中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 231-246.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00109
• • 上一篇
韩晓雨1( ), 迟云平1,2(
), 迟云平1,2( ), 谢远云1,2, 康春国3, 吴鹏1, 汪烨辉1, 孙磊1, 魏振宇1
), 谢远云1,2, 康春国3, 吴鹏1, 汪烨辉1, 孙磊1, 魏振宇1
收稿日期:2023-09-13
修回日期:2023-12-04
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-06-11
通讯作者:
迟云平
作者简介:迟云平(E-mail: 1982cyp@163.com)基金资助:
Xiaoyu Han1( ), Yunping Chi1,2(
), Yunping Chi1,2( ), Yuanyun Xie1,2, Chunguo Kang3, Peng Wu1, Yehui Wang1, Lei Sun1, Zhengyu Wei1
), Yuanyun Xie1,2, Chunguo Kang3, Peng Wu1, Yehui Wang1, Lei Sun1, Zhengyu Wei1
Received:2023-09-13
Revised:2023-12-04
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-11
Contact:
Yunping Chi
摘要:
科尔沁沙地是中国北方面积最大的半固定沙地,追踪其物质来源对认识沙地/沙漠的形成演化和重建碎屑物质的迁移路径至关重要。为此,本研究对科尔沁沙地风成沙的细颗粒组分(<63 μm和<11 μm)进行了岩石学分析、元素地球化学分析、Sr-Nd同位素分析、TIMA自动化矿物识别以及碎屑锆石U-Pb测年分析,全面表征科尔沁沙地物质组成并对其物源进行定量约束。结果表明:科尔沁沙地经历了较低的化学风化,分选和再循环的程度较低。重矿物组合以钛铁矿、绿帘石、锆石、石榴子石、磁铁矿+赤褐铁矿为主,与地球化学母岩判别图解共同指示科尔沁沙地沉积物主要来自中酸性岩浆母岩。Sr-Nd同位素进一步约束主要源区为中亚造山带南缘和华北克拉通北缘,少量粉尘来源于中国北方边界沙漠。沙地的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄集中在中生代至晚古生代(200~600 Ma)和古元古代(1 518~2 000 Ma、2 200~2 600 Ma)。与潜在源区锆石年龄谱的对比显示,科尔沁沙地细颗粒组分既有来自中亚造山带南缘大兴安岭经风力搬运和河流搬运而来的近源物质供给,也有经河流搬运自华北克拉通北缘燕山山脉出露的古老基岩。逆向蒙特卡罗模型的定量物源结果显示中亚造山带的贡献占53.7%、华北克拉通贡献占46.3%。风与河流的共同作用解释了科尔沁沙地风成沙细颗粒组分的形成。
中图分类号:
韩晓雨, 迟云平, 谢远云, 康春国, 吴鹏, 汪烨辉, 孙磊, 魏振宇. 科尔沁沙地风成细沙的物质组成特征及其对物源的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 231-246.
Xiaoyu Han, Yunping Chi, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Peng Wu, Yehui Wang, Lei Sun, Zhengyu Wei. Material composition characteristics of fine particles of eolian sand in Horqin Sandy Land and its indication to provenance[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 231-246.
| 样品 | 钛铁矿 | 绿帘石 | 锆石 | 赤铁矿/磁铁矿 | 铁铝榴石 | 榍石 | 金红石 | 石英 | 独居石 | 磷灰石 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 27.06 | 20.96 | 9.72 | 8.64 | 6.09 | 5.91 | 3.07 | 1.16 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Q2 | 35.36 | 10.16 | 15.49 | 5.14 | 13.01 | 4.01 | 3.03 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Q4 | 33.52 | 11.20 | 15.22 | 2.75 | 14.03 | 4.48 | 3.50 | 1.50 | 0.33 | 0.10 |
| Q5 | 28.87 | 14.84 | 11.51 | 14.92 | 6.45 | 4.34 | 2.60 | 1.11 | 0.39 | 0.12 |
| Q7 | 34.83 | 9.89 | 18.68 | 3.88 | 10.03 | 4.08 | 3.16 | 2.93 | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| 平均值 | 31.928 | 13.41 | 14.124 | 7.066 | 9.922 | 4.564 | 3.072 | 1.472 | 0.288 | 0.092 |
表1 科尔沁沙地<63 μm组分的沉积物TIMA自动定量矿物含量 (%)
Table 1 Automatic quantitative mineral content results of TIMA of <63 μm components in Horqin Sandy Land
| 样品 | 钛铁矿 | 绿帘石 | 锆石 | 赤铁矿/磁铁矿 | 铁铝榴石 | 榍石 | 金红石 | 石英 | 独居石 | 磷灰石 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 27.06 | 20.96 | 9.72 | 8.64 | 6.09 | 5.91 | 3.07 | 1.16 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Q2 | 35.36 | 10.16 | 15.49 | 5.14 | 13.01 | 4.01 | 3.03 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| Q4 | 33.52 | 11.20 | 15.22 | 2.75 | 14.03 | 4.48 | 3.50 | 1.50 | 0.33 | 0.10 |
| Q5 | 28.87 | 14.84 | 11.51 | 14.92 | 6.45 | 4.34 | 2.60 | 1.11 | 0.39 | 0.12 |
| Q7 | 34.83 | 9.89 | 18.68 | 3.88 | 10.03 | 4.08 | 3.16 | 2.93 | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| 平均值 | 31.928 | 13.41 | 14.124 | 7.066 | 9.922 | 4.564 | 3.072 | 1.472 | 0.288 | 0.092 |
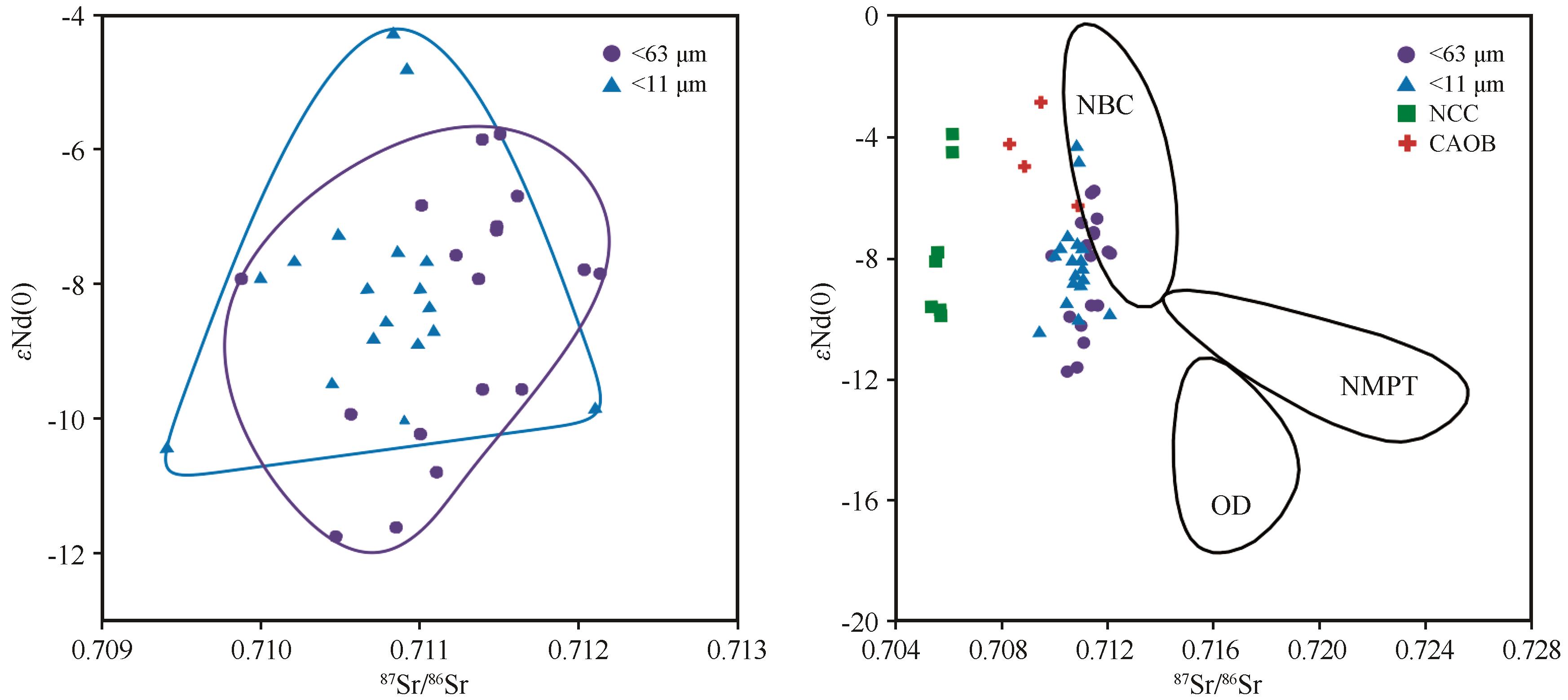
图4 科尔沁沙地沉积物Sr-Nd同位素组成注:Sr-Nd同位素数据引自文献[9,38-40];NBC为中国北方边界附近干旱区;NMPT为青藏高原北缘干旱区;OD为鄂尔多斯干旱区;NCC为华北克拉通;CAOB为中亚造山带
Fig.4 Sr-Nd isotopic composition of sediments from the Horqin Sandy Land
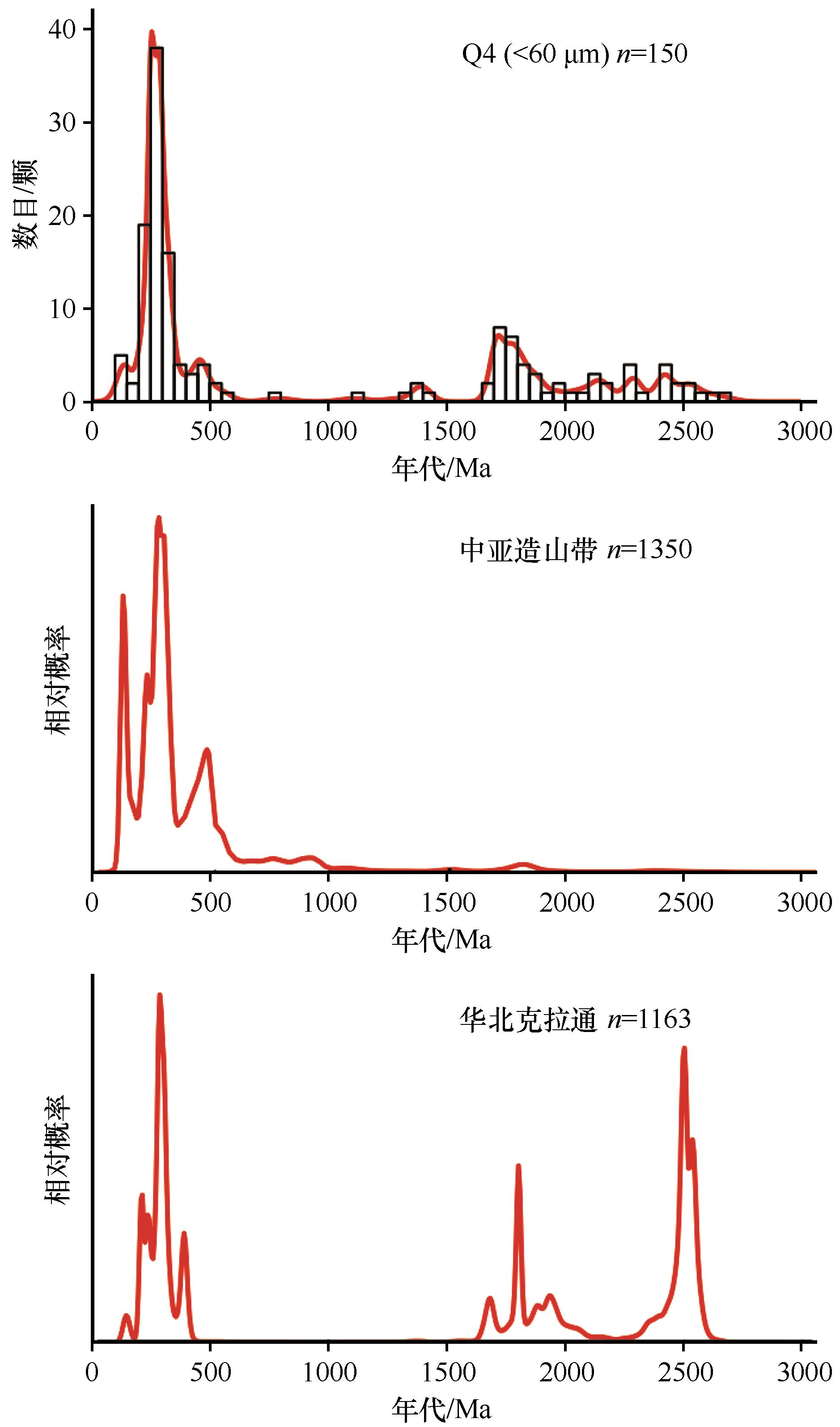
图9 科尔沁沙地与潜在物源区碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谱对比图注:中亚造山带锆石年龄数据引自文献[84,86-99];华北克拉通锆石年龄数据引自文献[100-111]
Fig.9 Comparison of U-Pb age spectrum of clastic zircon in the Horqin Sandy Land and potential source area
| 1 | Nie J S, Peng W B, Möller A,et al.Provenance of the upper Miocene-Pliocene Red Clay deposits of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2014,407:35-47. |
| 2 | Zhang H Z, Lu H Y, Xu X S,et al.Quantitative estimation of the contribution of dust sources to Chinese loess using detrital zircon U-Pb age patterns [J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2016,121(11):2085-2099. |
| 3 | 谢远云,孙磊,康春国,等.松嫩沙地Sr-Nd同位素组成特征[J].沉积学报,2020,38(4):771-780. |
| 4 | Anon.Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust[J].Science China(Earth Sciences),2011,54(9):1279-1301. |
| 5 | 段翰晨,王涛,薛娴,等.科尔沁沙地沙漠化时空演变及其景观格局:以内蒙古自治区奈曼旗为例[J].地理学报,2012,67(7):917-928. |
| 6 | 弋双文,鹿化煜,曾琳,等.末次盛冰期以来科尔沁沙地古气候变化及其边界重建[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):206-217. |
| 7 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980. |
| 8 | Rao W B, Chen J, Yang J D,et al.Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of eolian deposits in the Erdos Desert and Chinese Loess Plateau:implications for their provenances[J].Geochemical Journal,2008,42(3):273-282. |
| 9 | Chen J, Li G J, Yang J D,et al.Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts:implications for the provenances of Asian dust[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,2007,71:3904-3914. |
| 10 | 孙磊,谢远云,康春国,等.呼伦贝尔沙地重矿物、Sr-Nd同位素组成及其对亚洲风尘系统的指示[J].中国地质,2021,48(6):1965-1974. |
| 11 | Sun J M.Source regions and formation of the Loess sediments on the high mountain regions of northwestern China[J].Quaternary Research,2002,58(3):341-351. |
| 12 | 鹿化煜,李郎平,弋双文,等.中国北方沙漠-黄土体系的沉积和侵蚀过程与未来趋向探析[J].地学前缘,2010,17(5):336-344. |
| 13 | Song Y G, Fang X M, John W.Magnetic parameter variations in the Chaona loess/paleosol sequences in the central Chinese Loess Plateau,and their significance for the middle Pleistocene climate transition[J].Quaternary Research:An Interdisciplinary Journal,2014,81(3):433-444. |
| 14 | 谢静,吴福元,丁仲礼.浑善达克沙地的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成及其源区意义[J].岩石学报,2007(2):523-528. |
| 15 | Yang L R, Zou N, Yue L P,et al.Distribution of U-Pb ages of detrital zircon from the Hobq Desert and its implications for provenance[J].Quaternary Sciences,2017,37(3):560-569. |
| 16 | 郭绍礼.西辽河流域沙漠化土地的形成和演变[J].自然资源,1980(4):46-52. |
| 17 | 裘善文.试论科尔沁沙地的形成与演变[J].地理科学,1989(4):317-328. |
| 18 | 胡孟春.科尔沁土地沙漠化分类定量指标初步研究[J].中国沙漠,1991,11(3):60-63. |
| 19 | Kohfeld K E, Harrison S P.How well can we simulate past climates?Evaluating the models using global palaeoenvironmental datasets[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2000,19(1):321-346. |
| 20 | Ferrat M, Weiss D J, Strekopytov S,et al.Improved provenance tracing of Asian dust sources using rare earth elements and selected trace elements for palaeomonsoon studies on the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,2011,75:6374-6399. |
| 21 | Grousset F E, Biscaye P E.Tracing dust sources and transport patterns using Sr,Nd and Pb isotopes[J].Chemical Geology,2005,222(3):149-167. |
| 22 | Nie J S, Peng W B, Pfaff K,et al.Controlling factors on heavy mineral assemblages in Chinese loess and Red Clay[J].Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol,2013,381:110-118. |
| 23 | Thamó-Bozsó E.Heavy mineral composition of some loess and loess-like sediments in Hungary[J].Quaternary International,2012,279:489. |
| 24 | 汪进秋,谢远云,康春国,等.中更新世以来的哈尔滨黄土物源变化来自TIMA:自动定量矿物的证据[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(5):25-35. |
| 25 | 张瀚之,鹿化煜,弋双文,等.中国北方沙漠/沙地锆石形态特征及其对物源的指示[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):334-344. |
| 26 | 林旭,刘静,吴中海,等.中国北部陆架海碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和钾长石主微量元素物源示踪研究[J].地质学报,2020,94(10):3024-3035. |
| 27 | Yang J H, Wu F Y, Shao J,et al.Constraints on the timing of uplift of the Yanshan Fold and Thrust belt,North China[J].Earth And Planetary Science Letters,2006,246(3):336-352. |
| 28 | 谢静,杨石岭,丁仲礼.黄土物源碎屑锆石示踪方法与应用[J].中国科学:地球科学,2012,42(6):923-933. |
| 29 | 张启德,王玉秀.科尔沁沙地与大气环境[M].北京:科学出版社,1994. |
| 30 | 刘璐,谢远云,迟云平,等.地球化学组成对浑善达克沙地与科尔沁沙地风化和沉积循环特征及其物源的指示[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2021,41(4):192-206. |
| 31 | Chen B, Yang X P, Jiang Q D,et al.Geochemistry of aeolian sand in the Taklamakan Desert and Horqin Sandy Land,northern China:implications for weathering,recycling,and provenance[J].Catena,2022(6):208-218. |
| 32 | 徐园园,谢远云,康春国,等.松花江早更新世水系演化:来自TIMA矿物和地球化学的证据[J].地质科学,2022,57(1):190-206. |
| 33 | 蔡芃睿,王涛,王宗起,等.大兴安岭中段乐平统—中三叠统沉积物源分析:来自重矿物组合及碎屑锆石年代学证据[J].岩石学报,2019,35(11):3549-3564. |
| 34 | 翟明国.中国主要古陆与联合大陆的形成:综述与展望[J].中国科学:地球科学,2013,43(10):1583-1606. |
| 35 | 李秋杭,谢远云,康春国,等.基于人工和TIMA自动化方法的松花江水系重矿物组成:对源-汇物源示踪的指示[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2022,42(3):170-183. |
| 36 | Ludwig K R.Isoplot/Ex Version 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[Z].Berkeley,California,USA:Berkeley Geochronological Center,2003. |
| 37 | Joel E S, Jennifer N K, Brian K H,et al.Mixing of source populations recorded in detrital zircon U-Pb age spectra of modern river sands[J].Geology,2013,121(1):17-33. |
| 38 | Li G J, Chen J, Ji J F,et al.Natural and anthropogenic sources of East Asian dust[J].Geology,2009,37(8):727-730. |
| 39 | Li S Q, Chen F K, Siebel W,et al.Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Songliao basin,NE China:evidence from detrital zircon ages and Sr-Nd isotopes[J].Gondwana Research Acta,2012,22:934-955. |
| 40 | 马强.辽西三叠纪-侏罗纪火山岩:华北北缘东段下地壳再造与克拉通破坏[D].武汉:中国地质大学,2013. |
| 41 | McLennan S M.Weathering and global denudation[J].Geology,1993,101(2):295-303. |
| 42 | Cox R, Lowe R D, Cullers R L.The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J].Geochim Cosmochim Acta,1995,59(14):2919-2940. |
| 43 | Armstrong-Altrin S J, Lee I Y, Verma P S,et al.Geochemistry of sandstones from the upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation,southern India:implications for provenance,weathering,and tectonic setting[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,2004,74(2):285-297. |
| 44 | Asiedu D K, Dampare S B, Sakyi A P,et al.Geochemistry of Paleoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks from the Birim diamondiferous field,southern Ghana:implications for provenance and crustal evolution at the Archean-Proterozoic boundary[J].Geochemical Journal,2004,38(3):215-228. |
| 45 | Hao Q Z, Guo Z T, Qiao Y S,et al.Geochemical evidence for the provenance of middle Pleistocene loess deposits in southern China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2010,29(23):3317-3326. |
| 46 | Windley B F.The continental crust:its composition and evolution[J].Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,1986,42(3):196-197. |
| 47 | Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Unraveling the effects of potassium me tasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols,with implications for paleo weathering conditions and provenance[J].Geology,1995,23:921-924. |
| 48 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,299:715. |
| 49 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J].Geochim Cosmochim Acta,1984,48(7):1523-1534. |
| 50 | Harnois L.The ciw index:a new chemical index of weathering[J].Sedimentary Geology,1988,55(3):319-322. |
| 51 | 赵勇伟,樊祺诚.大兴安岭哈拉哈河-绰尔河第四纪火山岩地幔源区与岩浆成因[J].岩石学报,2012,28(4):1119-1129. |
| 52 | 李永飞,郜晓勇,卞雄飞,等.大兴安岭北段龙江盆地中生代火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报,2013,32(8):1195-1211. |
| 53 | 郭望,张卫刚,李玉宏,等.柴北缘大煤沟组七段页岩地球化学特征:对中侏罗世晚期物源及风化作用的指示及意义[J].沉积学报,2020,38(3):676-686. |
| 54 | 徐小涛,邵龙义.利用泥质岩化学蚀变指数分析物源区风化程度时的限制因素[J].古地理学报,2018,20(3):515-522. |
| 55 | Kimberley M M, Grandstaff D E.Profiles of elemental concentrations in Precambrian paleosols on basaltic and granitic parent materials[J].Precambrian Research,1986,32(2):133-154. |
| 56 | 王彤,朱筱敏,董艳蕾,等.基于微量元素分析的古沉积背景重建:以准噶尔盆地西北缘古近系安集海河组为例[J].地质学报,2020,94(12):3830-3851. |
| 57 | 孙杨,谢远云,迟云平,等.大兴安岭东麓龙江县白土山组地层特征:化学风化、沉积循环、源-汇体系和沉积环境[J].山地学报,2022,40(1):14-28. |
| 58 | 刘俊贺,迟云平,谢远云,等.松嫩沙地地球化学特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):252-263. |
| 59 | Armstrong-Altrin S J, Ramasamy N, Vysetti B,et al.Petrography and geochemistry of sands from the Chachalacas and Veracruz beach areas,western Gulf of Mexico,Mexico:constraints on provenance and tectonic setting[J].Journal of South American Earth Sciences,2015,64:199-216. |
| 60 | Roser B P, Cooper R A, Nathan S,et al.Reconnaissance sandstone geochemistry,provenance,and tectonic setting of the lower Paleozoic terranes of the West Coast and Nelson,New Zealand[J].New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics,2010,39(1):1-16. |
| 61 | Robert L C, Victor N P.Geochemistry of the Mesoproterozoic Lakhanda shales in southeastern Yakutia,Russia:implications for mineralogical and provenance control,and recycling[J].Precambrian Research,2000,104(1):77-93. |
| 62 | Xie Y Y, Yuan F, Zhan T,et al.Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of sediments for the Hulun Buir Sandy Land,Northeast China:implication for weathering,recycling and dust provenance[J].Catena,2018,160:170-184. |
| 63 | 袁方,谢远云,詹涛,等.地球化学组成揭示的杜蒙沙地化学风化和沉积再循环特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J].地理科学,2017,37(12):1885-1893. |
| 64 | 梁琛岳,刘永江,李伟,等.大兴安岭北段伸展隆升样式:来自科洛-嘎拉山韧性变形带的证据[J].岩石学报,2018,34(10):2873-2900. |
| 65 | Condie K C.Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust:contrasting results from surface samples and shales[J].Chemical Geology,1993,104:1-4. |
| 66 | 康春国,李长安,谢远云,等.哈尔滨地区风尘黄土重矿物特征及物源分析[J].自然灾害学报,2011,20(4):43-51. |
| 67 | 操应长,宋玲,王健,等.重矿物资料在沉积物物源分析中的应用:以涠西南凹陷古近系流三段下亚段为例[J].沉积学报,2011,29(5):835-841. |
| 68 | Wu P, Xie Y Y, Chi Y P,et al.Loess accumulation in Harbin with implications for Late Quaternary aridification in the Songnen Plain,Northeast China[J].Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol,2021,570:110365. |
| 69 | Xie Y Y, Liu L, Kang C G,et al.Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of the northeast sandy land,China and their implications for tracing sources of regional dust[J].Catena,2020,184:104303. |
| 70 | Mclennan S M, Taylor S R, Mcculloch M T,et al.Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic composition of deep-sea turbidites:crustal evolution and plate tectonic associations[J].Geochim Cosmochim Acta,1990,54(7):2015-2050. |
| 71 | Goldstein S L, Nions R K,et al.A Sm-Nd isotopic study of atmospheric dusts and particulates from major river systems[J].Earth Planet Science Letters,1984,70(2):221-236. |
| 72 | Li G J, Thomas P, Chen J.Increasing Nd isotopic ratio of Asian dust indicates progressive uplift of the north Tibetan Plateau since the middle Miocene[J].Geology,2011,39(3):199-202. |
| 73 | Chen Z, Li G J.Evolving sources of eolian detritus on the Chinese Loess Plateau since early Miocene:tectonic and climatic controls[J].Earth Planet Science Letters,2013,371/372:220-225. |
| 74 | Eisenhauer A, Meyer H, Rachold V,et al.Grain size separation and sediment mixing in Arctic Ocean sediments:evidence from the strontium isotope systematic[J].Chemical Geology,1999,158(3):173-188. |
| 75 | Smith J, Derek V, Rob A K,et al.Isotopic constraints on the source of Argentinian loess-with implications for atmospheric circulation and the provenance of Antarctic dust during recent glacial maxima[J].Earth Planet Science Letters,2003,212(1):181-196. |
| 76 | Jiang F Q, Frank M, Li T G,et al.Asian dust input in the western Philippine Sea:evidence from radiogenic Sr-Nd isotopes[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2013,14(5):1538-1551. |
| 77 | Christopher B, Liu K W, Oswald G.Geochemistry of sandstones and shales from the Ecca Group,Karoo Supergroup,in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa:implications for provenance,weathering and tectonic setting[J].Open Geosciences,2017,9(1):340-360. |
| 78 | Rao W B, Mao C P, Wang Y G,et al.Using Sr-Nd isotopes and rare earth elements to study sediment provenance of the modern radial sand ridges in the southwestern Yellow Sea[J].Applied Geochemistry,2017,81:23-35. |
| 79 | Julius D E.Strontium isotopes in weathering profiles,deep-sea sediments,and sedimentary rocks[J].Geochim Cosmochim Acta,1969,33(12):1521-1552. |
| 80 | Feng J L, Zhu L P, Zhen X L,et al.Grain size effect on Sr-Nd isotopic compositions in eolian dust:implications for tracing dust provenance and Nd model age[J].Geochemical Journal,2009,43(2):123-131. |
| 81 | Stephen D P, Williams I S, Allan R C.The use of protolith zircon-age fingerprints in determining the protosource areas for some Australian dune sands[J].Sedimentary Geology,1997,109(3):233-260. |
| 82 | Richards A, Argles T, Harris N,et al.Himalayan architecture constrained by isotopic tracers from clastic sediments[J].Earth Planet Science Letters,2005,236(3):773-796. |
| 83 | Veevers J J, Saeed A, Belousova E A,et al.U-Pb ages and source composition by Hf-isotope and trace-element analysis of detrital zircons in Permian sandstone and modern sand from southwestern Australia and a review of the paleogeographical and denudational history of the Yilgarn Craton[J].Earth Science Reviews,2004,68(3):245-279. |
| 84 | Wang W, Liu S W, Bai X,et al.Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic systematic of the Neoarchean Yixian-Fuxin greenstone belt,northern margin of the North China Craton:implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J].Gondwana Research,2011,20(1):64-81. |
| 85 | 刘显凡,卢秋霞.锆石形态标型特征及标型生长机制探讨[J].岩石矿物学杂志,1997(2):84-89. |
| 86 | 陈斌,赵国强, Wilde S.内蒙古苏尼左旗南部与俯冲和碰撞有关的花岗岩类:同位素年龄及其构造意义[J].地质评论,2001,47:361-367. |
| 87 | 陈斌,马星华,刘安坤,等.锡林浩特杂岩和蓝片岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及其对索仑缝合带演化的意义[J].岩石学报,2009,25(12):3123-3129. |
| 88 | 石玉若,刘敦一,张旗,等.内蒙古苏左旗地区闪长-花岗岩类SHRIMP年代学[J].地质学报,2004(6):789-799. |
| 89 | Shi Y R, Liu D Y, Miao L C,et al.Devonian A-type granitic magmatism on the northern margin of the North China Craton:SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating and Hf-isotopes of the Hongshan granite at Chifeng,Inner Mongolia,China[J].Gondwana Research,2009,17(4):632-641. |
| 90 | 葛文春,吴福元,周长勇,等.大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].岩石学报,2005(3):749-762. |
| 91 | Demoux A, Kroner A, Liu D Y,et al.Precambrian crystalline basement in southern Mongolia as revealed by SHRIMP zircon dating[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(6):1365-1380. |
| 92 | Guo F, Fan W M, Li C W,et al.Early Cretaceous highly positive εNd felsic volcanic rocks from the Hinggan Mountains,NE China:origin and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(6):1395-1411. |
| 93 | 李益龙,周汉文,葛梦春,等.内蒙古林西县双井片岩北缘混合岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄[J].矿物岩石,2008(2):10-16. |
| 94 | 李益龙,周汉文,钟增球,等.华北与西伯利亚板块的对接过程:来自西拉木伦缝合带变形花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄证据[J].地球科学(中国地质大学学报),2009,34(6):931-938. |
| 95 | Li D P, Chen Y L, Wang Z,et al.Detrital zircon U-Pb ages,Hf isotopes and tectonic implications for Palaeozoic sedimentary rocks from the Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt,middle-east part of Inner Mongolia,China[J].Geological Journal,2011,46(1):63-81. |
| 96 | Zhang J H, Ge W C, Wu F Y,et al.Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing'an Range,northeastern China[J].Lithos,2007,102(1):138-157. |
| 97 | 张海华,李永飞,张健,等.大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J].现代地质,2020,34(3):483-493. |
| 98 | Liu W, Pan X F, Liu D Y,et al.Three-step continental crust growth from subduction accretion and underplating,through intermediary differentiation,to granitoid production[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(6):1413-1439. |
| 99 | Liu Y S, Wang X H, Wang D B,et al.Triassic high-Mg adakitic andesites from Linxi,Inner Mongolia:insights into the fate of the Paleo-Asian ocean crust and fossil slab-derived melta-peridotite interaction[J].Chemical Geology,2012,328:89-108. |
| 100 | 郭敬辉,石昕,卞爱国,等.桑干地区早元古代花岗岩长石Pb同位素组成和锆石U-Pb年龄:变质与地壳熔融作用及构造:热事件演化[J].岩石学报,1999(2):40-48. |
| 101 | Miao L C, Qiu Y M, McNaughton N,et al.Shrimp U-Pb zircon geochronology of granitoids from Dongping area,Hebei Province,China:constraints on tectonic evolution and geodynamic setting for gold metallogeny[J].Ore Geology Reviews,2002,19(3):187-204. |
| 102 | Zhang S H, Zhao Y, Song B,et al.Carboniferous granitic plutons from the northern margin of the North China block:implications for a Late Palaeozoic active continental margin[J].Geological Society London,2007,162(2):451-463. |
| 103 | Zhang S H, Zhao Y, Song B,et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb and in-situ Lu-Hf isotope analyses of a tuff from Western Beijing:evidence for missing Late Paleozoic arc volcano eruptions at the northern margin of the North China Block[J].Gondwana Research,2006,12(1):157-165. |
| 104 | Zhang S H, Zhao Y, Alfred K,et al.Early Permian plutons from the northern North China Block:constraints on continental arc evolution and convergent margin magmatism related to the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences,2009,98(6):1441-1467. |
| 105 | Zhang H C.G,Zhao G C,Wang C,et al.Phase equilibria modelling and zircon U-Pb geochronology of Paleoproterozoic Mafic Granulites from the Chengde Complex,North China Craton[J].Precambrian Research,2022,371:106576. |
| 106 | 钟长汀,邓晋福,万渝生,等.华北克拉通北缘中段古元古代造山作用的岩浆记录:S型花岗岩地球化学特征及锆石SHRIMP年龄[J].地球化学,2007(6):585-600. |
| 107 | Wan Y S, Liu D Y, Xu Z Y,et al.Paleoproterozoic crustally derived carbonate-rich magmatic rocks from the Daqinshan area,North China Craton:geological,petrographical,geochronological and geochemical (Hf,Nd,O and C) evidence[J].American Journal of Science,2008,308(3):351-378. |
| 108 | Matthew L G, Simon A W, Wu F Y,et al.The application of zircon cathodoluminescence imaging,Th-U-Pb chemistry and U-Pb ages in interpreting discrete magmatic and high-grade metamorphic events in the North China Craton at the Archean/Proterozoic boundary[J].Chemical Geology,2009,261(1):155-171. |
| 109 | 李怀坤,苏文博,周红英,等.华北克拉通北部长城系底界年龄小于1670 Ma:来自北京密云花岗斑岩岩脉锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的约束[J].地学前缘,2011,18(3):108-120. |
| 110 | Liu J, Zhao Y, Liu X M,et al.Rapid exhumation of basement rocks along the northern margin of the North China Craton in the early Jurassic:evidence from the Xiabancheng Basin,Yanshan Tectonic Belt[J].Basin Research,2012,24(5):544-558. |
| 111 | Zou D Y, Zhang H F.Destruction of the lower crust beneath the North China Craton recorded by granulite and pyroxenite xenoliths[J].Science China (Earth Sciences),2023,66(2):190-204. |
| 112 | Kurt E S, Joel E S.Unmixing detrital geochronology age distributions[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2017,18(8):2872-2886. |
| [1] | 蔡明玉, 贾飚, 常学礼. 景观格局因子交互作用对科尔沁沙地沙漠化的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 99-108. |
| [2] | 孟庆爽, 左合君, 闫敏, 王海兵, 席成. 库布齐沙漠地表沉积物常量元素与粒度的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 107-117. |
| [3] | 刘俊贺, 迟云平, 谢远云, 康春国, 魏振宇, 吴鹏, 孙磊. 松嫩沙地地球化学特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 252-263. |
| [4] | 任雨, 张勃, 陈曦东. 科尔沁沙地土地荒漠化敏感性评估[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 159-169. |
| [5] | 张思悦, 李继彦, 张姚姚, 徐德华. 柴达木盆地西南缘山前沙丘区沉积物地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 222-233. |
| [6] | 闫蒙, 王旭洋, 周立业, 李玉强. 科尔沁沙地沙漠化过程中土壤有机碳含量变化特征及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 221-231. |
| [7] | 汪进秋, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 孙磊, 吴鹏, 魏振宇. 中更新世以来的哈尔滨黄土物源变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 25-35. |
| [8] | 冯净雪, 丁占良, 尤莉, 韩广. 科尔沁沙地西部横向沙丘间的风况和输沙势[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 110-119. |
| [9] | 贺超, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 王冠丽, 郝丽娜. 科尔沁沙地差巴嘎蒿( Artemisia halodendron )水分利用特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 190-198. |
| [10] | 王晓枝, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 李超, 高冲, 张欣. 拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 22-31. |
| [11] | 张亦然, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 贾天宇, 季亚新. 基于多源遥感和机器学习方法的科尔沁沙地植被覆盖度反演[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 187-195. |
| [12] | 赵啸龙, 谢玉鸿, 马旭君, 王少昆. 科尔沁沙质草地不同恢复年限草本层群落结构及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [13] | 高冲, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 刘铮瑶, 朱春鸣, 王晓枝, 肖南, 张欣. 古尔班通古特沙漠蜂窝状沙丘沉积物理化特征及沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 14-24. |
| [14] | 董苗, 严平, 王晓旭, 张国明, 孟小楠, 纪欣然, 王勇. 雅鲁藏布江山南宽谷段爬坡沙丘表层沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 153-163. |
| [15] | 詹瑾, 韩丹, 杨红玲, 李玉霖. 科尔沁沙地植被恢复过程中群落组成及多样性演变特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 194-206. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
