中国沙漠 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 145-155.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00061
李传华( ), 殷欢欢, 朱同斌, 周敏, 王玉涛, 孙皓, 曹红娟, 韩海燕
), 殷欢欢, 朱同斌, 周敏, 王玉涛, 孙皓, 曹红娟, 韩海燕
收稿日期:2020-04-30
修回日期:2020-06-29
出版日期:2021-01-29
发布日期:2021-01-29
作者简介:李传华(1979—),男,湖北监利人,副教授,主要研究方向为生态遥感和GIS应用研究。E-mail: lch_nwnu@126.com
基金资助:
Chuanhua Li( ), Huanhuan Yin, Tongbin Zhu, Min Zhou, Yutao Wang, Hao Sun, Hongjuan Cao, Haiyan Han
), Huanhuan Yin, Tongbin Zhu, Min Zhou, Yutao Wang, Hao Sun, Hongjuan Cao, Haiyan Han
Received:2020-04-30
Revised:2020-06-29
Online:2021-01-29
Published:2021-01-29
摘要:
干旱对生态系统碳循环具有重要影响,随着气候变暖,全球干旱事件频率不断上升,研究干旱对植被净初级生产力的影响具有重要意义。提高植被净初级生产力(NPP)的时间分辨率是认识干旱对其影响机制的重要途径。基于5天NDVI遥感数据,以河西走廊为研究区,利用CASA模型估算2010—2015年5天步长尺度的NPP,将5天降水为零定义为干旱基本单元,利用标准分数来探究干旱对植被NPP的影响。结果表明:基于高时间分辨率遥感数据能有效探测干旱对NPP的影响机制,研究期间河西走廊年干旱频次6—44次,干旱对该地NPP有负效应,对5天均值的影响为-0.23 g·m-2,影响幅度为-1.93%,整体影响较小。干旱对林地NPP影响最大,下降3.70%,草地次之,荒漠最小。随着干旱持续时间的增加,NPP变化趋势呈现为先降低,然后降低趋势增加,最后趋于稳定的过程。干旱对夏季的NPP影响最大,冬季最小,秋季干旱对林地影响最大。
中图分类号:
李传华, 殷欢欢, 朱同斌, 周敏, 王玉涛, 孙皓, 曹红娟, 韩海燕. 干旱对河西走廊植被净初级生产力的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 145-155.
Chuanhua Li, Huanhuan Yin, Tongbin Zhu, Min Zhou, Yutao Wang, Hao Sun, Hongjuan Cao, Haiyan Han. Impact of drought on net primary productivity of vegetation in arid and semi-arid areas: a case study of Hexi Corridor[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 145-155.
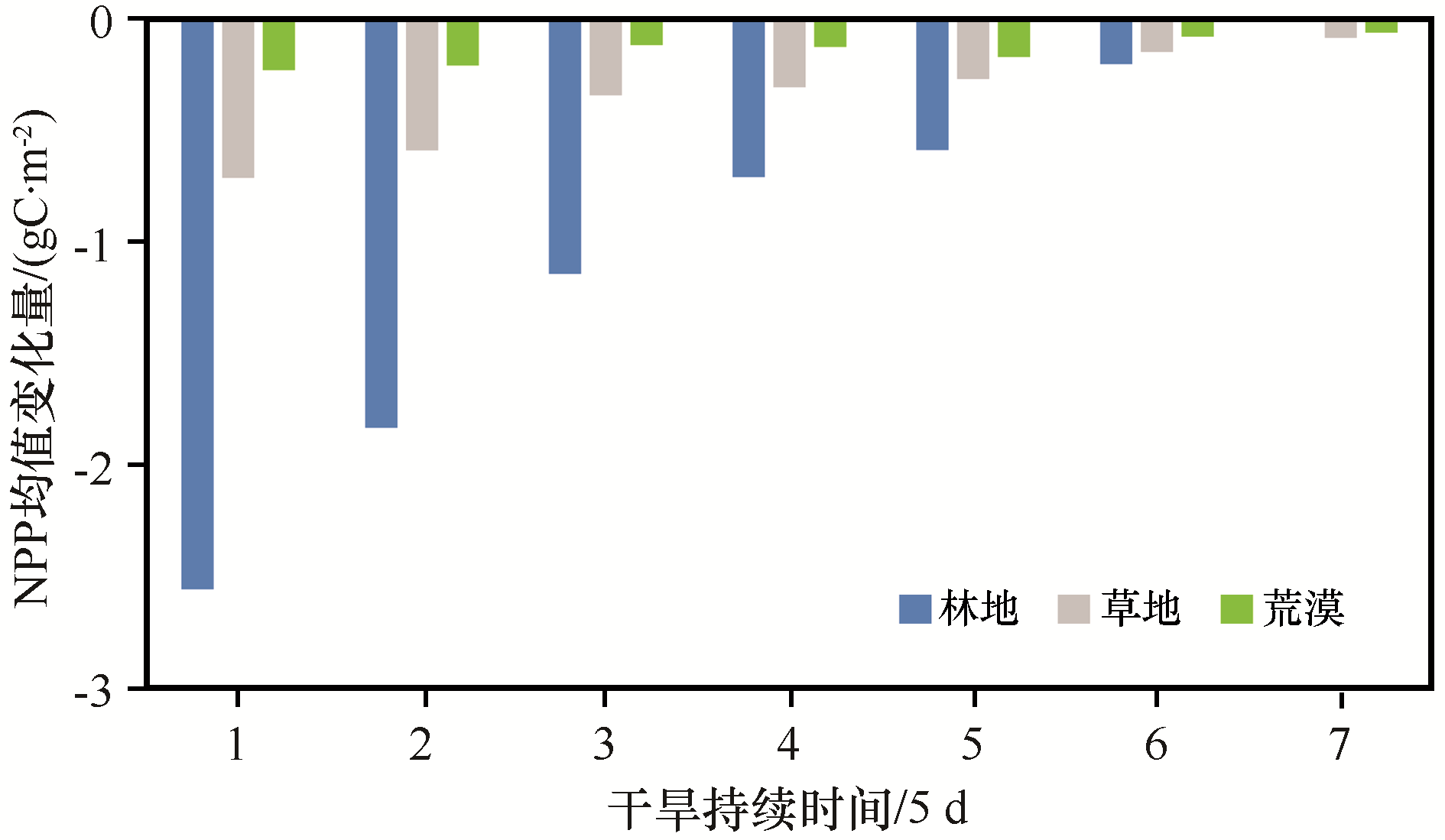
图6 河西走廊不同干旱持续时间段对不同植被类型NPP均值影响(横轴表示干旱持续的第n个5天)
Fig.6 Effects of different drought durations in Hexi Corridor of China on mean NPP of different vegetation types (horizontal axis represents the nth five days of drought duration)
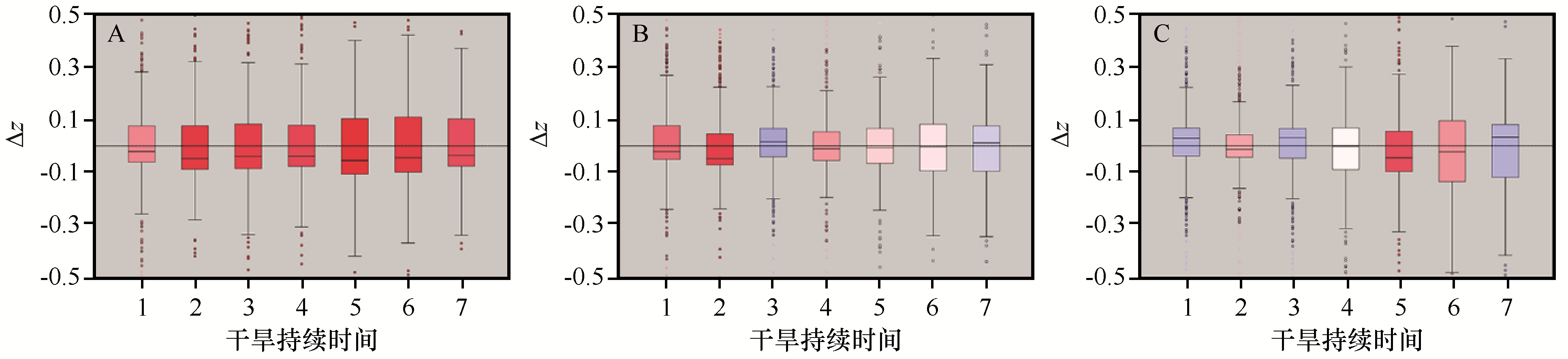
图7 河西走廊干旱持续时间段平均NPP相对均值标准分数变化量(A、B、C分别表示林地、草地、荒漠)
Fig.7 Variation of average NPP relative mean standard score of drought duration in Hexi Corridor of China (A, B, C, respectively representing forest land, grassland, desert)
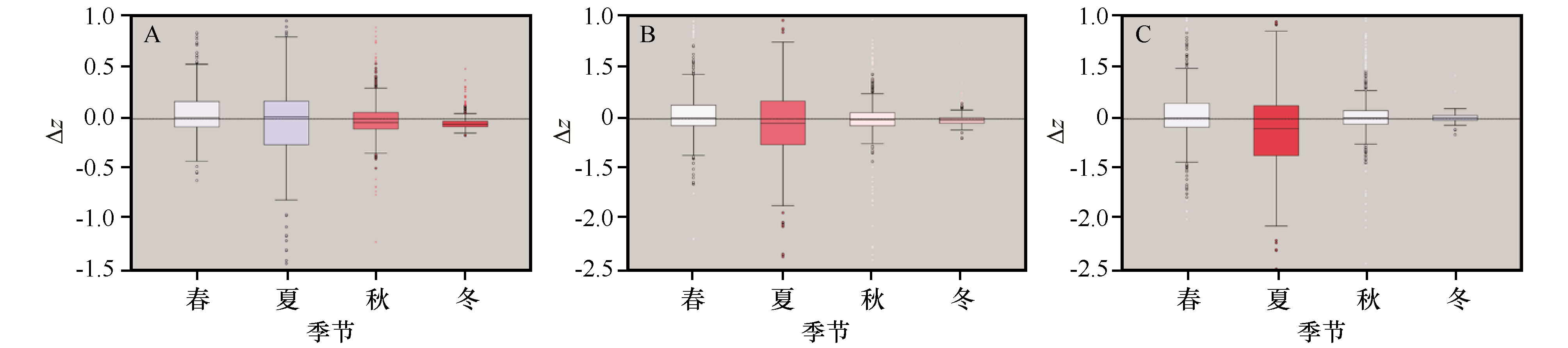
图8 干旱对河西走廊不同季节不同植被平均NPP相对均值标准分数变化量影响(A、B、C分别表示林地、草地、荒漠)
Fig.8 Drought changes in the average NPP relative mean standard score of different vegetations in different seasons in Hexi Corridor of China (A, B, C, respectively representing forest land, grassland, desert)
| 作者 | 研究区 | 研究时段 | 草地 | 林地 | 荒漠 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冯益明等[ | 甘肃省 | 2010年 | 43.6 | 172.3 | 11.1 |
| 周妍妍等[ | 疏勒河流域 | 2001—2015年 | 89.20 | 103.65 | 52.46 |
| 焦伟等[ | 西北干旱区 | 2000—2014年 | 252.2 | 400.2 | 51.5 |
| 杨冬辉[ | 石羊河流域 | 2009年 | 67.36 | 358.8 | — |
| 本研究 | 河西走廊 | 2010—2015年 | 80.51 | 332.47 | 22.06 |
表1 河西走廊NPP与文献值对比 (gC·m-2·a-1)
Table 1 Comparison of NPP and literature values in Hexi Corridor of China
| 作者 | 研究区 | 研究时段 | 草地 | 林地 | 荒漠 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冯益明等[ | 甘肃省 | 2010年 | 43.6 | 172.3 | 11.1 |
| 周妍妍等[ | 疏勒河流域 | 2001—2015年 | 89.20 | 103.65 | 52.46 |
| 焦伟等[ | 西北干旱区 | 2000—2014年 | 252.2 | 400.2 | 51.5 |
| 杨冬辉[ | 石羊河流域 | 2009年 | 67.36 | 358.8 | — |
| 本研究 | 河西走廊 | 2010—2015年 | 80.51 | 332.47 | 22.06 |
| 1 | Canadell J G,Mooney H A,Baldocchi D D,et al.Carbon metabolism of the terrestrial biosphere:a multitechnique approach for improved understanding[J].Ecosystems,2000,3(2):115-130. |
| 2 | Liu J,Chen J M,Cihlar J,et al.Net primary productivity distribution in the BOREAS region from a process model using satellite and surface data[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1999,104(D22):27735-27754. |
| 3 | Zhao M,Running S W.Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009[J].Science,2010, 329(5994):940-943. |
| 4 | Grime J P,Brown V K,Thompson K,et al.The response of two contrasting limestone grasslands to simulated climate change[J].Science,2000,289(5480):762-765. |
| 5 | Kahmen A,Buchmann J P.Diversity-dependent productivity in semi-natural grasslands following climate perturbations[J].Functional Ecology,2005,19(4):594-601. |
| 6 | Easterling D R,Meehl G A,Parmesan C,et al.Climate extremes:observations,modeling,and impacts[J].Science,2000,289(5487):2068-2074. |
| 7 | Dai A,Trenberth K E,Qian T.A global dataset of Palmer Drought Severity Index for 1870-2002:relationship with soil moisture and effects of surface warming[J].Journal of Hydrometeorology,2004,5(6):1117-1130. |
| 8 | 王志伟,翟盘茂.中国北方近 50 年干旱变化特征[J].地理学报,2003,58():61-68. |
| 9 | 马柱国,符淙斌.中国干旱和半干旱带的10年际演变特征[J].地球物理学报,2005,48(3):519-525. |
| 10 | Pandey S,Bhandari H S,Hardy B.Economic costs of drought and rice farmers' coping mechanisms:a cross-country comparative analysis[M].Manila,Phillipins:International Rice Research Institute,2007. |
| 11 | Van Dijk A I J M,Beck H E,Crosbie R S,et al.The millennium drought in southeast Australia (2001-2009):natural and human causes and implications for water resources,ecosystems,economy,and society[J].Water Resources Research,2013,49(2):1040-1057. |
| 12 | Zscheischler J,Mahecha M D,Von Buttlar J,et al.A few extreme events dominate global interannual variability in gross primary production[J].Environmental Research Letters,2014,9(3):35001. |
| 13 | Ciais P,Reichstein M,Viovy N,et al.Europe-wide reduction in primary productivity caused by the heat and drought in 2003[J].Nature,2005,437(7058):529-533. |
| 14 | Zeng N,Yoon J H,Marengo J A,et al.Causes and impacts of the 2005 Amazon drought[J].Environmental Research Letters,2008,3(1):14002. |
| 15 | Williams W D.Salinisation:a major threat to water resources in the arid and semi-arid regions of the world[J].Lakes & Reservoirs:Research & Management,1999,4(3/4):85-91. |
| 16 | Fernández Roberto J.Do humans create deserts?[J].Trends in Ecology & Evolution,2002,17(1):6-7. |
| 17 | Poulter B,Frank D,Ciais P,et al.Contribution of semi-arid ecosystems to interannual variability of the global carbon cycle[J].Nature,2014,509(7502):600-603. |
| 18 | Fay P A,Carlisle J D,Knapp A K,et al.Altering rainfall timing and quantity in a mesic grassland ecosystem:design and performance of rainfall manipulation shelters[J].Ecosystems,2000,3(3):308-319. |
| 19 | Gorissen A,Tietema A,Joosten N N,et al.Climate change affects carbon allocation to the soil in shrublands[J].Ecosystems,2004,7(6):650-661. |
| 20 | Xiao J F,Zhuang Q L,Liang E Y,et al.Twentieth-century droughts and their impacts on terrestrial carbon cycling in China[J].Earth Interactions,2009,13(10):1-31. |
| 21 | 朱学艺,王锁民,张承烈.河西走廊不同生态型芦苇对干旱和盐渍胁迫的响应调节[J].植物生理学报,2003(4):371-376. |
| 22 | 邱文君.干旱对西南地区植被净初级生产力的影响研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2013. |
| 23 | McKee T B,Doesken N J,Kleist J.The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales[C]//Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology,1993:179-183. |
| 24 | Shukla S,Wood A W.Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2008,35(2):41-46. |
| 25 | Tsakiris G,Vangelis H.Establishing a drought index incorporating evapotranspiration[J].European Water,2005,9(10):3-11. |
| 26 | Kreyling J,Wenigmann M,Beierkuhnlein C,et al.Effects of extreme weather events on plant productivity and tissue die-back are modified by community composition[J].Ecosystems,2008,11(5):752-763. |
| 27 | 刘莉红,翟盘茂,郑祖光.中国北方夏半年最长连续无降水日数的变化特征[J].气象学报,2008,66(3):474-477. |
| 28 | Frich P,Alexander L V,Della-Marta P M,et al.Observed coherent changes in climatic extremes during the second half of the twentieth century[J].Climate Research,2002,19(3):193-212. |
| 29 | 刘莉红,翟盘茂,郑祖光.中国北方夏半年极端干期的时空变化特征[J].高原气象,2010,29(2):403-411. |
| 30 | 张雪花,程扬,冯婧.海河流域干旱特征与旱涝交替降雨事件概率分析[J].人民长江,2017(13):7-11. |
| 31 | 冯益明,姚爱冬,姜丽娜.CASA模型的改进及在干旱区生态系统NPP估算中的应用[J].干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(8):39-43. |
| 32 | 张福平,冯起,李旭谱, 等.黑河流域NPP遥感估算及其时空变化特征[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1657-1664. |
| 33 | 李传华,曹红娟,范也平,等.基于校正的CASA模型NPP遥感估算及分析:以河西走廊为例[J].生态学报,2018,39(5):1616-1626. |
| 34 | 周妍妍,朱敏翔,郭晓娟,等.疏勒河流域气候变化和人类活动对植被 NPP 的相对影响评价[J].生态学报,2019,39(14):5127-5137. |
| 35 | 焦伟,陈亚宁,李稚.西北干旱区植被净初级生产力的遥感估算及时空差异原因[J].生态学杂志,2017,36(1):183-191. |
| 36 | 杨东辉.基于MODIS数据的石羊河上游植被净第一性生产力变化研究[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2011. |
| 37 | 倪向南,郭伟,乔凯.陕北风沙过渡带植被净初级生产力变化特征及原因[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(4):889-898. |
| 38 | Xiao X,Hollinger D,Aber J,et al.Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in an evergreen needleleaf forest[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2004,89(4):519-534. |
| 39 | Xiao X,Boles S,Frolking S,et al.Observation of flooding and rice transplanting of paddy rice fields at the site to landscape scales in China using VEGETATION sensor data[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,2002,23(15):3009-3022. |
| 40 | Bao G,Bao Y H,Qin Z H,et al.Modeling net primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystems in the semi-arid climate of the Mongolian Plateau using LSWI-based CASA ecosystem model[J].International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2016,46:84-93. |
| 41 | Wu C,Chen J M.The use of precipitation intensity in estimating gross primary production in four northern grasslands[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2012,82:11-18. |
| 42 | Thomey M L,Collins S L,Vargas R,et al.Effect of precipitation variability on net primary production and soil respiration in a Chihuahuan Desert grassland[J].Global Change Biology,2011,17(4):1505-1515. |
| 43 | 庞素菲,魏伟,郭泽呈,等.基于TVDI的甘肃省农业旱情特征及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志,2019,38(6):1849-1860. |
| 44 | 季定民.不同气象干旱指标在甘肃省的应用分析[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2015. |
| 45 | von Buttlar J,Zscheischler J,Rammig A,et al.Impacts of droughts and extreme-temperature events on gross primary production and ecosystem respiration:a systematic assessment across ecosystems and climate zones[J].Biogeosciences,2018,15:1293-1318. |
| 46 | Zavalloni C,Gielen B,De Boeck H J,et al.Greater impact of extreme drought on photosynthesis of grasslands exposed to a warmer climate in spite of acclimation[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2009,136(1):57-72. |
| 47 | Phillips O L,Aragão L E O C,Lewis S L,et al.Drought sensitivity of the Amazon rainforest[J].Science,2009,323(5919):1344-1347. |
| 48 | 赵林,徐春雪,刘雪莹,等.干旱对湖北省森林植被净初级生产力的影响[J].长江流域资源与环境,2014,23(11):1595-1602. |
| 49 | 朱妮.气候变化下蒙古沙拐枣(Calligonum mongolicum)适宜生境预测[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(3):136-144. |
| 50 | 张大彪,张元恺,唐进年.河西走廊沿沙防护林演变形式与积沙带稳定性研究[J].防护林科技,2016(1):1-4. |
| 51 | Lefi E,Medrano H,Cifre J.Water uptake dynamics, photosynthesis and water use efficiency in field-grown Medicago arborea and Medicago citrina under prolonged Mediterranean drought conditions[J].Annals of Applied Biology,2004,144(3):299-307. |
| 52 | 王碧霞,曾永海,王大勇,等.叶片气孔分布及生理特征对环境胁迫的响应[J].干旱地区农业研究,2010,28(2):122-126. |
| 53 | Griffin J J,Ranney T G,Pharr D M.Heat and drought influence photosynthesis, water relations, and soluble carbohydrates of two ecotypes of redbud (Cercis canadensis)[J].Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science,2004,129(4):497-502. |
| 54 | Wolf S,Eugster W,Ammann C,et al.Contrasting response of grassland versus forest carbon and water fluxes to spring drought in Switzerland[J].Environmental Research Letters,2013,8(3):35007. |
| 55 | Palta J A,Nobel P S.Root respiration for Agave deserti:influence of temperature, water status and root age on daily patterns[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,1989,40(2):181-186. |
| 56 | Burton A J,Pregitzer K S,Zogg G P,et al.Drought reduces root respiration in sugar maple forests[J].Ecological Applications,1998,8(3):771-778. |
| 57 | Davidson E C A,Belk E,Boone R D.Soil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest[J].Global Change Biology,1998,4(2):217-227. |
| 58 | Stitt M,Schulze D.Does Rubisco control the rate of photosynthesis and plant growth?an exercise in molecular ecophysiology[J].Plant,Cell & Environment,1994,17(5):465-487. |
| 59 | Reich P B,Borchert R.Water stress and tree phenology in a tropical dry forest in the Lowlands of Costa Rica[J].Journal of Ecology,1984,72(1):61-74. |
| 60 | 柏新富,朱建军,赵爱芬,等.几种荒漠植物对干旱过程的生理适应性比较[J].应用与环境生物学报,2008(6):763-768. |
| 61 | Frank D,Reichstein M,Bahn M,et al.Effects of climate extremes on the terrestrial carbon cycle:concepts,processes and potential future impacts[J].Global Change Biology,2015,21(8):2861-2880. |
| 62 | 吴庆贵,邹利娟,吴福忠,等.涪江流域丘陵区不同植被类型水源涵养功能[J].水土保持学报,2012,26(6):254-258. |
| 63 | Chen T,Van der Werf G R,De Jeu R A M,et al.A global analysis of the impact of drought on net primary productivity[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2013,17:3885-3894. |
| 64 | 孙立群,李晴岚,陈骥,等.欧亚大陆不同生态区植被生长对降水响应的季节变化规律[J].生态学报,2018,38(22):8051-8059. |
| [1] | 韩丹, 李玉霖, 杨红玲, 宁志英, 张子谦. 模拟增温和改变降雨频率对干旱半干旱区土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 100-108. |
| [2] | 王子婷, 杨磊, 李广, 柴春山, 张洋东, 刘冬皓. 黄土丘陵区坡面柠条(Caragana korshinskii)林地草本植物分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 120-128. |
| [3] | 宋琳琳, 张强, 任余龙, 李忆平, 韩兰英, 柳媛普, 王素萍. PDSI及sc_PDSI干旱指数在中国西南地区适用性分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 242-252. |
| [4] | 王同亮, 马绍休, 高扬, 宫毓来, 安志山. 小波包分解与多个机器学习模型耦合在风速预报中的对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 38-50. |
| [5] | 孙一梅, 田青, 吕朋, 郭爱霞, 李平平, 朱丽琴, 左小安. 科尔沁沙地沙质草地与固定沙丘植物群落结构对极端干旱的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 129-136. |
| [6] | 常学尚, 常国乔. 干旱半干旱区土壤水分研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 156-163. |
| [7] | 周晓兵, 张丙昌, 张元明. 生物土壤结皮固沙理论与实践[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 164-173. |
| [8] | 王姣月, 秦树高, 张宇清. 毛乌素沙地植被水分利用效率的时空格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 120-129. |
| [9] | 张润霞, 赵学勇, 李晶, 吕文强, 柴媛媛, 岳红琴. 干旱荒漠区土地利用方式快速转变对土壤入渗性能的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 146-153. |
| [10] | 李玲萍, 卢泰山, 刘明春, 胡丽莉, 王素萍. 基于标准化流量指数(SDI)的石羊河流域水文干旱特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 24-33. |
| [11] | 张雯莉, 朱恭, 黄文广, 张宇, 王蕾, 罗晓玲, 刘玉冰. 红花岩黄芪(Hedysarum multijugum)、灌木铁线莲(Clematis fruticosa)和互叶醉鱼草(Buddleja alternifolia)幼苗适应干旱的生理特征比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 159-167. |
| [12] | 周立峰, 杨荣, 赵文智. 荒漠人工固沙植被区土壤结皮斥水性发展特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 185-192. |
| [13] | 李端, 司建华, 张小由, 高雅玉, 罗欢, 秦洁, 任立新. 胡杨(Populus euphratica)对干旱胁迫的生态适应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 17-23. |
| [14] | 杨晶晶, 吕瑞恒, 梁继业, 冯建菊, 马国财, 康佳鹏. 塔里木盆地盐生和干旱生境柽柳(Tamarix)凋落物分解特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 215-222. |
| [15] | 马鹏里, 韩兰英, 张旭东, 刘卫平. 气候变暖背景下中国干旱变化的区域特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 209-215. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
