
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 255-265.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00090
Shilei Mu1( ), Zhihui Yuan2,3,4(
), Zhihui Yuan2,3,4( ), Wuritaoketaohu1
), Wuritaoketaohu1
Received:2022-05-26
Revised:2022-08-25
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
Zhihui Yuan
CLC Number:
Shilei Mu, Zhihui Yuan, Wuritaoketaohu. Spatial differentiation pattern and impacting mechanism of intangible cultural heritages in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 255-265.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00090
| 类型 | 判别标准 |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 | |
| 单因子非 线性减弱 | |
| 双因子增强 | |
| 独立 | |
| 非线性增强 |
Table 1 Geo-detector interaction detection type table
| 类型 | 判别标准 |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 | |
| 单因子非 线性减弱 | |
| 双因子增强 | |
| 独立 | |
| 非线性增强 |
| 区域 | 省(自 治区) | 类别 | 合计 /项 | 占比 /% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 民间 文学 | 传统 音乐 | 传统 舞蹈 | 传统 戏剧 | 曲艺 | 传统体育、 游艺与杂技 | 传统 美术 | 传统 技艺 | 传统 医药 | 民俗 | ||||
| 上游 | 青海 | 7 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 13 | 70 | 12.50 |
| 四川 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 1.07 | |
| 甘肃 | 3 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 11 | 2 | 6 | 60 | 10.71 | |
| 宁夏 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 28 | 5.00 | |
| 内蒙古 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 43 | 7.68 | |
| 小计 | 207 | 36.96 | |||||||||||
| 中游 | 陕西 | 5 | 11 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 2 | 11 | 11 | 2 | 8 | 79 | 14.11 |
| 山西 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 29 | 9 | 5 | 13 | 32 | 8 | 19 | 149 | 26.61 | |
| 小计 | 228 | 40.71 | |||||||||||
| 下游 | 河南 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 14 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 57 | 10.18 |
| 山东 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 14 | 8 | 3 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 68 | 12.14 | |
| 小计 | 125 | 22.32 | |||||||||||
| 合计 | 42 | 73 | 43 | 87 | 38 | 25 | 66 | 84 | 33 | 69 | 560 | 100.00 | |
Table 2 National-level intangible cultural heritage category in the Yellow River Basin-geographical quantity distribution table
| 区域 | 省(自 治区) | 类别 | 合计 /项 | 占比 /% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 民间 文学 | 传统 音乐 | 传统 舞蹈 | 传统 戏剧 | 曲艺 | 传统体育、 游艺与杂技 | 传统 美术 | 传统 技艺 | 传统 医药 | 民俗 | ||||
| 上游 | 青海 | 7 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 13 | 70 | 12.50 |
| 四川 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 1.07 | |
| 甘肃 | 3 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 11 | 2 | 6 | 60 | 10.71 | |
| 宁夏 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 28 | 5.00 | |
| 内蒙古 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 43 | 7.68 | |
| 小计 | 207 | 36.96 | |||||||||||
| 中游 | 陕西 | 5 | 11 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 2 | 11 | 11 | 2 | 8 | 79 | 14.11 |
| 山西 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 29 | 9 | 5 | 13 | 32 | 8 | 19 | 149 | 26.61 | |
| 小计 | 228 | 40.71 | |||||||||||
| 下游 | 河南 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 14 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 57 | 10.18 |
| 山东 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 14 | 8 | 3 | 9 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 68 | 12.14 | |
| 小计 | 125 | 22.32 | |||||||||||
| 合计 | 42 | 73 | 43 | 87 | 38 | 25 | 66 | 84 | 33 | 69 | 560 | 100.00 | |
| 类别 | 民间文学 | 传统音乐 | 传统舞蹈 | 传统戏剧 | 曲艺 | 传统体育、游艺与杂技 | 传统美术 | 传统技艺 | 传统医药 | 民俗 | 总数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 | 42 | 73 | 43 | 87 | 38 | 25 | 66 | 84 | 33 | 69 | 560 |
| R值 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 1.12 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.91 | 0.78 |
| P值 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
Table 3 The average nearest point index of intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin
| 类别 | 民间文学 | 传统音乐 | 传统舞蹈 | 传统戏剧 | 曲艺 | 传统体育、游艺与杂技 | 传统美术 | 传统技艺 | 传统医药 | 民俗 | 总数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量 | 42 | 73 | 43 | 87 | 38 | 25 | 66 | 84 | 33 | 69 | 560 |
| R值 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.81 | 1.12 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.91 | 0.78 |
| P值 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
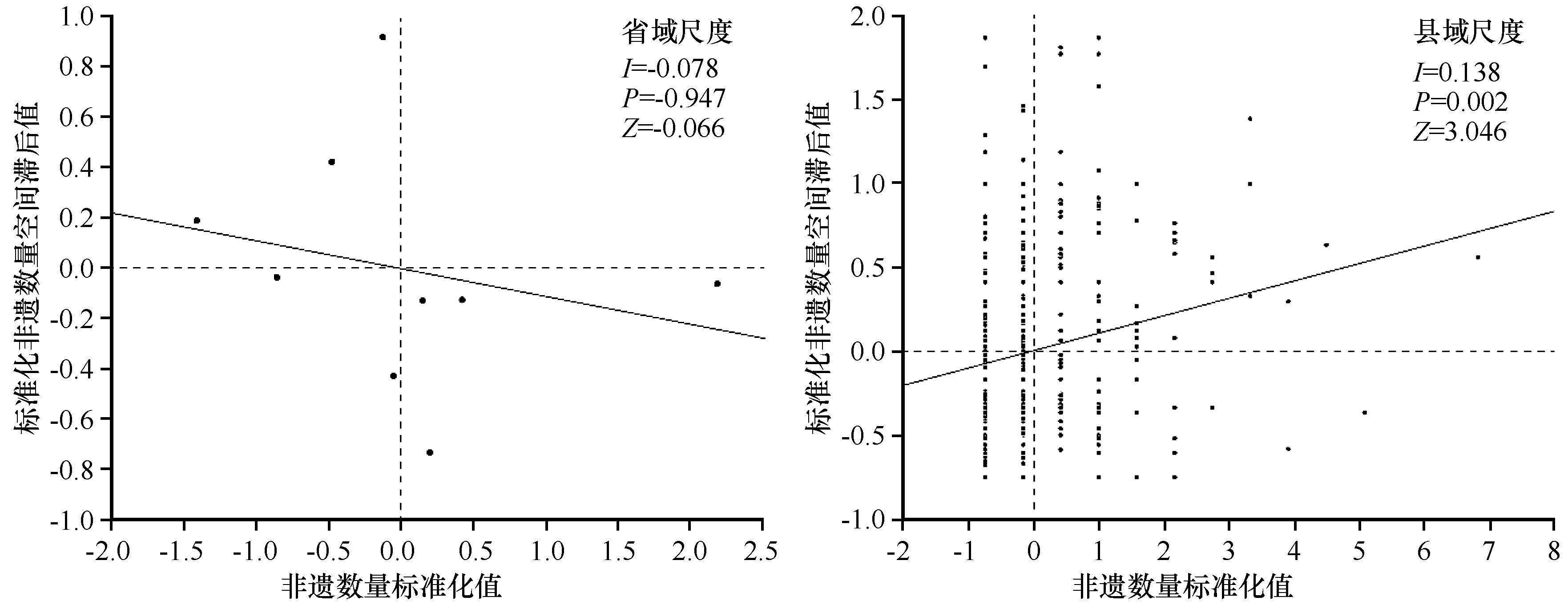
Fig.3 The global Moran index scatter plot of the distribution of intangible cultural heritage at the provincial and county scales in the Yellow River Basin
| 影响因素 | 因子 | 评价指标 | 单位 | 数据来源 | q | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
自然 地理 | 气温(X1) | 年平均气温 | ℃ | 国家气象科学数据中心 | 0.026 | 0.079 |
| 降水量(X2) | 年降水量 | mm | 国家气象科学数据中心 | 0.019 | 0.213 | |
| 地形地貌(X3) | 海拔 | m | 地理空间数据云中的DEM数据 | 0.031 | 0.042 | |
经济 社会 文化 | 地区生产总值(X4) | GDP | 万元 | 中国县域统计年鉴(县市卷)-2021 | 0.103 | 0.000 |
| 城镇化水平(X5) | 城镇化率 | % | 中国县域统计年鉴(县市卷)-2021、2021年各县(市、区、旗)国民经济和社会发展统计公报 | 0.035 | 0.027 | |
| 人口(X6) | 户籍人口数量 | 万人 | 中国县域统计年鉴(县市卷)-2021 | 0.104 | 0.000 | |
| 交通(X7) | 高速、国道、铁路和省道路网密度 | km | OpenStreetMap(OSM) | 0.061 | 0.013 | |
| 少数民族人口(X8) | 少数民族人口比重 | % | 2021年各县(市、区、旗)国民经济和社会发展统计公报 | 0.030 | 0.127 | |
| 国家历史文化名城(X9) | 国家历史文化名城数量 | 个 | 中华人民共和国国务院公报 | 0.002 | 0.390 | |
| 中国历史文化名镇名村(X10) | 中国历史文化名镇名村数量 | 个 | 住房和城乡建设部、国家文物局公布的中国历史文化名镇(村)(第一至七批) | 0.046 | 0.902 | |
| 博物馆(X11) | 博物馆数量 | 个 | 国家政务服务平台-国家文物局-全国博物馆名录 | 0.163 | 0.280 | |
| 全国重点文物保护单位(X12) | 全国重点文物保护单位数量 | 个 | 国家政务服务平台-国家文物局-全国重点文物保护单位名录 | 0.123 | 0.013 |
Table 4 Influencing factors of the spatial distribution of intangible cultural heritage in the Yellow River Basin, their explanatory effects and detection results
| 影响因素 | 因子 | 评价指标 | 单位 | 数据来源 | q | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
自然 地理 | 气温(X1) | 年平均气温 | ℃ | 国家气象科学数据中心 | 0.026 | 0.079 |
| 降水量(X2) | 年降水量 | mm | 国家气象科学数据中心 | 0.019 | 0.213 | |
| 地形地貌(X3) | 海拔 | m | 地理空间数据云中的DEM数据 | 0.031 | 0.042 | |
经济 社会 文化 | 地区生产总值(X4) | GDP | 万元 | 中国县域统计年鉴(县市卷)-2021 | 0.103 | 0.000 |
| 城镇化水平(X5) | 城镇化率 | % | 中国县域统计年鉴(县市卷)-2021、2021年各县(市、区、旗)国民经济和社会发展统计公报 | 0.035 | 0.027 | |
| 人口(X6) | 户籍人口数量 | 万人 | 中国县域统计年鉴(县市卷)-2021 | 0.104 | 0.000 | |
| 交通(X7) | 高速、国道、铁路和省道路网密度 | km | OpenStreetMap(OSM) | 0.061 | 0.013 | |
| 少数民族人口(X8) | 少数民族人口比重 | % | 2021年各县(市、区、旗)国民经济和社会发展统计公报 | 0.030 | 0.127 | |
| 国家历史文化名城(X9) | 国家历史文化名城数量 | 个 | 中华人民共和国国务院公报 | 0.002 | 0.390 | |
| 中国历史文化名镇名村(X10) | 中国历史文化名镇名村数量 | 个 | 住房和城乡建设部、国家文物局公布的中国历史文化名镇(村)(第一至七批) | 0.046 | 0.902 | |
| 博物馆(X11) | 博物馆数量 | 个 | 国家政务服务平台-国家文物局-全国博物馆名录 | 0.163 | 0.280 | |
| 全国重点文物保护单位(X12) | 全国重点文物保护单位数量 | 个 | 国家政务服务平台-国家文物局-全国重点文物保护单位名录 | 0.123 | 0.013 |
| 1 | 中华人民共和国非物质文化遗产法[J].中华人民共和国全国人民代表大会常务委员会公报,2011(2):145-149. |
| 2 | 文化和旅游部.“十四五”非物质文化遗产保护规划[EB/OL].(2021-05-25)[2022-08-01].. |
| 3 | 梁文达.论非物质文化遗产传承与少数民族地区文化软实力提升[J].贵州民族研究,2016,37(1):62-65. |
| 4 | 中共中央办公厅、国务院办公厅.关于进一步加强非物质文化遗产保护工作的意见[EB/OL].(2021-08-12)[2022-02-20].. |
| 5 | Blake J.On Defining the cultural heritage[J].International & Comparative Law Quarterly,2000,49(1):61-85. |
| 6 | Arizpe Lourdes.Intangible cultural heritage,diversity and coherence[J].Museum International,2004,56(1/2):130-136. |
| 7 | Kurin Richard.Safeguarding intangible cultural heritage in the 2003 UNESCO Convention:a critical appraisal[J].Museum International,2004,56(1):66-77. |
| 8 | Londres C.The registry of intangible heritage:the Brazilian experience[J].Museum International,2010,56(1/2):166-173. |
| 9 | Laiti O, Harrer S, Uusiautti S,et al.Sustaining intangible heri‐tage through video game storytelling:the case of the Sami Game Jam[J].International Journal of Heritage Studies,2020(4):1-16. |
| 10 | Bunten A C.Sharing culture or selling out?developing the commodified persona in the heritage industry[J].American Ethnologist,2008,35(3):380-395. |
| 11 | Kirshenblatt-Gimblett B.Intangible heritage as metacultural production1[J].Problems of Museology,2010,56(1/2):52-65. |
| 12 | Esfehani M H, Albrecht J N.Roles of intangible cultural heritage in tourism in natural protected areas[J].Journal of Heritage Tourism,2018,13(1):15-29. |
| 13 | Howard P.Heritage Management,Interpretation,Identity[M].London,UK:Continuum International Publishing Group,2003. |
| 14 | 谢菲.国外非物质文化遗产相关研究述评[J].贵州民族研究,2011,32(3):93-98. |
| 15 | Cozzani G, Pozzi F, Dagnino F M,et al.Innovative technolo-gies for intangible cultural heritage education and preservation:the case of i-Treasures[J].Personal & Ubiquitous Computing,2017,21(2):1-13. |
| 16 | Arizpe L.Culture,Diversity and Heritage:Major Studies[M].Heideberg,Germany:Springer International Publishing,2015:95-99. |
| 17 | 徐柏翠,潘竟虎.中国国家级非物质文化遗产的空间分布特征及影响因素[J].经济地理,2018,38(5):188-196. |
| 18 | 巴莫曲布嫫.非物质文化遗产:从概念到实践[J].民族艺术,2008(1):6-17. |
| 19 | 宋丽华,董涛,李万社.非物质文化遗产分类的问题解析与体系重构[J].国家图书馆学刊,2014,23(3):86-92. |
| 20 | 李荣启,唐骅.新世纪我国非物质文化遗产的保护与传承[J].广西民族研究,2010(1):194-201. |
| 21 | 欧阳正宇.丝绸之路非物质文化遗产旅游开发RMP分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2012,26(12):203-208. |
| 22 | 王宪昭.试论非物质文化遗产研究人才的培养[J].文化遗产,2010(4):31-36,136. |
| 23 | 任学婧,朱勇.论非物质文化遗产法律保护的完善[J].河北法学,2013,31(3):86-92. |
| 24 | 刘志军.非物质文化遗产保护的人类学透视[J].浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版),2009,39(5):36-45. |
| 25 | 魏雷,朱竑.地理学视角下非物质文化遗产的跨地方实践[J].地理学报,2022,77(2):492-504. |
| 26 | 褚乐阳,谭悦,陈卫东.非物质文化遗产传承教育的现状及对策研究[J].大众文艺,2018(3):223-224. |
| 27 | 王清,唐广东,马慧强,等.山西省非物质文化遗产空间分布格局及影响因素探析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(10):185-193. |
| 28 | 韩顺法,徐鹏飞,马培龙.江苏非物质文化遗产的时空分布及其影响因素[J].地理科学,2021,41(9):1598-1605. |
| 29 | 应奎,李旭东.贵州省国家级非物质文化遗产空间分布特征及其影响因素[J].湖南师范大学自然科学学报,2021,44(5):70-79. |
| 30 | 康雷,杨兆萍,韩芳.新疆非物质文化遗产的空间分布及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):158-166. |
| 31 | 吴清,李细归,张明.中国不同类型非物质文化遗产的空间分布与成因[J].经济地理,2015,35(6):175-183. |
| 32 | 程乾,凌素培.中国非物质文化遗产的空间分布特征及影响因素分析[J].地理科学,2013,33(10):1166-1172. |
| 33 | 习近平在河南主持召开黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展座谈会时强调共同抓好大保护协同推进大治理让黄河成为造福人民的幸福河[J].人民黄河,2019,41(10):2-3. |
| 34 | 中共中央、国务院.黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展规划纲要[EB/OL].(2021-10-08)[2022-02-23].. |
| 35 | 常媛媛,赵馨,刘耀龙.黄河流域体育非物质文化遗产空间集聚特征与影响因素分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2021,44(11):137-150. |
| 36 | 赵宏波,魏甲晨,苗长虹,等.黄河流域历史文化名城名镇名村的空间分异与影响因素分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(4):70-77. |
| 37 | 周成,柳炳华,张旭红,等.黄河流域文物保护单位空间分布特征及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(6):10-20. |
| 38 | 王洪桥,袁家冬,孟祥君.东北地区A级旅游景区空间分布特征及影响因素[J].地理科学,2017,37(6):895-903. |
| 39 | 江娟丽,杨庆媛,张忠训,等.重庆市非物质文化遗产的空间格局及旅游开发模式[J].经济地理,2019,39(6):205-213. |
| 40 | 李江敏,赵青青,陈静.长江经济带非物质文化遗产空间分布特征与影响因素[J].经济地理,2020,40(12):191-198. |
| 41 | Wang J F, Li X H, Christakos G,et al.Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China[J].International Journal of Geographical Information Science,2010,24(1/2):107-127. |
| 42 | 王劲峰,徐成东.地理探测器:原理与展望[J].地理学报,2017,72(1):116-134. |
| 43 | 苗红,张敏.基于GIS缓冲区分析的西北民族地区“非遗”旅游资源空间结构研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(4):179-186. |
| 44 | 黄永林.乡村文化振兴与非物质文化遗产的保护利用:基于乡村发展相关数据的分析[J].文化遗产,2019(3):1-12. |
| 45 | 章牧.非物质文化遗产活化研究:基于文旅融合的视角[J].社会科学家,2021(6):15-20. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech