称及缩写 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 分位数映射法 | Quantile Mapping (QM) |
| 2 | 多元线性回归 | Multiple linear regression (MLR) |
| 3 | 支持向量回归+Z-score | Support Vector Regression (SVR-Z) |
| 4 | 人工神经网络+Z-score | Artificial Neural Network (ANN-Z) |
| 5 | 极限学习机+Z-score | Extreme Learning Machine (ELM-Z) |
| 6 | 卷积长短时记忆网络+Z-score | Convolutional Long Short-term Memory (ConvLSTM-Z) |
| 7 | 支持向量回归+Minmax | Support Vector Regression (SVR-M) |
| 8 | 人工神经网络+Minmax | Artificial Neural Network (ANN-M) |
| 9 | 极限学习机+Minmax | Extreme Learning Machine (ELM-M) |
| 10 | 卷积长短时记忆网络+Minmax | Convolutional Long Short-term Memory (ConvLSTM-M) |
Table 4 The name of the downscaling model
| 序号 | 模型名称 | 英文名称及缩写 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 分位数映射法 | Quantile Mapping (QM) |
| 2 | 多元线性回归 | Multiple linear regression (MLR) |
| 3 | 支持向量回归+Z-score | Support Vector Regression (SVR-Z) |
| 4 | 人工神经网络+Z-score | Artificial Neural Network (ANN-Z) |
| 5 | 极限学习机+Z-score | Extreme Learning Machine (ELM-Z) |
| 6 | 卷积长短时记忆网络+Z-score | Convolutional Long Short-term Memory (ConvLSTM-Z) |
| 7 | 支持向量回归+Minmax | Support Vector Regression (SVR-M) |
| 8 | 人工神经网络+Minmax | Artificial Neural Network (ANN-M) |
| 9 | 极限学习机+Minmax | Extreme Learning Machine (ELM-M) |
| 10 | 卷积长短时记忆网络+Minmax | Convolutional Long Short-term Memory (ConvLSTM-M) |
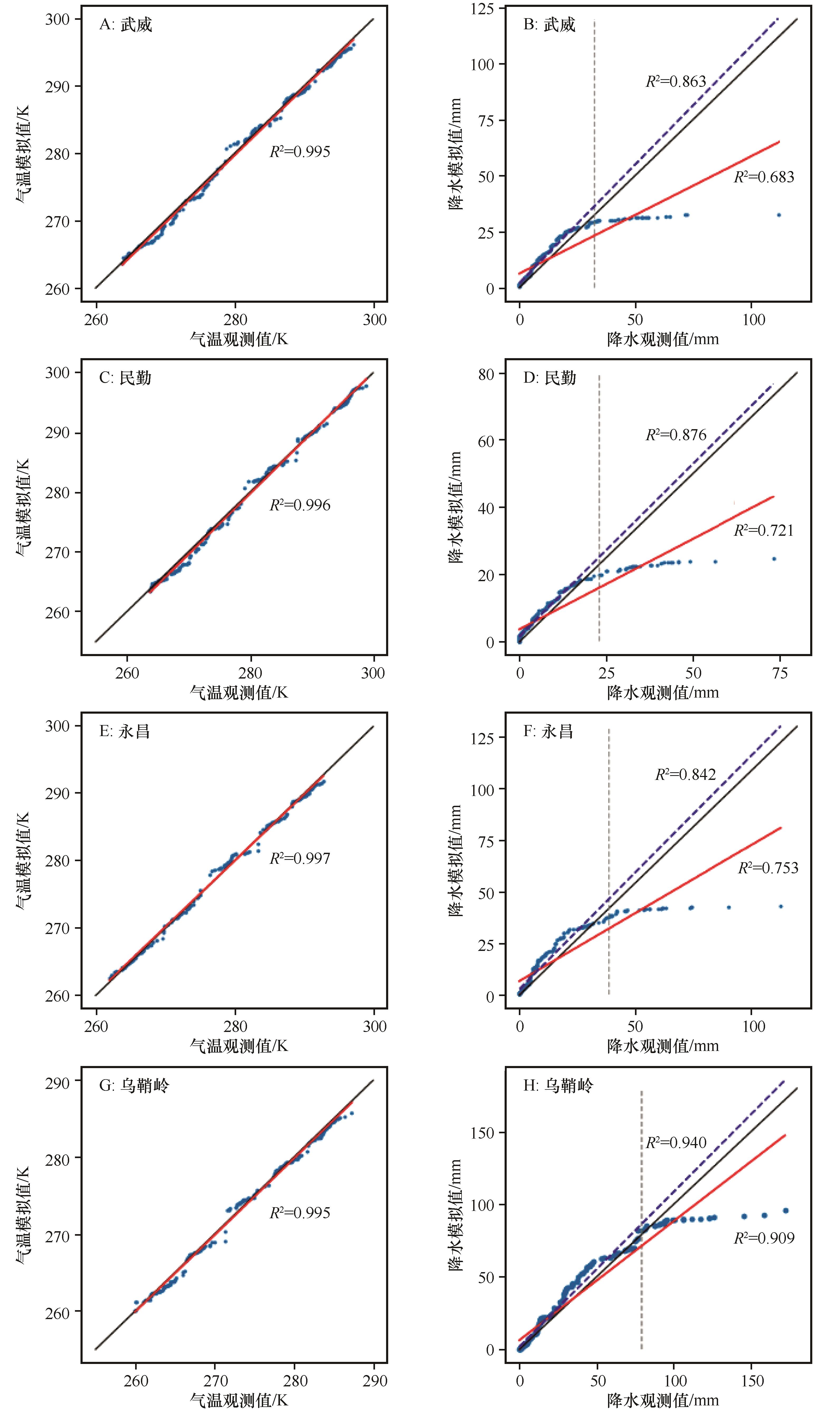
Fig.5 Monthly Quantile-Quantile plots of temperature and precipitation over four stations during validation period (The dotted line is the regression line for precipitation below 85%)
| 1 | Pan X,Li X,Cheng G,et al.Development and evaluation of a river-basin-scale high spatio-temporal precipitation data set using the WRF model:a case study of the Heihe River Basin[J].Remote Sensing,2015,7(7):9230-9252. |
| 2 | 徐忠峰,韩瑛,杨宗良.区域气候动力降尺度方法研究综述[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(3):487-498. |
| 3 | 范丽军,符淙斌,陈德亮.统计降尺度法对未来区域气候变化情景预估的研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2005(3):320-329. |
| 4 | 张明月,彭定志,胡林涓.统计降尺度方法研究进展综述[J].南水北调与水利科技,2013,11(3):118-122. |
| 5 | Lee T,Singh V P.Statistical Downscaling for Hydrological and Environmental Applications[M].Boca Raton,USA:CRC Press,2018. |
| 6 | 韩振宇,童尧,高学杰,等.分位数映射法在RegCM4中国气温模拟订正中的应用[J].气候变化研究进展,2018,14(4):331-340. |
| 7 | Yang Y,Tang J,Xiong Z,et al.An intercomparison of multiple statistical downscaling methods for daily precipitation and temperature over China:present climate evaluations[J].Climate Dynamics,2019,53(7/8):4629-4649. |
| 8 | Quan T A, Kenji T.Coupling dynamical and statistical downscaling for high-resolution rainfall forecasting:case study of the Red River Delta,Vietnam[J].Progress in Earth and Planetary Science,2018,5(1):28. |
| 9 | Jing W,Yang Y,Yue X,et al.A comparison of different regression algorithms for downscaling monthly satellite-based precipitation over north China[J].Remote Sensing,2016,8(10):835. |
| 10 | Wang B,Zheng L,Liu D L,et al.Using multi-model ensembles of CMIP5 global climate models to reproduce observed monthly rainfall and temperature with machine learning methods in Australia[J].International Journal of Climatology,2018,38(13):4891-4902. |
| 11 | 夏德锋,易善桢,谢文豪,等.基于WGEN天气发生器的石羊河流域降水模拟[J].水电能源科学,2020,38(5):1-5. |
| 12 | 李晓玲.石羊河流域气候对全球变暖的响应特征[J].甘肃科技纵横,2017,46(11):28-32. |
| 13 | 尚海洋,张志强.石羊河流域土地利用类型变化与转换效果分析[J].资源开发与市场,2015,31(1):40-43. |
| 14 | Giorgi F,Jones C,Asrar G R.Addressing climate information needs at the regional level:the CORDEX framework[J].WMO Bulletin,2009,53(3):10. |
| 15 | Taylor K E,Stouffer R J,Meehl G A.An overview of CMIP 5 and the experiment design[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,2012,93(4):485-498. |
| 16 | Zou L,Zhou T.A regional ocean-atmosphere coupled model developed for CORDEX East Asia:assessment of Asian summer monsoon simulation[J].Climate Dynamics,2016,47(12):3627-3640. |
| 17 | Thomson A M,Calvin K V,Smith S J,et al.RCP4.5:a pathway for stabilization of radiative forcing by 2100[J].Climatic Change,2011,109(1/2):77-94. |
| 18 | Riahi K,Rao S,Krey V,et al.RCP 8.5:a scenario of comparatively high greenhouse gas emissions[J].Climatic Change,2011,109(1/2):33-57. |
| 19 | Gebrechorkos S H,Hülsmann S,Bernhofer C.Statistically downscaled climate dataset for East Africa[J].Scientific Data,2019,6(1):31. |
| 20 | Cannon A J,Sobie S R,Murdock T Q.Bias correction of GCM precipitation by quantile mapping:how well do methods preserve changes in quantiles and extremes?[J].Journal of Climate,2015,28(17):6938-6959. |
| 21 | Wuthiwongyothin S,Mili S,Phadungkarnlert N.A study of correcting climate model daily rainfall product using quantile mapping in upper Ping River Basin,Thailand[M]//Nguyen T V,Dou X P,Tran T T.APAC 2019.Singapore:Springer,2020:1213-1219. |
| 22 | Volosciuk C,Maraun D,Vrac M,et al.A combined statistical bias correction and stochastic downscaling method for precipitation[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2017,21(3):1693-1719. |
| 23 | 童尧,高学杰,韩振宇,等.基于RegCM4模式的中国区域日尺度降水模拟误差订正[J].大气科学,2017,41(6):1156-1166. |
| 24 | 马轩龙,李春娥,陈全功.基于GIS的气象要素空间插值方法研究[J].草业科学,2008(11):13-19. |
| 25 | 王亚男,智协飞.多模式降水集合预报的统计降尺度研究[J].暴雨灾害,2012,31(1):1-7. |
| 26 | Li X,Li Z,Huang W,et al.Performance of statistical and machine learning ensembles for daily temperature downscaling[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2020,140(1/2):571-588. |
| 27 | Xu L,Chen N,Zhang X,et al.Improving the North American multi-model ensemble (NMME) precipitation forecasts at local areas using wavelet and machine learning[J].Climate Dynamics,2019,53(1/2):601-615. |
| 28 | 王同亮,马绍休,高扬,等.小波包分解与多个机器学习模型耦合在风速预报中的对比[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(2):38-50. |
| 29 | Alizamir M,Moghadam A M,Monfared H A,et al.Statistical downscaling of global climate model outputs to monthly precipitation via extreme learning machine:a case study[J].Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy,2018,37(5):1853-1862. |
| 30 | Shi X,Gao Z,Lausen L,et al.Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting:a benchmark and a new model[Z].arXiv1706.03458,2017. |
| 31 | Shi X,Chen Z,Wang H,et al.Convolutional LSTM network:a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[J].arXiv,2015. |
| 32 | 潘小多,马瀚青.2000—2016年基于WRF模式的0.05°×0.05°黑河流域近地表大气驱动数据[J].高原气象,2019,38(1):206-216. |
| 33 | Yang Y,Tang J,Xiong Z,et al.Evaluation of high-resolution gridded precipitation data in arid and semiarid regions:Heihe River Basin,Northwest China[J].Journal of Hydrometeorology,2017,18(12):3075-3101. |
| 34 | Su H,Xiong Z,Yan X,et al.An evaluation of two statistical downscaling models for downscaling monthly precipitation in the Heihe River basin of China[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2019,138(3/4):1913-1923. |
| 35 | 吴晶,王宝鉴,杨艳芬,等.CMIP3与CMIP5模式对中国西北干旱区气温和降水的模拟能力比较[J].气候变化研究进展,2017,13(3):198-212. |
| 36 | 陈晓晨,徐影,许崇海,等.CMIP5全球气候模式对中国地区降水模拟能力的评估[J].气候变化研究进展,2014,10(3):217-225. |
| 37 | 赵天保,陈亮,马柱国.CMIP5多模式对全球典型干旱半干旱区气候变化的模拟与预估[J].科学通报,2014,59(12):1148-1163. |
| 38 | Wang F,Tian D,Lowe L,et al.Deep learning for daily precipitation and temperature downscaling[J].Water Resources Research,2021,57(4):29308. |
| 39 | Osman Y Z,Abdellatif M E.Improving accuracy of downscaling rainfall by combining predictions of different statistical downscale models[J].Water Science,2016,30(2):61-75. |
| 40 | Bu C,Zhang Z.Research on overfitting problem and correction in machine learning[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2020,1693(1):12100. |
| [1] | Yanhui Lei, Guodong Ding, Zimeng Li, Wenfeng Chi, Guanglei Gao, Yuanyuan Zhao. Land use/cover change and its ecosystem service value response in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 29-40. |
| [2] | Xiaohui Ma, Jiangli Pang, Xiaokang Liu, Dan Ding, Xiaoxiao Yue, Feifei Jia. Early and Middle Holocene climate change inferred by Wayaogou Section in the Southeastern Mu Us Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 71-80. |
| [3] | Xiaomei Zhang, Heling Jin, Bing Liu. Environment changes in the Hobq Desert since the Last Glacial Maximum [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 81-93. |
| [4] | Yongtao Ma, Xiaozong Ren, Huifang Hu, Min Liu, Qi Meng. Vegetation dynamics and its driving force in Otindag Sandy Land based on Geodetector [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 195-204. |
| [5] | Lanying Han, Qiang Zhang, Pengli Ma, Youheng Wang, Tao Huang, Jianying Jia, Xin Wang, Xiaowei Wang, Weiping Liu, Danhua Li, Guoyang Lu, Pengcheng Huang, Bing Bai. Characteristics of drought disasters risk in the Yellow River Basin under the climate warming [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 225-234. |
| [6] | Youheng Wang, Dan Tan, Lanying Han, Danhua Li, xin Wang, Guoyang Lu, Jingjing Lin. Review of climate change in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 235-246. |
| [7] | Xiaohui He, Jianhua Si, Chunyan Zhao, Chunlin Wang, Dongmeng Zhou. Potential distribution of Hippophae thibetana and its predicted responses to climate change [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 101-109. |
| [8] | Yuanzheng He, Wenda Huang, Xin Zhao, Peng Lv, Huaihai Wang. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [9] | Di Deng, Zebin Zhao, Yuan Ma. Modeling of species distribution with GIS in arid regions: take Caragana korshinskii for example [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 74-80. |
| [10] | Han Chao, Xiao Shengchun, Ding Aijun, Teng Zeyu. Radial growth climatic response characteristics and tree ring climate records of conifer species at south margin of Tengger Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 50-58. |
| [11] | Li Xiang, Su Zhizhu, Ma Yijuan, Zhang Caixia, Liu Miaomiao. Holocene climatic instability record in the southeastern margin of Mu Us Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 109-117. |
| [12] | Zhao Zefang, Wei Haiyan, Guo Yanlong, Luan Wenfei, Zhao Zebin. Impact of climate change on the suitable habitatdistribution of Gymnocarpos przewalskii, a relict plant [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 125-133. |
| [13] | Chang Xi, Lu Huayu, Lü Nana, Cui Mengchun, Li Haiyu. Variation of desert and sandy field in China on the basis of remote sensing analysis and the relationship with climate change during 1992-2015 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 57-63. |
| [14] | Ma Qimin, Jia Xiaopeng, Wang Haibing, Li Yongshan, Li Shaoning. Recent Advances in Driving Mechanisms of Climate and Anthropogenic Factors on Vegetation Change [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 48-55. |
| [15] | Liu Liyun, Lu Ruijie, Liu Xiaokang. Climate Change in the Mu Us Desert since Holocene Based on Soil Chromaticity [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 83-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech