中国沙漠 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 164-173.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00093
收稿日期:2020-05-05
修回日期:2020-09-03
出版日期:2021-01-20
发布日期:2021-01-29
通讯作者:
张元明
作者简介:张元明(E-mail: zhangym@ms.xjb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Xiaobing Zhou1( ), Bingchang Zhang2, Yuanming Zhang1(
), Bingchang Zhang2, Yuanming Zhang1( )
)
Received:2020-05-05
Revised:2020-09-03
Online:2021-01-20
Published:2021-01-29
Contact:
Yuanming Zhang
摘要:
生物土壤结皮是由土壤微生物、藻类、地衣和苔藓等孢子植物类群与土壤颗粒形成的有机复合体,在全球干旱区地表广泛分布,是干旱地表生物覆被层的主要构建者。生物土壤结皮是荒漠植物群落演替的先锋类群,能够提高荒漠地表的稳定性,固定碳和氮等营养元素,增加土壤肥力,并在保持土壤水分方面发挥重要作用,因此在干旱区受损地表的生态修复方面具有广阔的应用前景。通过分析组成生物土壤结皮的物种更替与维持其结构的胶结方式转变之间的生态关系,阐释了生物土壤结皮固沙的生物学基础,提出在人工结皮恢复实践中,应选择以本地优势物种(如具鞘微鞘藻、齿肋赤藓和银叶真藓等)为目标种的生态学原则,并通过对目标物种的纯化、培养,完成由实验室至温室的扩繁过程,实现逐级扩大生产,为野外固沙应用提供充足种源。阐述了结皮野外接种恢复的最适物种组成、物理化学方式结合的组合模式,提出应从地表稳定性、土壤养分和结皮物种多样性等方面进行生长状况评估,梳理了中国在结皮人工恢复领域的研究进展和面临的问题与挑战,阐释了利用人工培养生物土壤结皮开展生态修复的应用前景。
中图分类号:
周晓兵, 张丙昌, 张元明. 生物土壤结皮固沙理论与实践[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 164-173.
Xiaobing Zhou, Bingchang Zhang, Yuanming Zhang. The theory and practices of biological soil crust rehabilitation[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 164-173.
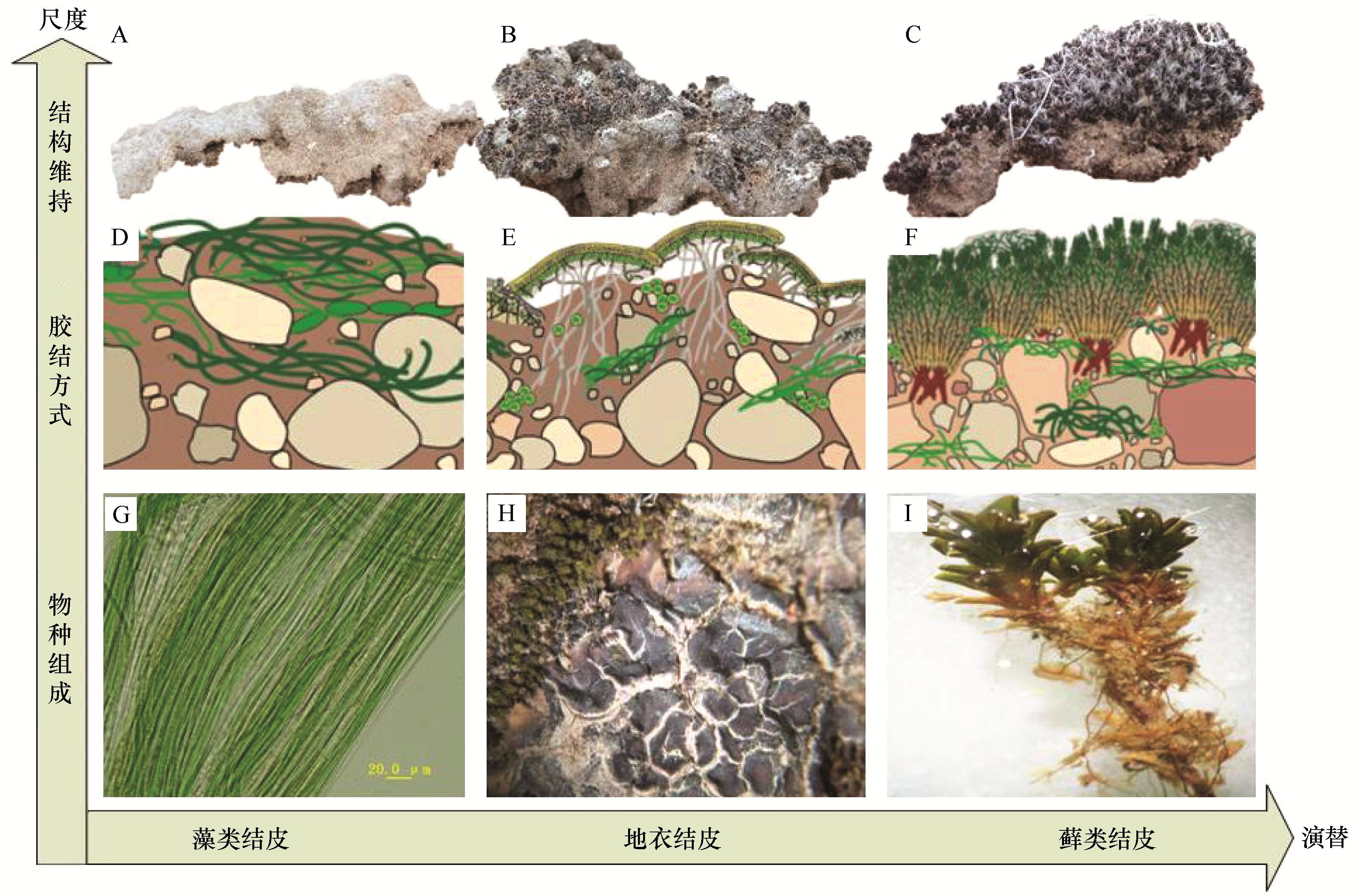
图2 生物结皮演替和不同尺度下结构组成与胶结方式A—C,3种生物结皮类型; D—F,胶结方式,修改自Colesie等[22]; G—I,物种组成
Fig.2 Composition, binding ways and appearance of biological soil crusts in three successional stages

图3 古尔班通古特沙漠藻类生物结皮的扩大化培养与野外接种A—C,室内培养与扩大化生产; D,温室接种; E,野外藻类结皮接种
Fig.3 Mass cultivation of cyanobacterial crust and field inoculation in the Gurbantunggut Desert
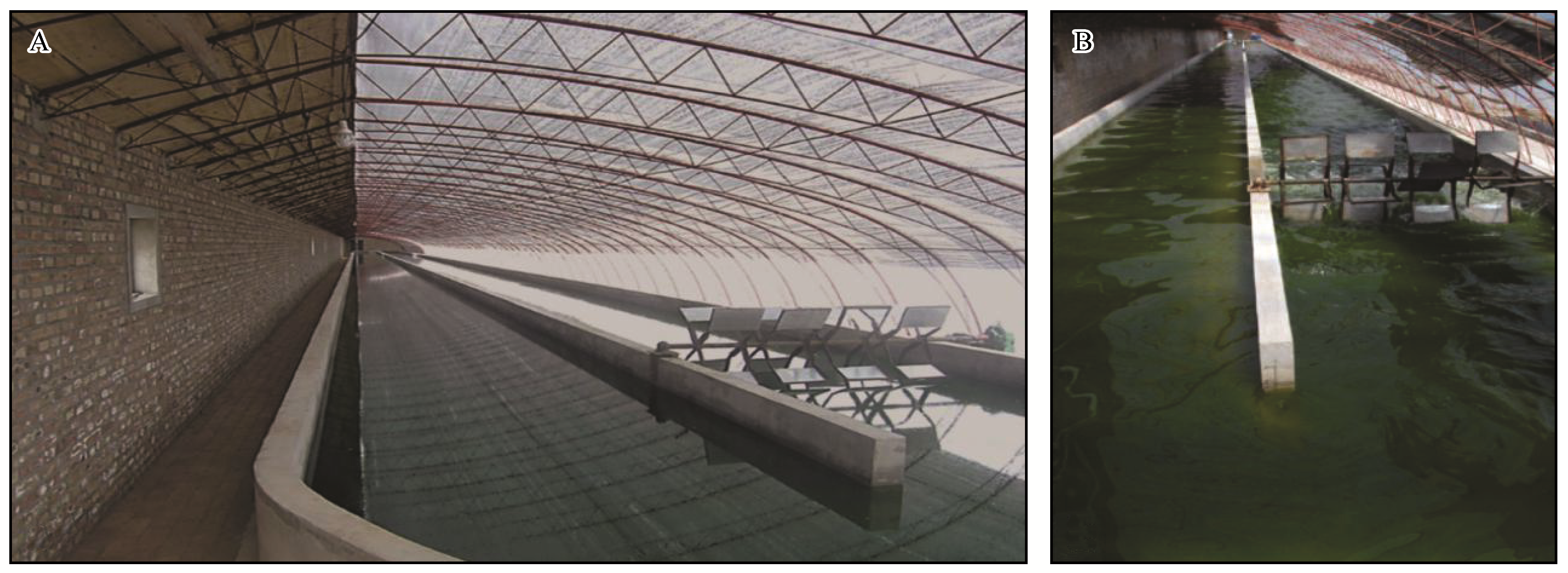

图4 中国科学院水生生物研究所内蒙古实验基地建造的藻类培养的跑道池[37]
Fig.4 The raceway pond operated by Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Inner-Mongolia[37]
| 结皮类型 | 地点 | 规模 | 结皮生长 | 评价 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻类结皮 | 库布齐沙漠 | 约200 hm2 | 2—3年形成3—5 mm藻类结皮,盖度48.5% | 结皮和植被得到较好恢复 | [ |
| 腾格里沙漠 | 2 m×2 m | 5个月后,0.39 mm,盖度达14.3%,生物量13.4 mg·g-1;盖度或先增后降,1年后13.8% | 长期效应未知 | [ | |
| 古尔班通古特沙漠 | 2 m×5 m | 15 d可达2.6 mg·cm-2(叶绿素a) | 未形成大规模生物结皮 | 未发表 | |
| 地衣结皮 | 腾格里沙漠 | 3个 0.5 m2 | 1年后形成4—6 cm生物结皮 | 长期效应未知 | [ |
| 藓类结皮 | 腾格里沙漠 | 10个1 m×1 m | 7 d内存活,3个月内死亡 | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ |
| 毛乌素沙地 | 18个1 m×1 m | 75 d后盖度70%,密度9.8 株·cm-2,4年盖度达98% | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ | |
| 杨凌 | 48个1 m×1 m | 30 d,盖度90%,最大密度120株·cm-2 | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ | |
| 库布齐沙漠 | 8个1 m×1 m | 3年后,盖度30%—70%,185株·cm-2 | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ |
表1 中国生物土壤结皮恢复实践研究案例
Table 1 Study case of biological soil crust rehabilitation in China
| 结皮类型 | 地点 | 规模 | 结皮生长 | 评价 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 藻类结皮 | 库布齐沙漠 | 约200 hm2 | 2—3年形成3—5 mm藻类结皮,盖度48.5% | 结皮和植被得到较好恢复 | [ |
| 腾格里沙漠 | 2 m×2 m | 5个月后,0.39 mm,盖度达14.3%,生物量13.4 mg·g-1;盖度或先增后降,1年后13.8% | 长期效应未知 | [ | |
| 古尔班通古特沙漠 | 2 m×5 m | 15 d可达2.6 mg·cm-2(叶绿素a) | 未形成大规模生物结皮 | 未发表 | |
| 地衣结皮 | 腾格里沙漠 | 3个 0.5 m2 | 1年后形成4—6 cm生物结皮 | 长期效应未知 | [ |
| 藓类结皮 | 腾格里沙漠 | 10个1 m×1 m | 7 d内存活,3个月内死亡 | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ |
| 毛乌素沙地 | 18个1 m×1 m | 75 d后盖度70%,密度9.8 株·cm-2,4年盖度达98% | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ | |
| 杨凌 | 48个1 m×1 m | 30 d,盖度90%,最大密度120株·cm-2 | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ | |
| 库布齐沙漠 | 8个1 m×1 m | 3年后,盖度30%—70%,185株·cm-2 | 接种藓类直接采自野外 | [ |
| 1 | Belnap J,Weber B,Büdel B.Biological soil crusts as an organizing principle in drylands[M]//Weber B,Büdel B,Belnap J.Biological Soil Crusts:An Organizing Principle in Drylands.Cham,Switzerland:Springer, 2016. |
| 2 | Rodriguez-Caballero E,Belnap J,Buedel B,et al.Dryland photoautotrophic soil surface communities endangered by global change[J].Nature Geoscience,2018,11:185-189. |
| 3 | Bowker M A,Reed S C,Maestre F T,et al.Biocrusts: the living skin of the earth[J].Plant and Soil,2018,429:1-7. |
| 4 | 魏江春.沙漠生物地毯工程:干旱沙漠治理的新途径[J].干旱区研究,2005,22(3):287-288. |
| 5 | Zhang Y M,Wang H L,Wang X Q,et al.The microstructure of microbiotic crust and its influence on wind erosion for a sandy soil surface in the Gurbantunggut Desert of Northwestern China[J].Geoderma,2006,132:441-449. |
| 6 | Hu C X,Liu Y D,Zhang D L,et al.Cementing mechanism of algal crusts from desert area [J].Chinese Science Bulltin,2002,47:1361-1368. |
| 7 | Barger N N,Weber B,Garcia-Pichel F,et al.Patterns and controls on nitrogen cycling of biological soil crusts[M]//Weber B,Büdel B,Belnap J.Biological Soil Crusts:An Organizing Principle in Drylands.Cham,Switzerland:Springer,2016. |
| 8 | Elbert W,Weber B,Burrows S,et al.Contribution of cryptogamic covers to the global cycles of carbon and nitrogen[J].Nature Geoscience,2012,5:459-462. |
| 9 | 刘永定,胡春香,张文军.荒漠藻类环境生物学与生物土壤结皮固沙[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013. |
| 10 | Chiquoine L P,Abella S R,Bowker M A.Rapidly restoring biological soil crusts and ecosystem functions in a severely disturbed desert ecosystem[J]. Ecological Applications,2016,26:1260-1272. |
| 11 | Roncero-Ramos B,Roman J R,Gomez-Serrano C,et al.Production of a biocrust-cyanobacteria strain (Nostoc commune) for large-scale restoration of dryland soils[J].Journal Applied Phycology,2019,31:2217-2230. |
| 12 | Zhao Y,Jia R L,Wang J.Towards stopping land degradation in drylands:water-saving techniques for cultivating biocrusts in situ[J].Land Degradation Development,2019,30:2336-2346. |
| 13 | Park C H,Li X R,Zhao Y,et al.Rapid development of cyanobacterial crust in the field for combating desertification[J].Plos One,2017,12. |
| 14 | Bu C,Li R,Wang C,et al.Successful field cultivation of moss biocrusts on disturbed soil surfaces in the short term[J].Plant and Soil,2018,429:227-240. |
| 15 | 李新荣,回嵘,赵洋.中国荒漠生物土壤结皮生态生理学研究[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2016:423. |
| 16 | 张元明,王雪芹.荒漠地表生物土壤结皮形成与演替特征概述[J].生态学报,2010,30(16):4484-4492. |
| 17 | 张元明.荒漠地表生物土壤结皮的微结构及其早期发育特征[J].科学通报,2005,50(1):42-47. |
| 18 | 钟泽璞,施定基.丝状体蓝藻藻殖段的分化及其调节机制[J].植物学通报,2000,17(3):204-210. |
| 19 | Krishnamurthy V.Reproductive biology of cyanophycota[M]//Johri B M,Srivastava P S.Reproductive Biology of Plants.Berlin,Germany:Springer,2001. |
| 20 | 胡春香,刘永定,黄泽波,等.荒漠藻壳的精细结构与发育[J].水生生物学报,2000,24(1):11-18. |
| 21 | Zhao Y,Bowker M A,Zhang Y,et al.Enhanced recovery of Bbiological soil crusts after disturbance[M]//Weber B,Büdel B,Belnap J.Biological Soil Crusts:An Organizing Principle in Drylands.Cham,Switzerland:Springer,2016. |
| 22 | Colesie C,Felde V J M N L,Büdel B.Composition and macrostructure of biological soil crusts[M]//Weber B,Büdel B,Belnap J,editors.Biological Soil Crusts:An Organizing Principle in Drylands.Cham,Switzerland:Springer,2016. |
| 23 | Sancho L G,Belnap J,Colesie C,et al.Carbon budgets of biological soil crusts at micro-,meso-,and global scales[M]//Weber B,Büdel B,Belnap J.Biological Soil Crusts: An Organizing Principle in Drylands.Cham,Switzerland: Springer,2016. |
| 24 | Baumann K,Siebers M,Kruse J,et al.Biological soil crusts as key player in biogeochemical P cycling during pedogenesis of sandy substrate[J].Geoderma,2019,338:145-158. |
| 25 | Garibotti I A,Gonzalez Polo M,Tabeni S.Linking biological soil crust attributes to the multifunctionality of vegetated patches and interspaces in a semiarid shrubland[J].Functional Ecology,2018,32:1065-1078. |
| 26 | Li Y G,Zhou X B,Zhang Y M.Moss patch size and microhabitats influence stoichiometry of moss crusts in a temperate desert,Central Asia[J].Plant and Soil,2019,443:55-72. |
| 27 | Sandoval Perez A L,Lucia Camargo-Ricalde S,Manuel Montano N,et al.Biocrusts,inside and outside resource islands of Mimosa luisana (Leguminosae),improve soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a tropical semiarid ecosystem[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2016,74:93-103. |
| 28 | Chamizo S,Belnap J,Eldridge D J,et al.The role of biocrusts in arid land hydrology[M]//Weber B,Büdel B,Belnap J.Biological Soil Crusts:An Organizing Principle in Drylands:Cham,Switzerland:Springer,2016. |
| 29 | Zhang J,Zhang Y M,Downing A,et al.The influence of biological soil crusts on dew deposition in Gurbantunggut Desert,Northwestern China [J].Journa of Hydrology,2009,379:220-228. |
| 30 | Liu L C,Li S Z,Duan Z H,et al.Effects of microbiotic crusts on dew deposition in the restored vegetation area at Shapotou,northwest China[J].Journa of Hydrology,2006,328:331-337. |
| 31 | Xie Z M,Liu Y D,Hua C X,et al.Relationships between the biomass of algal crusts in fields and their compressive strength[J].Soil Biology & Biochemistry,2007,39:567-572. |
| 32 | 王雪芹,张元明,张伟民,等.古尔班通古特沙漠生物结皮对地表风蚀作用影响的风洞实验[J].冰川冻土,2004,26(5):632-638. |
| 33 | Hu C X,Liu Y D,Song L R,et al.Effect of desert soil algae on the stabilization of fine sands[J].Journal of Applied Phycology,2002,14:281-292. |
| 34 | Li J,Okin G S,Alvarez L,et al.Effects of wind erosion on the spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients in two desert grassland communities[J].Biogeochemistry,2008,88:73-88. |
| 35 | Neff J C,Reynolds R L,Belnap J,et al.Multi-decadal impacts of grazing on soil physical and biogeochemical properties in southeast Utah [J].Ecological Applications,2005,15:87-95. |
| 36 | 魏江春,杨军,张涛,等.一种人工生物结皮治理荒漠的方法及专用地衣[P].中国,2012. |
| 37 | Rossi F,Li H,Liu Y,et al.Cyanobacterial inoculation (cyanobacterisation): perspectives for the development of a standardized multifunctional technology for soil fertilization and desertification reversal [J].Earth-Science Reviews,2017,171:28-43. |
| 38 | Wang W,Liu Y,Li D,et al.Feasibility of cyanobacterial inoculation for biological soil crusts formation in desert area[J].Soil Biology & Biochemistry,2009,41:926-929. |
| 39 | Chen L,Xie Z,Hu C,et al.Man-made desert algal crusts as affected by environmental factors in Inner Mongolia,China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2006,67:521-527. |
| 40 | 程向敏,魏鑫丽,魏江春.沙漠地衣结皮快速繁殖技术探索.多彩菌物 美丽中国[C].西安:中国菌物学会2019年学术年会,2019. |
| 41 | 曹同,陈静文,娄玉霞.苔藓植物组织培养繁殖技术及其应用前景[J].上海师范大学学报(自然科学版),2005,28(4):52-58. |
| 42 | 杨永胜.黄土高原苔藓结皮的快速培育及其对逆境的生理响应研究[D].北京:中国科学院研究生院,2015. |
| 43 | 陈彦芹,赵允格,冉茂勇.黄土丘陵区藓结皮人工培养方法试验研究[J].西北植物学报,2009,29(3):586-592. |
| 44 | 许红梅,李进,张元明.水分条件对人工培养齿肋赤藓光化学效率及生理特性的影响[J].植物生态学报,2017,41(8):882-893. |
| 45 | Xiao B,Zhao Y,Wang Q,et al.Development of artificial moss-dominated biological soil crusts and their effects on runoff and soil water content in a semi-arid environment [J].Journal of Arid Environments,2015,117:75-83. |
| 46 | 张侃侃.毛乌素沙地苔藓结皮的人工培育技术[D].陕西杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2012. |
| 47 | Zhou X,Zhao Y,Belnap J,et al.Practices of biological soil crust rehabilitation in China:experiences and challenges[J].Restoration Ecology,2020,28:S45-S55. |
| 48 | Peng C,Zheng J,Huang S,et al.Application of sodium alginate in induced biological soil crusts: enhancing the sand stabilization in the early stage [J].Journal of Applied Phycology,2017,29(3):1421-1428. |
| 49 | Buttars S M,St Clair L L,Johansen J R,et al.Pelletized cyanobacterial soil amendments: laboratory testing for survival,escapability,and nitrogen fixation [J].Arid Soil Research and Rehabilitation,1998,12(2):165-178. |
| 50 | Park C H,Li X R,Jia R L,et al.Combined application of cyanobacteria with soil fixing chemicals for rapid induction of biological soil crust formation [J].Arid Land Research and Management,2017,31(1):81-93. |
| 51 | 饶本强,王伟波,兰书斌,等.库布齐沙地三年生人工藻结皮发育特征及微生物分布[J].水生生物学报,2009,33(5):937-944. |
| 52 | 唐东山,王伟波,李敦海,等.人工藻结皮对库布齐沙地土壤酶活性的影响[J].水生生物学报,2007,31(3):339-344. |
| 53 | 吴丽,陈晓国,张高科,等.人工生物结皮的发育演替及表土持水特性研究[J].环境科学,2014,35(3):1138-1143. |
| 54 | Lan S B,Zhang Q Y,Wu L,et al.Artificially accelerating the reversal of desertification: cyanobacterial inoculation facilitates the succession of vegetation communities [J].Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48:307-315. |
| 55 | 毛晓雅.我国荒漠化和沙化面积连续15年“双缩减”[J].山西农经,2020,27(1):10. |
| 56 | 杨延哲.人工培育生物结皮在毛乌素沙地光伏电站施工迹地的风蚀防治研究[D].北京:中国科学院研究生院,2016. |
| 57 | 杨建振.陕北毛乌素沙地生物结皮的土壤水分效应及其人工培育技术初探[D].陕西杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2010. |
| 58 | 张丙昌,王敬竹,张元明,等.水分对具鞘微鞘藻构建人工藻结皮的作用[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(2):535-540. |
| 59 | 田桂泉,白学良,徐杰,等.腾格里沙漠固定沙丘藓类植物结皮层的自然恢复及人工培养试验研究[J].植物生态学报,2005,29(1):164-169. |
| 60 | 贾艳,白学良,单飞彪,等.藓类结皮层人工培养试验和维持机制研究[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(1):54-59. |
| 61 | Giraldo-Silva A,Nelson C,Barger N N,et al.Nursing biocrusts: isolation,cultivation,and fitness test of indigenous cyanobacteria[J].Restoration Ecology,2019,27(4):793-803. |
| 62 | Bowker M A,Antoninka A J,Chuckran P F.Improving field success of biocrust rehabilitation materials: hardening the organisms or softening the environment? [J].Restoration Ecology,2019,28:1-10. |
| 63 | Giraldo-Silva A,Nelson C,Penfold C,et al.Effect of preconditioning to the soil environment on the performance of 20 cyanobacterial strains used as inoculum for biocrust restoration [J].Restoration Ecology,2019,28(S2):13048. |
| 64 | Antoninka A,Bowker M A,Chuckran P,et al.Maximizing establishment and survivorship of field-collected and greenhouse-cultivated biocrusts in a semi-cold desert [J].Plant and Soil,2018,429(1/2):213-225. |
| 65 | Guo Y W,Zhao Y G.Effects of storage temperature on the physiological characteristics and vegetative propagation of desiccation-tolerant mosses [J].Biogeosciences,2018,15(3):797-808. |
| [1] | 任余龙, 李毅, 李红, 吴晶, 柳媛普. 地表能量平衡方程在新疆地表温度模拟中的应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 137-146. |
| [2] | 赵洋, 潘颜霞, 苏洁琼, 张志山. 中国干旱区沙化土地绿色环保治理技术综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 195-202. |
| [3] | 周虹, 吴波, 高莹, 成龙, 贾晓红, 庞营军, 赵河聚. 毛乌素沙地臭柏(Sabina vulgaris)群落生物土壤结皮细菌群落组成及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 130-141. |
| [4] | 张润霞, 赵学勇, 李晶, 吕文强, 柴媛媛, 岳红琴. 干旱荒漠区土地利用方式快速转变对土壤入渗性能的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 146-153. |
| [5] | 李得禄, 马全林, 张锦春, 陈芳, 李新荣, 袁宏波, 魏林源, 杨昊天, 张忠. 腾格里沙漠植被特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| [6] | 周立峰, 杨荣, 赵文智. 荒漠人工固沙植被区土壤结皮斥水性发展特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 185-192. |
| [7] | 王岩松, 刘玉冰, 王增如, 赵丽娜, 漆婧华, 张雯莉. 生物土壤结皮铁代谢微生物组成及其功能基因对演替的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 193-200. |
| [8] | 张瑞, 周晓兵, 张元明. 生物土壤结皮对温带荒漠植物凋落物分解的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 151-158. |
| [9] | 刘艳梅, 杨航宇, 贾荣亮, 李宜轩. 人为踩踏生物土壤结皮对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(4): 54-63. |
| [10] | 杨航宇, 刘长仲, 刘艳梅, 杨昊天. 荒漠区踩踏生物土壤结皮对土壤微生物量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(2): 35-44. |
| [11] | 马俊梅, 满多清, 李得禄, 刘有军, 郭春秀. 干旱荒漠区退耕地植被演替及土壤水分变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(4): 800-807. |
| [12] | 曹瑞, 刘果厚, 兰庆, 刘冠志, 慕宗杰, 桂荣, 刘利红, 王健. 浑善达克沙地飞播区植被动态[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 535-544. |
| [13] | 司守霞, 李宜轩, 回嵘, 刘立超, 谢敏, 王艳莉. 降雪对荒漠生物土壤结皮光合生理特性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 560-567. |
| [14] | 都军, 李宜轩, 杨晓霞, 李云飞, 马晓俊. 腾格里沙漠东南缘生物土壤结皮对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 111-116. |
| [15] | 罗维成, 赵文智, 孙程鹏, 闫加亮. 科尔沁沙地樟子松(Pinus sylvestris)人工固沙林演变过程中物种多样性和土壤水分特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 126-132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
